Abstract
A survey was performed to find out the intermediate hosts of Gnathostoma nipponicum in Jeju-do (Province), the Republic of Korea. In August 2009 and 2010, a total of 82 tadpoles, 23 black-spotted pond frogs (Rana nigromaculata), 7 tiger keelback snakes (Rhabdophis tigrinus tigrinus), 6 red-tongue viper snakes (Agkistrodon ussuriensis), and 2 cat snakes (Elaphe dione) were collected in Jeju-do and examined by the pepsin-HCl digestion method. Total 5 gnathostome larvae were detected in 3 (50%) of 6 A. ussuriensis, 70 larvae in 3 of 7 (42.9%) R. tigrinus tigrinus, and 2 larvae in 2 of 82 (8.7%) frogs. No gnathostome larvae were detected in tadpoles and cat snakes. The larvae detected were a single species, and 2.17×0.22 mm in average size. They had characteristic head bulbs, muscular esophagus, and 4 cervical sacs. Three rows of hooklets were arranged in the head bulbs, and the number of hooklets in each row was 29, 33, and 36 posteriorly. All these characters were consistent with the advanced third-stage larvae of G. nipponicum. It has been first confirmed in Jeju-do that R. nigromaculata, A. ussuriensis, and R. tigrinus tigrinus play a role for intermediate and/or paratenic hosts for G. nipponicum.
-
Key words: Gnathostoma nipponicum, larval gnathostome, snake, frog, intermediate host, Jeju-do (Province)
Gnathostoma species nematodes are clinically important and can cause food-borne zoonotic parasitism in humans. More than 12 species, including
Gnathostoma spinigerum, have been reported as valid species [
1]. In the Republic of Korea, Kim [
2] detected 2
G. spinigerum larvae in a snakehead,
Channa argus argus, from Kimhae, Gyeongsangnam-do (Province) [
2]. The third stage larvae of
G. hispidum were found in loaches and snakes from China [
3,
4] and in pit-viper snakes,
Agkistrodon brevicaudus, from Korea [
5]. Larval
G. nipponicum were also detected in imported Chinese loaches and also in tiger keelback snakes (
Rhabdophis tigrinus tigrinus) from Hongcheon-gun, Gangwon-do, Korea [
6,
7]. On the other hand,
G. nipponicum adults were found in the stomach of the Jeju weasel,
Mustela sibilica quelpartis, road-killed in Jeju-do [
8]. In the present study, we performed a survey on intermediate hosts of
G. nipponicum in Jeju-do, the Republic of Korea.
We collected 82 tadpoles, 23 black-spotted pond frogs (Rana nigromaculata), 6 red-tongue viper snakes (Agkistrodon ussuriensis), 7 tiger keelback snakes, and 2 cat snakes (Elaphe dione) from the vicinities of Jeju National University in August 2009 and 2010. They all were tranferred to the laboratory of Department of Veterinary Parasitology, Jeju National University College of Veterinary Medicine, Jeju, Korea, and examined by the pepsin-HCl digestion method. Some collected gnathostome larvae were fixed with 10% formalin, cleared in alcohol-glycerin solution, mounted in glycerin-jelly, and observed under a light microscope equipped with a micrometer. To observe the surface ultrastructure, some worms were washed several times with 0.2 M cacodylate buffer (pH 7.2) and fixed with 2.5% glutaraldehyde at 4℃. After washing 3 times with the buffer, they were dehydrated through a graded alcohol series (50%, 70%, 80%, 90%, 95%, and absolute alcohol), dried with hexamethyldisilazane, coated (JFC-1100E ion sputtering device) with gold, and observed with a scanning electron microscope (SEM, Philips XL-30S, London, UK) at a 15-kV accelerating voltage.
Total 5 gnathostome larvae were detected in 3 (50%) of 6
A. ussuriensis, 70 larvae in 3 of 7 (42.9%)
R. tigrinus tigrinus, and 2 larvae in 2 of 82 (8.7%) frogs (
Table 1). However, no gnathostome larvae were detected in tadpoles and cat snakes.
The larvae from tiger keelback snakes were 2.17×0.22 mm in average size, and they had a characteristic head bulb (0.05×0.12 mm in average size), muscular esophagus (0.81 mm), and 4 cervical sacs (0.40 mm). Three rows of hooklets were arranged in the head bulb, and the number of hooklets in each row was 29, 33, and 36 posteriorly. Transverse striations were regularly arranged on the tegumental surface, and their numbers were 229 in average (
Table 2) (
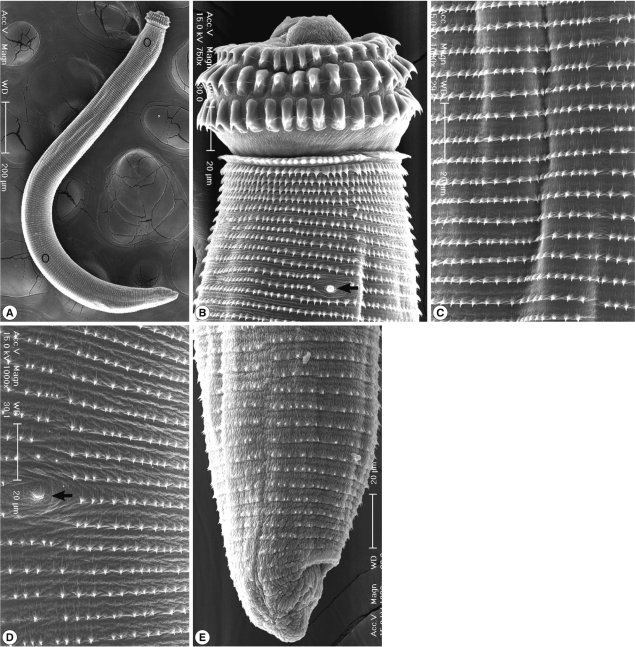
Fig. 1). In SEM observations, the head bulb beared 3 transverse rows of hooklets which were sharp-pointed and somewhat curved posteriorly, and numerous cuticular spines were regularly distributed on the transverse striations. A cervical papilla was located between the 12th and 13th transverse striations. Cuticular spines arranged on the transverse striations were sharp-pointed, and their densities were more sparse on the posterior part of the body surface. A body papilla was located on the posterior 1/3 level of the body. Near the posterior end of the larvae, smaller cuticular spines and an anus were presented (
Fig. 2).
Gnathostome larvae detected in this study were identified as the advanced third-stage larvae (AdL
3) of
G. nipponicum on the basis of their morphologic characters. The general body shape of
G. nipponicum larvae are similar to those of other species, including
G. spinigerum. However,
G. nipponicum can be discriminated from other species by the morphology of the head bulb. The larvae of
G. nipponicum have a head bulb with 3 transverse rows of hooklets, whereas those of other species have 4 rows [
1]. In SEM findings, most of them were corresponded with those of Han et al. [
7]. However, a cervical papilla was located between the 12th and 13th transverse striations in the present study, whereas a pair of cervical papillae was located bilaterally between the 8th and 12th transverse striations in Han et al. [
7]. We could not observe a phasmid near the posterior end of the larvae.
As the second intermediate or paratenic hosts of
G. nipponicum, snakes (
R. tigrinus and
Elaphe quadrivirgata), loaches (
M. anguillicaudatus), catfish (
Silurus asotus), sea rundaces (
Tribolodon hakonensis), and trouts (
Oncorhynchus masou masou) have been reported in Japan [
9-
13] and Korea [
7]. Koga and Ishii (1981) collected 3 larval
G. nipponicum from 3 (4.2%) of 72
R. tigrinus from Fukuoka Prefecture in Japan [
9]. In our study,
G. nipponicum larvae were detected from
R. nigromaculata,
A. ussuriensis, and
R. tigrinus tigrinus. By this study,
R. nigromaculata and
A. ussuriensis have been for the first time confirmed as new second intermediate or paratenic hosts for
G. nipponicum.
In the Republic of Korea,
G. spinigerum larvae were found in a snakehead [
2], the third stage larvae of
G. hispidum were detected in pit-viper snakes [
5], and larvae and adults of
G. nipponicum were found in the frogs, snakes, and Jeju weasel [
7,
8]. Therefore, definitely 3
Gnathostoma species,
G. spinigerum,
G. hispidum, and
G. nipponicum, are distributed indigenously in the Republic of Korea. However, no cases of indigenous gnathostomiasis have been reported yet. All gnathostomiasis cases reported by Korean workers are considered to have obtained the infection in foreign countries. In 1988, a
G. spinigerum infection in the brain was reported from a Thai woman suffering from meningoencephalitis [
14]. Later, in 2003, an outbreak of gnathostomiasis, presumably due to
G. spinigerum, was reported among 60 Korean emigrants in Yangon, Myanmar [
15]. Some patients returned to Korea after this outbreak, and one of them was reported as an imported case [
16]. Recently, an imported case from China was histologically diagnosed as
G. hispidum infection by cross sectional morphologies of the larva in skin biopsy [
17]. Although, until now, human gnathostomiasis cases have been imported from foreign countries, there exists possibility of indigenous human infections. Attentions should be paid to indigenous human gnathostomiasis in the Republic of Korea.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We thank Yong-Woo Kim, a student of Jeju National University College of Veterinary Medicine, for his help in collection of tadpoles and frogs.
References
- 1. Miyazaki I. Section III. Nematode Zoonoses. 33. Gnathostomiasis. An Illustrated Book of Helminthic Zoonoses. 1991, Tokyo, Japan. International Medical Foundation of Japan; pp 368-409.
- 2. Kim YK. A study on Gnathostoma (1) An investigation into the geographical distribution of larvae on the second and third stage in Gyeongsang Nam do. Bull Pusan Nat Univ (Natur Sci) 1973;15:111-116.
- 3. Sohn WM, Lee SH. Identification of larval Gnathostoma obtained from imported Chinese loaches. Korean J Parasitol 1996;34:161-167.
- 4. Cho SH, Kim TS, Kong Y, Na BK, Sohn WM. Larval Gnathostoma hispidum detected in the red banded odd-tooth snake, Dinodon rufozonatum rufozonatum, from China. Korean J Parasitol 2007;45:191-198.
- 5. Sohn WM, Lee SH. The first discovery of larval Gnathostoma hispidum (Nematoda: Gnathostomidae) from a snake host, Agkistrodon brevicaudus. Korean J Parasitol 1998;36:81-89.
- 6. Sohn WM, Kho WG, Lee SH. Larval Gnathostoma nipponicum found in the imported Chinese loaches. Korean J Parasitol 1993;31:347-352.
- 7. Han ET, Lee JH, Choi SY, Park JH, Shin EH, Chai JY. Surface ultrastructure of the advanced third-stage larvae of Gnathostoma nipponicum. J Parasitol 2003;89:1245-1248.
- 8. Woo HC, Oh HS, Cho SH, Na BK, Sohn WM. The Jeju weasel, Mustela sibilica quelpartis, a new definitive host for Gnathostoma nipponicum Yamaguti, 1941. Korean J Parasitol 2011;49:317-321.
- 9. Koga M, Ishii Y. Larval gnathostomes found in reptiles in Japan and experimental life cycle of Gnathostoma nipponicum. J Parasitol 1981;67:565-570.
- 10. Ando K, Tanaka H, Ohkawa C. A survey of geographical distribution of Gnathostoma nipponicum in Mie, Nara, Kyoto and Shiga prefectures, Japan. Jpn J Parasitol 1988;37:263-267.
- 11. Ando K, Tokura H, Matsuoka H, Taylor D, Chinzei Y. Life cycle of Gnathostoma nipponicum Yamaguti, 1941. J Helminthol 1992;66:53-61.
- 12. Oyamada T, Kudo N, Narai H, Sano T, Yoshikawa T. Prevalence of advanced third-stage larvae of Gnathostoma nipponicum in loaches (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus), in Aomori Prefecture, northern part of Honshu, Japan. Jpn J Parasitol 1995;44:222-227.
- 13. Oyamada T, Esaka Y, Kudo N, Oyamada T, Yoshikawa T, Kamiya H. Prevalence of Gnathostoma nipponicum larvae in Oncorhynchus masou (Salmonidae) and Tribolodon hakonensis (Cyprinidae) collected from eastern Aomori Prefecture, Japan. Jpn J Parasitol 1996;45:201-206.
- 14. Lee SH, Hong ST, Chai JY. Description of a male Gnathostoma spinigerum recovered from a Thai woman with meningoencephalitis. Korean J Parasitol 1988;26:33-38.
- 15. Chai JY, Han ET, Shin EH, Park JH, Chu JP, Hirota M, Nakamura-Uchiyama F, Nawa Y. An outbreak of gnathostomiasis among Korean emigrants in Myanmar. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2003;69:67-73.
- 16. Lee SD, Lee HJ, Kim JW. A case of gnathostomiasis. Korean J Dermatol 2001;39:1427-1429.
- 17. Kim HS, Lee JJ, Joo M, Chang SH, Chi JG, Chai JY. Gnathostoma hispidum infection in a Korean man returning from China. Korean J Parasitol 2010;48:259-261.
Fig. 1An advanced third-stage larva (AdL3) of G. nipponicum detected in a tiger keelback snake, Rhabdophis tigrinus tigrinus, from Jeju-do. It has a characteristic head bulb (arrow mark), muscular esophagus (E), intestine (I), and 4 cervical sacs (CS) (scale bar=0.5 mm).
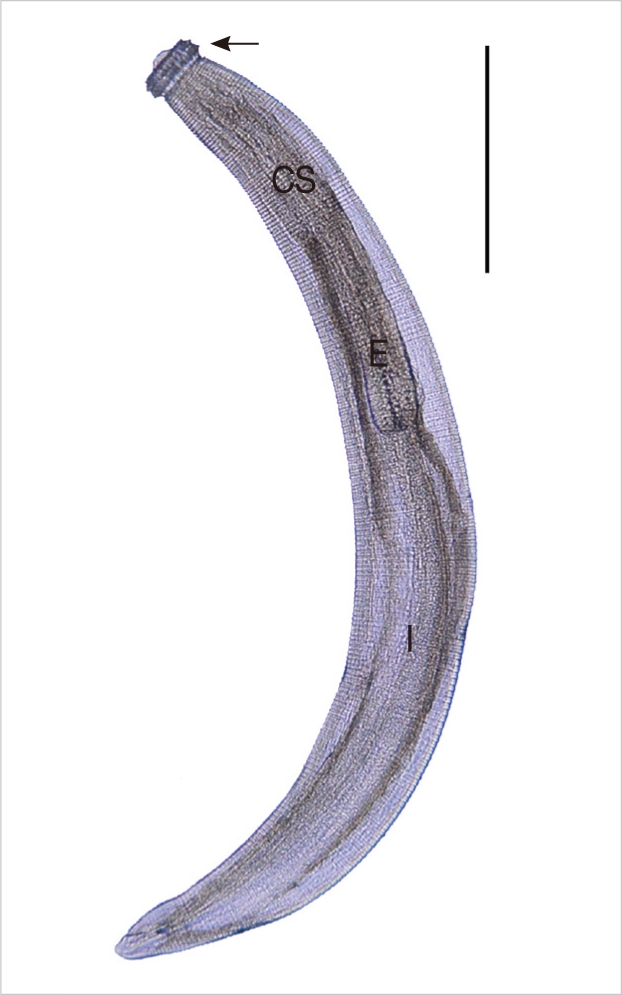

Fig. 2Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) view of the AdL3 of G. nipponicum from a tiger keelback snake. A. Whole body showing a head bulb, numerous transverse striations with cuticular spines, a cervical papilla (encircled), a body papilla (encircled in the posterior portion), and an anus. B. Anterior portion bearing the head bulb with 3 transverse rows of hooklets. Each hooklet with a sharp point somewhat curved posteriorly. A cervical papilla located between the 12th and 13th transverse striations (arrow mark). C. Tegumental surface of the anterior 1/3 level showing transverse striations with numerous cuticular spines. D. Tegumental surface of the posterior 1/3 level with numerous transverse striations and a body papilla (arrow mark). E. Posterior portion of a larva having smaller cuticular spines on the transverse striations and an anus.
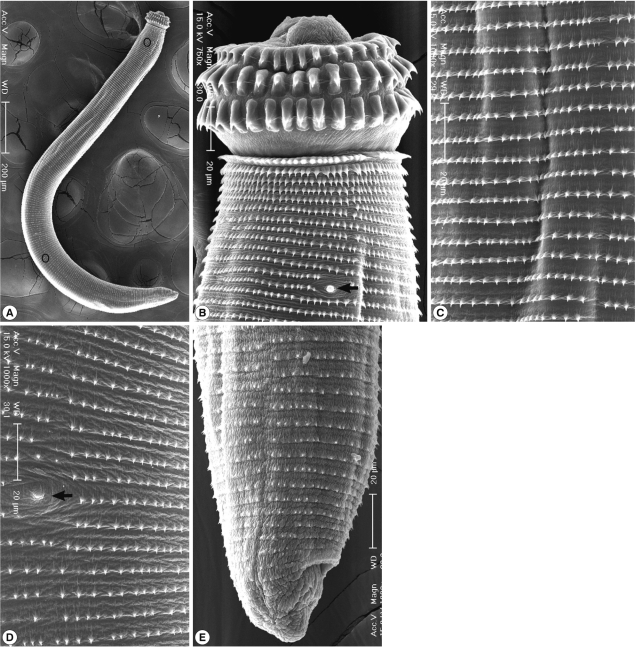
Table 1.The results of larval G. nipponicum recovery in amphibian and reptile hosts from Jeju-do (Province)
Table 1.
|
Name of host examined |
No. of hosts examined |
No. (%) hosts infected |
No. of larvae collected
|
|
Total |
Range |
Average |
|
Agkistrodon ussuriensis (Red-tongue viper snake) |
6 |
3 (50.0) |
5 |
1-3 |
1.7 |
|
Rhabdophis tigrinus tigrinus (Tiger keelback snake) |
7 |
3 (42.9) |
70 |
10-38 |
23.3 |
|
Elaphe dione (Cat snake) |
2 |
0 (0.0) |
- |
- |
- |
|
Rana nigromaculata (Black-spotted pond frog) |
23 |
2 (8.7) |
2 |
- |
1.0 |
|
Tadpole (species undetermined) |
82 |
0 (0.0) |
- |
- |
- |
Table 2.Measurements
a of the advanced third-stage larvae of
G. nipponicum from a tiger keelback snake,
Rhabdophis tigrinus tigrinus, and comparision with those of previous studies
Table 2.
|
Organs measured |
Present study (2011)b
|
Han et al. (2003)c
|
Oyamada et al. (1996)d
|
|
Body (length) |
2.0-2.4 (2.174) |
1.262-1.658 (1.460) |
1.068-1.872 |
|
Body (width) |
0.17-0.268 (0.222) |
0.180-0.185 (0.183) |
0.11-0.151 |
|
Head bulb (length) |
0.045-0.055 (0.049) |
0.050-0.080 (0.065) |
0.038-0.053 |
|
Head bulb (width) |
0.103-0.13 (0.119) |
0.110-0.115 (0.108) |
0.085-0.107 |
|
Esophagus (length) |
0.7-0.914 (0.811) |
- |
0.356-0.617 |
|
Cervical sac (length) |
0.36-0.45 (0.403) |
- |
0.186-0.309 |
|
Tail (length) |
0.033-0.045 (0.04) |
- |
0.018-0.068 |
|
No. of hooklets on head-bulb |
|
|
|
|
1st row |
28-32 (29.4) |
34-38 (36) |
29-36 |
|
2nd row |
30-36 (32.8) |
37-38 (38) |
31-38 |
|
3rd row |
34-38 (35.6) |
41-46 (43) |
33-44 |
|
No. of transverse striation |
200-270 (229) |
213-232 (222) |
214-253 |