Abstract
Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH) is a strong target antigen for the determination of infection with Plasmodium species specifically. However, a more effective antibody is needed because of the low sensitivity of the current antibody in many immunological diagnostic assays. In this study, recombinant Plasmodium vivax LDH (PvLDH) was experimentally constructed and expressed as a native antigen to develop an effective P. vivax-specific monoclonal antibody (mAb). Two mAbs (2CF5 and 1G10) were tested using ELISA and immunofluorescence assays (IFA), as both demonstrated reactivity against pLDH antigen. Of the 2 antibodies, 2CF5 was not able to detect P. falciparum, suggesting that it might possess P. vivax-specificity. The detection limit for a pair of 2 mAbs-linked sandwich ELISA was 31.3 ng/ml of the recombinant antigen. The P. vivax-specific performance of mAbs-linked ELISA was confirmed by in vitro-cultured P. falciparum and P. vivax-infected patient blood samples. In conclusion, the 2 new antibodies possessed the potential to detect P. vivax and will be useful in immunoassay.
-
Key words: Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase, monoclonal antibody
INTRODUCTION
Malaria is a serious and fatal disease caused by
Plasmodium parasites, which commonly infect a certain type of mosquito that feeds on humans. In 2015, an estimated 212 million cases of malaria occurred worldwide, and 429,000 people died, mostly children in the African region [
1].
P. vivax is one of the 5 species of malaria parasites that commonly infect humans. It is less virulent than
P. falciparum, the deadliest of the 5, but can lead to severe disease and death due to parasite adherence to vascular endothelial cells as sequestration [
2].
As there are diagnostic and treatment differences between
P. vivax malaria and
P. falciparum malaria, development of efficient differential diagnostic methods is necessary. Even before a patient shows symptoms,
P. vivax can live in the bloodstream as sexual-stage parasites, and mosquitoes will acquire and transmit this form to the next individual [
3], making outbreaks difficult to contain.
P. vivax is not immediately fatal, thus when symptoms appear, the parasite continues to multiply. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment are fundamental to prevent more severe malaria and death.
To validate the diagnostic results, rapid diagnostic test (RDT) s were tested with microscopy, which is the gold standard method to detect Plasmodium. Microscopy requires training, and microscopes are not always available in remote villages, thus specific monoclonal antibodies are necessary for RDTs.
Until now, RDTs have been mainly developed for
P. falciparum histidine-rich protein 2 (PfHRP-2) and 2 parasite-specific markers, such as
Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase (pLDH) and aldolase [
4]. Due to high homology of pLDH, most RDTs are not able to distinguish between
P. vivax and
P. falciparum. To overcome this limitation, aldolase was newly identified as an effective target for the generation of mAbs to detect
P. vivax specifically, thus contributing to the development of a
P. vivax-specific RDT [
5]. In particular, the sequence of aldolase 1 from other
Plasmodium species was found to be identical to
P. falciparum aldolase, whereas aldolase 2 had 13% sequence diversity [
6]. Alternatively, pLDH could be considered as a specific marker for the generation of a monoclonal antibody to detect
Plasmodium species differentially because it possesses species-specific isomers [
7].
However, pLDH has a low sensitivity for the detection of
P. vivax specifically, and a combination of both aldolase and LDH is necessary for diagnostic assays with pLDH [
8]. Therefore, the development of an efficient
P. vivax-specific monoclonal antibody (mAb) is favored. In this study, a novel pair of mAbs targeting pLDH was developed and evaluated for diagnostic specificity for detecting
P. vivax-infected patient blood samples.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Reagents
P. falciparum 3D7 (ATCC PRA-405D) was purchased from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, Virginia, USA). P. vivax-infected patient blood samples were collected from endemic areas, and healthy individual samples were collected from malaria-free areas of Gangwon-do (Province), Korea. The study was approved by the Kangwon National University Hospital Institutional Review Board (approval no. 2014-08-008-002).
Malaria culture
P. falciparum 3D7 was continuously cultured in RPMI 1,640 medium (24 mM sodium bicarbonate, 25 μg/ml gentamicin, 1% albumax, 0.05% hypoxanthine, and 1% penicillin) with 5% hematocrit of type O human red blood cells. The quantitative parasite content in the blood (parasitemia) was checked daily by Giemsa staining (Polysciences, Inc., Warrington, Pittsburg, USA). The medium was changed daily and divided when parasitemia reached 5–6%. The culture plates were maintained at 37°C with 5% CO2, 5% O2, and 90% N2 atmosphere.
Cloning, expression and purification of pLDH
The LDH sequences of P. vivax (GenBank no. DQ060151.1) and P. falciparum (GenBank no. XM_001349953.1) were amplified by PCR (Takara, Kusatsu, Japan) using primer pairs: Forward 5′-C ATATGACGCCGAAACCCAAA–3′ (NdeI restriction site), Reverse 5′-GGAGCTCGAAATGAGCGCCT-3′ (SacI restriction site) for PvLDH expression and Forward 5′-AGCTAGCATGGCACCAAAAGCAAAAATCGT-3′ (NheI restriction site), Reverse 5′-GGAGCTCGAAGCTAATGCCTTCATTCTCTTAGT-3′ (SacI restriction site) for PfLDH expression. PCR products were confirmed by electrophoresis and purified using a quick gel extraction kit (Qiagen, Germantown, Maryland, USA). The purified products were cloned in p-GEM-T Easy vector (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, USA) for transformation and culture. Positive clones were extracted and confirmed by sequencing. The expected DNA sequence was ligated into pET-21b vector (Novagen, Sydney, Australia) for expression. Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) (0.5 mM) was used to induce antigen expression and after 4 hr of culturing, cell lysates were harvested for analysis of antigen expression.
Purification and western blotting with anti-6x-His antibody
Recombinant antigen was obtained by native condition using Tris buffer (100 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris HCl, 5% glycerol, pH 7.5) and purified further. Briefly, the supernatant was incubated with Ni-NTA agarose (Qiagen) at 10 mM imidazole at room temperature for 30 min. Bound proteins were obtained with an elution buffer containing imidazole at concentrations of 50 mM, 100 mM, and 300 mM and then analyzed by 12% SDS-PAGE. For western blotting, the purified proteins were loaded onto 12% SDS-PAGE gels at 3 μg per lane and then transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, Massachusetts, USA). PBS with 0.1% Tween 20 (PBST) and 5% skim milk was used for blocking. The primary antibody was a 6×His-tag antibody (Thermos Fisher Scientific Inc.) diluted 12,000 folds. The secondary antibody was a rabbit polyclonal antibody to mouse IgG–horseradish peroxidase (anti-mouse HRP) (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) diluted 30,000 folds. The results were imaged by ChemiDoc XRS+ imaging system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA).
Production of monoclonal antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies were generated by immunizing mice. For the first injection, the recombinant PvLDH and PfLDH proteins (each 50 μg per 100 μl) were mixed with an equal volume of Freund’s complete adjuvant (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) and injected intraperitoneally into 7-week-old female BALB/c mice (Daehan Bio-Link Ltd., Eumseong, Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea). Then, the rPvLDH and rPfLDH proteins (each 25 μg per 100 μl) mixed with an equal volume of Freund’s incomplete adjuvant were boosted biweekly. After the third injection, a final injection of rPvLDH and rPfLDH proteins without adjuvant (each 5 μg per 100 μl) was administered intravenously. The cell fusion technique was performed according to previously established protocols [
9,
10]. Briefly, mouse splenocytes were fused with myeloma cell line FO obtained from the ATCC by adding 50% polyethylene glycol (Sigma-Aldrich) and then seeded in each well of a 96-well culture plate. Hybridoma cells were selected by subculture in HAT (hypoxanthine, aminopterin, and thymidine) and HT (hypoxanthine and thymidine) media, and the antibody formation was screened by ELISA. Hybridoma cells producing a mAb were selected, scaled up, and subjected to limiting dilution for the production of monoclones producing mAbs. Selected monoclonal cells were intraperitoneally injected into 10-week-old female BALB/c mice for large-scale mAb production. The mAbs obtained from mouse ascites were purified using a Protein A agarose column (Amersham Biosciences, Uppsala, Sweden) and confirmed by SDS-PAGE and western blotting.
Western blotting for candidate antibodies was performed with a 6×His-tag antibody. Recombinant protein (3 μg) was separated by SDS-PAGE gel and then transferred to PVDF membrane. After blocking the membrane with 5% skim milk in PBST, monoclonal 2CF5 and 1G10 antibodies were applied to the membrane (30 μg) as the primary antibody. The reaction of the antigen and primary antibody was recognized by anti-mouse HRP in diluted 1:30,000 folds. The result was imaged by ChemiDoc XRS+ imaging system.
Indirect ELISA
Indirect ELISA with parasites was performed with P. falciparum 3D7 in vitro cultures at 106 parasites/ml, using 96-well microtiter plates (SungwooLS, Uijeongbu-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea), followed by overnight incubation at 4°C. The plate was washed by addition of 200 μl PBST per well with gentle shaking for 2 min (3 times) and then blocked with blocking buffer (4% BSA dissolved in PBST). 2CF5 and 1G10 mAb (5 μg per 100 μl) were added to each well as the primary antibody. After incubation for 1.5 hr at 37°C, the plate was washed 3 times and incubated with anti-mouse HRP (Abcam, Bristol, UK) (1: 5,000) for 1 hr. Color was developed using 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.) and stopped with 0.18 M H2SO4. The absorbance was then read at 450 nm using an Infinite F200 microplate reader (TECAN, Männedorf, Switzerland).
Immunofluorescence assay
The in vitro-cultured P. falciparum was used to make a thin smear on a microscope slide for Giemsa staining and immunofluorescence assay (IFA). For IFA, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, followed by PBST washing and then incubated in PBS with 0.1% Triton X-100 for 40 min. The slide was blocked with 2% BSA for 2 hr. Subsequently, 2CF5 and 1G10 mAbs were added with overnight incubation at 4°C. After washing, anti-mouse IgG FITC (Sigma-Aldrich) was added (5,000-fold dilutions), and slides were incubated at room temperature for 1 hr. After washing, slides were dried and mounted with DAPI-containing mounting medium (Vector Lab, Burlingame, California, USA). Fluorescence was captured with an Olympus Fluoview FV1000 confocal laser scanning microscope (Tokyo, Japan).
Sandwich ELISA with recombinant antigen and clinical samples
Sandwich ELISA was performed to determine the specificity of the selected mAbs. For this test, 1G10 mAb was conjugated with HRP using EZ-Link Plus Activated Peroxidase Kit (Thermo Scientific Inc.). Each well of a microtiter plate was coated with 0.1 μg of the 2CF5 mAb with overnight incubation. After 1 day, the plate was washed with PBST and blocked with 4% BSA in PBST for 2 hr, followed by a wash step and addition of a serial dilution of analytes (PvLDH antigen, P. falciparum 3D7, and P. vivax-infected patient blood) to the wells. After 1 hr incubation, the plate was washed, and 1G10 mAb conjugated HRP was added at 0.1 μg per well. An hour later, color was developed using TMB substrate and stopped by 0.18 M H2SO4. Absorbance at 450 nm was then read on a microplate reader.
Statistical analysis
All results were statistically analyzed using GraphPad Prism 5.0. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to analyze ELISA data using of Tukey’s multiple comparisons. All data are shown as means±SD of biological replicates.
RESULTS
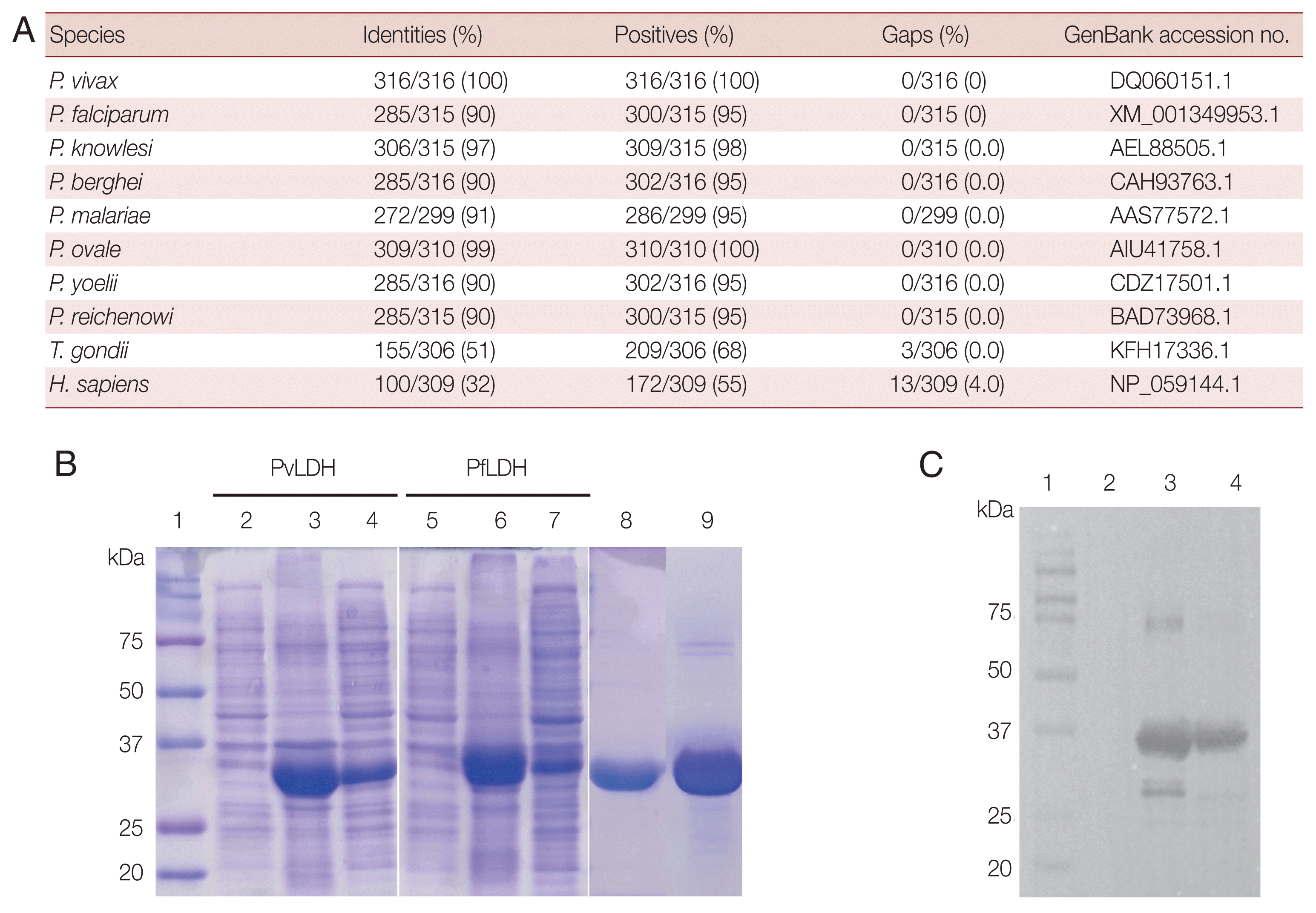
Homology of LDH protein between different Plasmodium species and expression of the pLDH protein
P. vivax LDH showed 90% sequence identity with that of
P. falciparum. In addition, it had high identity with
P. berghei and
P. malariae, being 90–91% identical. The highest homology was to
P. knowlesi and
P. ovale, up to 97–99%. Sequence homology between
P. vivax and other species of
Plasmodium genus (
P. yoelii and
P. reichenowi) was also significant (90%). In contrast, the amino acid identity of
P. vivax was low in
Toxoplasma gondii or
Homo sapiens, showing 51% and 32%, respectively. The sequences of all species were obtained from the NCBI (
Fig. 1A). Antigen expression of PfLDH and PvLDH was obtained in the soluble fraction in
Escherichia coli, showing dominant expression at 35.2 kDa (
Fig. 1B). The purified proteins were confirmed by western blot (
Fig. 1C).
Generation of monoclonal antibody (2CF5 and 1G10)
After antibody formation was observed in mice post-immunization (
Fig. 2A), cell fusion and limiting dilutions were performed, and then 8 monoclones, namely, 1BD6-AG5, 2AD8-C7, 2CF1-AD10, 2CF1-DA4, 2CF1-AG4, 2CF1-BF5 (2CF5), 3CH2-BB7, and 5DC3-BA5 for rPvLDH (left), and 7 monoclones (1B5, 1G11, 1B9, 1E6, 1C5, 1G10, and 1G5) for PfLDH (right) were produced (
Fig. 2A). The final selected monoclonal antibodies, 2CF5 for PvLDH and 1G10 for PfLDH, were purified and identified by SDS-PAGE, which showed the immunoglobulin heavy and light chains (
Fig. 2B). The interaction of selected mAbs against recombinant antigens was determined by western blotting (
Fig. 2C). Each mAb was tested for PfLDH and PvLDH, and the affinity between PvLDH and 2CF5 was stronger than that of PfLDH and 2CF5. 1G10 recognized both antigens aggressively (
Fig. 2D).
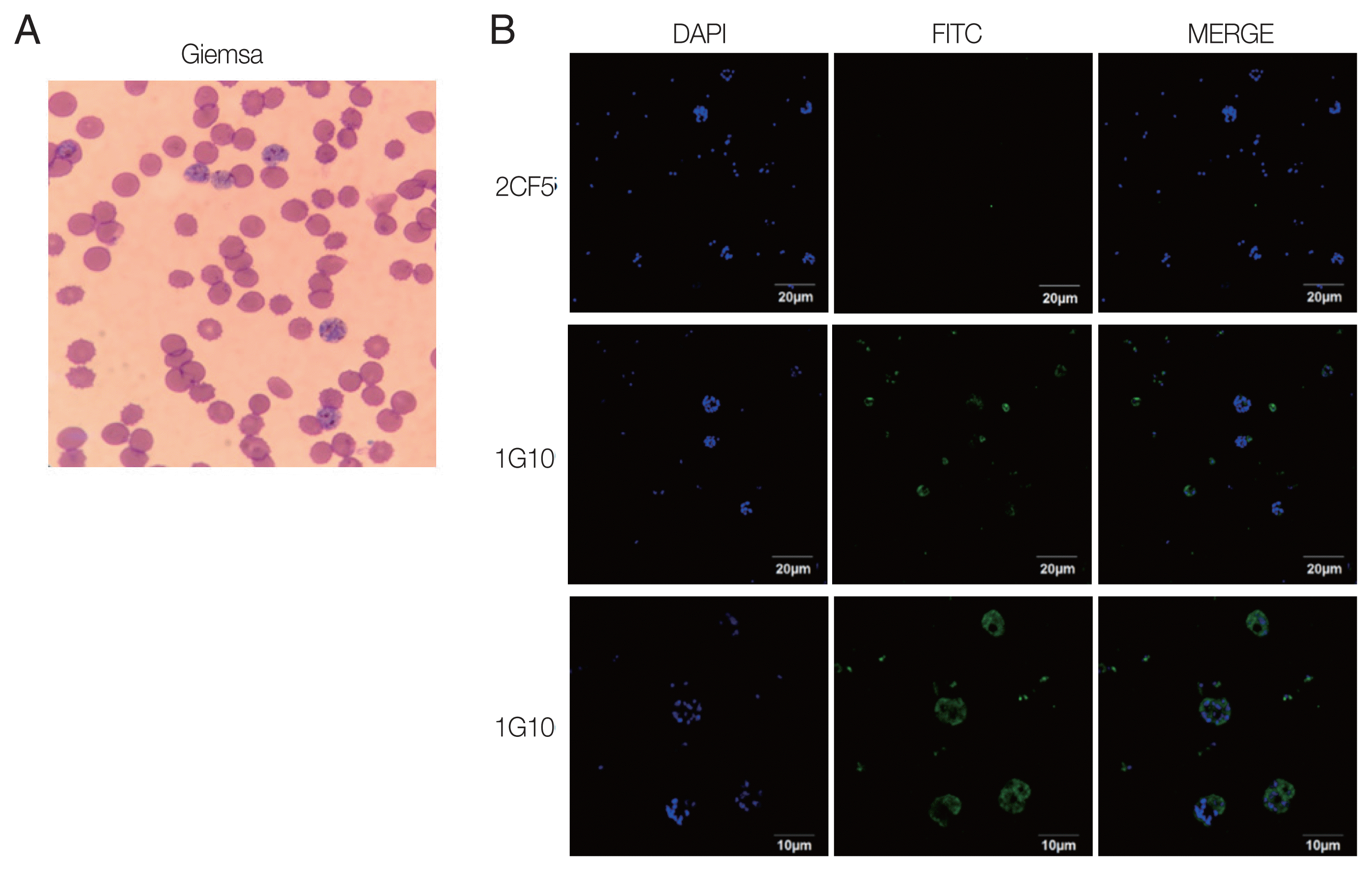
The reactivity of antigen and antibody was confirmed by IFA using the trophozoite and schizont stages of
P. falciparum according to Giemsa staining resulting (
Fig. 3A). Infected erythrocytes were fixed on glass slides, and 2 candidate antibodies were applied separately. The results showed that there was no fluorescence visible with the 2CF5 mAb (
Fig. 3B), implying that it could discriminate between
Plasmodium species. In contrast, positive fluorescence was captured from the 1G10 mAb and detected well in trophozoites and schizonts with a higher resolving power (
Fig. 3B, bottom panel).
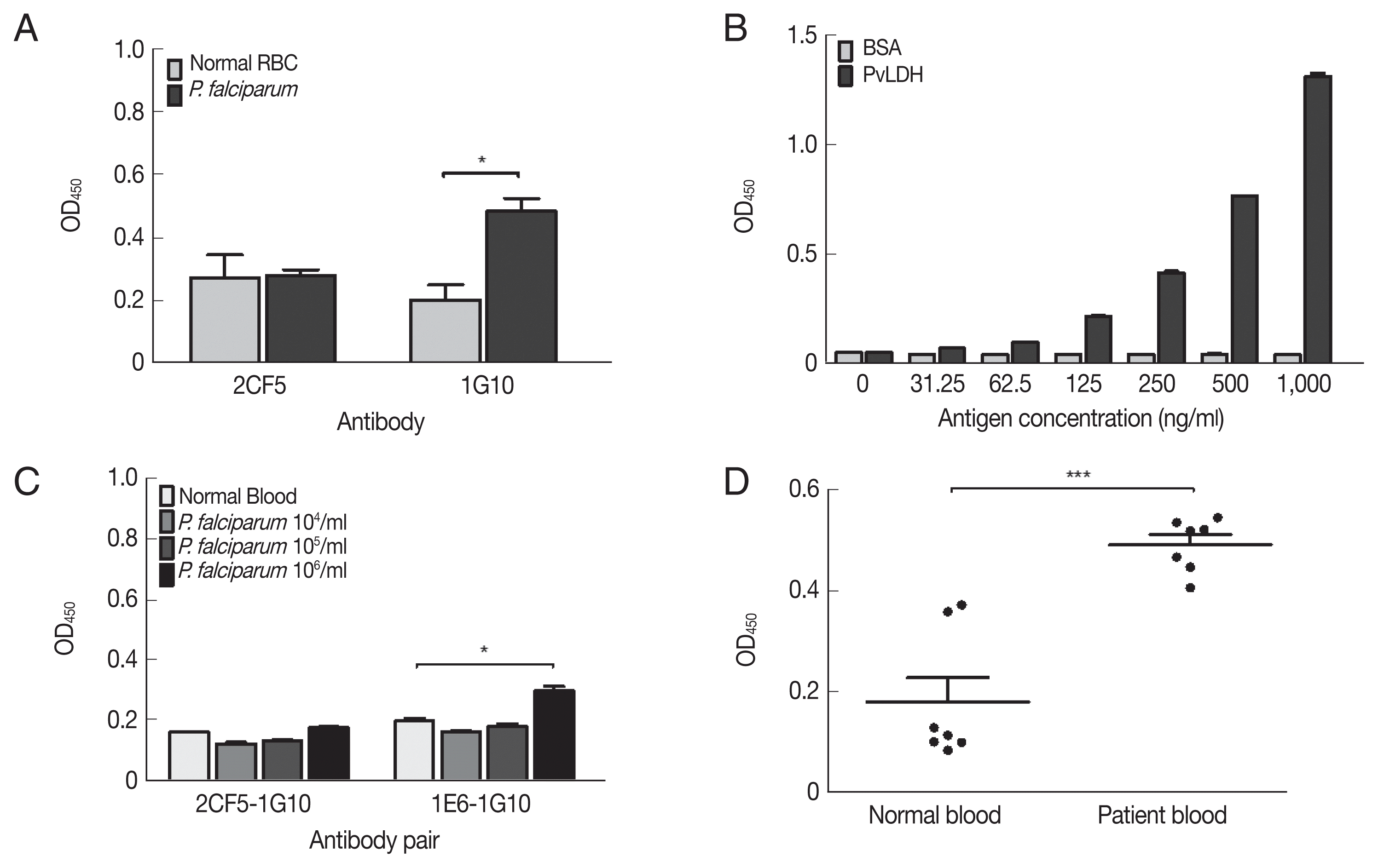
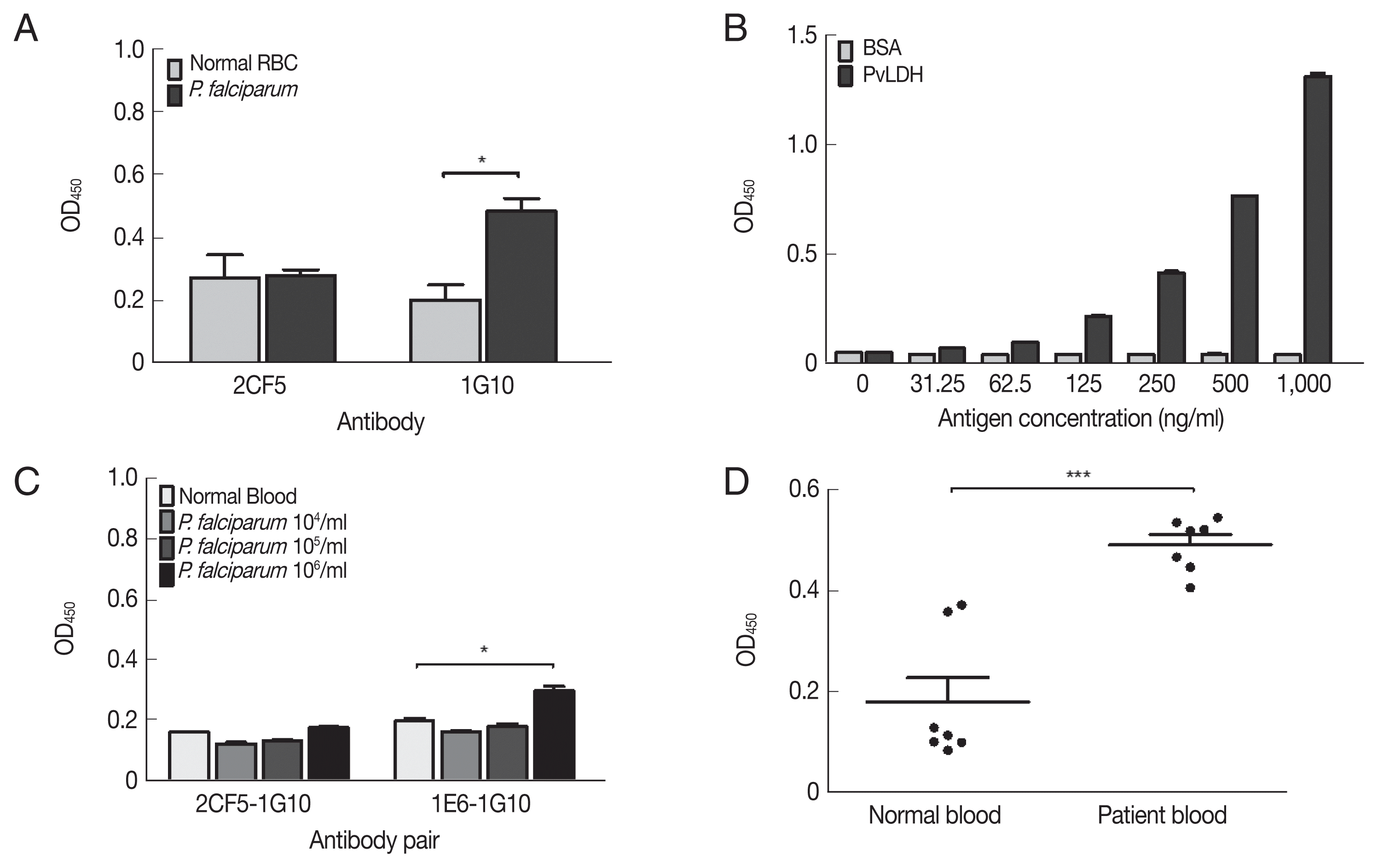
The non-reactivity of 2CF5 mAb to
P. falciparum was confirmed by indirect ELISA. The 1G10 mAb showed a positive reaction at 10
6 parasites/ml, but 2CF5 did not detect
P. falciparum (
Fig. 4A). Therefore, in the sandwich ELISA, the 1G10 mAb was used as the detection antibody, and the 2CF5 Pv-LDH mAb was used as the capturing antibody. 1E6 and 1G10 were used as a pair of positive control antibodies to detect
P. falciparum. Both normal blood and infected blood showed similar OD values for the 2CF5-1G10 pair (0.161±0.001 and 0.177±0.002, respectively). In contrast, the 1E6-1G10 antibody pair showed a positive value of 10
5 parasites (0.298±0.015) in comparison to the normal blood sample (0.198±0.01) (
Fig. 4A).
The limit of blank (LoB) and limit of detection (LoD) of the 2CF5-1G10 antibody pair was determined in a sandwich ELISA with serial dilution of PvLDH. The LoB and LoD was defined based on a previous study [
11]. The OD 450 nm illustrated the limited of blank (LoB) was 0.055, and the LoD was determined as 0.059. According to OD value of LoD 2CF5 and 1G10 antibody pair was able to detect 31.25 ng/ml of PvLDH (
Fig. 4B). The sandwich ELISA was used to determine if it could distingush
P. falciparum and
P. vivax using serial dilution of
in vitro-cultured
P. falciparum and
P. vivax-infected patient bloods. First of all, the pair of 2CF5 and 1G10 antibody was not able to detect
P. falciparum in the range of 10
6 parasites/ml which was detected positively by a pair of positive control mAbs (1E6-1G10) for
P. falciparum (
Fig. 4C).
A sandwich ELISA was performed for detection in patient blood infected with
P. vivax. The 2CF5-1G10 antibody pair was determined as a positive antibody pair for
P. vivax because OD values of all patients (n=7) were higher than those of negative bloods (n=7) (
Fig. 4D). Therefore, the pair of those antibodies could discriminate
P. falciparum and
P. vivax.
DISCUSSION
Among 5 human-infecting
Plasmodium species,
P. vivax is known as the most widespread parasite, infecting 80 million people every year and contributing to the highest number of malaria cases outside Africa [
12].
P. vivax tends to invade younger red blood cells (RBCs) and reticulocytes rather than mature RBCs and therefore circulate at low-levels in the blood with around 1–2% RBCs infected. It is therefore difficult to detect
P. vivax. Even using microscopy or PCR, RDT challenges still remain for each diagnostic method [
13]. RDT kits provide a quick and simple detection method and are easily applied in some countries with poor technology and small budgets. However, most RDT kits currently only diagnose
P. vivax indirectly as they can distinguish between
P. falciparum and non-
falciparum rather than detecting
P. vivax directly [
14,
15].
It is well known that PfHRP2 and aldolase are common target candidates for the development of malaria diagnostic tests. PfHRP2 is the most common and sensitive protein for diagnosis, and both PfHRP2 and pLDH-based tests are more sensitive than aldolase alone [
16]. However, PfHRP2-based tests are less specific than pLDH-based tests [
17] and can only determine
P. falciparum infection.
Plasmodium LDH is a soluble glycolytic enzyme produced in live parasites at the asexual and sexual stages and released from parasite-infected erythrocytes. It has been found in all 4 human
Plasmodium species. pLDH has been used as a target for a large number of immunocaptures, RDT, and dipstick assays [
18,
19]. Previously, specific polypeptides that encode Pv-LDH were used to generate monoclonal antibodies against Pv-LDH [
20]. The resulting mAbs had a LoD of 78–156 ng/ml in sandwich ELISA. In this study, we cloned and expressed a recombinant pLDH antigen in bacteria, and subsequently produced mAbs. In our sandwich ELISA, LoD was determined as 31.3 ng/ml following previously described methods [
11], indicating that an
E. coli-expressed antigen would be more efficient than a polypeptide-based antigen for antibody generation.
According to plasmoDB, LDH protein is expressed abundantly in the trophozoite stage of malaria and decreases at the schizont stage. In our IFA study, both trophozoite and schizont stages showed strong reactivity between pLDH and our novel antibody. In conclusion, the 2CF5 mAb had potential specificity for P. vivax detection and the 2CF5-1G10 antibody pair was useful as a component of the P. vivax-specific immune assay. We believe that these mAbs could facilitate the development of a P. vivax-specific rapid diagnostic system in future work.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was supported by Priority Research Centers Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Korea (NRF-2015R1A6A1A03032236).
Fig. 1Homology of P. vivax LDH to other species and generation of recombinant protein. (A) The percentage identity between P. vivax LDH and other species. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of recombinant LDH protein expression and purification. Lane 1, protein marker; lane 2, PvLDH before IPTG induction in E. coli; lanes 3–4, PvLDH after IPTG induction, pellet and lysate, respectively; lane 5, E. coli PfLDH before IPTG induction; lanes 6–7, E. coli PfLDH after IPTG induction, pellet and lysate, respectively; lanes 8–9, purified PvLDH and PfLDH, respectively. (C) Western blot of purified protein with 6×His tag antibody. Lane 1, protein marker; lane 2, BSA; lane 3, PfLDH; lane 4, Pv-LDH.

Fig. 2Development of monoclonal antibody (mAb). (A) Antibody formation in 75T culture flask after final limiting dilution was confirmed by ELISA. Eight monoclones for PvLDH (left) and 7 monoclones for PfLDH (right) were selected. (B) Two mAbs were purified from ascites fluid and confirmed by SDS-PAGE. 2CF5 stands for 2CF1-BF5. (C) Left panel shows the Coomassie blue staining for the presence of antigen. Western blot analysis for mAbs confirmed the antigen and mAb. Lane 1, protein marker; lane; 2, BSA; lane 3, purified PfLDH; lane 4, purified PvLDH. (D) The relative affinity of both antibodies against pLDH antigens were confirmed by direct ELISA). **P<0.01; ***P<0.001.
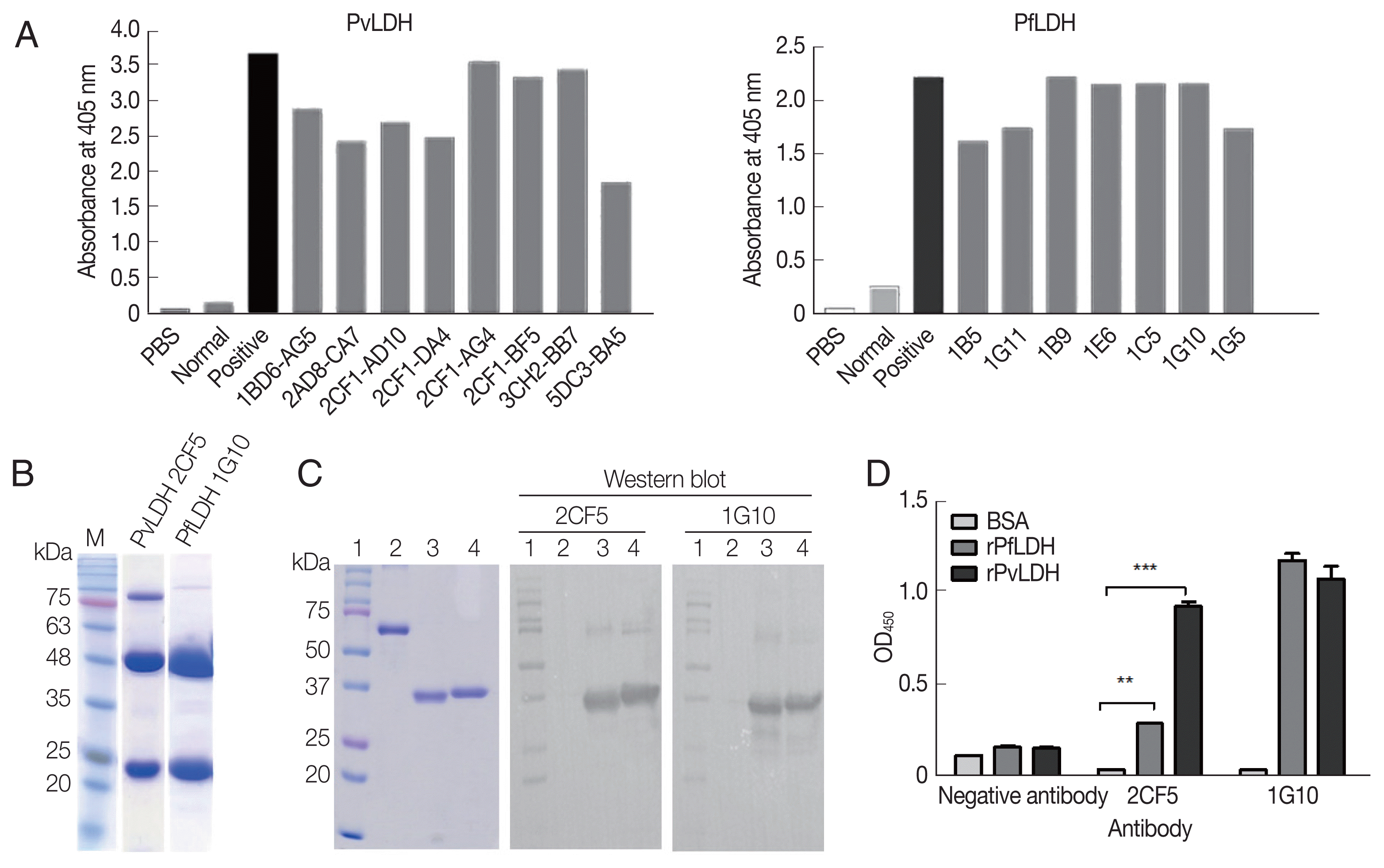
Fig. 3Immunofluorescence of selected mAbs for P. falciparum. (A) P. falciparum-infected RBCs were stained with Giemsa to confirm the blood stage. (B) IFA image was obtained by under a 100× oil immersion objective lens for 2CF5 (upper panel) and 1G10 (middle panel) for those infected RBC. The IFA result of 1G10 was also taken by 200× oil immersion objective lens (bottom panel).
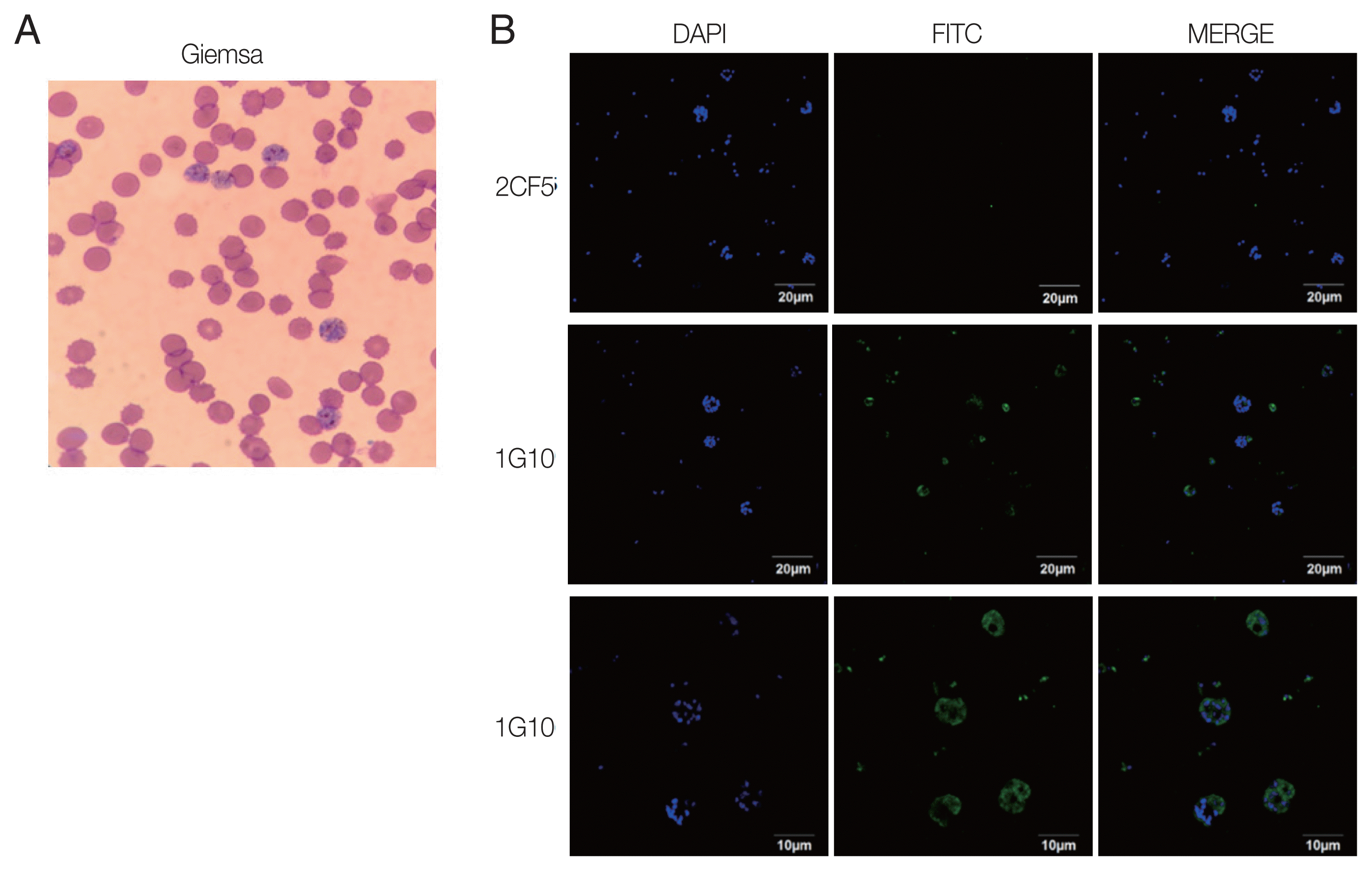
Fig. 4Evaluation of diagnostic performance of mAbs-linked ELISA. (A) Indirect ELISA of selected mAbs for P. falciparum (106 parasites/mL). (B) Sandwich ELISA of selected antibodies with serial dilution of PvLDH antigen. (C) Sandwich ELISA of selected antibodies with P. falciparum parasitemia from 104–106 parasites/ml. (D) Sandwich ELISA of selected antibodies with P. vivax-infected patient’s bloods (n=7) and negative bloods (n=7). *P<0.05; ***P<0.001.
References
- 1. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Malaria [Internet]; 2017. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/malaria/
- 2. Bartoloni A, Zammarchi L. Clinical aspects of uncomplicated and severe malaria. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis 2012;4:e2012026.
- 3. Baird JK, Valecha N, Duparc S, White NJ, Price RN. Diagnosis and treatment of Plasmodium vivax malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2016;95:35-51.
- 4. Verma P, Biswas S, Mohan T, Ali S, Rao DN. Detection of histidine rich protein and lactate dehydrogenase of Plasmodium falciparum in malaria patients by sandwich ELISA using in-house reagents. Indian J Med Res 2013;138:977-987.
- 5. Dzakah EE, Kang K, Ni C, Wang H, Wu P, Tang S, Wang J, Wang J, Wang X.
Plasmodium vivax aldolase-specific monoclonal antibodies and its application in clinical diagnosis of malaria infections in China. Malar J 2013;12:199.
- 6. Meier B, Dobeli H, Certa U. Stage-specific expression of aldolase isoenzymes in the rodent malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei
. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1992;52:15-27.
- 7. Harani MS, Beg MA, Khaleeq L, Adil SN, Kakepoto GN, Khurshid M. Role of ICT malaria immunochromatographic test for rapid diagnosis of malaria. J Pak Med Assoc 2006;56:167-171.
- 8. Dzakah EE, Kang K, Ni C, Tang S, Wang J, Wang J. Comparative performance of aldolase and lactate dehydrogenase rapid diagnostic tests in Plasmodium vivax detection. Malar J 2014;13:272.
- 9. Köhler G, Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 1975;256:495-497.
- 10. Galfrè G, Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol 1981;73:3-46.
- 11. Armbruster DA, Pry T. Limit of blank, limit of detection and limit of quantitation. Clin Biochem Rev 2008;29( suppl):49-52.
- 12. Mendis K, Sina BJ, Marchesini P, Carter R. The neglected burden of Plasmodium vivax malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2001;64:97-106.
- 13. Beeson JG, Chu CS, Richards JS, Nosten F, Fowkes FJ.
Plasmodium vivax malaria: challenges in diagnosis, treatment and elimination. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2015;34:529-531.
- 14. Moody A. Rapid diagnostic tests for malaria parasites. Clin Microbiol Rev 2002;15:66-78.
- 15. Heutmekers M, Gillet P, Maltha J, Scheirlinck A, Cnops L, Bottieau E, Van Esbroeck M, Jacobs J. Evaluation of the rapid diagnostic test CareStart pLDH Malaria (Pf-pLDH/pan-pLDH) for the diagnosis of malaria in a reference setting. Malar J 2012;11:204.
- 16. World Health Organization. Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Test Performance: result of WHO product testing of malaria RDTs Round 3 (2010–2011). [Internet]; 2011. Available from: http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/atoz/9789241502566/en/
- 17. Abba K, Deeks JJ, Olliaro P, Naing CM, Jackson SM, Takwoingi Y, Donegan S, Garner P. Rapid diagnostic tests for diagnosing uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria in endemic countries. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2011;CD008122.
- 18. Ouattara A, Doumbo S, Saye R, Beavogui AH, Traoré B, Djimdé A, Niangaly A, Kayentao K, Diallo M, Doumbo OK, Thera MA. Use of a pLDH-based dipstick in the diagnostic and therapeutic follow-up of malaria patients in Mali. Malar J 2011;10:345.
- 19. Bashir IM, Otsyula N, Awinda G, Spring M, Schneider P, Waitumbi JN. Comparison of PfHRP-2/pLDH ELISA, qPCR and microscopy for the detection of Plasmodium events and prediction of sick visits during a malaria vaccine study. PLoS One 2013;8:e56828.
- 20. Kim JH, Lee J, Sohn HJ, Song HO, Kim JY, Lee WJ, Park H, Shin HJ. Production of monoclonal antibodies for Plasmodium vivax lactate dehydrogenase and patient sera screening using sandwich ELISA. Parasitol Res 2012;111:1645-1650.