Abstract
Toxocara vitulorum has been rarely reported in yaks at high altitudes and remote areas of Sichuan Province of Tibetan Plateau of China. The current study was designed to investigate the prevalence, associated risk factors, and phylogenetic characteristics of T. vitulorum in yak calves on the Qinghai Tibetan plateau. Fecal samples were collected from 891 yak calves and were examined for the presence of T. vitulorum eggs by the McMaster technique. A multivariable logistic regression model was employed to explore variables potentially associated with exposure to T. vitulorum infection. T. vitulorum specimens were collected from the feces of yaks in Hongyuan of Sichuan Province, China. DNA was extracted from ascaris. After PCR amplification, the sequencing of ND1 gene was carried out and phylogenetic analyses was performed by MEGA 6.0 software. The results showed that 64 (20.1%; 95% CI 15.8–24.9%), 75 (17.2; 13.8–21.1), 29 (40.9; 29.3–53.2), and 5 (7.6; 2.5–16.8) yak calves were detected out to excrete T. vitulorum eggs in yak calve feces in Qinghai, Tibet, Sichuan, and Gansu, respectively. The present study revealed that high infection and mortality by T. vitulorum is wildly spread on the Qinghai Tibetan plateau, China by fecal examination. Geographical origin, ages, and fecal consistencies are the risk factors associated with T. vitulorum prevalence by logistic regression analysis. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of ND1 gene of T. vitulorum indicated that T. vitulorum in the yak calves on the Qinghai Tibetan plateau are homologous to preveiously studies reported.
-
Key words: Toxocara vitulorum, prevalence, risk factor, yak, ND1, Qinghai Tibetan plateau
INTRODUCTION
The common ascarid parasite of young
Bubalus and
Bos spp,
Toxocara vitulorum is spread worldwide dominating in tropical and subtropical climatic regions [
1]. Cattle calves were typically become infected in early postpartum by ingesting larvae excreted in the colostrum and milk causing highly morbidity and mortality in calves [
2]. The clinical signs of
T. vitulorum infection are sometimes present, while many infections are subclinical. However, previous studies have mentioned
T. vitulorum as paramount cause of death among buffalo calves in Bangladesh and described a fatal case in Turkey calf [
3]. A major impact of
T. vitulorum infection is the association of mortalities as well as morbidity, causing uncompensated stunted growth in calves that survive and result in serious economic losses due to lacking or inefficient control [
2,
4,
5].
The long haired animal, yak (
Bos grunniens) is a bovine species, which were mostly found throughout the Himalayan region and inhabits at high cold altitude (above 3,000 m) plateaus in China, Russia, Bhutan, Nepal, Mongolia, India, and other countries [
6,
7]. The distribution of yaks in Qinghai, Tibet, Sichuan and Gansu, China is account of as many as 90% of the world yaks [
8]. Its milk, meat, dung, and wool are all useful to native herdsmen, which makes yaks particularly important in economy. So, in such remote plateaus, any yak disease causes numerous losses [
6,
8]. However,
T. vitulorum is rarely reported in yaks at such high remote altitude regions. The current study was designed for the first time to investigate the prevalence, associated risk factors, and phylogeny of
T. vitulorum using PCR sequencing of a mitochondrial gene of
ND1, as previous publications suggested that the mitochondrial
ND1 gene had provided a universally accepted marker for molecular parasite identification [
9].
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethics statement
Each procedure was performed under the instructions and approval of the ethics committee of Huazhong Agricultural University (permit no. 4200695757).
Fecal collection and examination
Fecal samples were collected from 891 yak calves (1–15 weeks) in 2015 in Qinghai (Zaduo, Nangqian, Zhiduo), Tibet (Qamdo, Xigaze, Nyingchi, Lhasa), Sichuan (Hongyuan), and Gansu (Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture) (
Table 1). Each fecal sample was examined for
T. vitulorum eggs by the McMaster technique with a sensitivity of 50 eggs per gram of feces (EPG) [
10]. Fecal samples were scored as being either normal, soft, or watery according to its consistency as Dorny et al. [
2] described in 2015.
Adult ascaris worms were collected from the feces of yaks in Hongyuan of Sichuan, China during May and September in 2015. Parasites were first washed extensively with 0.9% sodium chloride solution, and then identified through morphological examinations [
11,
12]. After that, parasites were fixed in 75% alcohol (V/V) and stored at −20°C for further use [
12,
13]. Total genomic DNA of parasite extraction was performed be employing DNA extraction reagent kit (TIANamp Genomic DNA Kit, Tiangen Biotech Co., Beijing, China) according to manufacturer’s recommendations. The eluted DNA was stored at −20°C prior to PCR analysis.
A PCR amplification approach was used to amplified a fragment (−370 bp) of the NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 (ND1) of mitochondrial (mt) gene. During the PCR, the primer pairs (forward: 5′-TTCTTATGAGATTGCTTTT-3′ and reverse: 5′-TATCATAACGAAAACGAGG-3′) were used. The PCR mixture contained 9.75 μl autoclaved, distilled water, 5 μl PCR buffer (10×), 3 μl MgCl2 (25 mM), 2 μl dNTPs (2.0 mM), 1 μl DNA, 0.25 μl Taq, 2 μl of each forward and reverse primer (working concentration: 10 μmol/L) in a 25 μl reaction volume. Each of the 40 PCR cycles consisted of 94°C for 30 sec, 50°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 1 min after an initial hot start at 94°C for 5 min and ending with 72°C for 5 min. PCR products were analyzed on a 1% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide following electrophoresis. The PCR electrophoresis products were purified using a Hi-TIANgel Midi Purification Kit (Tiangen Biotech Co., Beijing, China) according to manufacturer’s recommendations.
Molecular cloning and sequencing of the ND1 gene
The purified amplifications were cloned into PGEM®-T Easy vector (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA), and blue-white colony screening method was used to identify the positive clones. Further confirmation was performed by PCR. The positive clones were sequenced using Sequenase Version 2.0 (USB) and [a-32P] dATP (Bresatec, Adelaide, South Australia). The remaining isolates were processed by cycle-sequencing reactions and run on an ABI 373A automated sequencer. The primers used for PCR amplification were also used for sequencing.
Sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis
Sequence data were compared with other ascarids available at NCBI (
http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi), while alignments and phylogenetic analysis were conducted using the software MEGA (6.06). These strains were
T. vitulorum (AJ937266.1),
Toxocara canis (KC293917.1),
Baylisascaris procyonis (JF951366.1),
Toxocara cati (JF833958.1),
Ascaris suum (HQ704901.1),
Anisakis simplex (JN786327.1),
Toxascaris leonina (NC_023504.1), and
Strongyloides stercoralis (NC_028624.1).
T. vitulorum fecal egg counts were summarized by their arithmetic mean and SD. The proportions of positive fecal samples were assessed among the 891 yak samples, as well as all factors (gender, geographical origin, fecal consistencies, and age). A multivariable logistic regression model was performed to explore variables potentially associated with exposure to T. vitulorum infection. Probability (P) value<0.05 was considered as statistically significant between levels within factors and interactions. Odds-ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) based on likelihood ratio statistics are reported. All statistical analyses were performed using the PASW Statistics17.0 (SPSS Inc., IBM Corporation, Somers, New York, USA).
RESULTS
A total of 819 yak calves were detected in the current study; 64 (20.1%; 95% CI 15.8–24.9%), 75 (17.2; 13.8–21.1), 29 (40.9; 29.3–53.2), and 5 (7.6; 2.5–16.8) yak calves were detected out to excrete
T. vitulorum eggs in yak calve feces in Qinghai, Tibet, Sichuan, and Gansu, respectively with significant differences in different regions on the Qinghai Tibetan plateau (
P<0.01). The prevalence in Qinghai ranged from 13.9% to 35.2%, with significant differences in different regions (
P<0.01). The prevalence in Tibet ranged from 11.3% to 18.8%, with significant differences in different regions (
P<0.01). In different genders, the prevalence was 22.9% and 16.6% in male and female yak calves, respectively. In different ages, the prevalence ranged from 12.9% to 32.1%, with significant differences in different ages (
P<0.01). In different fecal consistencies, the prevalence ranged from 9.5% to 37.3%, with significant differences in different fecal consistencies (
P<0.01) (
Table 1).
According to conditional stepwise logistic regression, type was not significant in the logistic regression analysis (
P>0.05). Three factors, geographical origins, ages, and fecal consistencies were considered as risk factors to influence the prevalence significantly. In Qinghai, yak calves in Nangqian (35.2%) had a 3 times (OR=3.349, 95% CI=1.809–6.199,
P<0.001) higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in region Zaduo, while no regional difference was found of Zhiduo compared to Zaduo (
P>0.05). In Tibet, yak calves in Xigaze (24.4%) and Lhasa (39.6%) had a 2.5 times (OR=2.530, 95% CI=0.987–6.483,
P<0.05) and 5 times (OR=5.137, 95% CI=2.009–13.131,
P<0.05) higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in region Nyingchi, respectively, while no regional difference was found of Qamdo compared to Nyingchi (
P>0.05). On the Qinghai Tibetan plateau, yak calves in Tibet (17.2%), Qinghai (20.1%), and Sichuan (40.9%) had a 2.5 times (OR=2.542, 95% CI=0.988–6.540,
P<0.05), 3 times (OR=3.062, 95% CI=1.182–7.933,
P<0.05), and 8 times (OR=8.424, 95% CI=3.016–23.530,
P<0.001) higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in region Gansu, respectively. Yak calves in age ≤28 days (21.2%) and in age 28–56 days (32.1%) had a 1.5 times (OR=1.819, 95% CI=1.208–2.740,
P<0.05) and 3 times (OR=3.205, 95% CI=2.126–4.833,
P<0.001) higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in age>56 days. In different fecal consistencies, yaks calves in normal (16.9%) and soft (37.3%) had a 1.5 times (OR=1.939, 95% CI=1.006–3.734,
P<0.05) and 5.5 times (OR=5.668, 95% CI=2.808–11.439,
P<0.001) higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in watery, respectively (
Table 2).
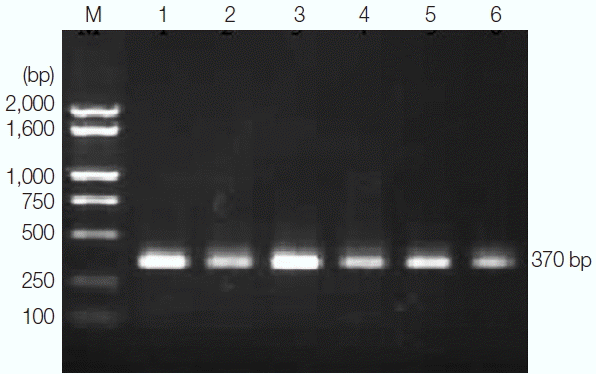
DNA was successfully PCR-amplified, fragments (−370 bp) from 56 ascaris out of 56 samples (success rate 100%) (
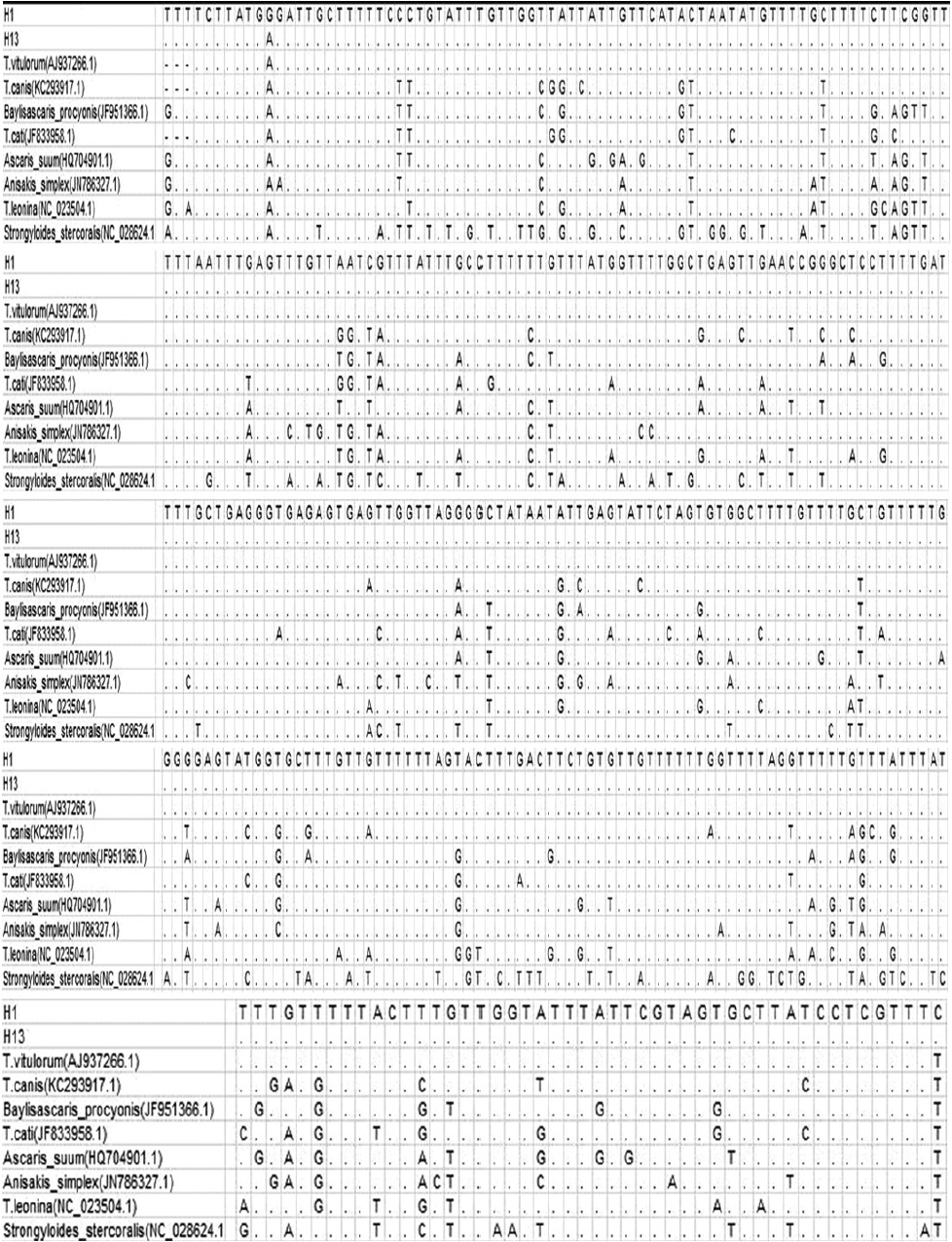
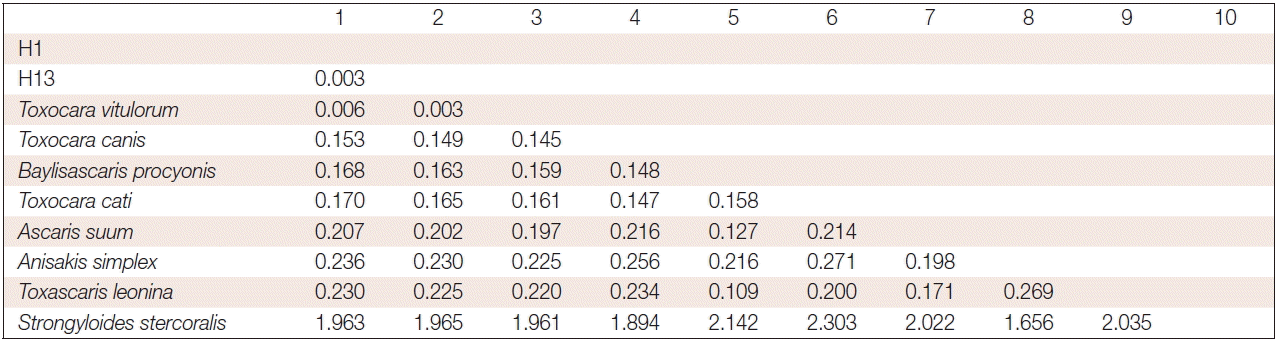
Fig. 1) (some data not shown). Analysis pairwise distances of the current parasite with other ascarids available indicated that the pairwise distance of the current parasite were 0.006 (H1) and 0.003 (H13) to
T. vitulorum (AJ937266.1), respectively (
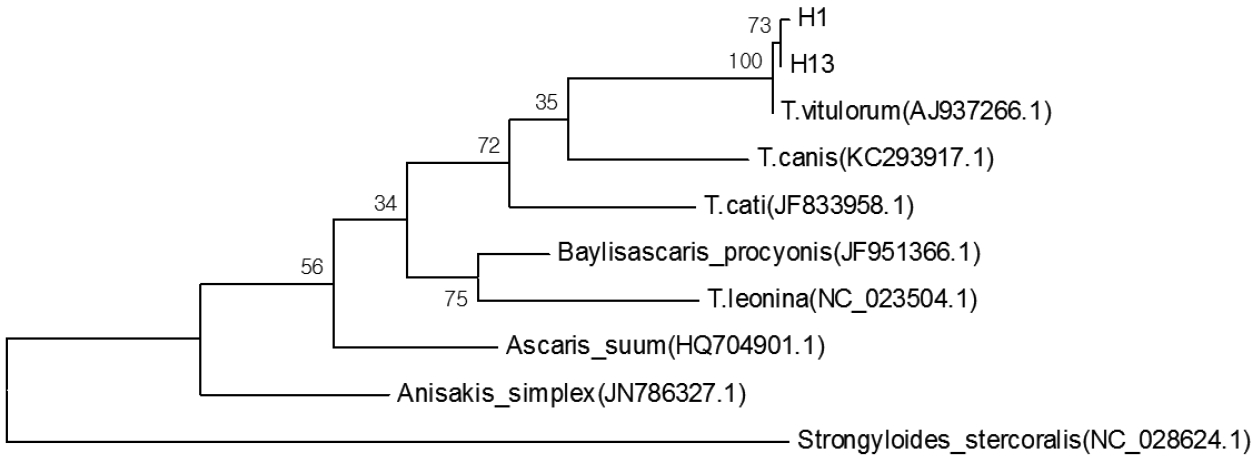
Fig. 2). The pairwise distance of H1 and H13 was 0.003. Sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree revealed that the present ascarids were
T. vitulorum (
Figs. 3,
4).
DISCUSSION
Molecular characterization of parasites is a crucial factor in understanding epidemiology and control of parasitic infections in medical and veterinary ssciences [
14]. As
T. vitulorum is a worldwidely spread parasite of the small intestine of ruminants with high morbidity and mortality rates [
15], it has been reported in many areas of the world. Previously, Souza et al. [
15] reported that the prevalence of
T. vitulorum infection in buffalo cows in Brzail was as high as 100%; the prevalence of
T. vitulorum in beef calves in different months in North Central Florida was 17.6% in less than 3 months of age, 0.4% in 3–4 months of age, and 0.0% in 5–6 months old, respectively [
1]. Though the reproductive rates are 0.6 and 0.4 calf per annum in cattle and buffalo, respectively, in South-East Asia, the annual calf infected with morbidity and mortality is 42.6% and 37.3% respectively [
5]. The prevalence of
T. vitulorum in yaks in Arunachal Pradesh located in Himalaya was 6.1% [
16]. Previous studies demonstrated a high infection rate in bovine calves, which is in line with the current study as high prevalence (20.1% in Qinghai, 17.2% in Tibet, 40.9% in Sichuan, and 7.6% in Gansu) (
Table 1) of yak calves infected with
T. vitulorum, and considerable mortality was observed during sample collection on the Qinghai Tibetan plateau. The high prevalence of
T. vitulorum in yak calves may lead to heavy economic losses, as it has enormous difficulties to employ anthelmintics in such special plateau.
The present study indicated that geographical origin, ages, and fecal consistencies are the risk factors associated with
T. vitulorum prevalence by logistic regression analysis. In Qinghai, yak calves in Nangqian had a 3 times higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in region Zaduo (
P<0.001), while no regional difference was found of Zhiduo compared to Zaduo (
P>0.05). In Tibet, yak calves in Xigaze and Lhasa had a 2.5 times (
P<0.05) and 5 times (
P<0.05) higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in region Nyingchi, respectively, while no regional difference was found of Qamdo compared to Nyingchi (
P>0.05). On the Qinghai Tibetan plateau, yak calves in Tibet, Qinghai, and Sichuan had a 2.5 times (
P<0.05), 3 times (
P<0.05), and 8 times (
P<0.001) higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in region Gansu, respectively (
Table 2). The results revealed that changes in climate conditions and altitude in different regions may play a predisposing factor for
T. vitulorum prevalence. However, the present results were not in accordance with Dorny et al. [
2] in which geographical origin was not a risk factor for
T. vitulorum infection in buffalo and cattle Calves in Cambodia [
2].
No significant difference was found in the different genders (
P≥0.05). The current study may demonstrate that gender is not a predisposing factor for
T. vitulorum prevalence in yak calves. Yak calves in age 28–56 days had a 3 times (
P<0.001) higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in age>56 days, which is in line with a previous study that the prevalence of
T. vitulorum infection in cattle calves in age 28–56 days was significant higher than those of age>56 days [
2]. However, yaks calves in age ≤28 days had a 1.5 times (
P<0.05) higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in age>56 days, which was not found in the study of Dorny et al. [
2]. In different fecal consistencies, yaks calves in normal and soft had a 1.5 times (
P<0.05) and 5.5 times (
P<0.001) higher risk of being positive compared to yak calves in watery, respectively, which was also not identified in a previous study of Dorny et al. [
2] (
Table 2).
Several genomic regions have been used for phylogenetic studies of different parasite species, including 18S and 28S ribosomal RNA as well as mitochondrial genes of
COX1 and
ND1 [
9,
12,
14]. In the present study, through analysis of pairwise distances, sequence alignment, and phylogenetic tree of NADH dehydrogenase subuni1 (
nd1) gene of the current parasite with other ascarids available indicated that the ascarids were
T. vitulorum, which was identified for the first time in yaks calves on the high, cold plateau. The current results showed that
T. vitulorum in yak calves on the Qinghai Tibetan plateau were 99.994% (H1) and 99.997% (H13) homologous to the previous report (AJ937266.1).
This parasite is acquired by calves by ingesting third stage larvae from a dam’s milk contaminated with infective larvae from infected cows [
4], though
T. vitulorum was reported mostly stayed in the infected pregnant buffalo; however, the parasites grew and migrated to the mammary gland before parturition [
17], which makes the infected yaks a potential threat to other yaks on the same plateau and even other areas as the yaks are social bovines living together and increasing trade in recent years [
6].
T. vitulorum in mature cattle is usually asymptomatic [
1]; however, a previous research on infected rabbits reported increased eosinophils, elevated creatine phosphokinase and alanine aminotransferase levels, and lower erythrocyte counts and PCV, possibly due to toxemic effects [
1]. This kind of intestinal toxocariasis is associated with diarrhea, poor performance, intestinal and biliary obstruction, and death [
1].
The present study reveals that high infection and mortality due to T. vitulorum is wildly spread on the Qinghai Tibetan plateau, China as evidenced by fecal examinations. Geographical origin, ages, and fecal consistencies are the risk factors associated with T. vitulorum prevalence by logistic regression analysis. Molecular detection and phylogenetic analysis of ND1 gene of T. vitulorum indicated that T. vitulorum in the yak calves on the Qinghai Tibetan plateau are homologous to the preveious studies. Therefore, it is essential to raise a public concern about the high infection and mortality parasite, as this kind of ascariasis is a local endemic disease. Further studies on the molecular characterization of the parasite are clearly required from more geographical localities on the Qinghai-Tibetan plateau.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by Key Science Fund of Science and Technology Agency of Tibet Autonomous Region and projects in the National Science and Technology Pillar Program during the 12th Five-year Plan Period (2012BAD3B03) and the Chinese Agricultural Research Systems (CARS-38). Basic application research plan of the first batch of science and technology key projects in 2015.
Fig. 1PCR amplification of ND1 gene fragment from T. vitulorum. PCR positive samples for T. vitulorum (−370 bp). Lane M, FastRuler Low Range DNA Ladder (Beijing Dingguo Changsheng Biotech Co. Ltd). Fragment sizes are as follows: 2,000, 1,600, 1,000, 750, 500, 250, and 100 bp.

Fig. 2Alignments of the 2 representative profiles of ND1 sequences with 8 ascarids available.

Fig. 3The number of base substitutions per site between sequences are shown. Analyses were conducted using the maximum composite likelihood model. The analysis involved 10 nucleotide sequences. Codon positions included were 1st+2nd+3rd+noncoding. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 357 positions in the final dataset. Evolutionary analyses were conducted in MEGA6.

Fig. 4Phylogenetic tree constructed with sequences of the presented parasite and other ascarids available conducted in MEGA6.

Table 1Prevalence of T. vitulorum infection in yak calves in different regions, genders, ages, and fecal consistency
Table 1
|
Variable |
No. samples |
No. positive (%; 95% CI) |
Mean EPG (SD) |
|
Regionsc
|
|
|
|
|
Qinghaia
|
Nangqian |
91 |
32 (35.2; 25.4–45.9) |
4,219 (12,217) |
|
Zhiduo |
63 |
9 (14.3; 6.7–25.4) |
3,566 (9,872) |
|
Zaduo |
165 |
23 (13.9; 9.0–20.2) |
2,891 (7,826) |
|
Total |
319 |
64 (20.1; 15.8–24.9) |
3,442 (9,128) |
|
|
Tibetb
|
Xigaze |
127 |
31 (24.4; 17.2–32.8) |
1,936 (5,612) |
|
Lhasa |
101 |
40 (39.6; 30.0–39.8) |
4,325 (21,234) |
|
Nyingchi |
53 |
6 (11.3; 4.3–23.0) |
987 (2,982) |
|
Qamdo |
154 |
29 (18.8; 13.0–25.9) |
2,955 (4,357) |
|
Total |
435 |
75 (17.2; 13.8–21.1) |
4,328 (9,827) |
|
|
Sichuan |
Hongyuan |
71 |
29 (40.9; 29.3–53.2) |
5,433 (13,289) |
|
Gansu |
Gannan |
66 |
5 (7.6; 2.5–16.8) |
1,277 (3,256) |
|
Genders |
|
|
|
|
Male |
397 |
91 (22.9; 18.9–27.4) |
4,592 (7,824) |
|
Female |
494 |
82 (16.6; 13.4–20.2) |
2,971 (4,963) |
|
Agesd (day) |
|
|
|
|
≤ 28 |
255 |
54 (21.2; 16.3–26.7) |
3,897 (6,899) |
|
28–56 |
193 |
62 (32.1; 25.6–35.2) |
5,219 (15,627) |
|
>56 |
443 |
57 (12.9; 9.9–16.3) |
1,533 (4,129) |
|
Faecal consistencye
|
|
|
|
|
Normal |
622 |
105 (16.9;14.0–20.1) |
3,255 (7,921) |
|
Soft |
153 |
57 (37.3; 29.6–45.4) |
5,685 (18,724) |
|
Watery |
116 |
11 (9.5; 4.8–16.3) |
2,983 (7,332) |
Table 2Odds ratios for geographical, ages, and fecal consistency of yaks as risk factors for T. vitulorum seroprevalence in yaks (n=891)
Table 2
|
Factor |
Category |
Prevalence (%) |
OR |
95% CI |
P-value |
|
Region (Qinghai) |
Zaduo |
13.9 |
reference |
|
|
|
Zhiduo |
14.3 |
1.029 |
0.448–2.364 |
0.946 |
|
Nangqian |
35.2 |
3.349 |
1.809–6.199 |
<0.001 |
|
|
Region (Tibet) |
Nyingchi |
11.3 |
reference |
|
|
|
Qamdo |
18.8 |
1.817 |
0.709–4.656 |
0.208 |
|
Xigaze |
24.4 |
2.53 |
0.987–6.483 |
0.048 |
|
|
Lhasa |
39.6 |
5.137 |
2.009–13.131 |
<0.001 |
|
Region |
Gansu |
7.6 |
reference |
|
|
|
Tibet |
17.2 |
2.542 |
0.988–6.540 |
0.046 |
|
Qinghai |
20.1 |
3.062 |
1.182–7.933 |
0.016 |
|
Sichuan |
40.9 |
8.424 |
3.016–23.530 |
<0.001 |
|
>56 |
12.9 |
reference |
|
|
|
|
Age |
≤28 |
21.2 |
1.819 |
1.208–2.740 |
0.004 |
|
28–56 |
32.1 |
3.205 |
2.126–4.833 |
<0.001 |
|
|
Fecal consistency |
Watery |
9.5 |
reference |
|
|
|
Normal |
16.9 |
1.939 |
1.006–3.734 |
0.044 |
|
Soft |
37.3 |
5.668 |
2.808–11.439 |
<0.001 |
References
- 1. Davila G, Irsik M, Greiner EC. Toxocara vitulorum in beef calves in North Central Florida. Vet Parasitol 2010;168:261-263.
- 2. Dorny P, Devleesschauwer B, Stoliaroff V, Sothy M, Chea R, Chea B, Sourloing H, Samuth S, Kong S, Nguong K, Sorn S, Holl D, Vercruysse J. Prevalence and associated risk factors of Toxocara vitulorum infections in buffalo and cattle calves in three provinces of central Cambodia. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:197-200.
- 3. Borgsteede FH, Holzhauer M, Herder FL, Veldhuis-Wolterbeek EG, Hegeman C. Toxocara vitulorum in suckling calves in the Netherlands. Res Vet Sci 2012;92:254-256.
- 4. Ferreira FP, Starke-Buzetti WA. Detection of antibody to Toxocara vitulorum perienteric fluid antigens (Pe) in the colostrum and serum of buffalo calves and cows by Western blotting. Vet Parasitol 2005;129:119-124.
- 5. Rast L, Toribio JA, Dhand NK, Khounsy S, Windsor PA. Why are simple control options for Toxocara vitulorum not being implemented by cattle and buffalo smallholder farmers in South-East Asia? Prev Vet Med 2014;113:211-218.
- 6. Li K, Gao JF, Shahzad M, Han Z, Nabi F, Liu M, Zhang D, Li J. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection in yaks (Bos grunniens) on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China. Vet Parasitol 2014;205:354-356.
- 7. Li JK, Li K, Shahzad M, Han ZQ, Nabi F, Gao JF, Han JM. Seroprevalence of bluetongue virus in domestic yaks (Bos grunniens) in Tibetan regions of China based on circulating antibodies. Trop Anim Health Prod 2015;47:1221-1223.
- 8. Li K, Shahzad M, Han ZQ, Li JK. Seroepidemiology of Mycoplasma bovis infection in yaks (Bos grunniens) in Tibet and Hongyuan of Sichuan, China. Pak Vet J 2015;35:516-518.
- 9. Nagataki M, Tantrawatpan C, Agatsuma T, Sugiura T, Duenngai K, Sithithaworn P, Andrews RH, Petney TN, Saijuntha W. Mitochondrial DNA sequences of 37 collar-spined echinostomes (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) in Thailand and Lao PDR reveals presence of two species: Echinostoma revolutum and E. miyagawai. Infect Genet Evol 2015;35:56-62.
- 10. Thienpont D, Rochette F, Vanparijs OFJ. Diagnosing helminthiasis by coprological examination. Beerse, Belgium. Janssen Research Foundation. 1986, p 205.
- 11. Li XR. Color atlas of animal parasitosis (Second Edition). Beijing, China. Agriculture Press. 2011.
- 12. Li K, Luo H, Zhang H, Lan Y, Han Z, Shahzad M, Wang X, Qiu G, Huang S, Jiang W, Li J. First report of Metastrongylus pudendotectus by the genetic characterization of mitochondria genome of cox1 in pigs from Tibet, China. Vet Parasitol 2016;223:91-95.
- 13. Liu GH, Wang Y, Song HQ, Li MW, Ai L, Yu XL, Zhu XQ. Characterization of the complete mitochondrial genome of Spirocerca lupi: sequence, gene organization and phylogenetic implications. Parasit Vectors 2013;6:45.
- 14. Rostami S, Salavati R, Beech RN, Babaei Z, Sharbatkhori M, Harandi MF. Genetic variability of Taenia saginata inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Parasitol Res 2015;114:1365-1376.
- 15. Souza EMD, Starke-Buzetti WA, Ferreira FP, Neves MF, Machado RZ. Humoral immune response of water buffalo monitored with three different antigens of Toxocara vitulorum. Vet Parasitol 2004;122:67-78.
- 16. Bam J, Deori S, Paul V, Bhattacharya D, Bera AK, Bora L, Baruah KK. Seasonal prevalence of parasitic infection of yaks in Arunachal Pradesh, India. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 2012;2:264-267.
- 17. Roberts JA. The life cycle of Toxocara vitulorum in Asian buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Int J Parasitol 1990;20:833-840.