Abstract
Chronic Opisthorchis viverrini-induced hepatobiliary disease is associated with significant leukocyte infiltration, including activated macrophages; however, the polarization of infiltrating macrophages remains to be fully characterized. In this study, we characterized macrophage polarization and phenotype in chronic O. viverrini-induced hepatobiliary disease in humans and hamsters using gene expression and histochemical analysis. Chronic O. viverrini infection and associated hepatobiliary diseases were associated with iron loaded M2-like macrophages in both humans and hamsters. This study provides suggestive evidence that iron loaded M2-like macrophages promote hepatobiliary disease in chronic O. viverrini infection.
-
Key words: Opisthorchis viverrini, M2-like macrophage, iron, hepatobiliary fibrosis, cancer
Several studies have demonstrated that persistent leukocyte infiltration, including monocytes/macrophages and associated chronic inflammation contributes to fibrosis and cancer development in different tissues, including the liver [
1]. Infiltrating macrophages are generally derived from blood monocytes and are generally classified into 2 broad classes M1 and M2-like macrophages [
2]. M1 macrophages are associated with Th1 immune response and play a critical role in intracellular pathogen clearance, while M2-like macrophages are associated with Th2 immune response and tissue remodeling and fibrosis [
3]. Macrophages represent a major class of immune cells within the fibrotic and tumor microenvironment and have been shown to exhibit pro-fibrotic/tumorigenic function in various diseases, including cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. M2-like macrophages have been shown to express the iron scavenger molecule (CD163, hemoglobin-heptaglobin complex) and mannose receptor (CD206), but lacks inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and co-stimulatory molecules (CD40, CD86, and CD80) [
3]. Additionally, owing to their high iron scavenger molecule (CD163) levels, M2-like macrophages exhibit high levels of labile iron [
6]. Additionally, several studies have demonstrated that M2-like macrophages exhibit giant cell morphology via cell fusion [
8]. Biliary fibrosis and CCA are rare liver diseases, most frequently occurring in Southeast Asia [
9]. Biliary fibrosis and CCA are predominately associated with chronic liver fluke, including chronic
Opisthorchis viverrini (OV) infection of the bile duct [
9]. High levels of infiltrating leukocytes, including macrophages within fibrotic/tumor tissues in chronic OV infected livers, support the role of chronic inflammation in fibrosis and carcinogenesis [
9]. In this study, we characterized macrophage polarization and associated pathological features in chronic OV-infected patient and hamster livers.
To examine macrophage polarization in chronic OV-induced hepatobiliary disease patients, liver tissues (n=307) were collected from CCA patients in OV endemic regions. Histologically confirmed hepatobiliary disease and CCA specimens were obtained from the Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University, Thailand after appropriate human subject approvals were in place and informed consent was obtained (protocol # HE480528). Tissue microarray slides were generated from individual patient liver samples. To examine macrophage polarization in chronic OV-induced hepatobiliary disease in a rodent model, Syrian golden hamsters at 6-8 weeks old, provided by the Animals Care Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University were infected via gastric tube with OV metacercariae obtained from cyprinoid fish from OV endemic area of Khon Kaen Province. This protocol was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine, Khon Kaen University. Animals were sacrificed under humane and approved guidelines at 6 months post infection (chronic OV infection), and tissues were fixed in 10% neutral formalin buffer overnight and transferred to 70% ethanol. Samples were later embedded in paraffin block and slides were generated.
Immunohistochemical staining was performed using an immunoperoxidase method. Briefly, tissue sections were dehydrated and incubated overnight with 1:200 mouse monoclonal anti-human CD68 (Dako), CD163 (Abcam), CD40 (RandD Systems), or iNOS (Abcam) followed by appropriate secondary antibody and detection reagents (Dako) following manufacturer's recommended procedures. Additionally, slides were stained with Prussian blue (iron stain) (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) or Sirius red/fast green (Sigma Aldrich) following manufactures' recommended procedures. Leukocytes from chronic OV-infected hamsters at 6 months post-infection were isolated using density gradient centrifugation method and RBC lysis. Monocytes/macrophages were isolated from leukocytes via the rapid adhesion method. Total RNA extraction was performed using Qiagen RNeasy Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) and following manufacturer's recommended procedures. Total RNA (500 ng) in 25 µl of sterile distilled water was heated at 65℃ for 10 min and chilled on ice for 5 min and cDNAs were generated using random hexamers and First Strand Synthesis Kit (Invitrogen; Carlsbad, California, USA). Relative gene (iNOS, and internal control; GAPDH) was measured using an adaptation of a 2-step real-time RT-PCR method. PCR was performed with cDNA sample using SYBR® Green PCR Master Mix Kit (Qiagen) with the ABI 7500 real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California, USA) and following manufacturer's recommended procedures. Sample groups were compared and analyzed with Student's t-test using GraphPad software. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant (P<0.0001=***).
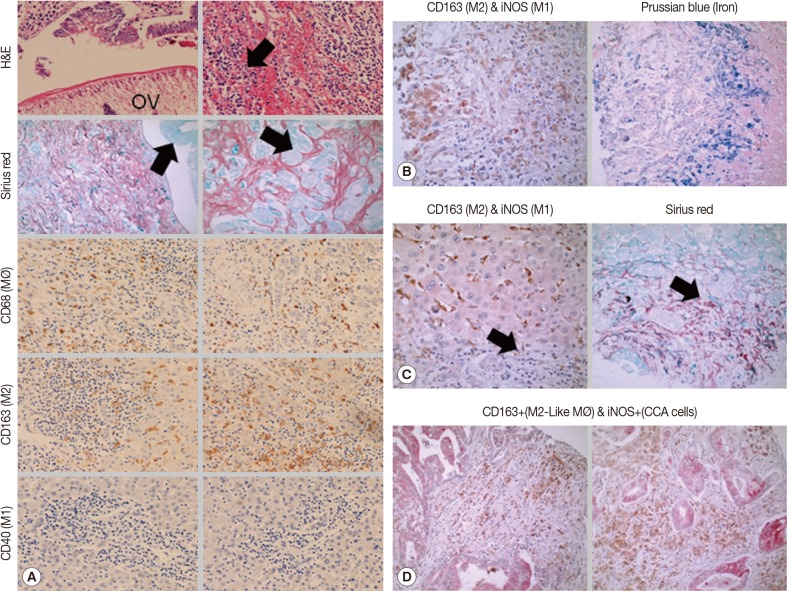
Analysis of chronic OV-associated hepatobiliary inflammation (H&E-blue cells with arrow), fibrosis (Sirius red and fast green stain, red stain), hyperplasia/neoplasia (Sirius red and fast green stain, green stain with arrow) in humans showed high levels of macrophages of predominately M2-like (CD68
high, CD163
high, and CD40
negative) lineage (
Fig. 1A). Additionally, chronic OV-associated M2-like (CD163
high and iNOS
negative) macrophages in human livers exhibited high levels of labile iron (
Fig. 1B). Furthermore, we also demonstrate that M2-like macrophages (CD163
high and iNOS
negative) are predominately localized adjacent to collagen regions (
Fig. 1C) (black arrows denote same location of the tissue). Tissue sections that are half collagen deposition (half red and half green) have high levels of iron loaded M2-like macrophages in regions adjacent to the collagen deposition regions (red regions), while the collagen deposition regions lacks significant iron loaded M2-like macrophages; this is expected because collagen depositions takes up the tissue space and limits micronutrient flow to those regions (data not shown). Analysis of chronic OV-associated biliary neoplastic regions showed elevated M2-like (CD163
high and iNOS
negative) macrophages (
Fig. 1D) co-localized with neoplastic biliary cells. Analysis of chronic OV-associated CCA liver specimens also showed elevated iNOS expression levels in neoplastic biliary cells (CCA cells), albeit absent in the inflammatory macrophages (
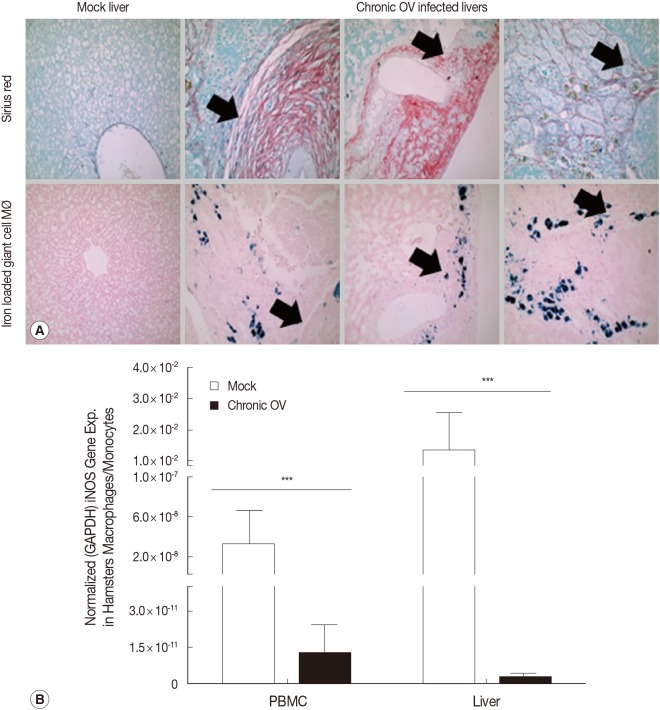
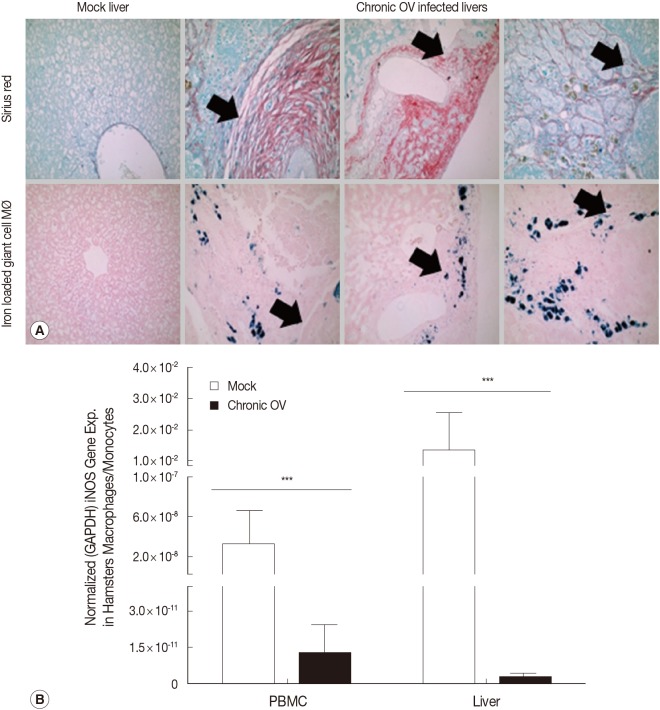
Fig. 1D). Analysis of chronic OV-associated liver inflammation in hamsters also showed high levels of iron loaded M2-like macrophages (giant cell macrophages, labile iron positive), which co-localized to fibrotic regions (
Fig. 2A). Furthermore, analysis of iNOS gene expression showed down-regulation in both blood and liver-derived monocytes/macrophages in chronic OV-infected hamsters compared to mock controls (
Fig. 2B).
Macrophages play critical roles in promoting host immune response and tissue repair; however, results from this study suggest that chronic M2-like macrophage activation promotes hepatobiliary fibrosis and neoplasia, with detrimental effects to the host. M2-like macrophages promote tissue fibrosis and neoplasia via the induction of polyamine biosynthesis, secretion of pro-fibrogenic/tumorigenic factors (e.g., TGFβ1 and PDGF) and impair host immune response via the secretion of immunosuppressive cytokines (e.g., IL-10) [
3]. Additionally, elevated tissue iron level is associated with oxidative stress which promotes tissue damage, fibrosis, and neoplasia [
10,
11]; thus M2-like macrophage-mediated liver iron overload could independently contribute to a hepatobiliary disease. Results from this study also suggest that induction of M2-like macrophage polarization could be a common mechanism by which chronic hepatotropic pathogens induced liver inflammatory disease, as recent studies in chronic HBV infections also demonstrated this link [
12]. Future studies addressing the mechanisms by which chronic OV infection and other hepatotropic pathogens induce M2-like macrophage polarization could provide clues on the mechanisms by which hepatotropic pathogens invade host immune responses and initiates/promotes hepatobiliary inflammatory diseases. Future studies should also address a limitation of this study, which only demonstrates a correlation between M2-like macrophages, parasite persistence, and liver fibrosis in chronic OV infection in hamsters and does not demonstrate the functionality of M2-like macrophages in pathogenesis. Furthermore, future studies should screen for the contribution of other liver infectious agents and co-morbidities in the induction of M2-like macrophages in chronic OV patients in endemic regions.
In conclusion, results from this study suggest that therapeutic targeting of iron loaded M2-like macrophages in chronic OV infection and associated hepatobiliary disease could be an effective strategy in attenuating fibrosis and cancer development and progression.
NIH-NIAIDP50AI 098639
Thailand-Tropical Diseases Research Programme02-2-HEL-05-054
Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University Project of ThailandOffice of the Higher Education CommissionHealth Cluster (SHeP-GMS), Khon Kaen UniversityACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by NIH-NIAID, award no. P50AI 098639, the Thailand-Tropical Diseases Research Programme (T-2, grant no. ID 02-2-HEL-05-054) and the Higher Education Research Promotion and National Research University Project of Thailand, Office of the Higher Education Commission, through the Health Cluster (SHeP-GMS), Khon Kaen University.
References
- 1. Sripa B, Brindley PJ, Mulvenna J, Laha T, Smout MJ, Mairiang E, Bethony JM, Loukas A. The tumorigenic liver fluke Opisthorchis viverrini-multiple pathways to cancer. Trends Parasitol 2012;28:395-407.
- 2. Lawrence T, Natoli G. Transcriptional regulation of macrophage polarization: enabling diversity with identity. Nat Rev Immunol 2011;11:750-761.
- 3. Murray PJ, Wynn TA. Protective and pathogenic functions of macrophage subsets. Nat Rev Immunol 2011;11:723-737.
- 4. Leyva-Illades D, McMillin M, Quinn M, Demorrow S. Cholangiocarcinoma pathogenesis: role of the tumor microenvironment. Transl Gastrointest Cancer 2012;1:71-80.
- 5. Ramachandran P, Iredale JP. Macrophages: central regulators of hepatic fibrogenesis and fibrosis resolution. J Hepatol 2012;56:1417-1419.
- 6. Papatriantafyllou M. Macrophages: iron macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol 2011;11:158-159.
- 7. Flemming A. Cancer: re-educating tumour-associated macrophages. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2011;10:177.
- 8. Binder F, Hayakawa M, Choo MK, Sano Y, Park JM. Interleukin-4-induced β-catenin regulates the conversion of macrophages to multinucleated giant cells. Mol Immunol 2013;54:157-163.
- 9. Sripa B, Kaewkes S, Sithithaworn P, Mairiang E, Laha T, Smout M, Pairojkul C, Bhudhisawasdi V, Tesana S, Thinkamrop B, Bethony JM, Loukas A, Brindley PJ. Liver fluke induces cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS Med 2007;4:e201.
- 10. Batts KP. Iron overload syndromes and the liver. Mod Pathol 2007;20:S31-S39.
- 11. Fargion S, Valenti L, Fracanzani AL. Beyond hereditary hemochromatosis: new insights into the relationship between iron overload and chronic liver diseases. Dig Liver Dis 2011;43:89-95.
- 12. Bility MT, Cheng L, Zhang Z, Luan Y, Li F, Chi L, Zhang L, Tu Z, Gao Y, Fu Y, Niu J, Wang F, Su L. Hepatitis B virus infection and immunopathogenesis in a humanized mouse model: induction of human-specific liver fibrosis and M2-like macrophages. PLoS Pathog 2014;10:e1004032.
Fig. 1Chronic O. viverrini infection and associated hepatobiliary disease is associated with iron loaded M2-like macrophages in humans. (A) Immunohistochemical analysis showed elevated levels of macrophages (CD68high, brown stain) with exclusively M2-like markers (CD163high, brown stain; CD40negative, red stain) in chronic O. viverrini infected human livers with hepatobiliary disease (N=307). (B) Analysis of representative samples (N=307) showed M2-like macrophages (CD163high, brown stain; iNOSnegative, red stain) in chronic O.viverrini infected human livers exhibit elevated iron loads (Prussian blue positive). Analysis of representative samples (N=307) showed M2-like macrophages (CD163high, brown stain; iNOSnegative, red stain) in chronic O. viverrini-infected human livers co-localized with tissue fibrosis (C) and neoplasia (D).
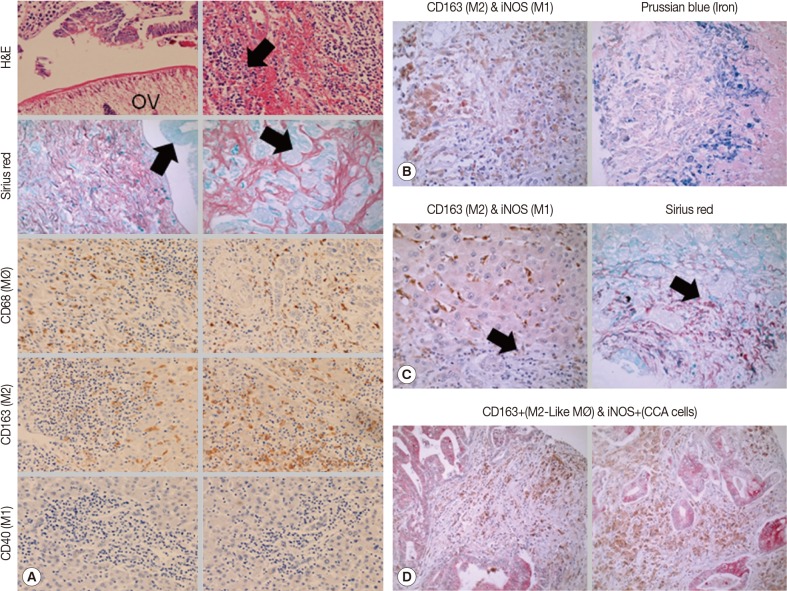
Fig. 2Chronic O. viverrini infection and associated hepatobiliary disease is associated with iron loaded M2-like macrophages in hamsters. (A) Histochemical analysis of representative samples showed elevated levels of iron loaded M2-like macrophages (Prussian blue positive, "Giant cell" macrophage morphology) in chronic O. viverrini infected hamster livers (n=3 Mock; n=6 chronic O. viverrini) and co-localization to fibrotic regions (black arrows denote same location of tissue). (B) Macrophages/monocytes in chronic O. viverrini-infected hamsters (n=6) exhibit reduced expression of the M1 gene iNOS (mormalized iNOS gene expression, iNOS/GAPDH) in the blood and liver compared to mock (n=3), thus suggesting chronic O. viverrini infection induces M2-like macrophage phenotype.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- Liver Fluke-Derived Molecules Accelerate Skin Repair Processes in a Mouse Model of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Anna Kovner, Yaroslav Kapushchak, Oxana Zaparina, Dmitry Ponomarev, Maria Pakharukova
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(22): 12002. CrossRef - Exploring the role of macrophages in determining the pathogenesis of liver fluke infection
Susel Loli Quinteros, Bronwyn O'Brien, Sheila Donnelly
Parasitology.2022; 149(10): 1364. CrossRef - Wound healing approach based on excretory-secretory product and lysate of liver flukes
Anna V. Kovner, Alena A. Tarasenko, Oxana Zaparina, Olga V. Tikhonova, Maria Y. Pakharukova, Viatcheslav A. Mordvinov
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The pathogenic potential of the combined action of chronic Opisthorchis felineus infection and repeated social defeat stress in C57BL/6 mice
Damira Avgustinovich, Anna Kovner, Elena Kashina, Natalia Shatskaya, Galina Vishnivetskaya, Natalia Bondar, Maria Lvova
International Journal for Parasitology.2021; 51(5): 353. CrossRef - High macrophage activities are associated with advanced periductal fibrosis in chronic Opisthorchis viverrini infection
Kanin Salao, Krongkarn Watakulsin, Eimorn Mairiang, Sutas Suttiprapa, Sirikachorn Tangkawattana, Steven W. Edwards, Banchob Sripa
Parasite Immunology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Chronic hepatitis C infection–induced liver fibrogenesis is associated with M2 macrophage activation
Moses T. Bility, Kouki Nio, Feng Li, David R. McGivern, Stanley M. Lemon, Eoin R. Feeney, Raymond T. Chung, Lishan Su
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef