Abstract
The present study was performed to record new definitive hosts of Isthmiophora hortensis, and to describe morphological characteristics derived from a variety of worm samples for clarification of its taxonomic validity. Morphological characteristics with dimensions were observed in worm samples (n=21) from naturally infected wild animals, including a raccoon dog Nyctereutes procyonoides from Gimhae-si (City), Gyeongsangnam-do, stray cats and a striped field mouse from several localities, and a wild boar Sus scrofa, from Gurye-gun (County), Jeollanam-do. In addition, adult flukes (n=45) recovered in albino rats experimentally infected with the metacercariae from a freshwater fish species were also subjected to morphological studies. The mean ratios of the body length (BL) to body width (BW) were 5.86 and 5.76 in worms from wild animals and experimental rats, respectively. Those of the ventral sucker to oral sucker were 2.92 and 3.01 in worms from 2 groups. The mean percentages of the hindbody length (HBL) to BL were 42.1 and 41.2 in 2 groups. Those of uterine fields to BL were 9.8 and 12.2 in the 2 worm groups. By the present study, the 2 species of wild animals, the raccoon dog and wild boar, have been added as new definitive hosts for I. hortensis. The morphological characteristics of adult flukes derived from a variety of host source were redescribed to support the taxonomic validity of this echinostome species.
-
Key words: Isthmiophora hortensis, raccoon dog, wild boar, differential index
INTRDUCTION
Isthmiophora hortensis (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) was originally described as
Echinostoma hortense from rats in Japan [
1]. After then, this fluke was also found in rats, dogs, cats, weasels, raccoons, and striped field mice naturally infected in Korea, Japan, China, and Vietnam [
2–
10]. Human infections with this fluke were reported in Japan, the Republic of Korea (=Korea), and China [
11–
17]. Especially in Korea, several endemic foci have been reported [
18–
21], and some clinical cases have been sporadically diagnosed by the recovery of worms in gastroduodenal endoscopy [
22–
26]. Therefore, this echinostome is a dominant species with clinical importance in Korea.
The generic conceptions and relationships of
Isthmiophora and
Euparyphium have not been clarified for a long time in the family Echinostomatidae. To clarify the validity of
Isthmiophora in relation to
Euparyphium, Kostadinova and Gibson [
27] analyzed the morphological characteristics of related specimens in 2 genera and redefined each generic character. They also made a differential key to the species of
Isthmiophora with the morphological characteristics of related worm samples. In their study,
I. hortensis was redescribed with nomination of a new combination from previously described as
Echinostoma hortense [
1]. However, Kostadinova and Gibson [
27] used only 4 worm specimens donated by a Korean parasitologist. Therefore, we seriously needed to describe the differential morphological indices derived from a variety of worm samples to support the taxonomic validity. In addition, new definitive hosts of this fluke, the raccoon dog and wild boar, were reported in this study.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We obtained a dead body of the raccoon dog, Nyctereutes procyonoides, which was captured from Jangyu-myeon (Township), Gimhae-si (City), Gyeongsangnam-do (Province), Korea. Several sets of the viscera of wild boars, Sus scrofa, which were captured from Masan-myeon in Gurye-gun (County), Jeollanam-do, Korea were donated from a local hunter. Five stray cats (Felis catus) and a striped field mouse (Apodemus agrarius) were captured in several different localities. The muscles of wild animals were examined to survey the infections of Trichinella larvae, and additionally their visceral organs were also examined to detect other helminths.
The metacercariae of I. hortensis were isolated and collected from the Korean dark sleeper, Odontobutis platycephala, from Yugucheon (a branch of Geum River) in Gongju-si, Chungcheongnam-do by the artificial digestion method. Then, 50–70 metacercariae were orally infected with a gavage needle to each of 4 albino rats. To obtain the age-controlled adult worms, rats experimentally infected with the metacercariae were killed by cervical dislocation at days 15, 18, 24, and 36 after infection. The small intestines of wild animals and rats were longitudinally opened with a scissors in 0.85% saline, and washed with same solution until the supernatant became cleared. The sediment of the intestinal content was carefully examined with the naked eyes and under a stereomicroscope. The recovered worms were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin under the slight pressure of a cover glass, stained with Semichon’s acetocarmine, and observed under a light microscope equipped with a micrometer (OSM-4, Olympus Co., Tokyo, Japan).
For the differential indices of
I. hortensis, total 76 worm samples were subjected to this analysis. Among them, 21 samples were recovered from wild animals, including a raccoon dog, stray cats, a striped field mouse, and a wild boar. The remaining 55 specimens were recovered from experimental rats (
Tables 1,
2,
4). We basically measured the body length (BL) and width (BW), the size of oral (OS) and ventral suckers (VS), pharynx, esophagus, head collar, cirrus sac, ovary, and 2 testes, and additionally the forebody length (FBL: from the anterior end to the anterior margin of the ventral sucker), hindbody length (HBL: from the posterior margin of the posterior testis to the posterior end), and uterus length (UL: from the posterior margin of the ventral sucker to the anterior margin of the ovary). Then, we also calculated the ratios of BL/BW, VS/OS, the length/width in ovary and 2 testes, and the percentages (%) of FBL/BL, HBL/BL, and UL/BL as the differential body indices of this fluke. Measurements and scales are in micrometers (μm) unless stated otherwise.
RESULTS
Recovery of worms from wild animals
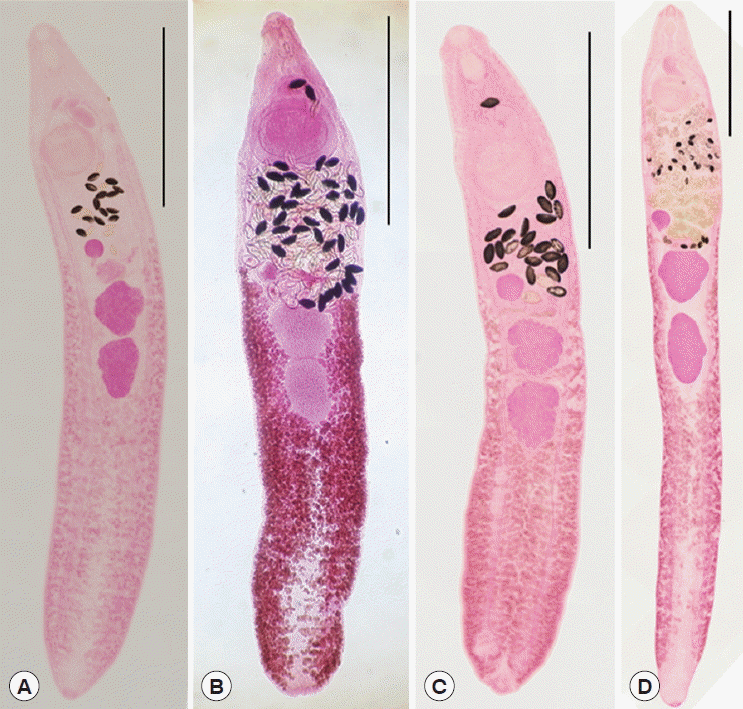
Total 3 adult specimens of
I. hortensis with some other species of echinostomes were recovered in the small intestines of a raccoon dog,
N. procyonoides, and 2 adult specimens were collected from a wild boar,
S. scrofa (
Fig. 1). Total 16 specimens of
I. hortensis were recovered from the small intestines of 5 stray cats and a field mouse.
The characteristic features of
I. hortensis included the presence of a head collar with total 27 collar spines and the dextral location of the ovary. Morphological characteristics of worm samples from wild animals (raccoon dog, stray cats, striped field mouse, and wild boar) were consistent with similar basic features (
Fig. 1). However, their dimensions, including the size of worms, were more or less different by the species of host animals (
Table 1). Dimensions of worms recovered from albino rats at days 15, 18, 24, and 36 after infection were revealed in
Table 2.
The ratios of BL to BW were 5.21–6.70 (5.86 in average) and 5.53–5.95 (5.76) in worms from wild animals and experimental rats, respectively. Those of VS to OS were 2.45–3.71 (2.92) and 2.93–3.26 (3.01) in worms from 2 groups. The ratios of length/width of the ovary were 0.92–1.05 (0.96) and 0.81–0.97 (0.88), those of the anterior testis were 0.83–1.11 (0.91) and 0.93–0.96 (0.95), and those of the posterior testis were 1.28–1.67 (1.41) and 1.28–1.49 (1.41) in worms from 2 groups, respectively. The percentages of FBL to BL were 10.7–16.6 (14.0) and 10.2–12.9 (11.6), and those of HBL to BL were 40.3–43.2 (42.1) and 38.7–42.5 (41.2) in 2 groups. The percentages of uterine field (U) to BL were 6.6–16.9 (9.8) and 9.9–15.6 (12.2) in 2 worm groups (
Table 3).
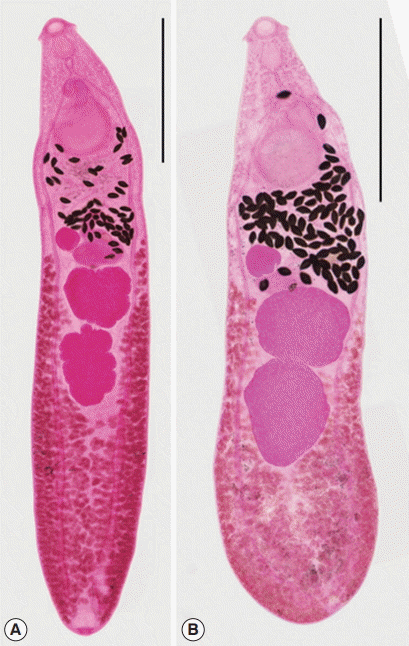
Among the worms recovered from an experimental rat at day 15 after infection, 2 morphologically different worm groups, normal slender and abnormal plump, were categorized (
Fig. 2). Normal slender worms were 6,075–7,000 (6,475) long and 1,100–1,275 (1,171) wide. Abnormal plump worms were 3,875–6,050 (4,846) long and 1,125–1,575 (1,343) wide. Dimensions of 2 worm groups and those from Kostadinova and Gibson [
26] were designated in detail in
Table 4.
The mean ratios of BL/BW were 5.53 and 3.61 in normal and abnormal worms, respectively. Those of VS/OS were 2.95 and 2.89 in 2 worm groups. The mean ratios of L/W in the ovary were 0.94 and 0.94, those in the anterior testis were 0.95 and 0.83, and in the posterior testis were 1.49 and 1.28 in 2 worm groups, respectively. The mean percentages of FBL/BL were 12.9 and 15.8, those of HBL/BL were 38.7 and 27.6, and of U/BL were 9.9 and 14.2 in 2 worm groups (
Table 5).
Body elongate, with attenuated anterior end, maximum width at mid-level of uterus. The average ratio BL/BW was 5.76. Head collar reniform, bearing 27 collar spines with 4 end group ones on each side. Tegumental spines distributed on the body surface from the posterior level of the collar to the posterior 1/3 of body. Oral sucker small, subterminal. Ventral sucker well developed, slightly elliptical. The average ratio VS/OS 3.01. The average percentage of FBL/BL 11.6. Prepharynx very short. Pharynx muscular, well developed. Esophagus short. Ceca bifurcating between the suckers or near the ventral sucker, extending to near the posterior end. Cirrus sac elongate. Seminal vesicle in the posterior portion of the cirrus sac, pars prostatica and ejaculatory duct present in anterior portion of cirrus sac. Ovary spheroidal or rarely oval, dextro-anterior to the anterior testis. The average ratio of L/W in the ovary 0.88. Mehlis’ gland large. Testes usually lobed or rarely entire, tandem; anterior testis usually wider than long; the posterior testis usually longer than wide. The average ratios of L/W in the anterior and posterior testis 0.95 and 1.41. The average percentage of HBL/BL 41.2. Vitelline glands well developed, follicular, laterally extending from anterior level of ovary to near the posterior end. Uterine coils transverse intercecal, extending from ovary-level to anterior level of acetabulum. The average percentage of U/BL 12.0. Eggs large, yellowish-brown, 93–128 (102) by 45–68 (57).
DISCUSSION
Several species of mammals, the black-striped field mouse, dog (
Canis lupus), cat, Manchurian reed vole (
Microtus fortis pellceus), mouse (
Mus musculus), house rat (
Rattus norvegicus), and black rat (
Rattus rattus alexandrinus), have been reported as the definitive hosts for
I. hortensis in Korea [
2–
4,
9,
10]. This fluke was also found in wild animals, i.e., rats, dogs, cats, weasels (
Mustela itatsi), and raccoons (
Procyon lotor), in Japan, China, and Vietnam [
5–
8]. By the present study, 2 species of mammals, raccoon dog (
N. procyonoides) and wild boar (
S. scrofa), are added in the list of the definitive hosts of this fluke.
Total 21 echinostome species in 14 genera have been reported from humans and/or animals in Korea, i.e.,
Acanthoparyphium marilae, A. tyosenense, Chaunocephalus ferox, Echinochasmus japonicus, E. perfoliatus, Echinoparyphium recurvatum, Echinostoma cinetorchis, E. gotoi, E. miyagawai, E. revolutum, Euparyphium murinum, Himasthla alincia, H. kusasigi, H. megacotyle, I. hortensis, Nephrostomum ramosum, Patagifer bilobus, Pegosomum bubulcum, Petasiger neocomense, Saakotrema metatestis, and
Stephanoprora sp., [
28–
32]. Among them, 4 species, namely,
A. tyosenense, E. japonicus, E. cinetorchis, and
I. hortensis, are known as the causative agents of human echinostomiasis in Korea [
28]. Especially, human cases with
I. hortensis have been sporadically and endemically occurred in this country since the first case was reported [
11,
13,
14,
16,
18–
21]. Some clinical cases by this fluke infection have been recently diagnosed by the recovery of worms in gastroduodenal endoscopy [
22–
26]. However, human cases with other 3 echinostome species were rarely reported in Korea [
28]. Accordingly,
I. hortensis is the predominant echinostome species in Korea.
Kostadinova and Gibson [
27] used only 4 worm specimens (3 from a rat and 1 from mouse) donated by a Korean parasitologist in the new nomination of this fluke. However, in the present study, total 76 worm samples were subjected to make the differential indices for the identification of
I. hortensis. Among them, 21 specimens were recovered from naturally infected wild animals (raccoon dog, stray cats, striped field mouse, and wild boar), and 55 specimens from rats (15-day, 18-day, 24-day, and 36-day-old) experimentally infected with the metacercariae. Each differential index was nearly similar in 2 worm groups (from wild animals and experimental rats). However, they were more or less different from those of Kostadinova and Gibson [
27]. The average ratios of BL/BW were 5.86 and 5.76 in 2 worm groups in the present study; however they were 3.75 (from rat) and 4.65 (from mouse) in a previous study. The average ratios of L/W in posterior testis were 1.41 in both worm groups, but they were 0.90 and 1.58 in Kostadinova and Gibson [
27].
We recovered 2 morphologically different types of worms, normal slender and abnormal plump, from rats experimentally infected with metacercariae from a freshwater fish species,
O. platycephala. Especially in the 15-day-old worms, the average ratios of BL/BW were 5.53 and 3.61 in the normal slender and abnormal plump worm groups. However, those from Kostadinova and Gibson [
30] were 3.75 (worms from rat) and 4.65 (worm from mouse). The ratio of BL/BW in worms (from rat) from Kostadinova and Gibson [
27] was similar to that of abnormal plump worms rather than normal slender worms obtained in the present study. The average percentage of HBL/BL was 27.6 in the abnormal worms, which did not correspond with that (>30%) of the worms of the genus
Isthmiophora [
27,
33].
Kostadinova and Gibson [
27] divided the species of
Isthmiophora into 2 groups by the number of collar spine (27 and 29), and they allocated 4 species, i.e.,
I. beaveri, I. inermis, I. melis, and
I. hortensis, in the worm group with 27 collar spines. Among the 27-collar spined group,
I. hortensis is very similar to
I. melis except for the location of the cirrus sac and size of eggs. The differential indices for
I. melis are also closely similar to those of
I. hortensis from a mouse of Kostadinova and Gibson [
27] and normal worms of the present study (
Table 5). The species validity between above 2
Isthmiophora is not obvious only in the morphological aspect. Therefore, the more reasonable taxonomic keys, such as molecular phylogenetic data, will be needed to support the validity of each species.
On the basis of data from 45 worms, which were recovered from experimental rats in the present study, the following diagnostic features were considered as the differential indices for I. hortensis. The worm body is long slender (the ratio of BL/BW: 5.53–5.95); the ventral sucker is larger about 3 times than the oral sucker (the ratio of VS/OS: 2.93–3.26); the ovary is transversely elliptical (the ratio of L/W in the ovary: 0.81–0.97); the anterior testis has a slightly larger transverse axis (the ratio of L/W in the anterior testis: 0.93–0.96); the posterior testis has a long vertical axis (the ratio of L/W in the posterior testis: 1.28–1.49); short forebody (% of FBL/BL: 10.2–12.9); long hindbody (% of HBL/BL: 38.7–42.5); short uterine field (% of UL/BL: 9.9–15.6); the head collar with 27 collar spines and the dextral position of the ovary.
By the present study, it has been confirmed for the first time that the raccoon dog (N. procyonoides) and wild boar (S. scrofa) are the definitive hosts of I. hortensis. Additionally, the morphological characteristics with differential indices derived from a variety of worm samples from wild animals naturally infected and rats experimentally infected could support the taxonomic validity of I. hortensis.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to this article.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Jung-A Kim and Hee-Ju Kim, Department of Parasitology and Tropical Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea, for their help in the collection of metacercariae from fish and recovery of worms from animals.
Fig. 1
Isthmiophora hortensis adults (Semichon’s acetocarmine stained) recovered from the small intestines of wild animals. (A) A specimen from the raccoon dog (Nyctereutes procyonoides). (B) Another from a wild boar (Sus scrofa). (C) A worm from a stray cat (Felis catus). (D) Another from a black-striped field mouse (Apodemus agrarius). Scale bar=1,500 μm.

Fig. 2
Isthmiophora hortensis adults (Semichon’s acetocarmine stained). (A) Normal slender. (B) Abnormal plump, recovered from a rat experimentally infected with metacercariae, which were collected form the Korean dark sleeper, Odontobutis platycephala, from Yugucheon (a branch of Geumgang) in Gongju-si, Chungcheongnam-do. Scale bar=1,500 μm.
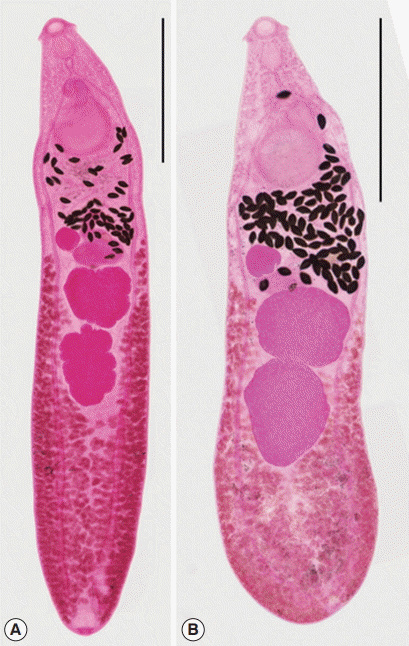
Table 1Dimensions
a of
Isthmiophora hortensis adults recovered from wild animals in Korea
Table 1
|
Organs |
Raccoon dog (n=3)
(Nyctereutes procyonoides)
|
Stray cat-1 (n=6)
(Felis catus) |
Stray cat-2 (n=6)
(Felis catus) |
Striped field mouse (n=4)
(Apodemus agrarius) |
Wild boar (n=2)
(Sus scrofa) |
|
Body |
|
(L) |
4,625–6,125 (5,433) |
3,925–4,775 (4,408) |
5,750–8,800 (6,850) |
4,675–9,950 (7,700) |
4,500–4,875 (4,688) |
|
(W) |
925–1,025 (983) |
675–875 (758) |
900–1,750 (1,196) |
1,000–1,300 (1,150) |
875–925 (900) |
|
|
Oral sucker |
|
(L) |
190–195 (193) |
125–165 (152) |
165–210 (190) |
160–175 (168) |
128–150 (139) |
|
(W) |
190–195 (192) |
175–185 (179) |
185–250 (215) |
150–185 (170) |
133–155 (144) |
|
|
Head crown (W) |
350–355 (352) |
315–350 (329) |
375–450 (416) |
300–375 (335) |
225–250 (238) |
|
|
Pharynx |
|
(L) |
165–180 (173) |
165–175 (171) |
160–200 (183) |
150–190 (165) |
145–158 (152) |
|
(W) |
140–150 (147) |
135–165 (150) |
145–215 (170) |
155–180 (169) |
110–120 (115) |
|
|
Esophagus (L) |
225–250 (233) |
75–150 (105) |
160–340 (223) |
125–235 (200) |
125–138 (132) |
|
|
Ventral sucker |
|
(L) |
400–490 (455) |
420–500 (455) |
500–710 (577) |
470–550 (520) |
470–530 (500) |
|
(W) |
450–510 (487) |
410–470 (450) |
500–710 (613) |
470–590 (540) |
550–560 (555) |
|
|
Cirrus sac |
|
(L) |
325–490 (403) |
270–400 (334) |
450–650 (512) |
420–550 (510) |
- |
|
(W) |
150–200 (183) |
120–200 (154) |
210–350 (262) |
170–300 (230) |
- |
|
|
Ovary |
|
(L) |
145–170 (155) |
145–175 (160) |
205–350 (254) |
140–300 (258) |
150–165 (158) |
|
(W) |
130–165 (148) |
155–185 (173) |
220–350 (273) |
200–310 (250) |
150–190 (170) |
|
|
Anterior testis |
|
(L) |
335–500 (443) |
300–400 (333) |
450–720 (582) |
400–790 (680) |
310–350 (330) |
|
(W) |
350–450 (400) |
330–480 (398) |
460–1,100 (673) |
470–880 (710) |
- (400) |
|
|
Posterior testis |
|
(L) |
400–630 (515) |
400–530 (470) |
580–970 (718) |
490–1,100 (898) |
425–510 (468) |
|
(W) |
350–410 (373) |
300–480 (355) |
400–800 (560) |
380–600 (538) |
270–325 (298) |
Table 2Dimensions
a of
Isthmiophora hortensis adults recovered from albino rats experimentally infected with metacercariae
Table 2
|
Organs |
15-day-old (n=10) |
18-day-old (n=10) |
24-day-old (n=15) |
36-day-old (n=10) |
|
Body |
|
(L) |
6,075–7,000 (6,475) |
5,925–7,800 (6,780) |
5,675–9,825 (7,447) |
9,450–10,850 (9,965) |
|
(W) |
1,100–1,275 (1,171) |
1,000–1,325 (1,158) |
1,050–1,625 (1,303) |
1,450–1,775 (1,675) |
|
|
Oral sucker |
|
(L) |
160–190 (174) |
160–185 (172) |
155–215 (188) |
170–220 (193) |
|
(W) |
185–205 (196) |
185–210 (204) |
190–240 (216) |
220–250 (238) |
|
|
Head crown (W) |
350–375 (368) |
315–400 (371) |
350–490 (398) |
410–440 (426) |
|
|
Pharynx |
|
(L) |
185–200 (189) |
175–210 (190) |
190–240 (212) |
210–240 (229) |
|
(W) |
130–175 (153) |
140–195 (168) |
130–210 (174) |
160–210 (187) |
|
|
Esophagus (L) |
90–250 (143) |
110–210 (152) |
75–180 (134) |
110–325 (173) |
|
|
Ventral sucker |
|
(L) |
480–600 (526) |
510–600 (555) |
480–630 (572) |
640–770 (689) |
|
(W) |
540–670 (564) |
500–610 (550) |
510–680 (613) |
680–770 (719) |
|
|
Cirrus sac |
|
(L) |
350–520 (450) |
370–530 (441) |
380–600 (459) |
550–720 (606) |
|
(W) |
160–270 (201) |
120–190 (160) |
190–275 (226) |
230–320 (278) |
|
|
Ovary |
|
(L) |
260–310 (284) |
225–340 (281) |
210–385 (274) |
250–310 (291) |
|
(W) |
250–340 (303) |
235–355 (290) |
230–435 (329) |
330–380 (360) |
|
|
Anterior testis |
|
(L) |
580–720 (657) |
560–930 (668) |
510–1,000 (703) |
750–1,050 (936) |
|
(W) |
530–810 (693) |
510–840 (693) |
520–1,030 (760) |
870–1,130 (980) |
|
|
Posterior testis |
|
(L) |
770–950 (871) |
600–1,160 (845) |
660–1,280 (899) |
1,000–1,230 (1,139) |
|
(W) |
480–650 (586) |
510–650 (577) |
470–800 (632) |
880–1,190 (1,016) |
Table 3Differential indices in the adults of Isthmiophora hortensis recovered from wild animals and experimental rats
Table 3
|
Items |
Differential indices (average) in worms from |
|
Wild animalsa
|
Experimental ratsb
|
|
Body length (BL)/Body width (BW) |
5.21–6.70 (5.86) |
5.53–5.95 (5.76) |
|
Ratio of ventral sucker (VS)/oral sucker (OS) |
2.45–3.71 (2.92) |
2.93–3.26 (3.01) |
|
Ratio of length (L)/width (W) in ovary |
0.92–1.05 (0.96) |
0.81–0.97 (0.88) |
|
Ratio of L/W in anterior testis |
0.83–1.11 (0.91) |
0.93–0.96 (0.95) |
|
Ratio of L/W in posterior testis |
1.28–1.67 (1.41) |
1.28–1.49 (1.41) |
|
Percentage (%) of forebody length (FBL)/BL |
10.7–16.6 (14.0) |
10.2–12.9 (11.6) |
|
Percentage (%) of hindbody length (HBL)/BL |
40.3–43.2 (42.1) |
38.7–42.5 (41.2) |
|
Percentage (%) of uterus length (UL)/BL |
6.6–16.9 (9.8) |
9.9–15.6 (12.0) |
Table 4Comparative dimensions of Isthmiophora hortensis adults from the present study and a previous study with those of I. melis
Table 4
|
Organs |
Present studya
|
Kostadinova and Gibson [27] from |
I. melisb
|
|
|
|
Normal (n=10) |
Abnormal (n=10) |
Rats (n=3) |
Mouse |
|
Body |
|
(L) |
6,075–7,000 (6,475) |
3,875–6,050 (4,846) |
5,376–6,463 |
4,043 |
4,564–7,346 (5,577) |
|
(W) |
1,100–1,275 (1,171) |
1,125–1,575 (1,343) |
1,362–1,826 |
869 |
1,014–1,348 (1,203) |
|
|
Oral sucker |
|
(L) |
160–190 (174) |
155–180 (167) |
159–246 |
145 |
188–261 (221) |
|
(W) |
185–205 (196) |
170–190 (183) |
203–246 |
159 |
203–261 (228) |
|
|
Head crown (W) |
350–375 (368) |
325–375 (364) |
319–391 |
261 |
377–464 (406) |
|
|
Pharynx |
|
(L) |
185–200 (189) |
165–195 (180) |
145–239 |
130 |
188–246 (221) |
|
(W) |
130–175 (153) |
130–180 (156) |
116–217 |
217 |
130–188 (169) |
|
|
Esophagus (L) |
90–250 (143) |
125–180 (149) |
0–145 |
130 |
116–290 (200) |
|
|
Ventral sucker |
|
(L) |
480–600 (526) |
460–575 (499) |
551–826 |
406 |
551–797 (676) |
|
(W) |
540–670 (564) |
455–600 (513) |
580–768 |
464 |
536–753 (668) |
|
|
Cirrus sac |
|
(L) |
350–520 (450) |
365–450 (404) |
377–420 |
406 |
246–652 (462) |
|
(W) |
160–270 (201) |
140–200 (176) |
217–232 |
174 |
203–362 (303) |
|
|
Ovary |
|
(L) |
260–310 (284) |
210–300 (246) |
232–275 |
188 |
203–319 (256) |
|
(W) |
250–340 (303) |
205–325 (261) |
275–319 |
188 |
in diameter |
|
|
Anterior testis |
|
(L) |
580–720 (657) |
450–660 (576) |
478–623 |
464 |
362–739 (568) |
|
(W) |
530–810 (693) |
580–860 (691) |
739–942 |
464 |
420–811 (590) |
|
|
Posterior testis |
|
(L) |
770–950 (871) |
570–980 (744) |
609–739 |
594 |
536–1,174 (734) |
|
(W) |
480–650 (586) |
480–700 (581) |
609–884 |
377 |
319–609 (476) |
Table 5Comparative differential indices of Isthmiophora hortensis adults from the present study and a previous study with those of I. melis
Table 5
|
Index |
Present studya
|
Kostadinova and Gibson [27] from |
I. melisb
|
|
|
|
Normal (n=10) |
Abnormal (n=10) |
Rats (n =3) |
Mouse |
|
Body length (BL)/Body width (BW) |
5.53 |
3.61 |
3.75 |
4.65 |
4.64 |
|
|
Ratio of ventral sucker (VS)/oral sucker (OS) |
2.95 |
2.89 |
3.18 |
2.86 |
2.99 |
|
|
Ratio of L/W in the ovary |
0.94 |
0.94 |
0.86 |
1.0 |
1.0 |
|
|
Ratio of L/W in the anterior testis |
0.95 |
0.83 |
0.66 |
1.0 |
0.96 |
|
|
Ratio of L/W in the posterior testis |
1.49 |
1.28 |
0.90 |
1.58 |
1.54 |
|
|
Percentage (%) of forebody length (FBL)/BL |
12.9 |
15.8 |
12.5 |
14.7 |
14.8 |
|
|
Percentage (%) of hindbody length (HBL)/BL |
38.7 |
27.6 |
40.6 |
37.6 |
41.0 |
|
|
Percentage (%) of uterus length (UL)/BL |
9.9 |
14.2 |
7.4 |
5.7 |
3.0 |
References
- 1. Asada J. On a new echinostomatid trematode and its life history. Trans Jpn Soc Pathol 1926;16:293-294. (in Japanese).
- 2. Park JT. A rat trematode, Echinostoma hortense Asada, from Korea. Keijo J Med 1938;9:283-286.
- 3. Seo BS, Cho SY, Hong ST, Hong SJ, Lee SH. Studies on parasitic helminths of Korea 5. Survey on intestinal trematodes of house rats. Korean J Parasitol 1981;19:131-136.
- 4. Cho SY, Kang SY, Ryang YS. Helminthes infections in the small intestine of stray dogs in Ejungbu City, Kyunggi Do, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1981;19:55-59.
- 5. Chen HT. Fauna Sinica. Platyhelminthes, Trematoda, Digenea (I). Beijing, China. Science Press; 1985, pp 333-497 (in Chinese).
- 6. Fan SQ, Sun MF. Echinostoma hortense. Bull Harbin Med Univ 1989;23:161.
- 7. Sato H, Suzuki K. Gastrointestinal helminths of feral raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Wakayama Prefecture, Japan. J Vet Med Sci 2006;68:311-318.
- 8. Nguyen LA, Madsen H, Dao TH, Hoberg E, Dalsgaard A, Murrell KD. Evaluation of the role of rats as reservoir hosts for fishborne zoonotic trematodes in two endemic northern Vietnam fish farms. Parasitol Res 2012;111:1045-1048.
- 9. Sohn WM, Na BK, Song HJ, Kim CM, Nam GJ. Intestinal helminthic infections in striped field mice, Apodemus agrarius, from two southern regions of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:419-423.
- 10. Shin SS, Oh DS, Ahn KS, Cho SH, Lee WJ, Na BK, Sohn WM. Zoonotic intestinal trematodes in stray cats (Felis catus) from riverside areas of the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2015;53:209-213.
- 11. Seo BS, Hong ST, Chai JY, Lee SH. Studies on intestinal trematodes in Korea. VIII. A human case of Echinostoma hortense infection. Korean J Parasitol 1983;21:219-223.
- 12. Miyamoto K, Nakao M, Inaoka T. Studies on the zoonoses in Hokkaido, Japan. 5. On the epidemiological survey of Echinostoma hortense Asada, 1926. Jpn J Parasitol 1983;32:261-269. (in Japanese).
- 13. Ryang YS, Ahn YK, Lee KW, Kim TS, Hhan MH. Two cases of natural human infection by Echinostoma hortense and its second intermediate host in Wonju area. Korean J Parasitol 1985;23:33-40.
- 14. Lee SK, Chung NS, Ko IH, Ko HI, Chai JY. Two cases of natural human infection by Echinostoma hortense. Korean J Parasitol 1986;24:77-81. (in Korean).
- 15. Chen XQ, Feng GX, Qian ZF. Survey on infection due to Echinostoma hortense in Liaoning Province. Chinese J Parasitol Parasit Dis 1993;11:226. (in Chinese).
- 16. Huh S, Lee SU, Huh SC. A follow-up examination of intestinal parasitic infections of the army soldiers in Whachon-gun, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1994;32:61-63.
- 17. Hamamoto T, Kawasaki H, Maejima J, Hirai K. A case of Echinostoma hortense infection diagnosed by the upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi 1997;94:487-491. (in Japanese).
- 18. Ryang YS. Studies on Echinostoma spp. in the Chungju Reservoir and upper stream of the Namhan River. Korean J Parasitol 1990;28:221-233. (in Korean).
- 19. Son WY, Huh S, Lee SU, Woo HC, Hong SJ. Intestinal trematode infections in the villagers in Koje-myon, Kochang-gun, Kyongsangnam-do, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1994;32:149-155.
- 20. Ahn YK, Ryang YS. Experimental and epidemiological studies on the life cycle of Echinostoma hortense Asada, 1926 (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae). Korean J Parasitol 1986;24:121-136. (in Korean).
- 21. Lee SK, Chung NS, Ko IH, Sohn WM, Hong ST, Chai JY, Lee SH. An epidemiological survey of Echinostoma hortense infection in Chongsong-gun, Kyongbuk Province. Korean J Parasitol 1988;26:199-206. (in Korean).
- 22. Chai JY, Hong ST, Lee SH, Lee GC, Min YI. A case of echinostomiasis with ulcerative lesions in the duodenum. Korean J Parasitol 1994;32:201-204.
- 23. Lee OJ, Hong SJ. Gastric echinostomiasis diagnosed by endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc 2002;55:440-442.
- 24. Cho CM, Tak WY, Kweon YO, Kim SK, Choi YH, Kong HH, Chung DI. A human case of Echinostoma hortense (Trematoda: Echinostomatidae) infection diagnosed by gastroduodenal endoscopy in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2003;41:117-120.
- 25. Chang YD, Sohn WM, Ryu JH, Kang SY, Hong SJ. A human infection of Echinostoma hortense in duodenal bulb diagnosed by endoscopy. Korean J Parasitol 2005;43:57-60.
- 26. Park CJ, Kim J. A human case of Echinostoma hortense infection diagnosed by endoscopy in area of southwestern Korea. Korean J Med 2006;71:229-234.
- 27. Kostadinova A, Gibson DI. Isthmiophora Lühe, 1909 and Euparyphium Diet, 1909 (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) redefined, with comments on their nominal species. Syst Parasitol 2002;52:205-217.
- 28. Chai JY. In Fried B, Toledo R eds, Echinostomes in Humans. The Biology of Echinostomes. 2009, New York, USA. Springer; pp 147-183.
- 29. Choe S, Lee D, Park H, Oh M, Jeon HK, Lee Y, Na KJ, Kim Y, Lee H, Eom KS. Three echinostome species from wild birds in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:513-520.
- 30. Choe S, Lee D, Park H, Jeon HK, Lee Y, Kim E, Na KJ, Eom KS. Two echinostome species, Pegosomum bubulcum and Nephrostomum ramosum (Digenea: Echinostomatidae), from an Eastern cattle egret, Bubulcus ibis coromandus, in Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:485-496.
- 31. Choe S, Lee D, Park H, Jeon HK, Lee Y, Na KJ, Park SR, Eom KS. A case of chaunocephalosis by Chaunocephalus ferox (Digenea: Echinostomatidae) in an oriental white stork, Ciconia boyciana, in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:659-665.
- 32. Lee YI, Chung OS, Seo M. Recovery of Oswaldotrema nacinovici from whimbrels (Aves) in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:809-812.
- 33. Kostadinova A. Family Echinostomatidae Looss. In Jones A, Bray RA, Gibson DI eds, Keys to the Trematoda. 2:Wallingford, UK. CABI; 2005, pp 9-64.