Abstract
Vivax malaria reemerged in Korea in 1993 and the outbreak has been continued with fluctuating numbers of annual indigenous cases. Understanding the nature of the genetic population of Plasmodium vivax circulating in Korea is beneficial for the knowledge of the nationwide parasite heterogeneity and in the implementation of malaria control programs in the country. Previously, we analyzed polymorphic nature of merozoite surface protein-1 (MSP-1) and MSP-3α in Korean P. vivax population and identified the Korean P. vivax population has been diversifying rapidly, with the appearance of parasites with new genetic subtypes, despite the recent reduction of the disease incidence. In the present study, we developed simple PCR-RFLP methods for rapid subtyping of MSP-1 and MSP-3α of Korean P. vivax isolates. These PCR-RFLP methods were able to easily distinguish each subtype of Korean P. vivax MSP-1 and MSP-3α with high accuracy. The PCR-RFLP subtyping methods developed here would be easily applied to massive epidemiological studies for molecular surveillance to understand genetic population of P. vivax and to supervise the genetic variation of the parasite circulating in Korea.
-
Key words: Plasmodium vivax, RCR-RFLP, MSP-1, MSP-3α, subtyping
INTRODUCTION
Plasmodium vivax is the most widely distributed human malaria parasite worldwide and has reemerged in many regions of the world where malaria has been eliminated [
1,
2]. Vivax malaria was eradicated in Korea in the late 1970’s as the result of a national malaria eradication program supported by the World Health Organization [
3]. However, malaria reemerged in the country in 1993 near the demilitarized zone (DMZ) bordering North Korea, and the outbreak has spread into cities and counties adjacent to the DMZ and has continued until now with fluctuating numbers of annual indigenous cases [
4].
Understanding the nature of genetic structure of
P. vivax population circulating in Korea is beneficial to figure out the nationwide parasite heterogeneity and to implement malaria control programs. Therefore, many studies have attempted to understand the genetic characteristics of
P. vivax Korean isolates [
5–
13]. In our previous study, we performed combinational analysis of genetic structures of 2 major polymorphic molecular markers of
P. vivax, i.e., merozoite surface protein-1 (MSP-1) and MSP-3α, in Korean
P. vivax isolates collected over an extended period from 1998 to 2013 [
14]. Both MSP-1 and MSP-3α are differentiated into 7 distinct subtypes (subtypes A to G for MSP-1 and subtype 1 to 7 for MSP-3α) among the analyzed Korean
P. vivax isolates. Combinational genetic analysis of polymorphic patterns of MSP-1 and MSP-3α in the isolates suggests that the
P. vivax population in Korea has been diversifying rapidly, with the appearance of parasites with new haplotypes, despite the recent reduction of the disease incidence [
14]. Several reports also supported the notion that Korean
P. vivax population is rapidly disseminated in recent years [
6,
8,
9,
15]. These results highlight the importance of molecular epidemiological surveillances to supervise the genetic variations of the parasite in Korea [
14]. However, routine amplification by PCR followed by sequencing analysis for polymorphic marker genes of
P. vivax is costly and time- and labor-consuming and does not provide large amounts of information quickly for epidemiological purposes. Therefore, an accurate and powerful tool that can replace the existing cumbersome and time-consuming sequencing method is needed.
In this study, we developed reliable PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) methods for rapid subtyping of MSP-1 and MSP-3α of P. vivax Korean isolates. These methods can easily distinguish different subtypes of MSP-1 and MSP-3α of P. vivax Korean isolates in a simple and single step.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Blood samples
The blood samples used in this study were obtained from Korean patients infected with
P. vivax in Korea between 1998–2013 [
14]. All the patients inhabited in malaria endemic areas, i.e., Ilsan, Kimpo, Paju, Gangwha, or Yoncheon, and have not been abroad at least in recent 2 years when their blood samples were collected. All the patients were confirmed to be infected with
P. vivax by microscopic examinations and PCR. Monoclonal
P. vivax infections were confirmed by genotyping of
P. vivax positive samples at the highly polymorphic loci MS16 and MSP-1F3 as described previously [
16]. Blood samples were collected under protocols reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committees of Inha University School of Medicine and Gachon University of Medicine and Science. Blood samples were stored as aliquots of heparinized blood frozen at −70°C.
Genomic DNA was extracted from 200 μL of each blood sample using a QIAamp DNA Blood Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
PCR
Polymorphic regions of MSP-1 (block 5 to 6) and MSP-3α (block I and II) were amplified with PCR using specific primers for each gene [
17–
19]. ExTaq DNA polymerase (Takara, Otsu, Japan) was used in all PCR amplifications to minimize possible amplification error.
Based on nucleotide sequences of 255 MSP-1 and 255 MSP-3α genes (GenBank accession nos. KU893351 to KU893860) amplified from Korean
P. vivax isolates [
14], we surveyed the restriction enzyme sites in each subtype of MSP-1 and MSP-3α using the Restriction Mapper program (
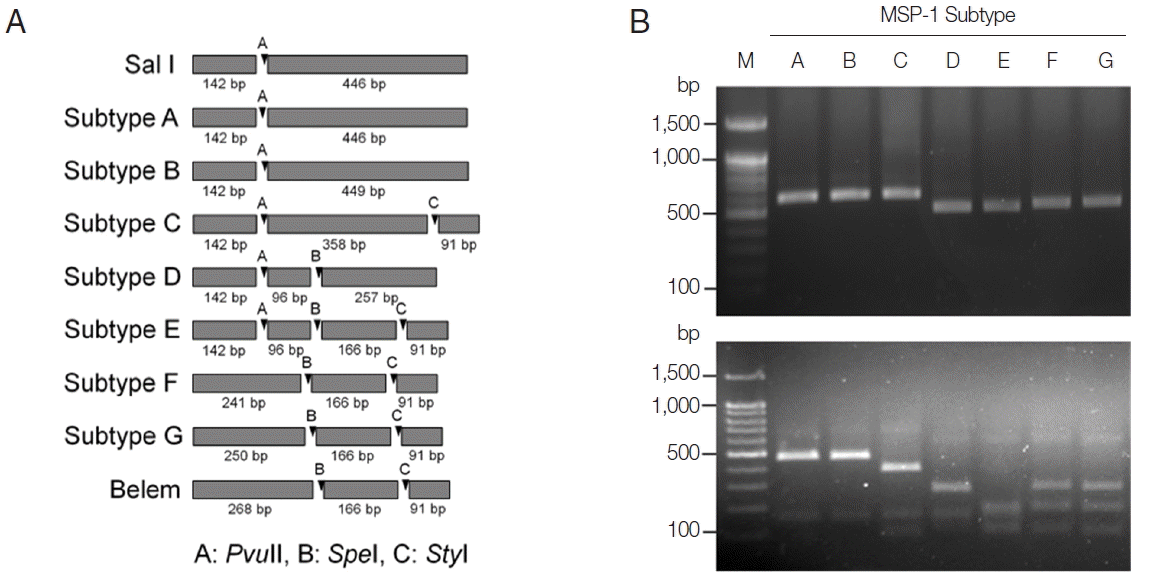
http://www.restrictionmapper.org/). The restriction enzymes with digestion sites that were conserved within a subtype in a given sequence were selected. The selected restriction enzymes and their predicted cleavage sites in each subtype of MSP-1 and MSP-3α were shown in
Fig. 1A and
Fig. 3A. PCR products of each subtype MSP-1 were digested with
PvuII
, SpeI, and
StyI (each 3 U; Takara) in a total volume of 30 μL at 37°C for 2 hr. RFLP analysis of each subtype of MSP-3α was carried out by digesting the PCR products with the
PvuII
, StyI, and
EcoRI (each 3 U; Takara) in a total volume of 30 μL at 37°C for 2 hr. The resulting digested fragments were separated in 3% agarose gels by electrophoresis in 0.5×Tris-acetate-EDTA (TAE) buffer, stained with RedSafe Nucleic Acid Staining Solution (Intron, Seongnam, Korea) and visualized under ultraviolet light. The 100-bp DNA ladder or 1-kb DNA ladder (Life Technologies, Rockville, Maryland, USA) was used as the DNA size marker.
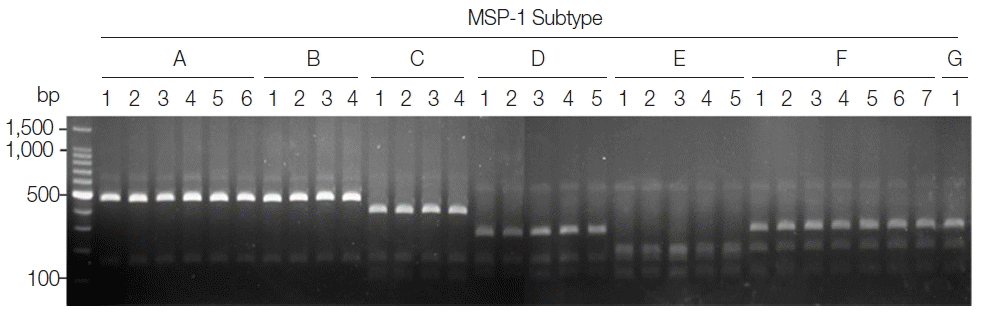
To evaluate the applicability of the developed PCR-RFLP methods for subtyping of MSP-1 and MSP-3α in Korean P. vivax isolates, a blind test was performed with 50 Korean P. vivax isolates. The PCR reactions were set to the same conditions as above, and the PCR products were subsequently digested with the corresponding restriction enzymes for MSP-1 and MSP-3α. The reactants were analyzed by 3% agarose gel electrophoresis as described above and observed the profiles of restriction fragments. Sequencing analysis of amplified MSP-1 and MSP-3α was also performed for each P. vivax isolate by automatic nucleotide sequencing to evaluate the accuracy of the PCR-RFLP methods.
RESULTS
MSP-1 subtyping PCR-RFLP
On the basis of computational restriction fragment analysis of currently known 7 MSP-1 subtypes in Korean
P. vivax isolates, restriction enzymes
PvuII
, SpeI, and
StyI were chosen, as they were expected to produce fragments of different sizes and subtype-specific restriction profiles (
Fig. 1A). PCR amplifications of polymorphic regions (block 5 to 6) of 7 distinct Korean
P. vivax MSP-1 subtypes (subtypes A to G) revealed that the amplified products showed only slightly different length polymorphisms between the subtypes (subtype A, 588 bp; subtype B, 591 bp; subtype C, 591 bp; subtype D, 495 bp; subtype E, 495 bp; subtype F, 498 bp; subtype G, 507 bp), which did not clearly discriminated each other on a gel (
Fig. 1B upper panel). Digestion of the amplified PCR products with
PvuII
, SpeI, and
StyI resulted in different sets of digestion profiles between the subtypes as expected (
Fig. 1B, lower panel). Subtypes A and B generated 2 fragments of approximate sizes of 450 bp and 140 bp, while subtype C yielded 3 fragments of 360, 140, and 90 bp in their approximate sizes. Subtype D produced 3 different sized fragments with approximate 260, 140, and 100 bp. Subtype E generated 4 digested fragments with approximate sizes of 170, 140, 100, and 90 bp. In the cases of subtypes F and G, 3 fragments with approximate lengths of 250, 170, and 90 bp were produced. These results showed that the 7 MSP-1 subtypes in Korean
P. vivax isolates produced different RFLP profiles that can be distinguished each other, even though Sal I type subtypes (subtypes A and B) and Belem type subtypes (subtypes F and G) did not clearly differentiated due to their high sequence identities. To evaluate the applicability of the PCR-RFLP, a blind analysis using 50 Korean
P. vivax isolates was performed. As expected, distinct RFLP profiles for each subtype were successfully obtained from the analyzed samples (
Fig. 2). The MSP-1 amplicons were sequenced for validation of the method and confirmed that the accuracy of this method was 100% in the analyzed 50 samples.
For subtype-specific PCR-RFLP method for MSP-3α,
PvuII,
StyI, and
EcoRI restriction enzymes were selected by in silico restriction fragment analysis (
Fig. 3A). PCR amplifications of polymorphic regions (block I and II) of the 7 Korean
P. vivax MSP-3α subtypes (subtypes 1 to 7) resulted in different sizes of amplicons, but they were not clearly discriminated into the corresponding subtypes on a gel (
Fig. 3B, upper panel). Amplifications of MSP-3α followed by RFLP analysis using the 3 restriction enzymes generated subtype-specific fragments of different numbers and sizes that can easily be discriminated into each subtype on an agarose gel (
Fig. 3B, lower panel). Subtype 1 produced 3 fragments with approximate lengths of 1,280, 340, and 310 bp. Subtype 2 generated 2 different sized fragments of about 1,600 and 310 bp. Subtype 3 produced 2 digested fragments with approximate sizes of 790 and 340 bp. Subtype 4 yielded 3 distinct sized fragments of about 1,030, 530, and 330 bp, while subtype 5 generated only a band of approximate size with 1,140 bp since it had not any cleavage site by the 3 restriction enzymes. In the case of subtype 6, 2 different sized restriction fragments with approximate sizes with 240 and 1,030 bp were produced. Meanwhile, subtype 7 produced 2 fragments with approximate sizes of 900 and 1,020 bp. A blind analysis of 50 Korean
P. vivax isolates for MSP-3α showed that they are well discriminated into each subtype (
Fig. 4). Further sequencing analysis of each MSP-3α amplicon to validate the accuracy of this method confirmed that the method showed 100% concordance for the 50 tested
P. vivax Korean isolates.
DISCUSSION
Malaria has been endemic in Korea more than 20 years after its reemergence, and there are reports suggesting various allelic variations in
P. vivax Korean population [
5–
14]. Despite reduced prevalence of malaria infections in Korea in recent years, the disseminating patterns of genetic structures of Korean
P. vivax population suggest that the population size is likely to be remained high enough to allow effective genetic recombination of the parasite and continued maintenance of genetic diversity [
14]. Therefore, molecular epidemiological surveillance to supervise the genetic variation of the parasite in Korea is essential to gain an in-depth insight for the genetic change and biological nature of
P. vivax population endemic in Korea. The MSP-1 and MSP-3α are the most abundant proteins expressed on the surface of
P. vivax merozoites and are potential targets for vaccine development [
20–
22]. Both genes are highly polymorphic among global
P. vivax population and have been identified as reliable molecular markers to investigate genetic structures of
P. vivax population [
14,
19,
23,
24]. Several attempts to apply PCR-RFLP methods to distinguish different types of the genes for molecular epidemiological purpose have been done [
25–
29]. However, those methods using
AluI and/or
HhaI did not clearly identify individual subtype or genotype of MSP-1 and MSP-3α of
P. vivax.
In this study, we aimed to develop simple and reliable PCR-RFLP methods that are easily applicable to molecular epidemiological surveys for Korean P. vivax genetic heterogeneity based on MSP-1 and MSP-3α polymorphisms. Our results suggested that the PCR-RFLP methods developed in this study could accurately identify currently identified 7 different subtypes of Korean P. vivax MSP-1 and MSP-3α. Sequence differences between each subtype of MSP-1 and MSP-3α allowed the selection of specific restriction enzymes for subtyping of Korean P. vivax MSP-1 and MSP-3α. The methods are simple and feasible and can be easily applied in clinical isolates for high-throughput analysis protocol for clinical trials or epidemiological purposes at a low cost.
The limitation of RFLP analysis is that some sequence changes, such as single point mutations, substitutions, and small deletions in the target sequences could result in loss of the restriction sites, leading to an incorrect outcome. However, the cleavage sites by the restriction enzymes used in this study are well conserved in MSP-1 and MSP-3α sequences in global
P. vivax isolates that have been reported to date. Indeed, in silico analysis of MSP-1 and MSP-3α in
P. vivax isolates from other endemic areas, including India, Myanmar, and Venezuela [
18,
19,
30,
31] suggested that the PCR-RFLP methods are also applicable for subtyping of global
P. vivax isolates. However, attention should be required to apply the methods to global
P. vivax isolates considering that the genetic diversities of MSP-1 and MSP-3α of
P. vivax circulating in tropical and subtropical endemic areas are much higher than those in Korean isolates [
17–
19,
24,
26,
30,
31]. Considering the rapid genetic dissemination observed in Korean
P. vivax population, we also could not exclude possibility of the appearance of new genotype of
P. vivax probably due to genetic recombination and/or introduction of new genotypes from other endemic countries, which may affect population structure of the Korean
P. vivax. Therefore, continuous molecular epidemiological surveillance to supervise the genetic variation of the parasite in Korea is warranted. The PCR-RFLP methods developed in this study can be applied as simple and powerful tools for this purpose.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by the grant of Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University, Jinju, Korea (no. lHS GNU-2014-1).
Fig. 1PCR-RFLP subtyping method for MSP-1 of Korean P. vivax isolates. (A) Schematic view for predicted restriction positions and expected sizes of restriction fragments of the 7 subtypes of Korean P. vivax MSP-1 by 3 restriction enzymes, PvuII, SpeI, and StyI. Subtypes A–B, Sal I types; subtypes C–E, recombinant types; subtypes F–G, Belem types. Predicted restriction positions for MSP-1 sequences of Sal I (AF435593) and Belem (AF435594) were also presented. (B) Amplification and PCR-RFLP analysis of the 7 subtypes of Korean P. vivax MSP-1. (Upper panel) PCR amplifications of each subtype MSP-1. Polymorphic region (block 5–6) of MSP-1 was amplified from each subtype and analyzed. (Lower panel) RFLP patterns for each MSP-1 subtype amplicon generated by digestion with PvuII, SpeI, and StyI. Different patterns of digested fragments for each subtype were identified. Lane M, 100 bp DNA ladder; lanes A–G, subtypes A to G, respectively.
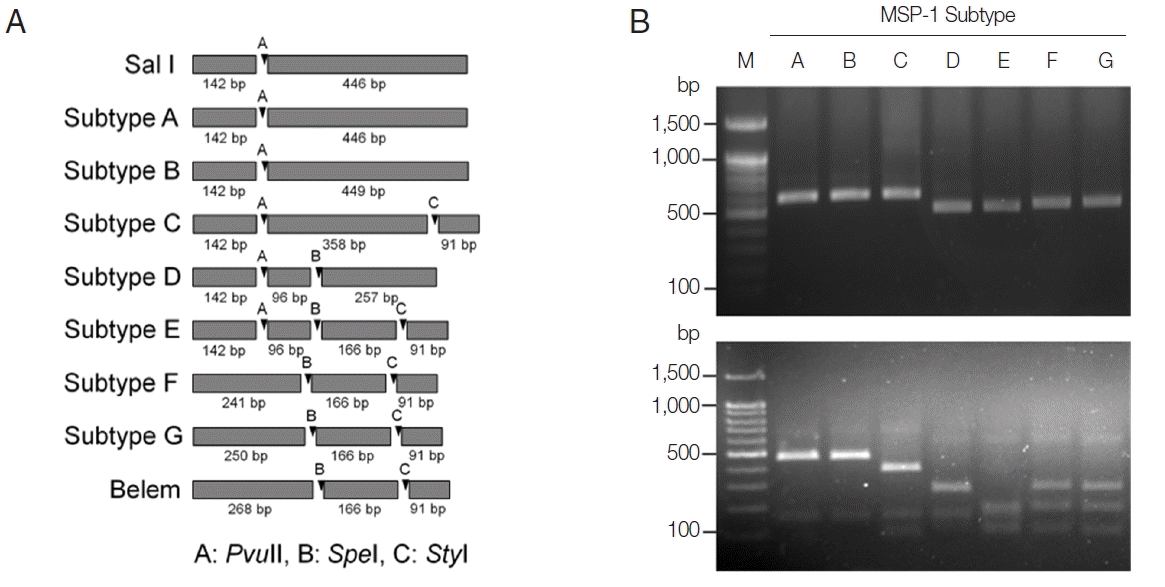
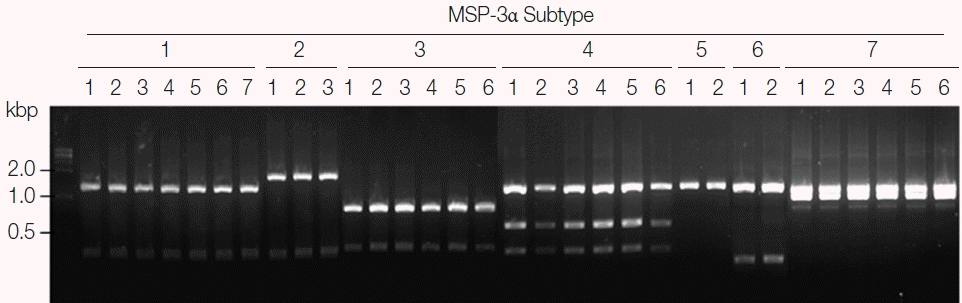
Fig. 2Blind evaluation of MSP-1 PCR-RFLP method for Korean P. vivax isolates. The MSP-1 polymorphic region (block 5–6) was amplified from genomic DNA purified from 50 P. vivax Korean isolates by PCR, respectively. Each PCR product was digested with PvuII, SpeI, and StyI and analyzed on a 3% agarose gel. The nucleotide sequence of each amplicon was also confirmed to evaluate the accuracy of the method. Only 32 representative results were presented.
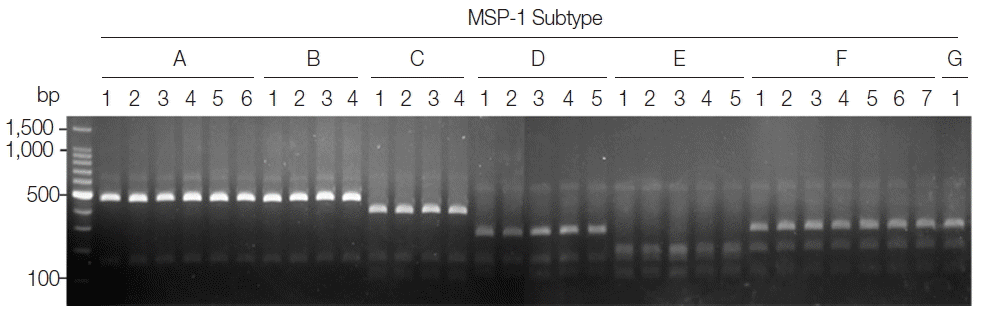
Fig. 3PCR-RFLP subtyping method for MSP-3α of Korean P. vivax isolates. (A) Schematic view for predicted restriction positions and expected sizes of restriction fragments of the 7 subtypes of Korean P. vivax MSP-3α by 3 restriction enzymes, PvuII, StyI, and EcoRI. Predicted restriction positions for MSP-3α sequences of Sal I (XM_001613154) and Belem (AF093584) were also presented. (B) Amplification and PCR-RFLP analysis of the 7 subtypes of Korean P. vivax MSP-3α. (Upper panel) PCR amplifications of each subtype MSP-3α. Polymorphic region (block I–II) of MSP-3α was amplified from each subtype and analyzed. (Lower panel) RFLP patterns for each MSP-3α subtype amplicon by digestion with PvuII, StyI, and EcoRI. Different patterns of digested fragments for each subtype were identified. Lane M, 1 kbp DNA ladder; lanes 1–7, subtypes 1 to 7, respectively.
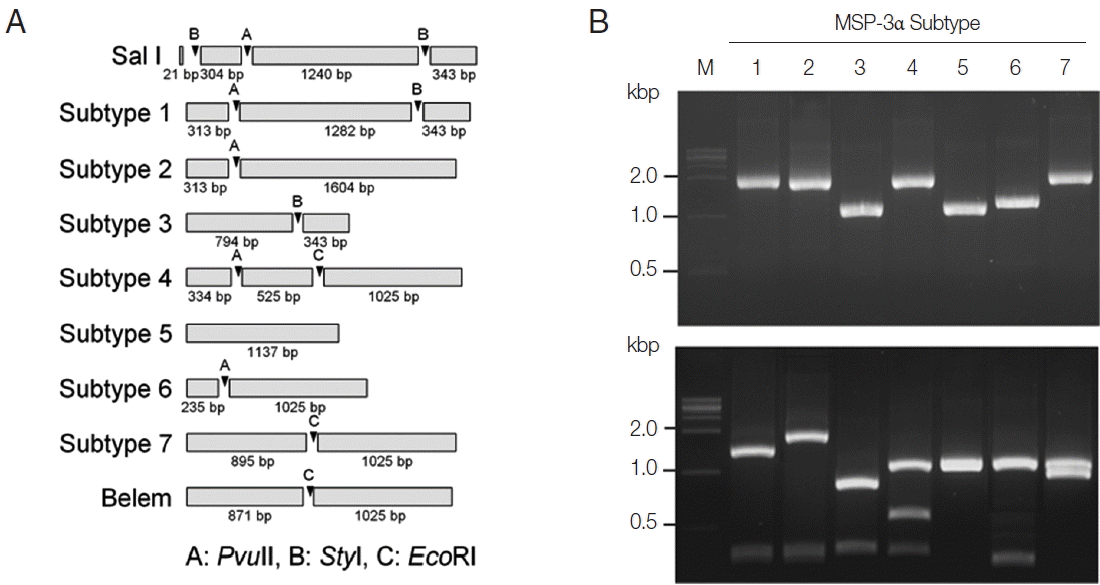
Fig. 4Blind evaluation of MSP-3α PCR-RFLP method for Korean P. vivax isolates. The MSP-3α polymorphic region (block I–II) was amplified from genomic DNA purified from 50 P. vivax isolates by PCR. Each PCR product was digested with PvuII, StyI, and EcoRI and analyzed on a 3% agarose gel. The nucleotide sequence of each amplicon was also confirmed to evaluate the accuracy of the method. Only 32 representative results were presented.
References
- 1. Mendis K, Sina BJ, Marchesini P, Carter R. The neglected burden of Plasmodium vivax malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2001;64:97-106.
- 2. Guerra CA, Hay SI, Lucioparedes LS, Gikandi PW, Tatem AJ, Noor AM, Snow RW. Assembling a global database of malaria parasite prevalence for the Malaria Atlas Project. Malar J 2007;6:17.
- 3. Soh CT, Lee KT, Im KI, Min DY, Ahn MH, Kim JJ, Yong TS. Current status of malaria in Korea. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1985;16:11-18.
- 4. Kim TS, Kim JS, Na BK, Lee WJ, Kim HC, Youn SK, Gwack J, Kim HS, Cho P, Ahn SK, Cha SH, Park YK, Lee SK, Kang YJ, Sohn Y, Hong Y, Lee HW. Decreasing incidence of Plasmodium vivax in the Republic of Korea during 2010–2012. Malar J 2013;12:309.
- 5. Lim CS, Kim SH, Kown SI, Song JW, Song KJ, Lee KN. Analysis of Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein-1 gene sequences from resurgent Korean isolates. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2000;62:261-265.
- 6. Choi YK, Choi KM, Park MH, Lee EG, Kim YJ, Lee BC, Cho SH, Rhie HG, Lee HS, Yu JR, Lee JS, Kim TS, Kim JY. Rapid dissemination of newly introduced Plasmodium vivax genotypes in South Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2010;82:426-432.
- 7. Han ET, Wang Y, Lim CS, Cho JH, Chai JY. Genetic diversity of the malaria vaccine candidate merozoite surface protein 1 gene of Plasmodium vivax field isolates in Republic of Korea. Parasitol Res 2011;109:1571-1576.
- 8. Honma H, Kim JY, Palacpac NM, Mita T, Lee W, Horii T, Tanabe K. Recent increase of genetic diversity in Plasmodium vivax population in the Republic of Korea. Malar J 2011;10:257.
- 9. Kang JM, Ju HL, Kang YM, Lee DH, Moon SU, Sohn WM, Park JW, Kim TS, Na BK. Genetic polymorphism and natural selection in the C terminal 42kDa region of merozoite surface protein-1 among Plasmodium vivax Korean isolates. Malar J 2012;11:206.
- 10. Ju HL, Kang JM, Moon SU, Bahk YY, Cho PY, Sohn WM, Park YK, Park JW, Kim TS, Na BK. Genetic diversity and natural selection of Duffy binding protein of Plasmodium vivax Korean isolates. Acta Trop 2013;125:67-74.
- 11. Kang JM, Ju HL, Cho PY, Moon SU, Ahn SK, Sohn WM, Lee HW, Kim TS, Na BK. Polymorphic patterns of the merozoite surface protein-3β in Korean isolates of Plasmodium vivax. Malar J 2014;13:104.
- 12. Goo YK, Moon JH, Ji SY, Chung DI, Hong Y, Cho SH, Lee WJ, Kim JY. The unique distribution of the Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein 1 in parasite isolates with short and long latent periods from the Republic of Korea. Malar J 2015;14:299.
- 13. Kang JM, Lee J, Cho PY, Moon SU, Ju HL, Ahn SK, Sohn WM, Lee HW, Kim TS, Na BK. Population genetic structure and natural selection of apical membrane antigen-1 in Plasmodium vivax Korean isolates. Malar J 2015;14:455.
- 14. Kang JM, Lee J, Chi PY, Kim TI, Sohn WM, Park JW, Kim TS, Na BK. Dynamic changes of Plasmodium vivax population structure in South Korea. Infect Genet Evol 2016;45:90-94.
- 15. Kim JY, Goo YK, Zo YG, Ji SY, Trimarsanto H, To S, Clark TG, Price RN, Auburn S. Further evidence of increasing diversity of Plasmodium vivax in the Republic of Korea in recent years. PLoS One 2016;11:e0151514.
- 16. Koepfli C, Mueller I, Marfurt J, Goroti M, Sie A, Oa O, Genton B, Beck HP, Felger I. Evaluation of Plasmodium vivax genotyping markers for molecular monitoring in clinical trials. J Infect Dis 2009;199:1074-1080.
- 17. Bruce MC, Galinski MR, Barnwell JW, Snounou G, Day KP. Polymorphism at the merozoite surface protein-3α locus of Plasmodium vivax: global and local diversity. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1999;61:518-525.
- 18. Leclerc MC, Gauthier C, Villegas L, Urdaneta L. Genetic diversity of merozoite surface protein-1 gene of Plasmodium vivax isolates in mining villages of Venezuela (Bolivar State). Acta Trop 2005;95:26-32.
- 19. Moon SU, Lee HW, Kim JY, Na BK, Cho SH, Lin K, Sohn WM, Kim TS. High frequency of genetic diversity of Plasmodium vivax field isolates in Myanmar. Acta Trop 2009;109:30-36.
- 20. Udagama PV, Gamage-Mendis AC, David PH, Peiris JS, Perera KL, Mendis KN, Carter R. Genetic complexity of Plasmodium vivax parasites in individual human infections analyzed with monoclonal antibodies against variant epitopes on a single parasite protein. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1990;42:104-110.
- 21. Arévalo-Herrera M, Chitnis C, Herrera S. Current status of Plasmodium vivax vaccine. Hum Vaccin 2010;6:124-132.
- 22. Mourão LC, Morais CG, Bueno LL, Jimenez MC, Soares IS, Fontes CJ, Guimarães Lacerda MV, Xavier MS, Barnwell JW, Galinski MR, Braga EM. Naturally acquired antibodies to Plasmodium vivax blood-stage vaccine candidates (PvMSP-119 and PvMSP-3α359-798 and their relationship with hematological features in malaria patients from the Brazilian Amazon. Microbes Infect 2012;14:730-739.
- 23. Zakeri S, Barjesteh H, Djadid ND. Merozoite surface protein-3α is a reliable marker for population genetic analysis of Plasmodium vivax. Malar J 2006;5:53.
- 24. Zakeri S, Raeisi A, Afsharpad M, Kakar Q, Ghasemi F, Atta H, Zamani G, Memon MS, Salehi M, Djadid ND. Molecular characterization of Plasmodium vivax clinical isolates in Pakistan and Iran using pvmsp-1, pvmsp-3α and pvcsp genes as molecular markers. Parasitol Int 2010;59:15-21.
- 25. Cui L, Mascorro CN, Fan Q, Rzomp KA, Khuntirat B, Zhou G, Chen H, Yan G, Sattabongkot J. Genetic diversity and multiple infections of Plasmodium vivax malaria in Western Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2003;68:613-619.
- 26. Cristiano FA, Pérez MA, Nicholls RS, Guerra AP. Polymorphism in the Plasmodium vivax msp 3: gene in field samples from Tierralta, Colombia. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2008;103:493-496.
- 27. Véron V, Legrand E, Yrinesi J, Volney B, Simon S, Carme B. Genetic diversity of msp3α and msp1_b5 markers of Plasmodium vivax in French Guiana. Malar J 2009;8:40.
- 28. Prajapati SK, Joshi H, Valecha N. Plasmodium vivax merozoite surface protein-3α: a high-resolution marker for genetic diversity studies. J Vector Borne Dis 2010;47:85-90.
- 29. Khan SN, Khan A, Khan S, Ayaz S, Attaullah S, Khan J, Khan MA, Ali I, Shah AH. PCR/RFLP-based analysis of genetically distinct Plasmodium vivax population of Pvmsp-3α and Pvmsp-3β genes in Pakistan. Malar J 2014;13:355.
- 30. Zakeri S, Djadid ND, Zeinali S. Sequence heterogeneity of the merozoite surface protein-1 gene (MSP-1) of Plasmodium vivax wild isolates in Southeastern Iran. Acta Trop 2003;88:91-97.
- 31. Verma A, Joshi H, Singh V, Anvikar A, Valecha N. Plasmodium vivax msp-3α polymorphisms: analysis in the Indian subcontinent. Malar J 2016;15:492.