Abstract
Mosquitoes secrete saliva that contains biological substances, including anticoagulants that counteract a host's hemostatic response and prevent blood clotting during blood feeding. This study aimed to detect heparin, an anticoagulant in Aedes togoi using an immunohistochemical detection method, in the salivary canal, salivary gland, and midgut of male and female mosquitoes. Comparisons showed that female mosquitoes contained higher concentrations of heparin than male mosquitoes. On average, the level of heparin was higher in blood-fed female mosquitoes than in non-blood-fed female mosquitoes. Heparin concentrations were higher in the midgut than in the salivary gland. This indicates presence of heparin in tissues of A. togoi.
-
Key words: Aedes togoi, heparin, anticoagulant, salivary gland
INTRODUCTION
Mosquitoes feed on plant nectar and/or animal blood and during blood feeding transmit many pathogens, for example, malaria, lymphatic filariasis, dengue, and yellow fever to their hosts [
1,
2]. During the blood feeding, the proboscis of female mosquitoes pierces the inner layer of the skin, injuring the host's tissues and blood vessels resulting in host hemostatic responses [
3]. To overcome host hemostatic responses, mosquitoes secrete many inhibitors that prevent blood coagulation, platelet aggregation, host immunity, inflammation, and other biological processes in a host's system [
4]. Arthropod saliva also affects immunological responses. For instance, mosquito saliva-specific IgE is important in host systemic allergic reactions to mosquito bites [
5]. In addition, arthropod secretions serve as a vehicle to transmit zoonotic and human pathogens, and suppress or enhance the host's immune responses [
2]. However, the pharmacological functions of arthropod saliva have not been fully investigated [
6].
The mosquito midgut provides a potential barrier that impedes the development in the arthropod host [
7,
8]. The midgut of male and female arthropods performs at least 3 endocrine functions; diuresis, synthesis, and secretion of digestive enzymes; peritrophic membrane protection; and nutrient absorption [
9]. Inside the mosquito midgut, anticoagulants inhibit exflagellation, cellular invasion, and parasite survival [
10].
Heparin is an unfractionated anticoagulant acting on the coagulation cascade [
11]. Heparin is a highly sulfated form of heparan sulfate and belongs to a family of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) [
12]. However, studies have not yet obtained evidence revealing the presence of heparin that belongs to GAGs in the mosquito midgut. This study was conducted to quantify and detect the presence of heparin in the proboscis, salivary glands, midgut, and thorax muscles of male and female mosquitoes. Heparin was detected using an immunohistochemical detection method, heparin ELISA kit, and western blot.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Mosquito rearing
Mosquitoes (
Aedes togoi) were reared at 27℃, 80% relative humidity, and 16 hr:8 hr light/dark photoperiod [
13]. Larvae were fed a mixture of ground fish food and baker's yeast. Pupae were removed daily, placed in an open container with tap water, and placed in a screened cage until emergence. Adults were transferred to a cage after pupation and provided a 10% sucrose-soaked cotton rod. One of the female mosquito groups were fed on mice, under an approved animal use protocol, for egg production.
The detailed dissection procedures of the midgut and salivary glands in a female mosquito were previously well described [
14]. Mosquito sample was anesthetized by subjecting to a cold temperature of 4℃, until it was immobilized. The mosquito was kept in a Petri dish placed on ice. Thereafter, the mosquito was transferred to PBS solution onto a glass slide. Using a needle-tip probe and forceps, the salivary glands and midgut were dissected from each mosquito sample.
Feeding and non-feeding mosquitoes were anesthetized in an ice bath for 5-10 min and then inoculated with 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 1 hr at 4℃. The samples were fixed, washed, and incubated for 12 hr in 25% sucrose in PBS solution. The resulting samples were infiltrated in OCT™ compound (Sakura Finetek, Torrance, California, USA) and cut into sections with thickness ranging from 15-20 µm in thickness. Test samples was transferred to glass slides air dried at ambient temperatures, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) with 0.25% Triton X-100 for 1 hr at 4℃. After fixation, the slides were washed and incubated for 1 hr in 2% normal goat serum mixed with blocking solution. Anti-heparin (Kamiya Biomedical Company, Seattle, Washington, USA) was incubated with goat anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 488 (1:200, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA) overnight at 4℃ and with TOTO®-3 (1:100) as a nuclear DNA counterstain. All of the fluorescent images were observed using a LSM 510 LASER scanning microscope (Carl Zeiss Inc., Thornwood, New York, USA).
Detection of heparin in mosquitoes
The concentration of heparin in mosquitoes was quantified using a heparin ELISA kit (Lifespan Technologies, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA). The mosquito samples were mixed with detector-enzyme conjugate in the wells of the heparin-coated plate. The amount of heparin in each test mosquito was compared with the heparin bound to the plate. The concentration of heparin was determined based on the standard curve obtained from the heparin-coated plate.
Western blotting
The salivary gland and midgut of each female mosquito sample were dissected. The detailed procedures are described in detail [
15]. Total proteins (40 µg) were extracted from the salivary gland and midgut using Tissue protein extraction reagent (Thermo Scientific, Wilmington, Delaware, USA). We loaded the proteins in a 10% acrylamide gel with sample buffer. The proteins were transferred to a polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane and then blocked the membrane with 5% milk TBS/T solution for 1 hr room temperature. Anti-heparin was used as the primary antibody. Monoclonal anti-β-actin (Santi Cruz Technology, Santa Cruz, California, USA) was used for loading control. Bound antibody was detected by using the Supersignal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate (Pierce, Rockford, Illinois, USA). Chemiluminescent signals were captured with the LAS 3000 system (Fuji, Tokyo, Japan).
Statistical analyses were conducted using the SigmaPlot 10.0 software (Systat Software, San Jose, California, USA).
RESULTS
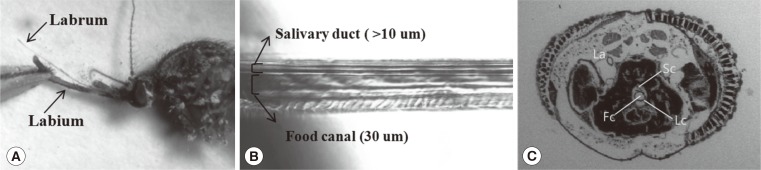
Head and mouthpart of A. togoi
The head of an adult mosquito is equipped with 3 different types of appendages: antennae; maxillary palps; and proboscis. In a previous study, each appendage was surgically removed and showed that the antennae and maxillary palps were involved in host detection [
3]. The mouthpart (proboscis) of a mosquito consists of 6 piercing stylets that include the labrum, paired mandibles, hypopharynx, and paired maxillae. The labrum, approximately 30 µm in diameter, functions as food canal and is the largest and stiffest stylet among the fascicles (
Fig. 1) [
16].
An opaque cuticle wrapping the 6 stylets prevents the stylets to be observed clearly (
Fig. 1A). The labrum was removed by microsurgical treatment using keen-edged forceps to strip off the opaque cuticle to show the salivary duct and food canal (
Fig. 1B). The cross-sectional image of the proboscis shows the labrum (La), food canal (Fc), salivary canal (Sc), and Laciniae (Lc) (
Fig. 1C).
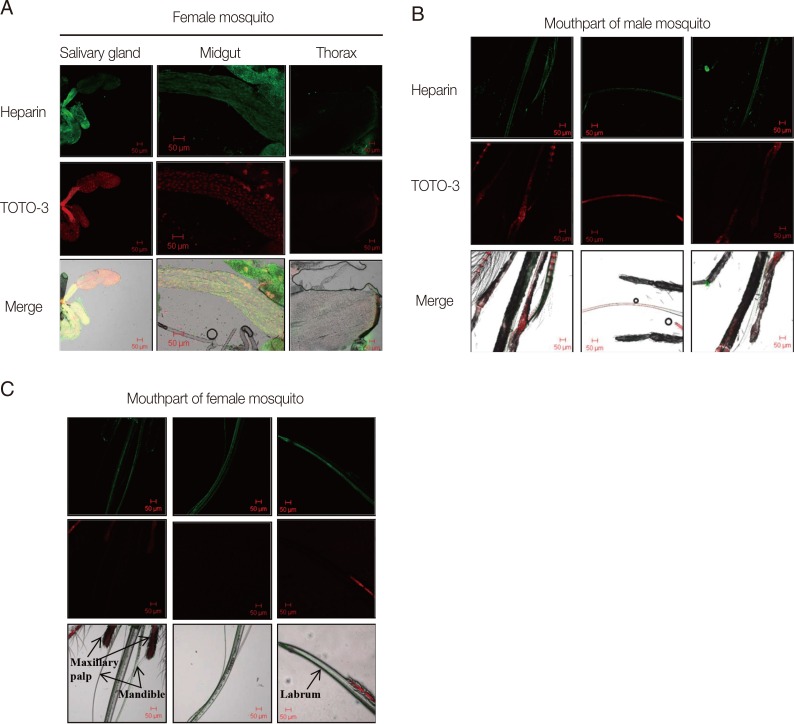
The salivary gland consists of 2 lateral lobes and 1 median lobe. Each lobe is composed of an epithelial cell layer distributed around a central cuticle-lined salivary duct and bounded externally by a basal lamina. A narrow tube-like midgut is positioned in the anterior region [
9]. The presence of heparin was observed in some parts of the salivary gland of female mosquitoes (
Fig. 2A). The midgut also exhibited a fluorescence signal for heparin. However, no fluorescence signals were detected in the thorax muscle tissues (
Fig. 2A). Heparin was detected in the paired mandibles, inside the labrum, and in the salivary canals of both male and female mosquitoes (
Fig. 2B and C), but not in the maxillary palp of the males.
The saliva of mosquitoes contains an anticoagulant to prevent formation of blood clots [
17]. Mosquitoes and other blood-feeding arthropods have been known to possess effective anti-hemostatic mechanisms to prevent blood loss by using anti-hemostatic factors such as mosquito saliva. In addition, the coagulant of blood in the midgut can inhibit the ingested pathogens by consistent streaming of ingested blood. This phenomenon has influence on the prevalence of infection by mosquito-borne parasites [
18].
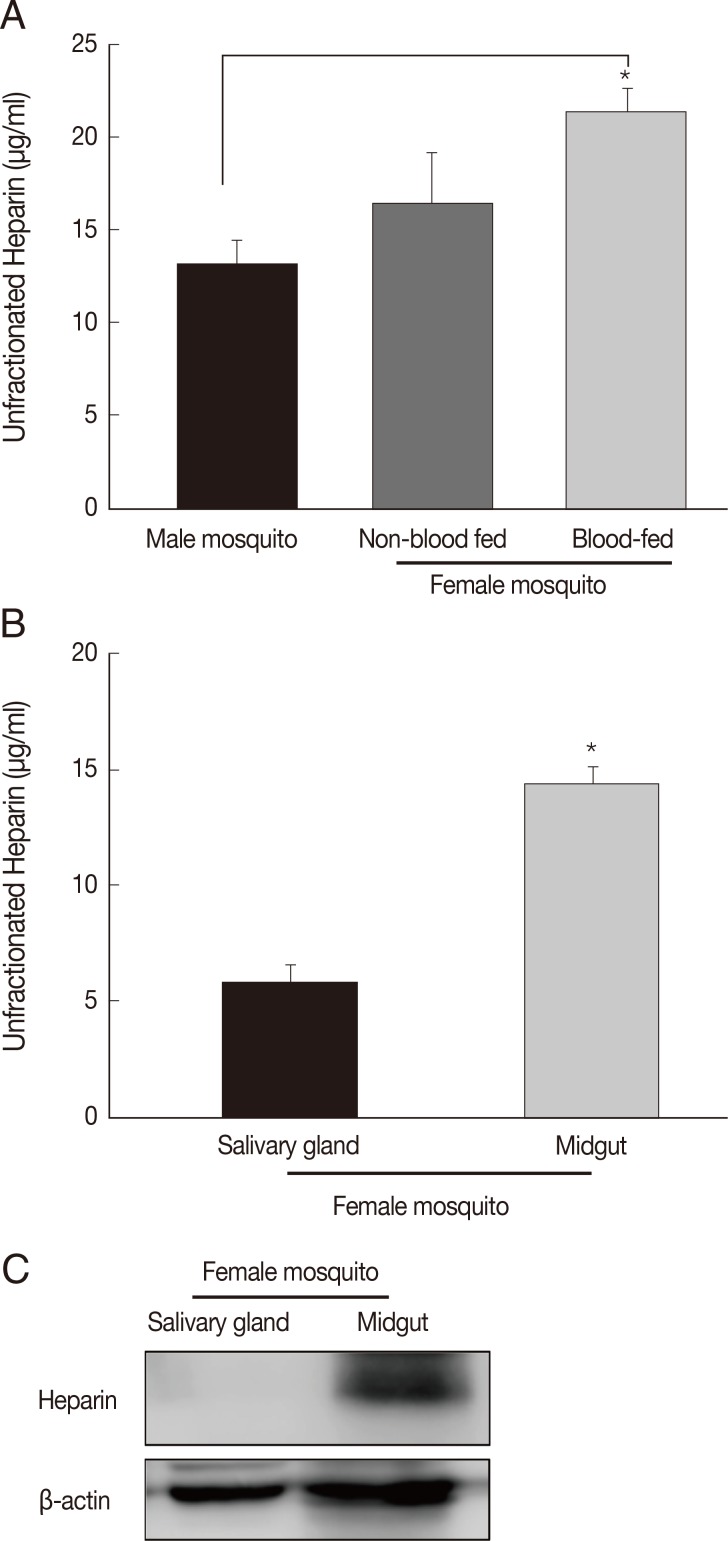
In this study, we tried to quantify the expression of heparin, as 1 of anticoagulants, in the salivary glands and midgut of a female mosquito. The mean heparin concentration for male
A. togoi (13.1±1.3 µg/ml) was not significantly different from the mean heparin concentrations in non-blood-fed females (16.4±2.8 µg/ml). However, the mean heparin concentrations for blood-fed females (21.3±1.3 µg/ml) was significantly higher than those for males (
P<0.05) and non-blood fed females (
P<0.5). Higher heparin concentrations were observed in blood-fed mosquitoes than non-blood-fed female mosquitoes (
Fig. 3A). The salivary gland mean heparin concentration of females was 5.9±0.7 µg/ml. The midgut mean heparin concentration was 14.6±0.7 µg/ml, and were significantly higher (
P<0.05) than that in the salivary glands of blood-fed or non-blood-fed female mosquitoes (
Fig. 3B). Western blot analysis showed a remarkable expression of heparin in the midgut of female mosquitoes, compared to the salivary gland (
Fig. 3C).
DISCUSSION
Female and male mosquitoes both feed on nectar, and females also take blood meals for egg development or as a meal. The salivary glands of male mosquitoes are smaller than those of female mosquitoes, which may account for higher mean heparin concentrations in unfed females.
Mosquito saliva contains various bioactive substances that are involved in the blood-feeding process of female mosquitoes [
17]. These bioactive substances inhibit hemostasis by any of the following mechanisms: injection of an anticoagulant factor, inhibition of platelet aggregation by apyrase, or salivary factor that inhibits collagen-induced platelet aggregation, inhibition of thrombin activity, and vasodilation of the host's blood vessels [
19]. The components of saliva differ depending on mosquito species and affect the survival of parasites in the mosquito midgut, with each anticoagulant eliciting different effects on the coagulation cascade [
8,
10,
20].
Heparin, a negatively charged mucopolysaccharide, is a highly sulfated anticoagulant that is involved in many biological processes; cell attachment, growth-factor binding, cell proliferation, migration, morphogenesis, and viral pathogenicity [
21]. In a previous study [
4], heparin exhibited a high affinity to alboserpin, which is one of the major anticoagulants in the salivary gland of
Aedes albopictus. The binding between heparin and alboserpin interacts with phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine but not with phosphatidylserine and exhibits potent antithrombotic properties under in vivo conditions. Heparin can accelerate the inhibition rate of vertebrate plasma antithrombin. Heparin also binds to a tissue factor pathway inhibitor and vascular endothelial growth factor that contributes to endothelial cells and other GAG-bearing cells [
4].
Furthermore, heparin binds to erythrocytes infected with
Plasmodium falciparum. This binding induces severe malarial symptoms in children. Therefore, heparin was once used to treat severe malaria accompanied by disseminated intravascular coagulation because this binding is more easily isolated from normal blood. However, this kind of treatment is no longer administered because of several side effects, such as intracranial bleeding. Heparin can reduce anticoagulation by oxidizing a pentameric sequence; as a result, GAG is depolymerized and a low anticoagulant heparin (LAH) is generated. LAH can disrupt rosettes and reduce cytoadherence under in vitro and in vivo conditions. An intravenous injection of LAH prevents the infected erythrocytes from binding to the microvasculature of a rat and releases the sequestered
P. falciparum-infected erythrocytes in the circulatory system. In addition, LAH inhibits merozoite invasion under in vitro conditions [
12]. However, previous studies have obtained clear evidence of the presence of heparin or GAGs in the mosquito midgut [
22]. Furthermore, GAGs have been used to investigate pathogen-host cell interactions. Heparin and GAGs induce the proliferation of
Leishmania amazonensis and
Leishmania major in the midgut of phlebotomine sandflies. As a result, parasite proliferation and potential for transmission of parasite is increased in
Leishmania-infected sandflies [
23].
In this study, heparin was detected in the salivary gland duct, salivary glands, and midgut of
A. togoi. The mean concentrations of heparin were higher in blood-fed female mosquitoes, compared to non-blood fed females. Heparin is secreted to induce the coagulation cascade. Heparin levels are largely increased during the salivation of a blood-feeding mosquito. In addition, the expression of heparin show a similar pattern with ELISA results. The heparin protein expression exhibits a high level in the midgut, compared to the salivary gland of blood-feeding mosquitoes. From this result, we can hypothesize that the anticoagulant is applied from the feeding behaviors or secretion from the midgut of a mosquito to prevent the formation of blood clots. In a previous study, blood-feeding insects were found to show the expression of tsetse thrombin inhibitor (TTI), anticoagulant peptide, in their salivary glands and gut tissues [
24]. Therefore, we assumed that blood-fed female mosquitoes may also express the anticoagulant enzyme in their salivary gland and midgut, together. Otherwise, the detected heparin may contain anticoagulants in the host blood, at least partially.
In our study, the presence and amount of heparin were visualized and quantified in various tissues and ducts of A. togoi. Heparin was detected in the midgut and salivary gland duct but not in the thorax muscles. Heparin concentrations were higher in female mosquitoes than in male mosquitoes, in response to blood-feeding activities. The pathological interactions of heparin and A. togoi-borne pathogens remain unknown, and further studies should be conducted to determine the underlying mechanisms of heparin in A. togoi.
National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean GovernmentMSIP; Grant no. 2008-0061991
Notes
-
The authors declare no competing interests.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean Government (MSIP; Grant no. 2008-0061991).
References
- 1. Maramorosch K. Biological transmission of disease agents. New York and London. Academic Press; 1962.
- 2. Dhar R, Kumar N. Role of mosquito salivary glands. Curr Sci 2003;85:1308-1313.
- 3. Maekawa E, Aonuma H, Nelson B, Yoshimura A, Tokunaga F, Fukumoto S, Kanuka H. The role of proboscis of the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles stephensi in host-seeking behavior. Parasit Vectors 2011;4:10.
- 4. Calvo E, Mizurini DM, Sa-Nunes A, Ribeiro JM, Andersen JF, Mans BJ, Monteiro RQ, Kotsyfakis M, Francischetti IM. Alboserpin, a factor Xa inhibitor from the mosquito vector of yellow fever, binds heparin and membrane phospholipids and exhibits antithrombotic activity. J Biol Chem 2011;286:27998-28010.
- 5. Peng Z, Beckett AN, Engler RJ, Hoffman DR, Ott NL, Simons FE. Immune responses to mosquito saliva in 14 individuals with acute systemic allergic reactions to mosquito bites. J Allergy Clin Immun 2004;114:1189-1194.
- 6. Ribeiro JM, Rossignol PA, Spielman A. Role of mosquito saliva in blood vessel location. J Exp Biol 1984;108:1-7.
- 7. Gupta L, Kumar S, Han YS, Pimenta PF, Barillas-Mury C. Midgut epithelial responses of different mosquito-Plasmodium combinations: the actin cone zipper repair mechanism in Aedes aegypti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005;102:4010-4015.
- 8. Dubrulle M, Mousson L, Moutailler S, Vazeille M, Failloux AB. Chikungunya virus and Aedes mosquitoes: saliva is infectious as soon as two days after oral infection. PLoS One 2009;4:e5895.
- 9. Clements AN. The Biology of Mosquitoes: Development, Nutrition, and Reproduction. Michigan University, Chapman & Hall; 1992.
- 10. Solarte Y, Manzano Mdel R, Rocha L, Castillo Z, James MA, Herrera S, Arévalo-Herrera M. Effects of anticoagulants on Plasmodium vivax oocyst development in Anopheles albimanus mosquitoes. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2007;77:242-245.
- 11. Cox MND. Lehninger, Principles of Biochemistry. Freeman; 2004, p 1100.
- 12. Leitgeb AM, Blomqvist K, Cho-Ngwa F, Samje M, Nde P, Titanji V, Wahlgren M. Low anticoagulant heparin disrupts Plasmodium falciparum rosettes in fresh clinical isolates. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2011;84:390-396.
- 13. Kim BH, Kim HK, Lee SJ. Experimental analysis of the blood-sucking mechanism of female mosquitoes. J Exp Biol 2011;214:1163-1169.
- 14. Coleman J, Juhn J, James AA. Dissection of midgut and salivary glands from Ae. aegypti mosquitoes. J Vis Exp 2007;228.
- 15. Chen JJ, Yao PL, Yuan A, Hong TM, Shun CT, Kuo ML, Lee YC, Yang PC. Up-regulation of tumor interleukin-8 expression by infiltrating macrophages: its correlation with tumor angiogenesis and patient survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2003;9:729-737.
- 16. Wahid I, Sunahara T, Mogi M. Maxillae and mandibles of male mosquitoes and female autogenous mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae). J Med Entomol 2003;40:150-158.
- 17. Isawa H, Yuda M, Orito Y, Chinzei Y. A mosquito salivary protein inhibits activation of the plasma contact system by binding to factor XII and high molecular weight kininogen. J Biol Chem 2002;277:27651-27658.
- 18. Beerntsen BT, James AA, Christensen BM. Genetics of mosquito vector competence. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2000;64:115-137.
- 19. Kebaier C, Voza T, Vanderberg J. Neither Mosquito Saliva nor Immunity to Saliva Has a Detectable Effect on the Infectivity of Plasmodium Sporozoites Injected into Mice. Infect Immun 2010;78:545-551.
- 20. Wright KA. The anatomy of salivary glands of Anopheles stephensi Liston. Can J Zool 1969;47:579-589.
- 21. Rathore D, McCutchan TF. Role of cysteines in Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein: interactions with heparin can rejuvenate inactive protein mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000;97:8530-8535.
- 22. Dinglasan RR, Alaganan A, Ghosh AK, Saito A, van Kuppevelt TH, Jacobs-Lorena M. Plasmodium falciparum ookinetes require mosquito midgut chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans for cell invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007;104:15882-15887.
- 23. de Castro Cortes LM, de Souza Pereira MC, da Silva FS, Pereira BA, de Oliveira Junior FO, de Araujo Soares RO, Brazil RP, Toma L, Vicente CM, Nader HB, de Fátima Ma deira M, Bello FJ, Alves CR. Participation of heparin binding proteins from the surface of Leishmania (Viannia) braziliensis promastigotes in the adhesion of parasites to Lutzomyia longipalpis cells (Lulo) in vitro. Parasit Vectors 2012;5:142.
- 24. Cappello M, Li S, Chen X, Li CB, Harrison L, Narashimhan S, et al. Tsetse thrombin inhibitor: bloodmeal-induced expression of an anticoagulant in salivary glands and gut tissue of Glossina morsitans morsitans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998;95:14290-14295.
Fig. 1Head and mouthpart of Aedes togoi. (A) Proboscis comprising a labrum and a labium. (B) Food canal and salivary canal inside the labrum. (C) Cross-sectional image of a proboscis, showing the labium (La), food (Fc), salivary (Sc) canals, and Laciniae (Lc).

Fig. 2Immunohistochemical detection of heparin (green) and nuclear DNA (TOTO®-3) (red) spatial distributions in sections of Aedes togoi. (A) Salivary gland, midgut, and thorax of a female mosquito. Mouthparts of a male mosquito (B) and a female mosquito (C).

Fig. 3Quantification of heparin in male and female Aedes togoi mosquitoes. (A) Comparision of heparin concentrations measured in male mosquitoes as well as non-blood-fed and blood-fed female mosquitoes. (B) Heparin concentration in the gut (P<0.5) of female blood-fed mosquitoes is higher than that in the salivary gland. (C) Western blotting of the heparin expression levels of salivary gland and midgut of female mosquitoes. *Bars denote SD.