Abstract
In Brazil, visceral leishmaniasis (VL) is expanding and becoming urbanized, especially in non-endemic areas such as the State of Rio Grande do Sul. Considering that infected dogs are the main reservoir for zoonotic VL, this study evaluated the prevalence of canine visceral leishmaniasis (CVL) in the metropolitan area of Porto Alegre, a new area of expansion of VL in Brazil. Serum and plasma from 405 asymptomatic dogs from the municipalities of Canoas (n=107), São Leopoldo (n=216), and Novo Hamburgo (n=82) were tested for CVL using immunochromatographic (DPP®) and ELISA EIE® assays (2 assays officially adopted by the Brazilian government for the diagnosis of CVL) and real-time PCR to confirm the results. There was no agreement among serological and real-time PCR results, indicating that the Leishmania infection in asymptomatic animals with low parasite load, confirmed by negative parasitological tests (smears and parasite culture), need to be evaluated by molecular methods. The prevalence of LVC in the metropolitan region of Porto Alegre, confirmed by real-time PCR was 4% (5.6% in Canoas and 4.6% in São Leopoldo). The use of molecular method is essential for accurate diagnosis of CVL, especially in asymptomatic dogs in non-endemic areas.
-
Key words: Leishmania sp., dog, prevalence, immunoassay, real-time PCR
INTRODUCTION
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) in the New World, primarily in Brazil, is caused by
Leishmania (
Leishmania)
infantum, and it is widespread in Latin America, with 90% of the cases occurring in Brazil [
1]. Actually, VL is suffering an epidemiological transition, with urbanization and geographic expansion to non-endemic areas, including cities in the South of the country [
2–
4]. Until 2008, the south region of Brazil was not considered an endemic area for VL, with few imported human cases reported [
5]. However, in the year of 2008, an outbreak of canine visceral leishmaniasis (CVL) occurred in the municipality of São Borja, State of Rio Grande do Sul [
6]. Moreover, between 2009 and 2014, a total of 2,251 cases of CVL were diagnosed in dogs from cities of Itaqui (n=518), Porto Alegre (46), Santa Cruz do Sul (52), São Borja (681), Uruguaiana (951), and Viamão (3) [
7]. In addition, the presence of the vector
Lutzomya longipalpis was confirmed in several municipalities of Rio Grande do Sul [
5]. Concerning to human infections, between 2008 and 2017, 23 autochthonous cases of VL occurred in the State of Rio Grande do Sul with 5 deaths [
8].
In endemic areas of VL, infected dogs are the primary reservoir for zoonotic disease and play a central role to the human transmission [
9]. According to the World Health Organization, CVL is widespread, with up to 20% of dogs infected in the endemic localities [
10]. The correlation between canine and human infection is well establishment. Hence, the surveillance based on diagnosis and control of CVL is fundamental to the control of human infections [
11]. Regarding the CVL diagnosis, the Brazilian Ministry of Health recommends the use of immunochromatographic assay as a screening test and ELISA to confirm the cases [
12]. However, the moderate sensitivity and specificity of these serological tests are limited by cross-reactivity with other parasitic infections. The high sensitivity and specificity of PCR assay associated with the possibility of confirming infections using different biological matrices can contribute to a more accurate diagnosis. Thus, considering the current lack of epidemiologic data about the CVL in the Metropolitan Area of Porto Alegre (MAPA), this study evaluated the prevalence of CVL using immunochromatographic and ELISA assays followed by real-time PCR.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Studied area and animals
A cross-sectional study was conducted in kennels located in the municipalities of Canoas (latitude 29°55′8″ and longitude 51°10′41″), São Leopoldo (latitude 29°45′39″ and longitude 51°9′8″), and Novo Hamburgo (latitude 29°41′5″ and longitude 51°8′31″), which integrate the Metropolitan region of the state’s Capital City, Porto Alegre. Canoas and Novo Hamburgo kennel is located in urban areas, while São Leopoldo kennel is located in an area that contains both urban and rural residences, with lush vegetation, which characterizes a transition area. The sample size was calculated based on previous data reporting the prevalence of CVL in Porto Alegre (4.1%) [
12], setting a total of 378 dogs. The present study evaluated 405 mongrel dogs characterized according to sex, race, coat type, and reproductive capabilities and underwent a careful clinical evaluation by veterinarians. The exclusion criteria covered puppies (<1 year of age), aggressive dogs, and those immunized against CVL. This study was approved by the Animals Ethics Committee of the University (UFCSPA), under reference no. 118/13 and followed the STROBE guidelines.
From January to July 2014, blood samples from 405 dogs from the municipalities of Canoas (n=107), São Leopoldo (n=216), and Novo Hamburgo (n=82) were collected using jugular or cephalic venipuncture. Portions of each blood sample were transferred to tubes with and without EDTA, centrifuged at 2,000 rpm for 10 min, and plasma and serum aliquots were kept at −80°C until serological analysis.
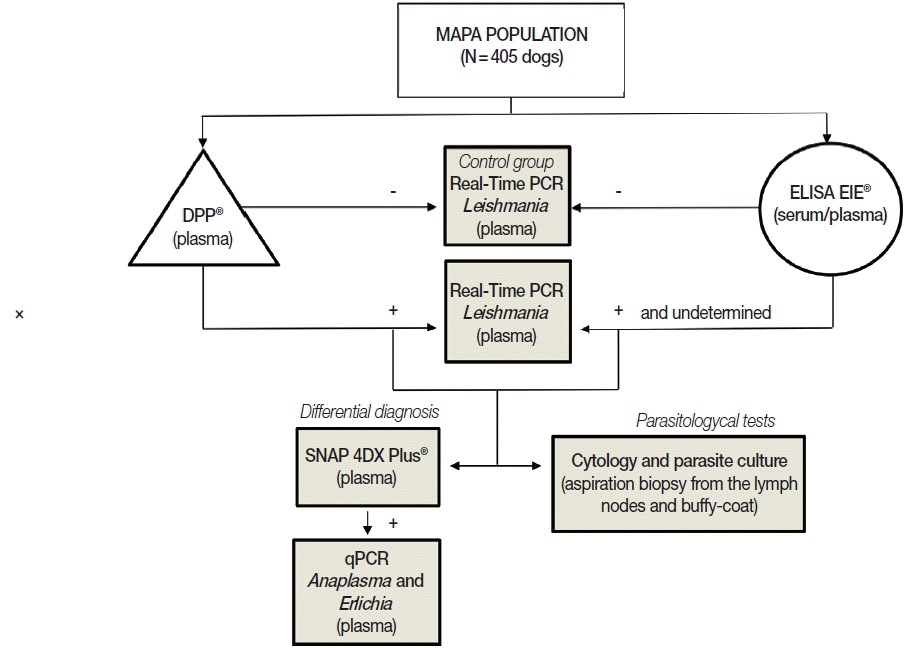
All 405 dogs were analyzed using immunochromatographic and ELISA assays. To obtain specimens for parasitological tests (smears and parasite culture), aspiration biopsy from the lymph nodes and peripheral blood samples were obtained from animals with positive or undetermined results in serological tests. An equal number of the dogs (matched for age and sex) with negative test (in both serological methods) were used as negative control. To evaluate possible cross-reactivity with other parasitic diseases in serological methods (false-positives) or co-infections, a SNAP 4DX Plus (IDEXX Laboratories, Westbrook, Maine, USA) was conducted with samples that were either positive or with a suspicion of CVL in sorology. In order to confirm
Leishmania infection, all samples that had a positive or undetermined result in one or both serological tests were evaluated by real-time PCR. In addition, samples positive to
Anaplasma in the SNAP 4DX Plus (IDEXX Laboratories) were tested by quantitative real-time PCR to confirm or rule out the presence of
Anaplasma or
Ehrlichia. The experimental protocol is represented in
Fig. 1.
Dual Path Platform (DPP®) (Bio-Manguinhos, Fiocruz, Brazil) is a rapid test based on recombinant chimeric protein (rk28) obtained from fusion of L. infantum genes that has been adopted by the Brazilian Ministry of Health for CVL diagnosis as screening test. Plasma from a symptomatic dog previously identified as positive for Leishmania infection using DPP, ELISA, and parasitological tests was used as positive control.
ELISA for canine visceral leishmaniasis
The ELISA EIE® assay (Bio-Manguinhos) has been used since 2012 in Brazil as a means to confirm DPP results. This assay was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Serum samples from all dogs (n=405) were tested, and samples classified as positive or undetermined in ELISA and/or in DPP were retested by ELISA using both serum and plasma matrices. Plasma from a symptomatic dog with positive serological (DPP and ELISA) and parasitological tests was used as positive control.
Real-time PCR for leishmaniasis
The DNA was isolated from 200 μl of plasma using the commercial Nucleic Acid and Protein Purification kit (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA was resuspended in 30 μl of the kit elution buffer and was stored in −20°C until use. The primers 13A (5′-GTG GGG GAG GGG CGT TCT-3′) and 13B (5′-ATT TTA CAC CAA CCC CCA GTT-3′), as described by Rodgers et al. [
13] were used to amplify the DNA. The amplification targeted 120 base pair regions of the kinetoplast DNA (kDNA) minicircles of the genus
Leishmania, which are present in multiple copies in a conserved region of the kDNA. The real-time PCR amplification was conducted in a StepOne
TM real-time PCR System (Applied Byosystems, Foster City, California, USA) and the amplified products were detected using a SYBR® Green system (Applied Biosystems). The reaction was standardized in a final volume of 20 μl containing 15 μl of the Fast SYBR® Green mastermix, 10 pmol of each primer and 5 μl of the extracted DNA. The amplification conditions were activation of the enzyme at 95°C for 20 sec, and 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 1 sec, and annealing/ extension at 61°C for 20 sec. The amplification and dissociation curves were analyzed in the StepOne
TM equipment software (
Fig. 2). The sample was defined as positive when it had a detectable cycle threshold (Ct) and the melting temperature (Tm) was the same as for positive control. To access for the presence of inhibitors, all samples that tested negative in PCR were spiked with human DNA and amplified with the β-globin primers PCO3 (5′ACACAACTGTGTTCACTAGC3′) and PCO4 (5′CAACTTCATCCACGTTCACC3′) [
14]. A negative reaction control (PCR mixture containing ultrapure water) was used for each amplification run, with a positive control that consisted of purified
L. (
L).
amazonensis DNA (MHOM/BR/73/M2269 strain). All plasma samples and controls were run in duplicate.
In order to perform cytological examinations, samples from either mandibular, cervical, or popliteal lymph node were obtained by aspiration. A tissue smear of the lymph node cells was stained with fast panoptic (Laborclin, Pinhais, Paraná, Brazil) and direct amastigote presence was investigated at 100× magnification (Olympus CX 22LED, Tokyo, Japan).
Lymph node and white blood cells (buffy-coat) samples were inoculated in M199 or Schneider’s medium supplemented with 20% fetal bovine serum, 2% human urine, 10 U/ml penicillin and 10 mg/ml streptomycin. Cultures were incubated at 26°C in a BOD incubator for allow
Leishmania growth [
15] and
Leishmania cultures were inspected for the presence of promastigotes weekly under an inverted microscope for up to 4 weeks.
Twenty-one plasma samples that were considered Leishmania-positive or undetermined in DPP, ELISA, or both methods were tested on the SNAP 4DX Plus (Idexx Laboratories) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. SNAP 4DX Plus detects Dirofilaria immitis antigens and antibodies against Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Anaplasma platys, Borrelia burgdorferi, and Erlichia canis in serum, plasma or whole blood canine samples.
Quantitative PCR high-resolution melting (qPCR-HRM) for Anaplasma and Erlichia
The qPCR-HRM was performed to confirm or rule out the possible infection by
Anaplasma or
Erlichia in SNAP 4DX Plus reactive samples. The genomic DNA was used as the templates to amplify 16S rRNA gene segment by using
Ehrlichia/
Anaplasma common forward primer (5′CTCAGAACGAACGCTGG 3′) and a modified
Ehrlichia/Anaplasma common reverse primer (5′ ACCATTTCTARTGCTATYCCRTACTA 3′) described by Sirigireddy and Ganta [
16]. The PCRs were performed with 200 ng of genomic DNA using the Melt Doctor mix (Applied Biosystems) and 300 nM of each primer. The thermal cycles performed in 7500 real-time PCR systems (Applied Biosystems) included the initial denaturation for 10 min at 95°C, 50 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec and 60°C for 60 sec, followed by a HRM curve from 65 to 95°C, with an increase of 0.1°C at each step. The amplification of
Anaplasma or
Ehrlichia genera was confirmed by melting curve analysis with HRM Software 2.0.1 (Applied Biosystems).
The program SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois, USA) was used for statistical analysis, with data presented as frequency and percentage. The chi-square assay was used to evaluate the association between diagnostic assay. The agreement was found using Kappa’s coefficient [
17].
RESULTS
Based on the epidemiological inquiry, dogs from the MAPA (n=405) were characterized according to the data presented in
Table 1. Most of animals of the studied population was composed by castred dogs (78.8%) with short-length coat (82.7%). Concerning sex, the male and female populations were balanced when the whole sample was analyzed. According to the clinical evaluation, none of the dogs showed clinical signs of visceral leishmaniasis, being all considered asymptomatic for leishmaniasis (
Table 1).
Two serological tests were used to determine the frequency of CVL. Of the 405 dogs, 12 animals were considered positive for CVL in DPP, 5 of them from Canoas, 6 from São Leopoldo, and 1 from Novo Hamburgo, with a prevalence of 4.7%, 2.8%, and 1.2% for each municipality, respectively, and 3.0% for the MAPA area. Three dogs from Canoas (2.8%) and 4 dogs from São Leopoldo (1.9%) had positive ELISA. In MAPA the positivity in ELISA was 1.7% (
Table 2).
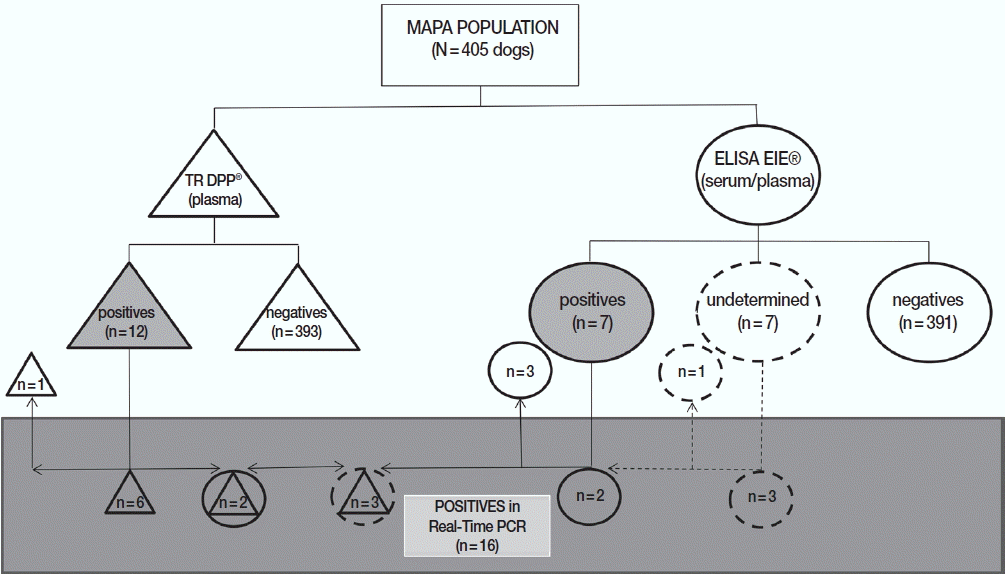
Regarding the distribution of positive (n=17) or undetermined (n=4) samples in at least 1 of 2 official serological tests adopted by Brazilian Government (n=21), 10 dogs were considered positive only in DPP (3 undetermined in ELISA), 5 only in ELISA, and 2 in both assays. In addition, 4 animals were considered negative in DPP and undetermined in ELISA regardless of the matrix used (serum or plasma). It is important to mention that
Leishmania parasites were not identified in cytology or cultures of samples from 21 dogs considered positives and/or undetermined by serological methods (
Table 3).
Concerning the results of SNAP 4DX Plus performed with samples positive and undetermined for CVL (n=21), 5 (23.8%) were positive for
Anaplasma. Moreover, among these positive samples for
Anaplasma in SNAP 4DX Plus, only 1 was confirmed by qPCR-HRM
Anaplasma spp. and
Erlichia spp. (
Table 3). Regarding MAPA (n=405), among the positive samples for CVL in DDP (n=12) and ELISA (n=7), 11 and 4 dogs had the results confirmed by real-time PCR, respectively (
Table 3;
Fig. 2). Of a total of 21 positive samples in one or both serological tests (or undetermined in ELISA), 16 (76.2%) were confirmed by real-time PCR for
Leishmania (
Table 3;
Fig. 2), 1 (4.8%) had concomitant infection with
Anaplasma and
Ehrlichia, while 2 (9.5%) presented cross-reactivity with antigens in the SNAP-4DX Plus assay (
Table 3).
Animals positive for Leishmania by real-time PCR (n=16) were characterized as being composed in majority by male (62.5%), short-length coat dogs (81.3%), castred (68.8%), and asymptomatic (93.8%). Although 1 dog from Canoas presented a limb node, this sign was not related to CVL. Comparing DDP and ELISA results using Kappa’s coefficient, no agreement was found between serological tests (kappa= −0.286; P <0.001, chi-square). Fair agreement was found between DDP and real-time PCR (kappa=0.382; P =0.055, chi-square), and no agreement was found between ELISA and real-time PCR (kappa=−0.216; P =0.147, chi-square). Finally, after confirmation by molecular method, the prevalence of CVL evaluated in 405 dogs from the metropolitan area of Porto Alegre was 4.0%.
DISCUSSION
In this study performed in non-endemic areas for leishmaniasis in the State of Rio Grande do Sul, Southern Brazil, the prevalence of CVL confirmed by real-time PCR was 4.0%. This prevalence is considered low compared with those found in endemic areas of Brazil, such as Santarém (north of Brazil, Amazon region) and Araçatuba (São Paulo State, in southeast of Brazil) with 23.3% and 29.6%, respectively [
18,
19]. It is important to highlight that the current study provides the first data for CVL prevalence in Canoas, São Leopoldo, and Novo Hamburgo municipalities.
The establishment of CVL in new geographic areas is related to the migration of dogs and humans either parasitized or susceptible [
20]. According to Costa et al. [
21], environmental changes due to intense human migration following socio-economic pressure, accompanied by growing urbanization partially explain the expansion of CVL and the appearance of new
Leishmania focus. The dogs included in this study were located in both urban or close-to-urban areas, near Porto Alegre, the capital of the state of Rio Grande do Sul, where the prevalence in 2010 was estimated at 4.1% using ELISA and indirect immunofluorescence (RIFI) [
5].
In this study, the prevalence of CVL varied according to the serological method used. The screening immunochromatographic assay showed a prevalence of 3.0%, while ELISA found 1.7% of positivity. Considering the official protocol adopted by Brazilian Government (DPP as the screening test and ELISA as the confirmatory test) only 2 (0.5%) of a total of 405 asymptomatic dogs would be considered positives. Although it is expected a higher prevalence in the screening test in relation to the confirmatory test, no association was found between them, since some positive samples in the confirmatory test were not detected in the screening test. In fact, some samples negative in DPP were positive or undetermined in ELISA, with posterior confirmation by real-time PCR. In addition, some samples considered positive only in immunochromatographic assay were also confirmed by real-time PCR. In agreement, Grimaldi et al. [
11] showed that DPP® CVL rapid test displayed high specificity (96%) but very low sensitivity (47%) in identifying parasite-positive dogs without signs of CVL. On the other hand, Laurenti et al. [
22], in a study comparing the performance of DPP® with the ELISA produced by BioManguinhos (Brazil), using serum samples from clinically symptomatic and asymptomatic infected dogs from an endemic area of CVL, found that DPP® showed a sensitivity of 90.6% and specificity of 95.1%, while ELISA showed a good sensitivity (90.6%) but low specificity (77.8%). In addition, they showed that DPP® provided highest accuracy of 92.7%. This data indicates that the DPP® performed well as serological test for CVL, and detected both asymptomatic and symptomatic dogs in equal proportions in endemic area [
22], but not in non-endemic area as indicated by our data.
It is important to highlight that the specificity of a diagnostic assay depends on the antigens used. The use of recombining proteins could provide more accurate results [
23]. Laurenti [
24] reported that
L. major antigen used by ELISA EIE® produces false-positives and false-negatives because it comes from promastigote forms. According to Laurenti [
25], the use of homologous antigens, such as
L. infantum, would improve the accuracy of the assay.
In relation to possible differential diagnoses, considering that, there was no association between ELISA and SNAP 4DX Plus, we did not discard the possibility of co-infection with
Anaplasma or false-positive results for CVL. Despite the lack of data in the literature regarding cross-reactivity or even co-infections with
Leishmania and
Anaplasma, in a study conducted by Souza et al. [
26], a dog seropositive to
L. infantum also presented positivity to
Anaplasma and
Leishmania by nested PCR. According to Otranto et al. [
27],
Anaplasma platys could harm the immune response and improve the transmission of other pathogens or increase the severity of infections caused by other parasites. A co-infection result must be interpreted according to information from its geographical region, the subject’s history of exposition to the vector and the individual’s clinical status [
28].
Couto et al. [
29], in a study using SNAP 4DX Plus and
Leishmania SNAP, found 3 positive dogs (2.3%) for both
Anaplasma and
L. infantum (co-infection). In addition, the prevalence of
Anaplasma appears to be higher in sheltered dogs, compared to those coming from private clinics. In a similar result, Miró et al. [
30], using the same diagnostic assay found a high positivity between
Anaplasma and
L. infantum in samples from dogs that lived outdoors [
30].
Concerning the cytology analyses, the low parasite load is common in asymptomatic animals, resulting in false-negatives, or even hamper morphological identification [
7], a problem enhanced by the fact that parasites are not homogenously distributed in tissues [
31]. In this study, we did not observe the presence of amastigotes in the smears of lymph nodes of animals with serological or molecular positive tests. Additionally, the failure to recuperate promastigote forms from the lymph node and blood samples of animals may be related to the low quantity of aspirated material or to the low density of parasites in samples, mainly in the peripheral blood as reported by Maia et al. [
32].
The low accuracy of the protocol demonstrated in this study can be justified by the low density of parasites evidenced. In general, the diagnostic methods for CVL should be progressively reviewed since there is still no truly accurate test for diagnosing asymptomatic dogs in non-endemic areas. The use of more accurate diagnostic tools based on molecular methods is crucial to avoid the culling of false-positive dogs, the maintenance of false-negative dogs that contributes to the parasite life cycle and the consequent increase of the human infections in non-endemic areas, such as Rio Grande do Sul State in southern Brazil.
In conclusion, the prevalence of LVC in the metropolitan area of Porto Alegre, confirmed by real-time PCR, was 4% (5.6% in Canoas and 4.6% in São Leopoldo).
Notes
-
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors would like to thank Fiocruz/Biomanguinhos for the donation of all DPP® and ELISA EIE® kits and to the staff of animal welfare from the municipalities of Canoas, São Leopoldo and Novo Hamburgo. The authors are grateful to the Brazilian agencies Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS) for financial support. PRTR and MLRR also thank CNPq for fellowships.
Fig. 1Flowchart of the experimental protocol used in this study.

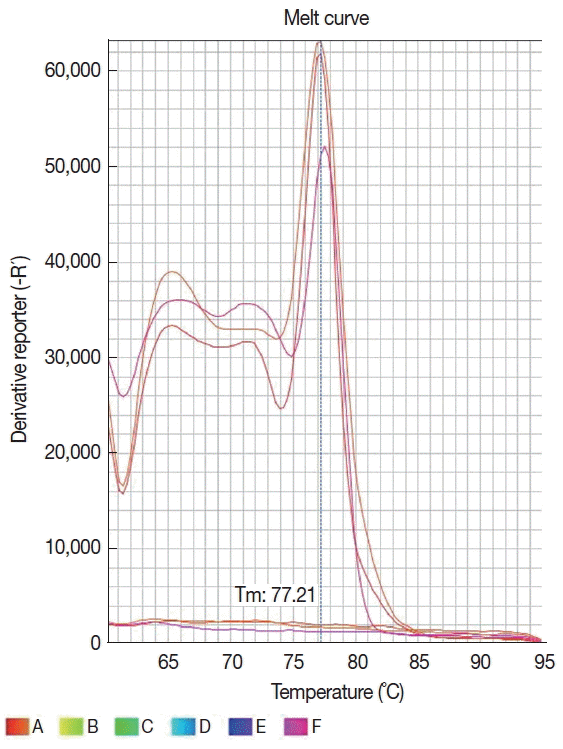
Fig. 2Dissociation curve of 6 samples showing the same melting temperature (77.2°C) for 3 Leishmania infantum positive samples and none profile for 3 negative samples.
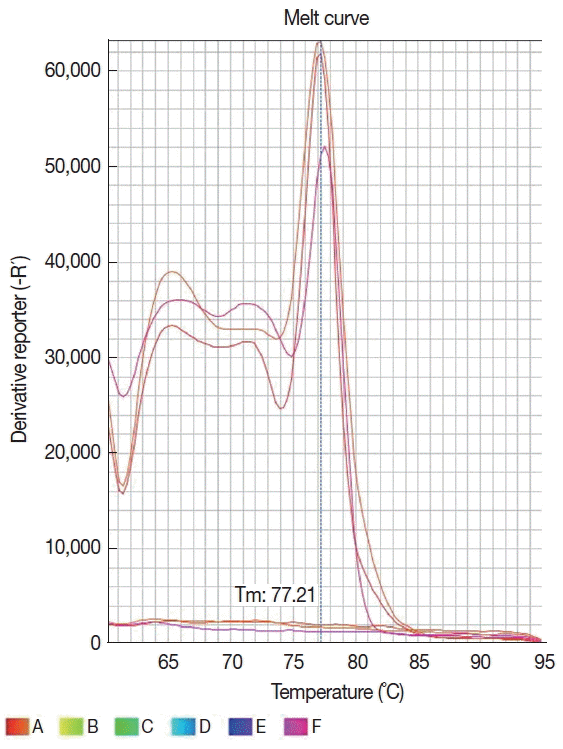
Fig. 3Distribution of results from dogs of the metropolitan area of Porto Alegre according to serological and molecular methods for canine visceral leishmaniasis. DPP® assay and their results are represented by triangles. ELISA EIE® assay and their results are represented by circles. Real-time PCR and their results are represented by a rectangle. Undetermined results in ELISA EIE® are represented by dotted circles. Positive results are represented by geometric figures filled in gray.
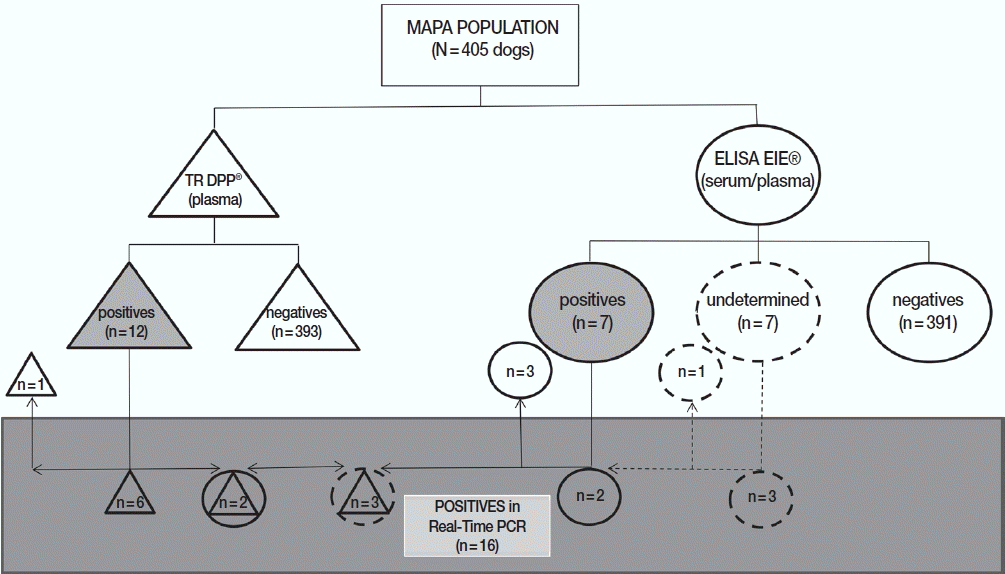
Table 1Characteristics of dogs from the metropolitan area of Porto Alegre tested for visceral leishmaniasis
Table 1
|
Characteristics |
Percentage of tested dogs (%) |
|
Canoas (n=107) |
São Leopoldo (n=216) |
Novo Hamburgo (n=82) |
MAPA (n=405) |
|
Female |
29.9 |
57.9 |
59.8 |
50.9 |
|
Male |
70.1 |
42.1 |
40.2 |
49.1 |
|
Castred |
100.0 |
64.4 |
89.0 |
78.8 |
|
Short-length coat |
84.1 |
86.6 |
70.7 |
82.7 |
|
Long coat |
15.9 |
13.4 |
29.3 |
17.3 |
|
Symptomatica
|
1.9 |
7.0 |
2.4 |
4.7 |
|
Asymptomatic |
98.1 |
93.0 |
97.6 |
95.3 |
Table 2Distribution of dogs from the metropolitan area of Porto Alegre according to serological and molecular tests for visceral leishmaniasis
Table 2
|
Locala
|
Diagnostic Tests |
|
|
|
DPP®
|
ELISA EIE®
|
Real-time PCR |
|
Analyzed samples |
MAPA |
405 |
405 |
21 |
|
Positives |
CN |
5 |
3 |
6 |
|
SL |
6 |
4 |
10 |
|
NH |
1 |
0 |
0 |
|
MAPA |
12 |
7 |
16 |
|
|
Undeterminedb
|
MAPA |
- |
7 |
- |
|
|
Negatives |
CN |
102 |
103 |
1 |
|
SL |
210 |
206 |
3 |
|
NH |
81 |
82 |
1 |
|
MAPA |
393 |
391 |
5 |
Table 3Distribution of dog samples according to serological and molecular tests for canine visceral leishmaniasis and other parasitic diseases
Table 3
|
Dog Samples |
DPP®
|
ELISA EIE®
|
Parasitological tests |
Real-time PCR |
SNAP 4DX Plus®
|
qPCR |
|
|
|
|
|
N=21 |
Leishmania spp. |
Anaplasma spp. |
Anaplasma spp. and Erlichia spp. |
|
CN004 |
P |
N |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
CN010 |
P |
N |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
CN016 |
N |
P |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
CN027 |
P |
P |
NI |
P |
P |
N |
|
|
CN059 |
P |
N |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
CN065 |
N |
P |
NI |
N |
P |
N |
|
|
CN082 |
P |
UN |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
SL016 |
N |
UN |
NI |
P |
P |
P |
|
|
SL052 |
N |
UN |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
SL059 |
N |
P |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
SL087 |
P |
UN |
NI |
P |
P |
N |
|
|
SL119 |
P |
P |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
SL146 |
P |
N |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
SL152 |
N |
P |
NI |
N |
N |
|
|
|
SL154 |
N |
P |
NI |
N |
P |
N |
|
|
SL158 |
N |
UN |
NI |
N |
N |
|
|
|
SL166 |
P |
N |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
SL172 |
P |
UN |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
SL185 |
N |
UN |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
SL210 |
P |
N |
NI |
P |
N |
|
|
|
NH072 |
P |
N |
NI |
N |
N |
|
References
- 1. Albuquerque PLMM, Junior GBS, Freire CCF, Oliveira SBC, Almeida DM, Silva HF, Cavalcante MS, Sousa AQ. Urbanization of visceral leishmaniasis (kala-zar) in Fortaleza, Ceará, Brazil. Rev Panam Salud Publica 2009;26:330-333.
- 2. Savani ES, Schimonsky Bv, Camargo MC, D’auria SR. Vigilância de leishmaniose visceral americana em cães de área não endêmica, São Paulo. Rev Saude Publica 2003;37:260-262. (in Portuguese).
- 3. Alves WA, Bevilacqua PD. Reflexões sobre a qualidade do diagnóstico da leishmaniose visceral canina em inquéritos epidemiológicos: o caso da epidemia de Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, Brasil, 1993–1997. Cad Saude Publica 2004;20:259-265.
- 4. Andrade AM, Queiroz LH, Nunes GR, Perri SHV, Nunes CM. Reposição de cães em área endêmica para leishmaniose visceral. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 2007;40:594-595. (in Portuguese).
- 5. Rio Grande do Sul, Secretaria da Saúde. Centro estadual de vigilância em Saúde. Divisão de Vigilância Epidemiológica, 2011. Boletim Epidemiológico Porto Alegre 2011;13:1-8.
- 6. Deboni SC, Barbosa M, Ramos RR. Leishmaniose visceral no Rio Grande do Sul. Bol Epidemiol 2011;13:1-3.
- 8. Rio Grande do Sul, Secretaria da Saúde. Centro Estadual de Vigilância em Saúde. Situação epidemiólogica da leishmaniose visceral no Rio Grande do Sul;
http://www.cerv.rs.gov.br/mater-ids-complementares-5a2ac937ebbab
Accessed on Dec 2017.
- 9. Monteiro EM, Silva JCF, Costa RT, Costa DC, Barata RA, Paula EV, Machado-Coelho GLL, Rocha MF, Fortes-Dias CL, Dias ES. Leishmaniose visceral: estudo de flebotomíneos e infecção canina em Montes Claros, Minas Gerais. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 2005;38:147-152.
- 10. WHO. Leishmaniasis: country profiles. [Internet]; 2010. Available from: http://www.who.int/leishmaniasis/resources/BRAZIL.pdf
- 11. Grimaldi G Jr, Teva A, Ferreira AL, Santos CB, Pinto IS, Azevedo CT, Falqueto A. Evaluation of a novel chromatographic immunoassay based on Dual-Path Platform technology (DPP® CVL rapid assay) for the serodiagnosis of canine visceral leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2012;106:54-59.
- 12. Ministério da Saúde, Secretaria de Vigilância em Saúde, Departamento de Vigilância das Doenças Transmissíveis. Nota Técnica Conjunta n∘ 1, de 2011. Esclarecimentos sobre substituição do protocolo diagnóstico da leishmaniose visceral canina (LVC). Brasília. Coordenação Geral de Doenças Transmissíveis/Coordenação Geral de Laboratórios de Saúde Pública; 2011.
- 13. Rodgers MR, Popper SJ, Wirth DF. Amplification of kinetoplast DNA as a tool in the detection and diagnosis of Leishmania
. Exp Parasitol 1990;71:267-275.
- 14. Saiki RK, Scharf S, Faloona F, Mullis KB, Horn GT, Erlich AH, Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 1985;230:1350-1354.
- 15. Dagnino AP, Barros FM, Ccana-Ccapatinta GV, Prophiro JS, Poser GL, Romão PR. Leishmanicidal activity of lipophilic extracts of some Hypericum species. Phytomedicine 2015;22:71-76.
- 16. Sirigireddy KR, Ganta RR. Multiplex detection of Ehrlichia and Anaplasma species pathogens in peripheral blood by real time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. J Mol Diagn 2005;7:308-316.
- 17. Zar JH. Biostatistical Analysis. 5th ed. New Jersey, USA. Prentice Hall; 2010, pp 466-469.
- 18. Valadas S, Minervino AH, Lima VM, Soares RM, Ortolani EL, Gennari SM. Occurrence of antibodies anti-Neospora caninum, anti-Toxoplasma gondii, and anti-Leishmania chagasi in serum of dogs from Pará State, Amazon, Brazil. Parasitol Res 2010;107:453-457.
- 19. Viol MA, Lima VM, Aquino MC, Gallo G, Alves IP, Generoso D, Perri SH, Lucheis SB, Langoni H, Nunes CM, Bresciani KD. Detection of cross infections by Leishmania spp. and Trypanosoma spp. in dogs using indirect immunoenzyme assay, indirect fluorescent antibody test and polymerase chain reaction. Parasitol Res 2012;111:1607-1613.
- 20. Dantas-Torres F, Sollano-Gallego L, Baneth G, Ribeiro VM, de Paiva-Cavalcanti M, Otranto D. Canine leishmaniasis in the Old and New Worlds: unveiled similarities and differences. Trends Parasitol 2012;28:531-538.
- 21. Costa CHN, Tapety CMM, Werneck GL. Controle da leishmaniose visceral em meio urbano: estudo de intervenção randomizado fatorial. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 2007;40:415-419.
- 22. Laurenti MD, de Santana Leandro MV Jr, Tomokane TY, De Lucca HR, Aschar M, Souza CS, Silva RM, Marcondes M, Matta VL. Comparative evaluation of the DPP® CVL rapid assay for canine serodiagnosis in area of visceral leishmaniasis. Vet Parasitol 2014;205:444-450.
- 23. Badaró R1, Benson D, Eulálio MC, Freire M, Cunha S, Netto EM, Pedral-Sampaio D, Madureira C, Burns JM, Houghton RL, David JR, Reed SG. rK39: a cloned antigen of Leishmania chagasi that predicts active visceral leishmaniasis. J Infect Dis 1996;173:758-761.
- 24. Laurenti MD. Patologia e patogenia das leishmanioses [dissertation]. São Paulo (SP): Universidade de São Paulo; 2010. 84 (in Portuguese).
- 25. Laurenti MD. Correlação entre o diagnóstico parasitológico e sorológico na leishmaniose visceral americana canina. Bol Epidemiol Paul 2009;6:13-23. (in Portuguese).
- 26. de Sousa KC, André MR, Herrera HM, de Andrade GB, Jusi MM, dos Santos LL, Barreto WT, Machado RZ, de Oliveira GP. Molecular and serological detection of tick-borne pathogens in dogs from na area endemic for Leishmania infantum in Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 2013;22:525-531.
- 27. Otranto D, Testini G, Dantas-Torres F, Latrofa MS, Diniz PP, de Caprariis D, Lia RP, Mencke N, Stanneck D, Capelli G, Breitschwerdt EB. Diagnosis of canine vector-borne diseases in young dogs: a longitudinal study. J Clin Microbiol 2010;48:3316-3324.
- 28. Cardoso L, Mendão C, Carvalho LM. Prevalence of Dirofilaria immitis, Erlichia canis, Borrelia burgdorferi, Anaplasma spp. and Leishmania infantum in apparently healthy and CVBD-suspect dogs in Portugal–a national serological study. Parasit Vectors 2012;62:1-9.
- 29. Couto CG, Lorentzen L, Beall MJ, Shields J, Bertolone N, Couto JI, Couto KM, Nash S, Slack J, Kvitko H, Westendorf N, Marin L, Iazbik MC, Vicario FC, Sanz P, Ruano R. Serological study of selected vector-borne diseases in shelter dogs in central Spain using point-of-care assay. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2010;10:885-888.
- 30. Miró G, Montoya A, Roura X, Gálvex R, Sainz A. Seropositivity rates for agents for canine vector-borne diseases in Spain: a multicentre study. Parasit Vectors 2013;117:1-9.
- 31. Mykolanis ME, Papaioannou N, Saridomichelakis MN, Koutinas AF, Billinis C, Kontos VI. Cytologic patterns of lymphadenopathy in dogs afected with Leishmania infantum
. Vet Clin Pathol 2005;34:243-247.
- 32. Maia CS, Monteiro MC, Gavioli EC, Oliveira FR, Oliveira GB, Romão PR. Neurological disease in human and canine leishmaniasis--clinical features and immunopathogenesis. Parasite Immunol 2015;37:385-393.