Abstract
Proteomic tools allow large-scale, high-throughput analyses for the detection, identification, and functional investigation of proteome. For detection of antigens from Haemaphysalis longicornis, 1-dimensional electrophoresis (1-DE) quantitative immunoblotting technique combined with 2-dimensional electrophoresis (2-DE) immunoblotting was used for whole body proteins from unfed and partially fed female ticks. Reactivity bands and 2-DE immunoblotting were performed following 2-DE electrophoresis to identify protein spots. The proteome of the partially fed female had a larger number of lower molecular weight proteins than that of the unfed female tick. The total number of detected spots was 818 for unfed and 670 for partially fed female ticks. The 2-DE immunoblotting identified 10 antigenic spots from unfed females and 8 antigenic spots from partially fed females. Matrix Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization-Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF) of relevant spots identified calreticulin, putative secreted WC salivary protein, and a conserved hypothetical protein from the National Center for Biotechnology Information and Swiss Prot protein sequence databases. These findings indicate that most of the whole body components of these ticks are non-immunogenic. The data reported here will provide guidance in the identification of antigenic proteins to prevent infestation and diseases transmitted by H. longicornis.
-
Key words: Haemaphysalis longicornis, tick, antigenic protein, proteomic approach
INTRODUCTION
Ticks are ectoparasitic, blood-feeding arthropods that are transmitting pathogens to domestic and wild animals, and rank second only to mosquitoes as vectors of human diseases [
1,
2]. Vector control by immunological way represents a most important part of the current global strategy for the control of major vector-borne diseases. However, the success depends on detection, identification, and functional investigation of antigenic proteome that targets specific molecules which play key roles in tick physiological processes such as blood feeding or digestion process in ticks [
3-
5].
Tick control by vaccination has been for almost 70 years [
6], but progress in effective vaccines has been slow. For immunological control, identification of protective antigens is crucial. Several immunological approaches have been used to control disease vectors. Two types of antigenic target have been explored for vaccine development as exposed and concealed antigens. Immunological responses of different animal species to concealed tick antigens have been extensively reviewed [
7]. As concealed antigens as crude extracts of salivary gland, midgut, ovary, hemolymph, or whole tick has effect on tick detachment, increase feeding time, and less body weight of tick [
8]. Gene of
Boophilus microplus midgut associated molecules, Bm 86 and Bm 91 [
9], have been cloned and expressed and at present only Bm-86 based tick vaccine is commercially available. Other several exposed tick antigen vaccine targets, such as histamine binding protein [
10], troponin I like protein, p 27/30 [
11], heat shock protein [
12], and serine protease inhibitor serpin [
13], have been evaluated for control of ticks, and immunized rabbits showed partial or no protection against biting ticks. This may help researchers identify tick proteins as potential targets for further studies aimed to develop novel tick control strategies that may affect both the tick and the pathogen transmitted by it.
Recently, sensitive and reliable methods of protein separation were used for characterizing tick protein profiles. The characterization of protein profiles were performed by 2-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (2-DE) [
14] using commercial immobilized pH gradient (IPG) strips for isoelectric focusing in the first dimension [
15]. Proteins excised from 2-DE gels are digested with trypsin, and the resulting peptides are analyzed by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry (MALDI-MS) to make peptide mass fingerprints that are often used to identify proteins [
16].
Valenzuela et al. [
17] described a proteomic study using 1-DE gels and N-terminal sequence analysis for identification of sialome of the tick
Ixodes scarpularis. In addition, since the first paper was published by Madden et al. [
18] who described the proteomic approach using 2-DE gels and MALDI-MS to characterize protein profiles of 2 related tick species,
Amblyomma americanum and
A. maculatum, several papers using the above approach have been published in the tick field [
19-
24]. The purpose of present study is to identify the antigenic proteins of whole unfed and partially fed female
Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ticks
The Jeju strain of the hard tick H. longicornis has been maintained on rabbits in our laboratory since 2003. For the analysis of proteins expressed at blood-feeding, partially fed (ticks on rabbits for 2-3 days) female ticks were used.
Generation of rabbit anti-tick serum
To generate tick-immune rabbit sera at least 100 clean H. longicornis adults were placed on each ear of 4-5 weeks old female New Zealand white rabbits (Samtako, Osan, Korea). Tick-immune rabbit sera were collected after the 3rd challenge by ear-bleed or by cardiac puncture using protocols approved by the Chonbuk Animal Care and Use (approved no. CBU 2011-0063). The sera of rabbits, not infested with H. longicornis, were collected to use as a negative control. Those sera were tested for reactivity to tick whole body extracts by immunoblot analysis as described below.
Sample preparation
The female whole body was washed with PBS containing penicillin/streptomycin (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA) and then suspended with 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0). After homogenizing and sonication, it was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 30 min at 4˚C. After quantification, the sample was stored at -20˚C until next use. As the samples for 2-DE, washed female ticks were homogenized with lysis buffer A (9.5 M urea, 1.2% w/v DTT), and the homogenate was then centrifuged at 13,000 g for 20 min at 4˚C. The supernatant was transferred to a new tube and adjusted to 500 μl with lysis buffer A. After adding CHAPS (Sigma, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) (final concentration of 4% w/v), the mixture was shaken for 30 min at room temperature (RT) and centrifuged at 13,000 g for 1 hr at 4˚C. Finally, the supernatant was moved to a new tube and stored at -20˚C until next use after quantification by the PlusOne 2-D Quant Kit (GE Healthcare, Vienna, Austria).
SDS-PAGE
The prepared tick sample was mixed with sample buffer, i.e., 125 mM Tris-HCl, pH 6.8, 20% v/v glycerol, 4% w/v SDS, 10% v/v 2-mercaptoethanol, and a few crystals of bromophenol blue (Wako, Wako, Japan), and then boiled for 5 min. After sample loading (15 μg/lane), protein was separated on 12.5% polyacrylamide gel with discontinuous buffer system of pH 6.8 and 8.8 by constant current of 24 mA.
Isoelectric focusing (IEF) and SDS-PAGE
IEF was performed using the IPGphor™ system (Amersham Bioscience, Uppsala, Sweden) with IPG strips (Immobiline DryStrip™, pH 3-10 and 4-7, 13 cm; Amersham Bioscience). Electrophoresed gels stained by Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) R250 solution (Elpis Biotech, Daejeon, Korea) according to the manufacturer’s instructions and silver-stained as previously described [
25].
Proteins were electro-transferred from gels to millipore PVDF membranes (0.45 μm; Millipore, Bedford, Massachusetts, USA) for 90 min at 5 V for 1-DE gels and 20 V for 2-DE gels. The membranes were blocked with 3% skim milk in Tris-based saline (TBS) for 1 hr at RT and then rinsed with TBS containing 0.05% (v/v) Tween 20 (Sigma). Following this procedure, the membranes were incubated with anti-H. longicornis rabbit sera at 1:1,000 dilution at RT for 3.5 hr. After 3 new washes, the blots were incubated with an alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG (Bethyl Laboratories, Montgomery, Texas, USA) at a 1:5,000 dilution and washed again 3 times. Incubations were performed at room temperature for 1 hr and washed. Finally, the antigenic spots were developed with BCIP/NBT solution (BioFX, Owings Mills, Maryland, USA) and their images were scanned with the Epson Perfection V700 Photo (Seiko Epson Corp., Tokyo, Japan). Immunoblots and their homologous silver-stained gels were aligned to isoelectric point (pI) and molecular weight (MW) and then matched by ImageMaster 2-DE Platinum Softwarev5.0 (Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway, New Jersey, USA) in order to identify antigenic spots in the gels.
Identification of antigenic proteins
Antigenic spots from 2-DE gels were identified by peptide mass fingerprinting (PMF) using MALDI-TOF MS, as described by Shin et al. [
25]. MALDI plate was performed using the solution-phase nitrocellulose method. The α-cyano-4-hydroxycinamic acid (40 mg/ml) and nitrocellulose (20 mg/ml) were prepared separately in acetone and mixed with isopropanol in a ratio of 2:1:1 (v/v). The mixed solution (1 μl) was spotted onto target circles on the MALDI plate and dried. The dried samples were analyzed using a Voyager-DE STR MALDI-TOF mass spectrometer (PerSeptive Bio-systems, Framingham, Massachusetts, USA). Internal calibration of MALDI-TOF mass spectra was performed using 2 trypsin autolysis ions with m/z ¼ 842.510 and 2211.105; for MALDI-MS/MS. The generated PMF were submitted to the MASCOT search program for identifying protein in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) and SwissProt protein sequence databases.
RESULTS
Comparative 1-DE analysis of unfed and partially fed female ticks
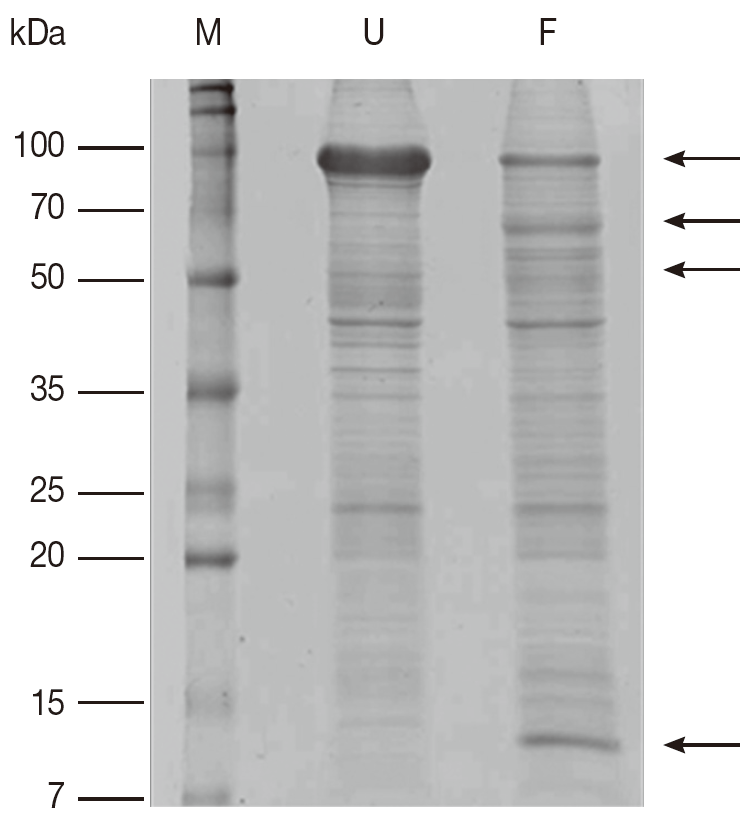
A comparison of proteins obtained from unfed and partially fed female ticks on 1-DE gel showed some differences (
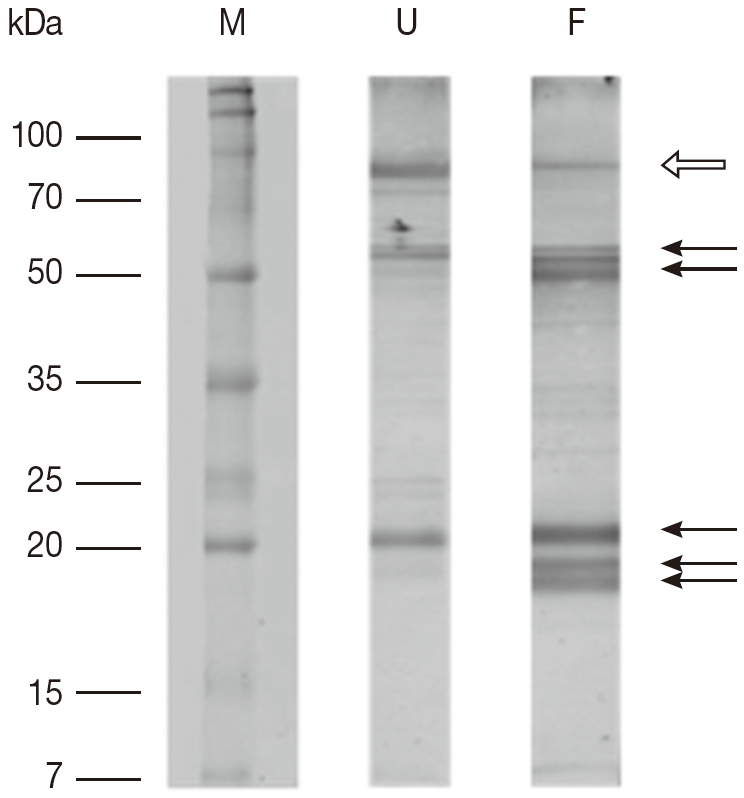
Fig. 1). There is decrease in proteins in partially fed female ticks with molecular masses of approximately 90 kDa, whereas a few proteins in the molecular mass range below 70 kDa were expressed in a higher number. The immunoblots comparing proteins extracted from unfed and partially fed female ticks showed differences in low abundance proteins (
Fig. 2). The predominant immune reactions were shown in a range of 16-20, 50-60, and 90 kDa proteins from both groups of ticks.
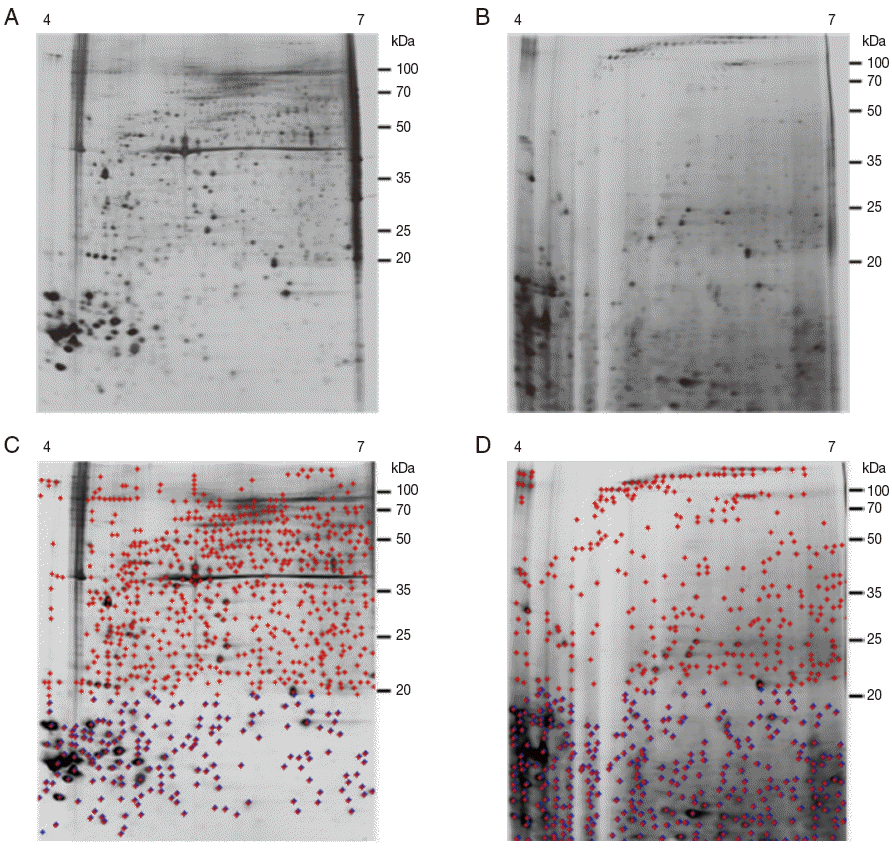
The 2-DE gel of proteins from partially fed female ticks (
Fig. 3B,
D) showed the more intense spots localized in a molecular mass range below 20 kDa, whereas spots in the immunoblot of samples from unfed female ticks were in a wider range. The total number of detected spots was 818 for unfed female ticks and 670 for partially fed female ticks, and spots detected under 20 kDa in size were 186 and 370 spots for unfed and fed ticks, respectively (
Fig. 3C,
D).
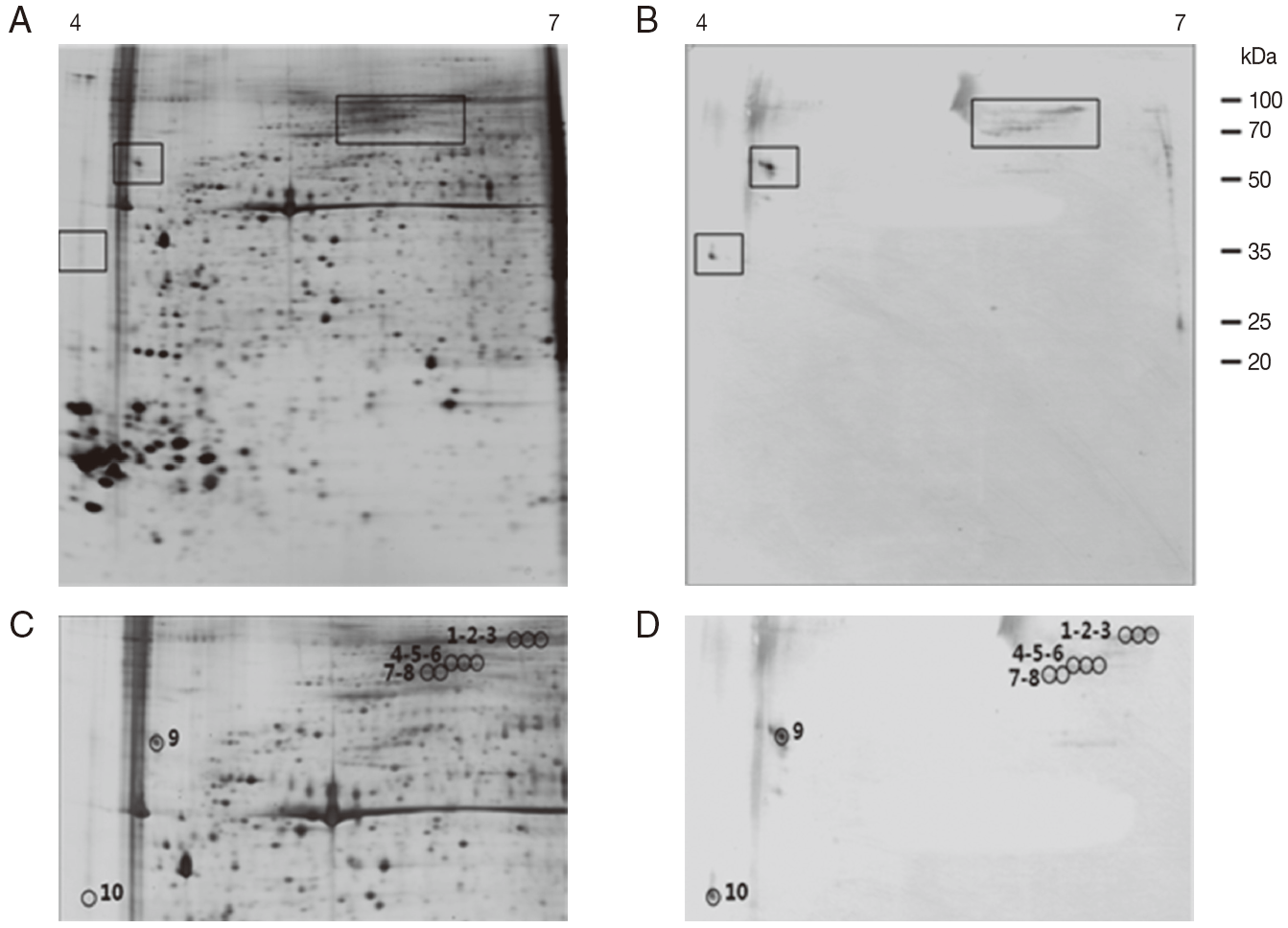
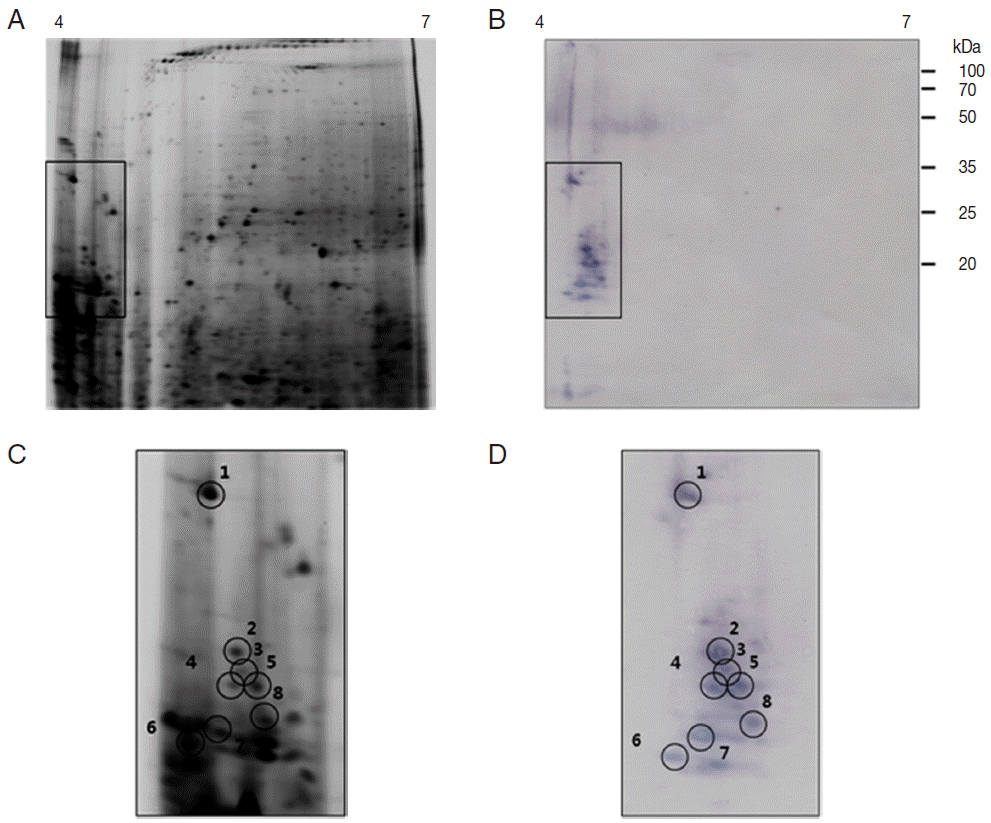
As shown in
Fig. 4B and
D, the 2-DE immunoblot analysis of the proteins from unfed female ticks with sera from rabbits infested by
H. longicornis revealed around 10 major spots in the range of pI 4.0-6.5 and 35-100 kDa. Matching of the immunoblot with its homologous silver-stained gel allowed us to localize these 10 major antigenic spots in the 2-DE gels (
Fig. 4C,
D). The 2-DE immunoblot analysis of the proteins from partially fed female ticks with sera from rabbits infested by
H. longicornis revealed around 8 major spots in a narrow range of pI (4.0-5.0) and molecular weight (16-35 kDa), and some minor and poorly resolved spots in the range of pI 5.5-6.0 and 25-30 kDa (
Fig. 5B,
D). Matching of the immunoblot with its homologous silver-stained gel allowed us to localize the 8 major antigenic spots in the 2-DE gels (
Fig. 5C,
D).
Antigenic proteins in 2-DE analysis of unfed female ticks were found in the range of 20, 60, and 90 kDa, similar to what was seen in 1-DE analysis whereas antigenic proteins in 1-DE analysis of partially fed female ticks were found in a range of 16-20, 50-60, and 90 kDa and in 2-DE analysis they were shown in a range of 18-23 and 32 kDa (
Table 1). Tryptic peptides were initially assessed by MALDI-TOF MS and PMF were obtained for all 18 antigenic proteins. Spot no. 1 from partially fed female ticks (
Fig. 5C) was closely related to calreticulin. The predicted MW (43.25-47.20 kDa) and pI (4.50-4.54) of calreticulin were different from the measured values of the spot no. 1 from partially fed female ticks. Spot nos. 6 and 8 from partially fed female ticks were closely related to a putative secreted WC salivary proteins of
I. scapularis (GenBank accession no. AAY66524; protein score 29; calculated MW in kDa/pI: 12.56/6.54) and a conserved hypothetical protein of
I. scapularis (GenBank accession no. XP_002435538; protein score 32; calculated MW/pI: 9.73/6.54), respectively (
Table 2). The identities of the other 15 spots remain unknown.
DISCUSSION
The aim of this study was to provide proteome of unfed and partially fed
H. longicornis female and uncover proteins that express at the stage of blood ingestion and react with sera of rabbits exposed to ticks. To accomplish this goal, we carried out a proteomic study of the whole body proteins of both female ticks based on 2-DE-electrophoresis, immunoblot, MS, and database searching in a similar way to that of the scant proteomic studies carried out with tick saliva and salivary gland extracts [
18,
20,
21], tick midgut [
19,
22], ovaries [
22], hemolymph, or with extracts of whole tick larvae [
23].
The proteomic maps of the unfed and partially fed female ticks showed differences between them. Regarding the total number of spots detected, the proteome of the partially fed female ticks showed a larger number in range of lower molecular weight than that of the unfed female ticks. The ratio of spots detected under 20 kDa to the total number of spots were 186/818 in unfed female ticks and 370/670 in partially fed female ticks. These suggest that lower molecular proteins of partially fed female ticks were expressed at the stage of blood ingestion.
In this study, we detected several antigenic proteins from the whole body of female unfed and partial fed ticks and only 3 antigenic proteins match with available databank. These all 3 proteins are from partially fed female tick as calreticulin, putative secreted WC salivary protein, and a conserved hypothetical protein.
An antigenic protein from partially fed female ticks showed 32 kDa in size and pI 4.0 in 2-DE gel closely related with calreticulin from several tick species (
Table 2). The recombinant tick calreticulin showed approximately 55-60 kDa [
26-
29] or 64 kDa [
30] size in SDS-PAGE, although the predicted molecular weights lay around 46 kDa, which is derived from a C-terminal acidic domain [
31]. These discrepancies of molecular mass could be attributed to the high content of charged residues (D, E, and K) in the amino acid sequence leading in mobility during electrophoresis. Calreticulin, a calcium-binding protein, is secreted by ticks into their hosts and play a role in blood feeding through host immune-suppression or antihemostasis [
28,
29]. Calreticulin has been found in a variety of vertebrates and invertebrates, including a large number of tick species [
2,
29]. Calreticulin is not detectable in the unfed salivary glands, but is strongly present in the salivary glands around the third day after feeding [
28]. Based on current knowledge, calreticulin is being examined as a possible target for the development of novel anti-thrombotic agents [
31]. Rabbits experimentally immunized with
A. americanum calreticulin exhibited local necrotic lesions in the tick bite sites, indicating that host immune reaction could confuse the feeding cycle [
28]. Sera of
B. microplus-infested bovines suggested that calreticulin may not be able to induce an IgG-based humoral response in its natural host [
26]. However,
A. americanum calreticulin was recognized by sera from rabbits and humans exposed to tick bites [
30]. In our results, for the first time,
H. longicornis calreticulin-like protein was recognized by sera from rabbits exposed to tick bites. As a vaccine candidate, more work about this protein is clearly needed to understand its antigenic significance.
Spots no. 6 and 8 from partially fed female ticks were closely related to a putative secreted WC salivary protein of
I. scapularis (GenBank accession no. AAY66524; protein score 29; calculated MW/pI: 12.56/6.54) and a conserved hypothetical protein of
I. scapularis (GenBank accession no. XP_002435538; protein score 32; calculated MW/pI: 9.73/6.54), respectively (
Table 2). These proteins are not found in unfed ticks suggesting that they have functional role during blood feeing. The 1-DE immunoblot results represent 3 bands from unfed ticks and 5 bands form partially fed. This may be due to that during blood meal ingestion salivary glands undergo remarkable growth and differentiation accompanied by significant increase in protein synthesis [
32].
In addition to identification of antigenic proteins, we identified abundant proteins in unfed female ticks. In
Fig. 5A, protein spots between 35 and 50 kDa in size and pI between 5.0 and 6.0 were identified as actin of
Aedes aegypti (GenBank accession no. XP_001659963; protein score 46; calculated MW/pI: 41.75/5.22). Also, the protein spot, approximately 20 kDa in size and pI 4.0, was identified as tropomyosin of
H. longicornis (GenBank accession no. Q8IT89; protein score 103; calculated MW/pI: 32.85/4.69). It might be because we used whole body proteins including legs of ticks but other papers which used midguts also showed actin and tropomyosin in the protein identification [
19,
33]. Actin has molecular functions such as ATP binding, protein binding, nucleotide binding, and structural molecule activity. Actin is highly conserved proteins that are involved in various types of cell motility and are ubiquitously expressed in all eukaryotic cells [
33]. Tropomyosin plays a central role in the Ca
++-dependant regulation of muscle contraction [
33]. In a recent study, tropomyosin plays an important role in host-protective immune responses in several helminthic infections of animals [
34]. Therefore, an additional investigation about the relationship between host immune reaction and tick tropomyosin is required.
Quantitative analysis of 2-DE gels stained with CBB showed that intense spots in acidic conditions and with lower molecular weight were in fact most abundant and common spots between them. According to Untalan et al. [
23], urea-soluble proteins, acidic and with low molecular mass, derived from unfed larvae of
B. microplus were identified as putative cuticular proteins. Untalan et al. [
23] used whole body proteins from hard ticks distinct from others who used salivary glands or midguts, which were the same in our study. This would mean that intense spots shown in our results were exo-skeletal proteins. However, Hackman [
35] described cuticular proteins from engorged, adult female
B. microplus as being >25 kDa in size and of a pI between 6.0 and 9.0, which is in contrast to the much more acidic, low molecular weight proteins observed from larvae. This suggests that there may be different subsets of cuticular proteins expressed at various life cycle stages of the tick, or as described above, post-translational modifications caused those differences.
In this study, we detected several antigenic proteins from the whole body of female ticks, and most are still unidentified as 15 antigenic proteins are unknown proteins that did not match with available databank. The limited amount of protein samples that can be obtained from H. longicornis made difficult to be characterized by LC MS/MS. Recent improvements in 2-dimensional gel electrophoresis, MS, and bioinformatics provide new tools to characterize small amounts of proteins. The whole body proteins of unfed and partially fed female ticks differed in number and distribution of the antigenic spots detected by sera of infested rabbits. In both ticks, the ratio of antigenic spots to the total number of spots was low. This observation indicates that most of the whole body components of these ticks are not immunogenic.
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
Fig. 1.Comparison of Coomassie brilliant blue R250-stained proteins on 1-DE gel from unfed and partially fed female ticks. F, proteins from partially fed female ticks; M, relative molecular weight and position of standards; U, proteins from unfed female ticks. Arrows mark differences in protein amounts between unfed and partially fed female ticks.
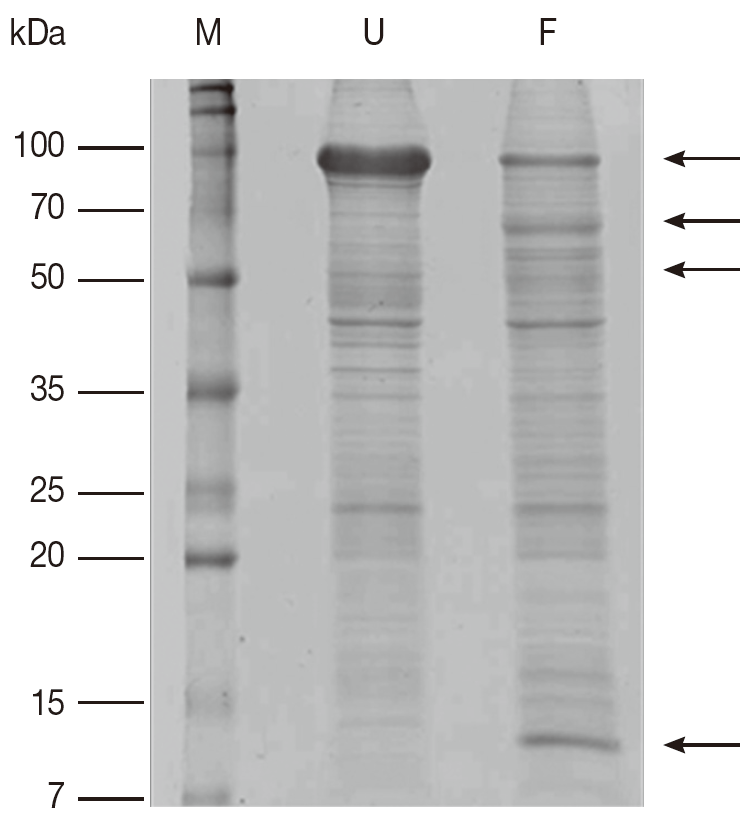
Fig. 2.The results of 1-DE immunoblot SDS/12.5% PAGE comparing proteins extracted from unfed and partially fed female ticks. F, proteins from partially fed female ticks; M, relative molecular weight and position of standards; U, proteins from unfed female ticks. Fifteen μg of whole body proteins from unfed and partially fed female ticks were used in the experiment. Representative images are based on 3 independent experiments. Arrows mark differences in protein amounts between unfed and partially fed female ticks. White arrow indicates a decrease in immune reaction in fed female ticks.
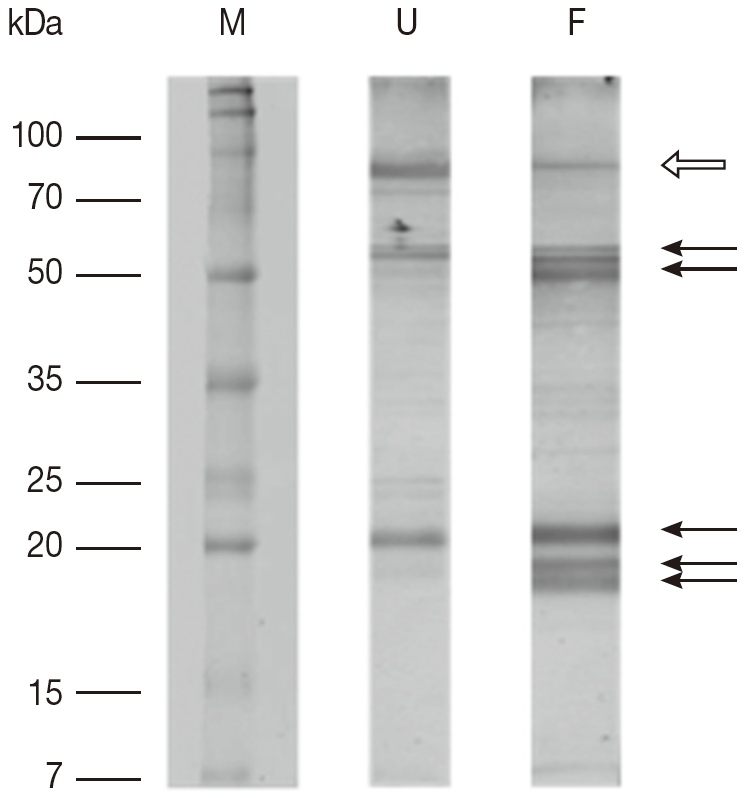
Fig. 3.Representative silver-stained 2-DE images of whole body proteins from female ticks. (A) Proteins from unfed female ticks. (B) Proteins from partially fed female ticks. Proteins (240 μg) were focused on pH 4-7 IPG strips (13 cm) and were then separated by SDS/12.5% PAGE. Reference molecular masses are indicated on the right of the gel. Representative images are based on 3 independent experiments. (C, D) Analysis of A and B using ImageMaster 2-D Platinum Software. The total number of detected spots (red crossed) was 818 for unfed female ticks and 670 for partially fed female ticks. The numbers of spots detected below 20 kDa (blue crossed) were 186 and 370 spots for unfed and partially fed ticks, respectively.

Fig. 4.Representative 2-DE images of the whole body proteins from unfed female ticks of H. longicornis. (A) Silver stained gel. (B) Immunoblot probed with polyclonal antibodies against H. longicornis. Proteins (240 μg) were focused on pH 4-7 IPG strips (13 cm) and were then separated by SDS/12.5% PAGE. Reference molecular masses are indicated on the right. 2-DE immunoblot shows the antigenic spots revealed by a pool of sera from rabbits experimentally infested with H. longicornis. The proteins of interest are marked in the image (rectangles). (C, D) Magnifications of panels A and B. In D, antigenic spots are indicated by black numbered circles and are equivalent to the proteins identified in panel C.

Fig. 5.Representative 2-DE images of the whole body proteins from partially fed female ticks of H. longicornis. (A) Silver stained gel. (B) Immunoblot probed with polyclonal antibodies against H. longicornis. Proteins (240 μg) were focused on pH 4-7 IPG strips (13 cm) and were then separated by SDS/12.5% PAGE. Reference molecular masses are indicated on the right of the gel. 2-DE immunoblot shows the antigenic spots revealed by a pool of sera from rabbits experimentally infested with H. longicornis. The proteins of interest are marked in the image (rectangles). (C, D) Magnifications of panels A and B. In D, antigenic spots are indicated by black numbered circles and are equivalent to the proteins identified in panel.

Table 1.Comparison of molecular weights of the antigenic proteins from unfed and partially fed female ticks
Table 1.
|
|
Molecular weight (kDa) of antigenic proteins |
|
Unfed female ticks |
1-DE |
20, 60, 90 |
|
2-DE (pI 4-7) |
35 (no. 10), 60 (no. 9), 70-90 (no. 1-8) |
|
Partially fed female ticks |
1-DE |
16-20, 50-60, 90 |
|
2-DE (pI 4-7) |
18-20 (no. 6-8), 20-23 (no. 2-5), 32 (no. 1) |
Table 2.Summary of antigenic proteins identified in the whole body of H. longicornis by MALDI-TOF
Table 2.
|
Spot no. |
Protein ID (GenBank accession no.) |
Protein scores |
Sequence coverage (%) |
No. peptides P < 0.05 |
Calculated MW/PI |
|
Partially fed female ticks |
1 |
Calreticulin [Amblyomma scutatum] (AAR29938) |
56 |
28 |
1 |
47.15 / 4.50 |
|
|
Calreticulin [Amblyomma rotundatum] (AAR29937) |
54 |
27 |
12 |
47.27 / 4.52 |
|
|
Calreticulin [Rhipicephalus annulatus (Boophilus annulatus)] (AAR29939) |
54 |
30 |
13 |
47.724 / 4.48 |
|
|
Calreticulin [Haemaphysalis longicornis] (AAQ18695) |
49 |
27 |
10 |
47.22 / 4.52 |
|
|
Calreticulin [Haemaphysalis leporispalustris] (AAR29947) |
45 |
23 |
9 |
43.25 / 4.54 |
|
6 |
Putative secreted WC salivary protein [Ixodes scapularis] (AAY66524) |
29 |
31 |
4 |
12.56 / 6.54 |
|
8 |
Conserved hypothetical protein [Ixodes scapularis] (XP_002435538) |
32 |
31 |
4 |
9.73 / 6.54 |
References
- 1. Wang H, Kaufman WR, Cui WW, Nuttall PA. Molecular individuality and adaptation of the tick Rhipicephalus appendiculatus in changed feeding environments. Med Vet Entomol 2001;15:403-412.
- 2. Xu G, Fang QQ, Keirans JE, Durden LA. Cloning and sequencing of putative calreticulin complementary DNAs from four hard tick species. J Parasitol 2004;90:73-78.
- 3. Imamura S, da Silva Vaz I Jr, Konnai S, Yamada S, Nakajima C, Onuma M, Ohashi K. Effect of vaccination with a recombinant metalloprotease from Haemaphysalis longicornis. Exp Appl Acarol 2009;48:345-358.
- 4. You M, Fujisaki K. Vaccination effects of recombinant chitinase protein from the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae). J Vet Med Sci 2009;71:709-712.
- 5. You M, Xuan X, Tsuji N, Kamio T, Igarashi I, Nagasawa H, Mikami T, Fujisaki K. Molecular characterization of a troponin I-like protein from the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2001;32:67-73.
- 6. Trager W. Acquired immunity to ticks. J Parasitol 1939;25:57-81.
- 7. Wikel SK. Host immunity to ticks. Ann Rev Entomol 1996;41:1-22.
- 8. Allen JR, Humphreys SJ. Immunisation of guinea pigs and cattle against tick. Nature 1979;280:491-493.
- 9. Rand KN, Moore T, Sriskantha A, Spring K, Tellam R, Willadsen P, Cobon GS. Cloning and expression of a protective antigen from the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989;86:9657-9661.
- 10. Paesen GC, Adams PL, Harlos K, Nuttall PA, Stuart DI. Tick histamine-binding proteins: isolation, cloning, and three-dimensional structure. Mol Cell 1999;3:661-671.
- 11. You MJ. Immunization of mice with recombinant P27/30 protein confers protection against hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) infestation. J Vet Sci 2005;6:47-51.
- 12. Nuttall PA, Trimnell AR, Kazimirova M, Labuda M. Exposed and concealed antigens as vaccine targets for controlling ticks and tick-borne diseases. Parasite Immunol 2006;28:155-163.
- 13. Imamura S, da Silva Vaz I Jr, Sugino M, Ohashi K, Onuma M. A serine protease inhibitor (serpin) from Haemaphysalis longicornis as an anti-tick vaccine. Vaccine 2005;23:1301-1311.
- 14. O'Farrell PH. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem 1975;250:4007-4021.
- 15. Bjellqvist B, Ek K, Righetti PG, Gianazza E, Görg A, Westermeier R, Postel W. Isoelectric focusing in immobilized pH gradients: principle, methodology and some applications. J Biochem Biophys Methods 1982;6:317-339.
- 16. Gevaert K, Vandekerckhove J. Protein identification methods in proteomics. Electrophoresis 2000;21:1145-1154.
- 17. Valenzuela JG, Francischetti IM, Pham VM, Garfield MK, Mather TN, Ribeiro JM. Exploring the sialome of the tick Ixodes scapularis. J Exp Biol 2002;205:2843-2864.
- 18. Madden RD, Sauer JR, Dillwith JW. A proteomics approach to characterizing tick salivary secretions. Exp App Acarol 2002;28:77-87.
- 19. Kongsuwan K, Josh P, Zhu Y, Pearson R, Gough J, Colgrave ML. Exploring the midgut proteome of partially fed female cattle tick (Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus). J Insect Physiol 2010;56:212-226.
- 20. Mans BJ, Venter JD, Vrey PJ, Louw AI, Neitz AW. Identification of putative proteins involved in granule biogenesis of tick salivary glands. Electrophoresis 2001;22:1739-1746.
- 21. Oleaga A, Escudero-Población A, Camafeita E, Pérez-Sánchez R. A proteomic approach to the identification of salivary proteins from the argasid ticks Ornithodoros moubata and Ornithodoros erraticus. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2007;37:1149-1159.
- 22. Rachinsky A, Guerrero FD, Scoles GA. Differential protein expression in ovaries of uninfected and Babesia-infected southern cattle ticks, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2007;37:1291-1308.
- 23. Untalan PM, Guerrero FD, Haines LR, Pearson TW. Proteome analysis of abundantly expressed proteins from unfed larvae of the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2005;35:141-151.
- 24. Vennestrøm J, Jensen PM. Ixodes ricinus: the potential of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis as a tool for studying host-vector-pathogen interactions. Exp Parasitol 2007;115:53-58.
- 25. Shin GW, Palaksha KJ, Yang HH, Shin YS, Kim YR, Lee EY, Oh MJ, Jung TS. Partial two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) maps of Streptococcus iniae ATCC29178 and Lactococcus garvieae KG9408. Dis Aquat Organ 2006;70:71-79.
- 26. Ferreira CA, da Silva Vaz I, da Silva SS, Haag KL, Valenzuela JG, Masuda A. Cloning and partial characterization of a Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) calreticulin. Exp Parasitol 2002;101:25-34.
- 27. Gao J, Luo J, Fan R, Fingerle V, Guan G, Liu Z, Li Y, Zhao H, Ma M, Liu J, Liu A, Ren Q, Dang Z, Sugimoto C, Yin H. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding calreticulin from Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis (Acari: Ixodidae). Parasitol Res 2008;102:737-746.
- 28. Jaworski DC, Simmen FA, Lamoreaux W, Coons LB, Muller MT, Needham GR. A secreted calreticulin protein in ixodid tick (Amblyomma americanum) saliva. J Insect Physiol 1995;41:369-375.
- 29. Parizi LF, Rech H, Ferreira CA, Imamura S, Ohashi K, Onuma M, Masuda A, da Silva Vaz I Jr. Comparative immunogenicity of Haemaphysalis longicornis and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus calreticulins. Vet Parasitol 2009;164:282-290.
- 30. Sanders ML, Jaworski DC, Sanchez JL, DeFraites RE, Glass GE, Scott AL, Raha S, Ritchie BC, Needham GR, Schwartz BS. Antibody to a cDNA-derived calreticulin protein from Amblyomma americanum as a biomarker of tick exposure in humans. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1998;59:279-285.
- 31. Coppolino MG, Dedhar S. Calreticulin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1998;30:553-558.
- 32. Leboulle G, Rochez C, Louahed J, Ruti B, Bollen A, Godfroid E. Isolation of Ixodes ricinus salivary gland mRNA encoding factors induced during blood feeding. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2002;66:225-233.
- 33. Rachinsky A, Guerrero FD, Scoles GA. Proteomic profiling of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus midgut responses to infection with Babesia bovis. Vet Parasitol 2008;152:294-313.
- 34. Jenkins RE, Taylor MJ, Gilvary NJ, Bianco AE. Tropomyosin implicated in host protective responses to microfilariae in onchocerciasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998;95:7550-7555.
- 35. Hackman RH. The soluble cuticular proteins form three arthropod species: Scylla serrata (Decapoda: Portunidae), Boophilus microplus (Acarina: Ixodidae) and Agrianome spinicollis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Comp Biochem Physiol (Part B) 1974;49:457-462.