Abstract
Toxoplasmic encephalitis is caused by reactivation of bradyzoites to rapidly dividing tachyzoites of the apicomplexan parasite Toxoplasma gondii in immunocompromised hosts. Diagnosis of this life-threatening disease is problematic, because it is difficult to discriminate between these 2 stages. Toxoplasma PCR assays using gDNA as a template have been unable to discriminate between an increase or decrease in SAG1 and BAG1 expression between the active tachyzoite stage and the latent bradyzoite stage. In the present study, real-time RT-PCR assay was used to detect the expression of bradyzoite (BAG1)- and tachyzoite-specific genes (SAG1) during bradyzoite/tachyzoite stage conversion in mice infected with T. gondii Tehran strain after dexamethasone sodium phosphate (DXM) administration. The conversion reaction was observed in the lungs and brain tissues of experimental mice, indicated by SAG1 expression at day 6 after DXM administration, and continued until day 14. Bradyzoites were also detected in both organs throughout the study; however, it decreased at day 14 significantly. It is suggested that during the reactivation period, bradyzoites not only escape from the cysts and reinvade neighboring cells as tachyzoites, but also converted to new bradyzoites. In summary, the real-time RT-PCR assay provided a reliable, fast, and quantitative way of detecting T. gondii reactivation in an animal model. Thus, this method may be useful for diagnosing stage conversion in clinical specimens of immunocompromised patients (HIV or transplant patients) for early identification of tachyzoite-bradyzoite stage conversion.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, SAG1, BAG1, RT-PCR, gene expression, bradyzoite, tachyzoite
INTRODUCTION
The primary infection in healthy people with the protozoan
Toxoplasma gondii is often asymptomatic or specified with only general symptoms. The parasite produces chronic infection by differentiating from the rapidly dividing, infective tachyzoites into latent bradyzoites, which stay inside human tissue cysts without symptoms. The stage conversion from
T. gondii bradyzoites to tachyzoites is the first step in reactivation of toxoplasmic encephalitis (TE) in immunosuppressed patients and particularly in those with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) [
1-
3]. The early events of the stage conversion are thought to be of critical importance, during which the expression of bradyzoite-specific genes is decreased and that of tachyzoite-specific ones starts to be up-regulated. The stage conversion between tachyzoite and bradyzoite forms is associated with morphological and molecular biological changes, including stage-specific gene expression and alterations in metabolism [
1,
2].
In order to intervene with prophylaxis and treatment before severe clinical signs appear, it is critical to detect differentiation of bradyzoites into tachyzoites (stage conversion) at the earliest stage. Therefore, a more reliable and efficient technique for the rapid diagnosis of TE is needed.
T. gondii-specific antibody production in immunocompromised patients is impaired [
4,
5]. Other diagnostic methods, such as direct microscopic detection of the parasite or mouse inoculation are inconvenient, time consuming, and insensitive. The use of molecular diagnosis is appropriate for immunosuppressed patients, because it does not depend on the immunological status of the host. Molecular diagnosis based on conventional PCR has become an important method for toxoplasmosis diagnosis [
6,
7]. However, some difficulties in its use in laboratory practice have been reported [
1], for example, it does not specify parasite differentiation status (bradyzoite-tachyzoite in stage conversion) [
2]. The parasite levels in blood and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are very low in some patients. As a result, a reduced amplification of PCR products is seen in agarose gels resulting in false reading of the PCR product [
1].
Quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) has recently been applied to parasitology. This method is truly quantitative, quick to perform, and needs no manipulations post-amplification. It can be used to count genome numbers and to study the level of gene expression in stage conversion. This technique has been shown to be significantly less variable than conventional RT-PCR techniques [
8,
9].
Newly, many stage-specific genes of
T. gondii have been clarified coincident with the development of serological and molecular biological technologies, for example, the surface and bradyzoite antigens [
10]. Among these, the surface antigen-1 (SAG1), a popular tachyzoite-specific, is the major surface protein and composes 3.0-5.0% of surface membrane proteins expressed per cell. It plays an important role in parasite attachment, penetration into the host cell, and immune modulation [
11]. The bradyzoite antigen-1 (BAG1), is the most important bradyzoite-specific gene. It can be found in the cytoplasm and has homology to small heat shock proteins in plants. BAG1 expression is up-regulated early in the differentiation stages. Cells expressing BAG1 are seen within 24 hr exposure to stress conditions in vitro and 10 days post-infection (PI) in mice infected with tachyzoites [
12].
The aim of this study was to examine the expression of the stage-specific genes, SAG1-tachyzoites and BAG1-bradyzoites, for detecting early-stage conversion in T. gondii Tehran strain using the real-time RT-PCR assay in an animal model. Since this strain might form more cysts in infected individuals, reactivation of TE could be a more usual event in AIDS patients who were infected with cysts of this parasite. The present study is the first study about T. gondii Tehran strain reactivation in immunosuppressed mice using the quantitative real-time RT-PCR method.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Experimental TE reactivation
This project was approved by the Ethical Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS), Iran and accepted the project no: 9538-27-03-88. The infected mice with
T. gondii Tehran strain were sacrificed, and their brains were removed and homogenized with 1 ml PBS by passing through a 22-gauge needle. The average size of the brain cyst was 47.0±5.1 µm; therefore, the number was identified by placing 2 drops each of 20 µl brain homogenate on slides and counting under a light microscope. According to the World Organization for Animal Health procedures [
13], the number of cysts per brain was estimated by multiplying the number of counted cysts in 2 drops by 25.
A total of 35 female Swiss Webster mice, aged 4-5 weeks with an average weight of 20-25 g, supplied by the Animal Center, Tehran University, were used throughout the study. To produce chronic toxoplasmosis, each mouse was infected by intraperitoneal injection with 25 tissue cysts of avirulent Tehran strain. All infected Swiss Webster mice (with tissue cysts of T. gondii Tehran strain) were reared for 3 months.
For survey of experimental TE reactivation, infected Swiss Webster mice were divided into 4 groups, 1 group consisting of 20 mice (TE group) in which TE was induced by 50 g/kg of DXM administration via subcutaneous injection 3 times a week [
14], and 3 control groups of 5 mice per each group (a: uninfected-treated, b: uninfected-untreated, and c: infected-untreated). TE groups of mice were sacrificed at day 6 (T6), 10 (T10), and 14 (T14) after DXM administration. The mice in the control groups were sacrificed at day 14. No mice survived after day 14 of drug administration, as the result, we could not follow up the 4th group in TE group. Any obvious symptoms of mice were recorded daily.
The brain and lung tissues were removed and washed in PBS. Total RNA was extracted using Tripure reagent according to the manufacturer's instruction (Roche, Berlin, Germany). Briefly, 90-100 mg tissues were cut into small pieces and homogenized by pressing through 20 guage needles in 1 ml of Tripure reagent. For preventing cross-contamination, all needles and syringes were changed each time when a new tissue specimen was homogenized. The RNA concentration was identified using a spectrophotometer, followed by denaturing gel electrophoresis to reveal RNA integrity.
cDNA synthesis
The cDNA synthesis was carried out using the Quantitect reverse transcription kit (Qiagen, Berlin, Germany) with some minor modifications. The mixture of 1 µg RNA, 2 µl gDNA Wipeout buffer, and 11 µl RNAse-free water in a sample tube was incubated at 42℃ for 2 min. Then, 1 µl of Quantiscript reverse transcriptase, 4 µl of RT buffer, and 1 µl of RT primer were added to the sample tube and incubated for 15 min at 42℃ and finally 3 min at 95℃ to inactivate the enzyme.
Primer design and RT-PCR
The NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) website was used to design specific primers for SAG1, BAG1, and β-actin (as internal control). Then, the specificity of primers was evaluated using conventional RT-PCR. To prevent the amplification of contaminating gDNA, the primer set for BAG1 was selected to span an intron yielding 2 likely PCR products; cDNA amplified product of 200 bp, and contaminating gDNA amplified product of 627 bp. To minimize the possibility of the primers binding unspecifically to other organisms, the sequence of the bradyzoite- and tachyzoite-specific
T. gondii primers was checked for matching to any other pathogens using the NCBI BLAST (
Table 1). The expected size of amplified products for SAG1 and β-actin were 350 bp and 190 bp, respectively. The β-actin primer set was designed so that no amplification can be observed in normal mice (untreated and uninfected).
Each cDNA sample (1 µl) was added to PCR tubes containing Syber Green master mix (12.5 µl) (Qiagen, Berlin, Germany), specific primer set (1 µl) for either SAG1 or BAG1, and sterile water (4.5 µl). Following assay optimization using negative samples (no template control and no RTase), all test samples of cDNA were subjected to amplification using 6500HRM Corbette real-time PCR instrument. The thermal cycling conditions consisted of an initial denaturation of 5 min at 95℃ followed by 40 cycles of 95℃ for 20 sec, 57℃ for 20 sec, 72℃ for 30 sec and a final extension step at 72℃ for 3 min.
After real-time PCR amplification, the machine was programmed to do a melt curve. At the melting point, the 2 strands separated and the fluorescence rapidly decreased. It is an important means of quality control to check that all samples with similar primers have a similar melting temperature.
The specificity of results of real-time RT-PCR was confirmed by agarose gel electrophoresis for single band of expected size of amplicon [
15]. Finally, the expression level for SAG1 and BAG1 of each sample was normalized by subtracting the cycle threshold (CT) of housekeeping gene from the gene of interest to calculate the ΔCT.
Tachyzoite and bradyzoite occurrences in organs (brain and lung) between the control and test groups were compared by Fisher's exact test. The level of statistical significance was P=0.05.
RESULTS
General appearance of immunosupprssed mice
Infected and treated mice showed signs of malaise with reduced activity, and ruffled fur. They lost appetite and progressively lost weight. Some developed neurological signs (hunch back appearance, locomotors alterations, and paralysis) compatible with the clinical symptoms of TE within 7 days of starting the experiment. In contrast, all mice in the control groups ('b' and 'c') survived until the last day of experiment without clinical signs. However, in control group 'a' (uninfected-treated mice) showed signs of general weakness and 2 mice died on day 6 PI. Some mice in TE group died of toxoplasmosis at days 9, 11, 12, and 15 PI, respectively.
SAG1 and BAG1 gene expression in immunosuppressed mice
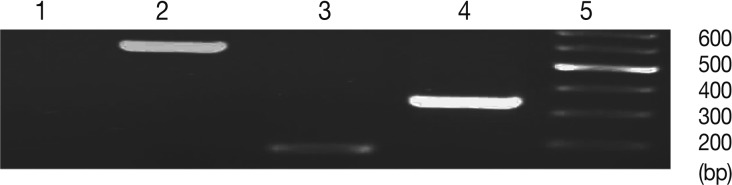
The RT-PCR conditions were optimized to amplify the expected products. It was obtained by optimizing the annealing temperature, number of amplification cycles, and concentration of the cDNA and primers. This condition was used in subsequent experiment (real-time RT-PCR). As mentioned before, BAG1 primers were designed so that the gDNA amplification products can be detected by agarose gel electrophoresis from those acquired by cDNA target amplification. This was performed by using primers that span the exon-exon junction of the BAG1 gene, resulting in larger amplicon than the one from cDNA, it also allow the detection of any contamination of DNA in the RNA extraction process. Unfortunately, this strategy could not be applied to SAG1, since it does not contain any intron; therefore, we used no RTase control for solving this problem. No RTase control does not have reverse transcriptase enzyme. Consequently, we must not observe any band in this sample after RT-PCR (
Fig. 1).
The qRT-PCR conditions were optimized to amplify the expected products. As expected, the SAG1 transcripts were abundant in the tachyzoite but not in the bradyzoite stage, whereas BAG1 transcripts were found only in the bradyzoite stage.
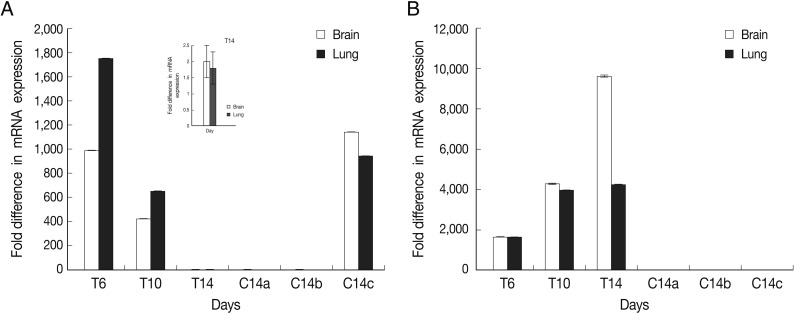
The results showed that expression of BAG1 in the lung tissue was significantly higher at days 6 and 10 in comparison to the brain tissue. This expression of BAG1 decreased at days 10 and 14 in comparison with the control ('c': infected-untreated) in the lung and brain tissues.
SAG1 expression was the highest at day 14 PI in the brain compare to the lung tissue. Expression of SAG1 increased from day 6 to 14 in comparison to the control in both tissues (
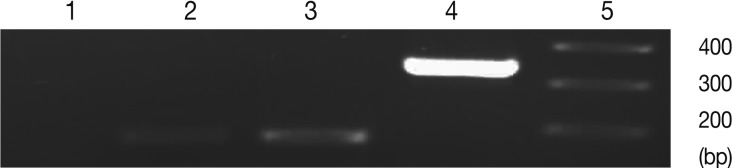
Fig. 2). In control group 'b' (uninfected-untreated) and group 'a' (uninfected-treated), no amplification for SAG1 and BAG1 were observed. In control group 'c' (infected-untreated), only expression of BAG1 but not SAG1 was observed in the tested tissues. Agarose gel electrophoresis of amplified samples confirmed the amplification of a single band for SAG1 and BAG1 with expected size (
Fig. 3). The NTC and no RTase negative control samples showed no amplified bands indicating the lack of DNA contamination.
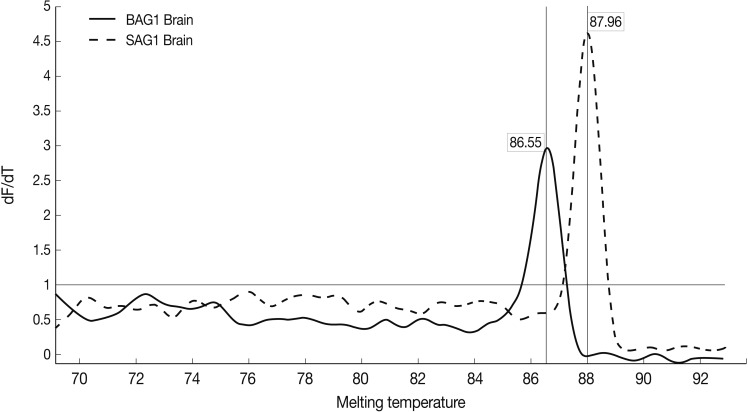
Results of the melting curve showed all real-time RT-PCR products for a particular pimer pair had the same melting temperature. Melting curve results showed 2 peaks for SAG1 and BAG1 in the test groups separately, and no peak in NTC samples (no template control). It was confirmed that there was no contamination, mispriming, primer dimer artifacts, or any other problem (
Fig. 4).
DISCUSSION
Reactivation, indicated by a large amount of tachyzoites and death from recurrent encephalitis, has been observed in humans with AIDS or after immunosuppressive therapy [
16,
17]. For evaluation of the potential risk of reactivation of toxoplasmosis following the administration of immunosuppressive therapy, we surveyed the effects of dexamethasone on chronic infection in an animal model. This drug has been successfully used to make immunosuppressed mouse [
14,
18,
19]. We used Tehran strain of
T. gondii. This strain was originally isolated from the lymph node of patients. This strain belongs to the type 2 strain
T. gondii that usually induces a chronic infection in mice [
20].
Since tachyzoites and bradyzoites are alike in their structures and cannot be discriminated under a light microscope, some techniques are used to detect
Toxoplasma tachyzoite-bradyzoite stage conversion, for example, electron microscopy, microarray, RT-PCR, and lately transfection with fluorescent proteins [
21,
22]. Microarrays are abundantly used to analyze genome-wide gene expression pattern, but gene expression data are typically only semi-quantitative [
23]. Efficacy of RT-PCR for qualitative detection of
T. gondii bradyzoite gene expression in CSF samples from AIDS patients was confirmed by Cultrera et al. [
2]. They showed that MAG1 and SAG4 genes were specific to bradyzoite stage in TE relapse patients. In our study, BAG1 seems to have an enough expression level for discrimination of the bradyzoite stage. Therefore, we selected BAG1 as the marker to determine the bradyzoite stage.
RT-PCR assay has been used for analyzing the stage conversion in a mouse model infected with
T. gondii O Toole strain, using SAG1 and BAG1 genes [
24,
25]. They showed that 3 weeks after immunosuppression by oral administration of DXM, SAG1 and BAG1 genes were expressed in most of tissues. Some of the problems of this method are poor precision, time consuming, low resolution, non-automated, size-based discrimination only, and qualitative results. In comparison with these techniques, quantitative real-time PCR assay is a reliable and fast method for gene expression studies. Real-time permits detection of PCR amplification during the early phase of reaction. It decreases the risk of contamination and doesn't need to post PCR processing [
26-
28].
In the present study, expression of BAG1 in the lung tissue was the highest at days 6 and 10 after DXM administration in comparison to the brain. It seems that immunosuppressive drugs can alter the natural course of infection with a prolonged persistence of parasites in the lungs. Meanwhile, BAG1 expression exists during the reactivation process (post DXM administration), which approved the hypothesis that bradyzoites escape from cysts and they were not only reinvade neighboring cells as tachyzoites, but they also develop as new bradyzoites [
29]. In our experiments, subcutaneous injection of DXM was quickly followed by increasing SAG1 expression especially at day 14 post DXM administration. It was significantly higher when compared to days 6 and 10 (
P<0.05) but bradyzoite rate on day 14 was significantly fewer than the other days. While in previous studies [
19,
25], after oral administration of corticoids, only an increase in the cyst number, small numbers of tachyzoites, and mixed groups of both organisms were observed with different methods. They appear to have obtained a slight degree of immunosuppression but not reactivation. This is because of conjugation of some of the oral corticoid during the first passage through the liver before it reached immunologic effector sites. In addition, oral administration results in gradual absorption over a period of days or weeks. Reactivation of toxoplasmosis in mice dose not necessarily follow the administration of corticosteroids. The daily dose, type of corticosteroid, its solubility, the route of administration, the host, strain of
Toxoplasma, and kind of method may be other factors that are important in giving rise to sufficient immunosuppression for reactivation to occur.
Toxoplasma PCR assays using gDNA as a template have been unable to discriminate between an increase or decrease in SAG1 and BAG1 expression between the active tachyzoite stage and the latent bradyzoite stage [
30]. Our real-time RT-PCR used cDNA as a template, and it was certainly able to amplify both stage-specific genes with different expression levels, and even low levels of stage-specific mRNAs could be successfully amplified by this method. SAG1 and BAG1 mRNAs have hardly identified by conventional hybridization methods like Northern analysis [
31], but these techniques need large amounts of target RNA. This method would be useful for in vivo drug efficacy studies, detection of parasite stages, and for designing a new drug to omit tissue cysts. This real-time RT-PCR technique can be used to clinical specimens of immunocompromised patients (HIV patients or transplant patients) for early identification of tachyzoite-bradyzoite stage conversion.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was financially supported by Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
References
- 1. Mesquita RT, Ziegler AP, Hiramoto RM, Vidal JE, Pereira-Chioccola VL. Real-time quantitative PCR in cerebral toxoplasmosis diagnosis of Brazilian human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. J Med Microbiol 2010;59:641-647.
- 2. Cultrera R, Seraceni S, Segala D, Contini C. Expression of toxoplasmic 65 kDa cystic mRNA by RT-PCR in patients with Toxoplasma gondii infection relapses. J Eukaryot Microbiol 2001;(Suppl):193S-194S.
- 3. Mariuz P, Steigbigel RT. In Joynson DHM, Wreghitt TG eds, Toxoplasma infection in HIV-infected patients. Toxoplasmosis: A Comprehensive Clinical Guide. 2001, Cambridge, UK. Cambridge University Press; pp 147-177.
- 4. Joseph P, Calderon MM, Gilman RH, Quispe ML, Cok J, Ticona E, Chavez V, Jimenez JA, Chang MC, Lopez MJ, Evans CA. Optimization and evaluation of a PCR assay for detecting toxoplasmic encephalitis in patients with AIDS. J Clin Microbiol 2002;40:4499-4503.
- 5. Sukthana Y. Toxoplasmosis: beyond animals to humans. Trends Parasitol 2006;22:137-142.
- 6. Vidal JE, Colombo FA, de Oliveira AC, Focaccia R, Pereira-Chioccola VL. PCR assay using cerebrospinal fluid for diagnosis of cerebral toxoplasmosis in Brazillian AIDS patients. J Clin Microbiol 2004;42:4765-4768.
- 7. Clombo FA, Vidal JE, Penalva de Oliveira AC, Hernandez AV, Bonasser-Filho F, Nogueria RS, Focaccia R, Pereira-Chioccola VL. Diagnosis of cerebral toxoplasmosis in AIDS patients in Brazil: importance of molecular and immunological methods using peripheral blood samples. J Clin Microbiol 2005;43:5044-5047.
- 8. Wittwer CT, Hermann MG, Moss AA, Rasmussen RP. Continuous fluorescence monitoring of rapid cycle DNA amplification. Biotechniques 1997;22:130-138.
- 9. Lin MH, Chen TC, Kuo TT, Tseng CC, Tseng CP. Real-time PCR for quantitative detection of Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol 2000;38:4121-4125.
- 10. Lyons RE, McLeod R, Roberts CW. Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoite-bradyzoite interconversion. Trends Parasitol 2002;18:198-201.
- 11. Seng S, Yokoyama M, Suzuki R, Maki Y, Kato M, Lim C, Zayatiin B, Inoue N, Xuan X, Igarashi I, Nagasawa H, Fujisaki K, Mikami T, Suzuki N, Toyoda Y. Expression of SAG1 of Toxoplasma gondii in transgenic mice. Parasitol Res 2000;86:263-269.
- 12. Weiss LM, Kim K. The development and biology of bradyzoites of Toxoplasma gondii. Front Biosci 2000;4:391-405.
- 13. Ole A. Toxoplasmosis. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals. 2008, p 1286.
- 14. Kang KN, Choi IU, Shin DW, Lee YH. Cytokine and antibody responses of reactivated murine toxoplasmosis upon administration of dexamethasone. Korean J Parasitol 2006;44:209-219.
- 15. Azizi E, Namazi A, Kaabinejadian S, Fouladdel Sh, Rezaei P, Ramezani M. Molecular analysis of MEN1 expression in MCF7, T47D and MDA-MB 468 breast cancer cell lines treated with adrimycin using RT-PCR and Immunocytochemistry. Daru 2010;18:17-22.
- 16. Frenkel JK, Nelson BM, Arias-Stella J. Immunosuppression and toxoplasmic encephalitis: clinical and experi mental aspects. Hum Pathol 1975;6:97-111.
- 17. Bertoli F, Espino M, Arosemena JR 5th, Fishback JL, Frenkel JK. A spectrum in the pathology of toxoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med 1995;119:214-224.
- 18. Nicoll S, Wright S, Maley SW, Burns S, Buxton D. A mouse model of recrudescence of Toxoplasma gondii infection. J Med Microbiol 1997;46:263-266.
- 19. Odaert H, Soête M, Fortier B, Camus D, Dubremetz JF. Stage conversion of Toxoplasma gondii in mouse brain during infection and immunodepression. Parasitol Res 1996;82:28-31.
- 20. Zia-Ali N, Fazaeli A, Khoramizadeh M, Ajzenberg D, Dardé M, Keshavarz-Valian H. Isolation and molecular characterization of Toxoplasma gondii strains from different hosts in Iran. Parasitol Res 2007;101:111-115.
- 21. Ellis J, Sinclair D, Morrison D. Microarrays and stage conversion in Toxoplasma gondii. Trends Parasitol 2004;20:288-295.
- 22. Buchbinder S, Blatz R, Rodloff AC. Comparison of real-time PCR detection methods for B1 and P30 genes of Toxoplasma gondii. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 2003;45:269-271.
- 23. Velmurugan GV, Tewari AK, Rao JR, Baidya S, Kumar MU, Mishra AK. High level expression of SAG1 and GRA7 gene of Toxoplasma gondii (Izantnagar isolate) and their application in serodiagnosis of goat toxoplasmosis. Vet Parasitol 2008;154:185-192.
- 24. Belal US, Norose K, Aosai F, Mun HS, Ahmed AK, Chen M, Mohamed RM, Piao LX, Iwakura Y, Yano A. Evaluation of the effects of sulfamethoxazole on Toxoplasma gondii loads and stage conversion in IFN-gamma knockout mice using QC-PCR. Microbiol Immunol 2004;48:185-193.
- 25. Mahittikorn A, Wickert H, Sukthana Y. Toxoplasma gondii: Simple duplex RT-PCR assay for detecting SAG1 and BAG1 genes during stage conversion in immunosuppressed mice. Exp Parasitol 2010;124:225-231.
- 26. Edvinsson B, Lappalainen M, Evengard B. ESCMID Study Group for Toxoplasmosis. Real-time PCR targeting 529-bp repeat element for diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Clin Microbiol Infect 2006;12:131-136.
- 27. Hierl T, Reisschl U, Lang P, Hebart H, Stark M, Kyme P, Autenrieth IB. Preliminary evaluation of one conventional nested and two real-time PCR assays for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii immunocompromised patients. J Med Microbiol 2004;53:629-632.
- 28. Brenier-Pinchart MP, Morand-Bui V, Fricker-Hidalgo H, Equy V, Marlu R, Pelloux H. Adapting a conventional PCR assay for Toxoplasma gondii detection to real-time quantitative PCR including a competitive internal control. Parasite 2007;14:149-154.
- 29. Gazzinelli R, Xu Y, Hieny S, Cheever A, Sher A. Simultaneous depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes is required to reactivate chronic infection with Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol 1992;149:175-180.
- 30. Chabbert E, Lachaud L, Crobu L, Bastien P. Comparison of two widely used PCR primer systems for detection of Toxoplasma in amniotic fluid, blood, and tissues. J Clin Microbiol 2004;42:1719-1722.
- 31. Gross U, Holpert M, Goebel S. Impact of stage differentiation on diagnosis of toxoplasmosis. Ann Ist Super Sanita 2004;40:65-70.
Fig. 1Comparison of amplification products from bradyzoite and tachyzoite stages of Toxoplasma gondii (Tehran strain), and between gDNA vs. cDNA. Lanes are shown as 1, no RTase; 2, BAG1 (gDNA); 3, BAG1 (cDNA); 4, SAG1 (cDNA).

Fig. 2Normalized expression levels of SAG1 and BAG1 in test and control groups. Expression level of BAG1 (A) and SAG1 (B) in the brain and lung tissues at days 6 (T6), 10 (T10), and 14 (T14) after DXM administration in TE groups and at day 14 in control groups (a: uninfected-treated), (b: uninfected-untreated), (c: infected-untreated) was determined using the real-time RT-PCR as described in the methods section. Data are mean ± SD of experiments. In control groups (a: uninfected-treated, b: uninfected-untreated), no amplification for BAG1 were observed and in all of control groups (a, b, and c) no amplification for SAG1 were observed.
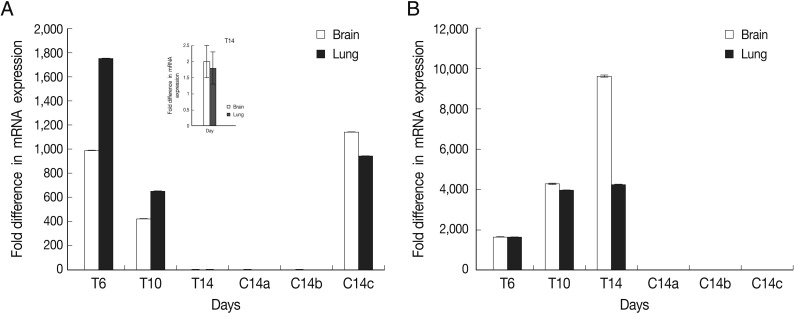
Fig. 3Representative images of gel electrophoresis of amplified cDNA samples following the real-time RT-PCR. Amplified samples by real-time RT-PCR were examined by agarose gel electrophoresis for a single band of expected size. Lanes are shown as 1, NTC; 2, β-actin; 3, BAG1; 4, SAG1; 5, size marker.
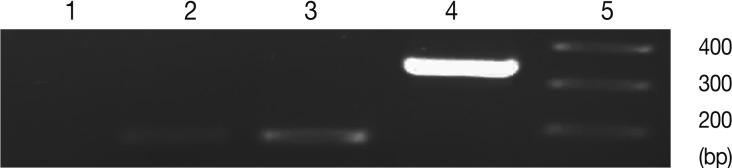
Fig. 4Representative graphs of real-time RT-PCR for SAG1 and BAG1 melting temperature. Melting curves of SAG1 and BAG1 for test and control groups of samples were determined using the real-time RT-PCR as explained in the methods section. The specific SAG1 product is shown with a Tm of 87.96℃, whereas specific BAG1 product is shown with a Tm of 86.55℃.
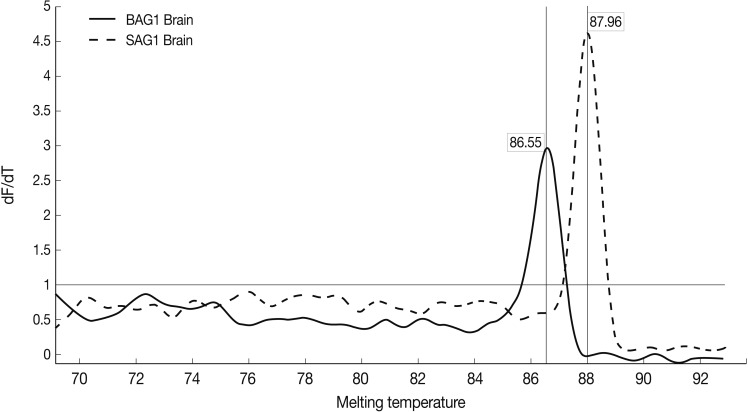
Table 1.
Table 1.
|
Gene |
Primer |
Temperature annealing (˚C) |
|
SAG1 |
F: 5´-GCTGTAACATTGAGCTCCTTGASTTCCTG-3´ |
58.5 |
|
R: 5´-CCGGAACAGTACTGATTGTTGTCTTGAG-3´ |
|
|
BAG1 |
F: 5´-AGTCGACAACGGAGCCATCGTTATC-3´ |
57.0 |
|
R: 5´-ACCTTGATCGTGACACGTAGAACGC-3´ |
|
|
β-actin |
F: 5´-GACCTTACCGAGTACATGATGAAG-3´ |
58.0 |
|
R: 5´-CCATCGGGCAATTCATAGGAC-3´ |
|