Abstract
This study was done to characterize distribution of Rickettsia spp. in ticks in the northwestern and southwestern provinces in the Republic of Korea. A total of 2,814 ticks were collected between May and September 2009. After pooling, 284 tick DNA samples were screened for a gene of Rickettsia-specific 17-kDa protein using nested PCR (nPCR), and produced 88 nPCR positive samples. Of these positives, 75% contained 190-kDa outer membrane protein gene (ompA), 50% 120-kDa outer membrane protein gene (ompB), and 64.7% gene D (sca4). The nPCR products of ompA, ompB, and sca4 genes revealed close relatedness to Rickettsia japonica, R. heilongjiangensis, and R. monacensis. Most Rickettsia species were detected in Haemaphysalis longicornis. This tick was found a dominant vector of rickettsiae in the study regions in the Republic of Korea.
-
Key words: Haemaphysalis longicornis, ompA, ompB, sca4, spotted fever, rickettsia
INTRODUCTION
Spotted fever group rickettsiae (SFGR) are obligatory intracellular bacteria commonly found in arthropods such as ticks. Some of the SFGR cause rickettsioses after arthropods transmit them to animals and humans. Common clinical symptoms of SFG rickettsioses are fever, headache, and rash [
1]. Currently, SFGR comprise more than 30 species classified into multiple genogroups including:
Rickettsia japonica - R. heilongjiangensis;
R. massiliae including
R. montanensis;
R. helvetica including
R. tamurae and
R. monacensis; and
R. akari [
2]. Members of the
R. japonica -
R. heilongjiangensis genogroup have been detected in Japan and the Far East [
3]. Specifically, the first clinical case of
R. japonica was known in Japan in 1984. It was reported as Japanese spotted fever [
3,
4]. Since then, it has been detected in Japan, the Philippines, the Republic of Korea, and Thailand [
5–
8].
R. heilongjiangensis was first isolated from
Dysmicoccus sylvarum ticks in Heilongjiang Province of China in 1983. It belongs to
R. japonica subgroup of SFGR [
10]. Rickettsioses caused by
R. heilongjiangensis have appeared in China, Russia, Kazakhstan, and Japan [
9–
12].
In the Republic of Korea, a variety of SFGR including
R. japonica, R. conorii, R. akari, R. australis, and
R. monacensis have been reported over 15 years ago [
13–
18].
R. japonica was first detected from
Haemaphysalis spp. ticks in 2003 and human sera in 2004 while
R. monacensis was first detected from
Haemaphysalis spp. ticks in 2009 [
13,
14,
18]. Additionally, various unidentified
Rickettsia spp. were detected in ticks from 5 provinces (including Jeolla-do) during 2011–2013 [
19].
Recently, various
Rickettsia spp. in other countries have been reported. Nine species or subspecies of tick-borne rickettsiae have been identified in China in the past 30 years [
21]. Guo et al. [
22] first reported on the existence of
R. raoultii in
H. erinacei from wild marbled polecat (
Vormela peregusna) in China in 2014. It may be assumed that there is a need to examine geographical features (i.g. China-Kazakhstan border) in the identification of various
Rickettsia species [
21]. Also, since tick-borne disease can be prevalent throughout the country due to climate change, it is important to investigate seasonal occurrence and status of ticks to predict the potential of transovarial transmission [
22]. Therefore, the objective of this study was to identify and characterize rickettsiae in ticks collected at different geographical regions in the Republic of Korea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Collecting and identifying ticks
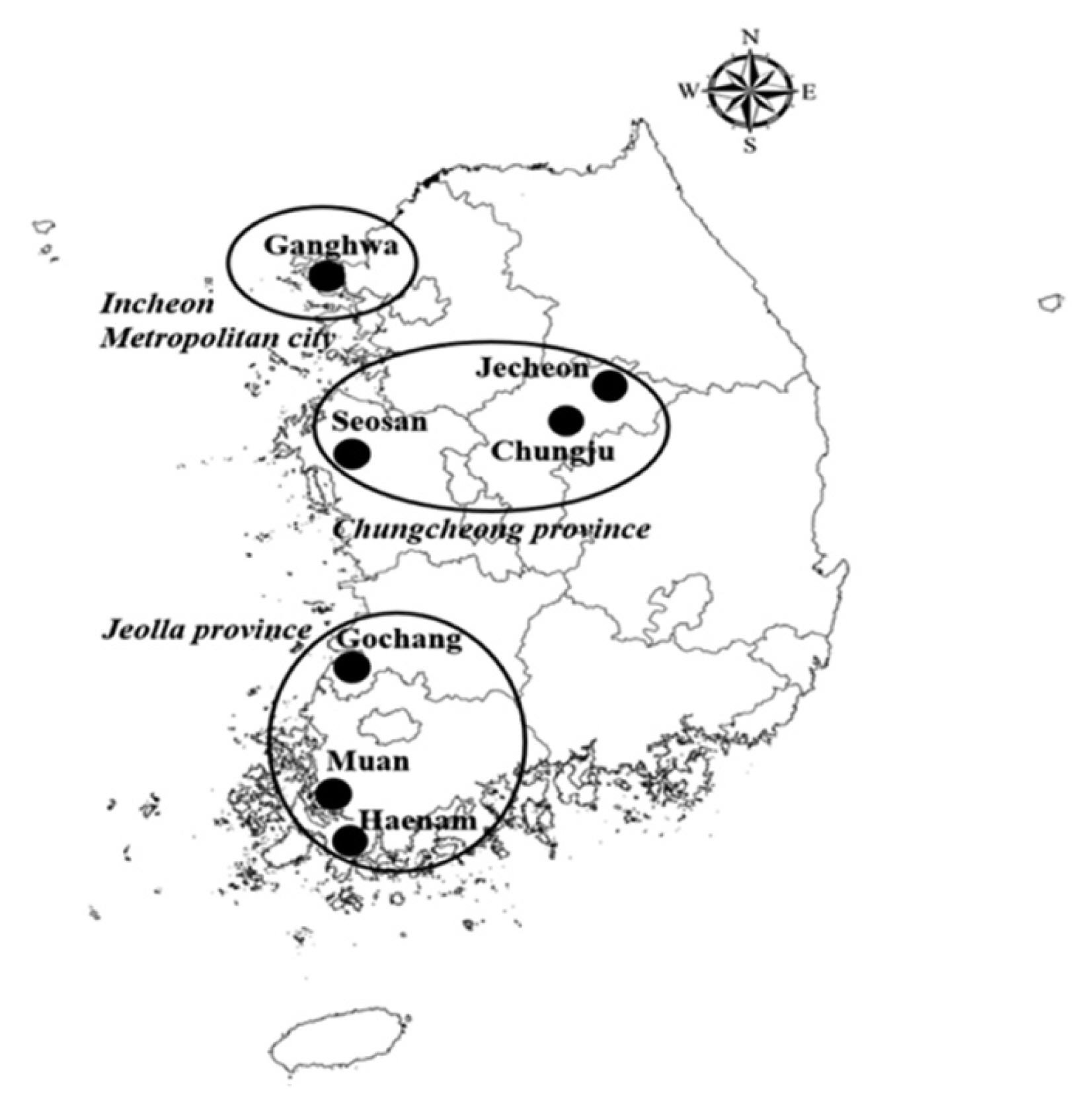
All ticks were collected using tick dragging in the northwestern province (4 regions in Incheon-si, including Gangwha-do (37°44′10.5″N/126°31′47.5″E and 37°45′02.9″N/126°25′26.9″E), Samsung-dong (37°43′47.9″N/126°29′36.6″E), Gilsang-myeon (37°37′31.1″N/126°29′34.1″E), and Bureun-myeon (37°37′04.6″N/126°28′35.3″E)) and 2 southwestern provinces (3 regions in Jeolla-do: Muan (34°51′06.9″N/126°25′03.8″E), Haenam (34°35.68.6″N/126°38.45.3″E and 34°34.01.8″N/ 126°38.16.1″E), and Gochang (36°35′67.6″N/126°33′55.7″E); and 3 regions in Chungcheong-do: Seosan (36°44′26.0″N/ 126°34′05.0″E), Chungju (37°01′43.3′ ′N/127°50′50.0″E), and Jecheon (37°13′39.5″N/128°05′11.5″E) in Republic of Korea from May to September of 2009 (
Fig. 1). Ticks were identified and their developmental stages such as larva, nymph, adult male, and adult female were determined under a stereomicroscope. Pooled tick samples were transferred to 2 ml microcentrifuge screw-cap tubes and stored at −70°C.
Pooled tick samples were washed with 70% ethanol and rinsed with distilled water. Total DNAs were extracted from these samples using G spin total DNA extraction kit (iNtRON, Gyeonggi, Korea) according to the manufacture’s introductions. DNA samples were stored at −20°C until use for DNA amplification.
nPCR to detect rickettsial agents
First, we performed nPCR screening to select positive DNA samples using specific primers for 17-kDa gene: R17K31F (GCTCTTGCAGCTTCTATGTTACA) and Rr2608R (CATTGTCCGTCAGGTTGGCG). The reaction mixture was prepared by adding 2 μl DNA extract and 8 pmole of each primer into a tube of AccuPower® PCR premix (Bioneer Corp., Daejeon, Korea) composed of 1U Taq DNA polymerase, 250 μM dNTP, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.3), 40 mM KCl, and 1.5 mM MgCl2. After adjusting the final volume to 20 μl with distilled water, and PCR reaction was performed on a VeritiTM 96-well Thermal Cycler (Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, California, USA).
Amplification of partial ompA/B and sca4
To amplify partial
ompA, ompB, and
sca4 genes from SFG
Rickettsia positive DNA samples, nPCR was performed. Primers are listed in
Table 1.
To identify
Rickettsia species by sequencing, we used
ompA primers (
Table 1). Sequencing was performed by Genotech Co. Ltd. (Daejeon, Korea). To acquire partial
ompA nucleotide sequences, all samples were sequenced in duplicates. Sequence analyses were performed with MegAlign software (DNAStar, Madison, Wisconsin, USA).
RESULTS
Tick collection
A total of 2,814 ticks were collected from 3 provinces in the Republic of Korea in May 2009, including 1,056
H. flava, 1,725
H. longicornis, 32
I. nipponensis, and one
A. testudinarium. These ticks consisted of 1,994 (70.8%) larvae, 791 (28.1%) nymphs, 16 (0.5%) adult males, and 13 (0.4%) adult females. Dominant species were
H. longicornis (61.3%) followed by
H. flava (37.5%) and
I. nipponensis (
Table 2).
nPCR screening of 284 tick pools identified 88 (30.9%) positive samples using rickettsial 17-kDa antigen gene-specific primers. These nPCR positive samples were used for nPCR amplification of
ompA, ompB, and
sca4 genes. nPCR results showed that 66 (75.0%), 44 (50.0%), and 57 (64.7%) samples were positive for
ompA, ompB, and
sca4, respectively (
Table 3).
Subsequently, we randomly selected 30 nPCR positive samples (10 from northwestern and 20 from southwestern province) for ompA gene to performed sequencing analysis.
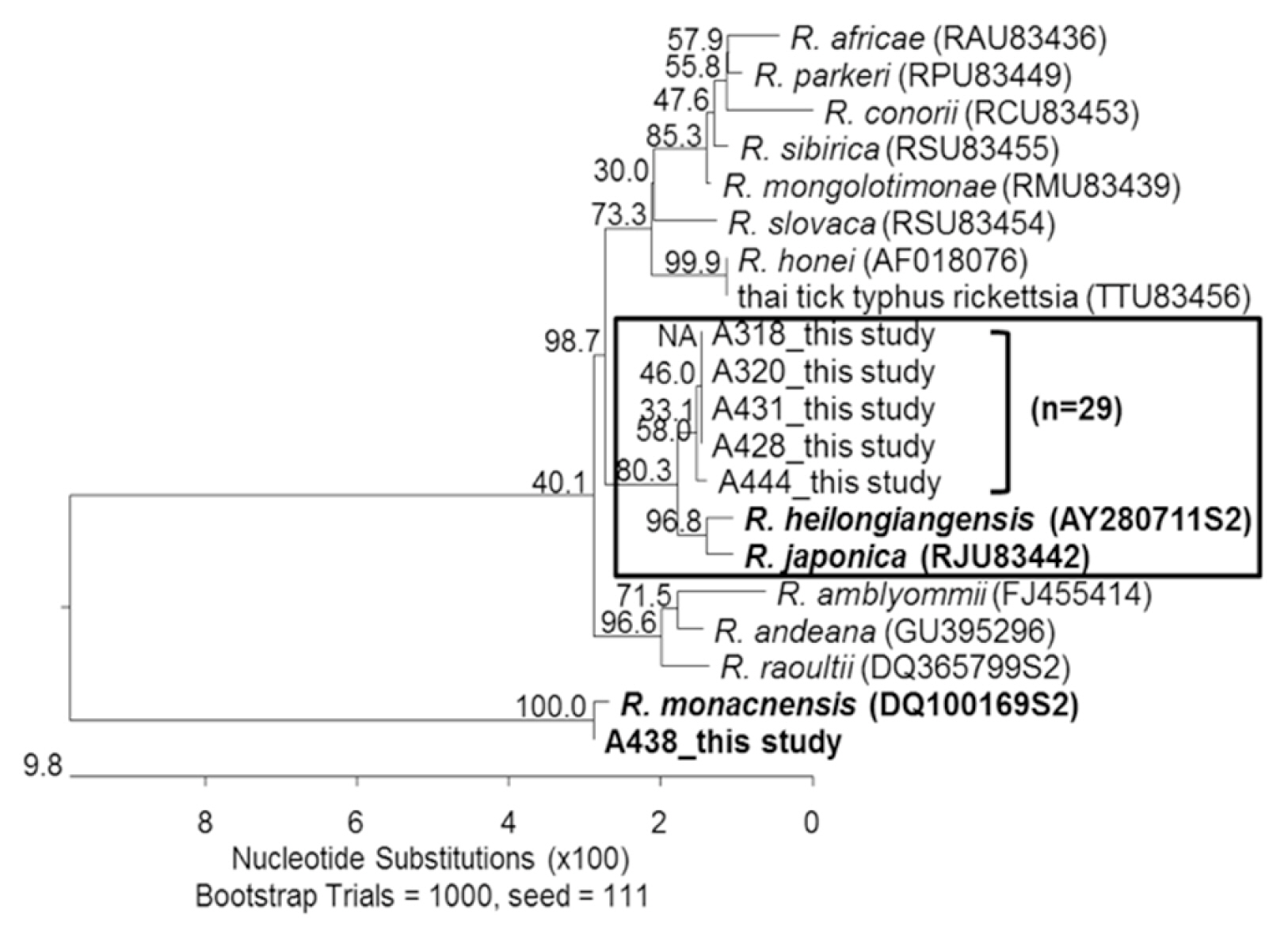
Sequences of
ompA from 2
H. flava pool samples collected from Jeolla-do shared 97.8–99.1% similarities with those of
R. heilongjiangensis. Most of 27
H. longicornis pools shared 97.8–98.8% sequence similarities with
R. heilongjiangensis while 1
H. longicornis tick pool shared 99.9% sequence similarity with
R. monacensis (
Fig. 2).
R. monacensis was first detected in
I. nipponensis collected from Jeolla-do, Gyeonggi-do, and Gangwon-do [
22,
23]. Interestingly,
R. monacensis was first detected in
H. longicornis collected from Incheon metropolitan city of a northwestern province.
DISCUSSION
First cases of Far East spotted fever (FESF) caused by
R. heilongjiangensis have been reported in Russia and China [
24]. Rickettsiae from ticks collected in Korea in 2003 [
13] showed high sequence similarities with
R. japonica YH (GenBank accession number: AP011533).
R. japonica was detected in Korean human sera in 2004 and 2005 [
14,
16].
Although this study was limited to a short period of 5 months, most tick-related pathogens such as tick-borne pathogens found in other Korean studies [
19,
26,
27] were commonly detected in Southern provinces such as Jeolla-do and Chungcheong-do that were also included in the present study.
To obtain more data on the distribution of rickettsiae, we investigated species of Rickettsia from ticks in 2 provinces of Republic of Korea. In particular, the number of ticks collected from Incheon metropolitan city was more than that collected from other regions and H. longicornis predominated. Its number collected from Incheon metropolitan city was twice of that collected from Jeolla-do and 9 times of that collected from Chungcheong-do.
Incheon metropolitan city is located in the northwestern part of Seoul. It is the third largest city after Seoul and Busan in Republic of Korea. Interestingly, the 8 areas of Incheon-si where ticks were collected were mostly flat areas not exceeding 100 m in height with a humid subtropical climate [
28,
29]. This environment is a suitable place for the survival of tick vectors and the area with low grass height may be advantageous for human and vector contact. This shows the potential that human infections can be caused by ticks in urban areas. It also reminds us that we need to continuously monitor geographical changes of vector distribution and disease incidence.
In summary, we used nucleic acids and found that rickettsial agents from Ixodid ticks collected from northwestern and southwestern provinces of the Republic of Korea were closely related to R. heilongjiangensis, R. japonica, and R. monacensis.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Yeon-Joo Choi and Ju Jiang contributed equally. Funding for portions of this work was provided by the Armed Forces Health Surveillance Branch-Global Emerging Infections Surveillance and Response System (AFHSB-GEIS), Silver Spring, Maryland, USA. The views expressed in this article are those of the authors do not reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, the Department of the Army, the Department of Defense, nor the US Government.
Fig. 1Map of the tick sampling sites. Ticks were collected in the northwestern (Incheon-si) and southwestern (Chungcheong-do, Jeolla-do) provinces of Korea.

Fig. 2Phylogenic tree representing phylogenetic relationships between partial ompA sequence of various rickettsial strains and 625 bp of ompA product amplified from 30 selected DNA samples. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using MegAlign software and Bootstrap analysis was performed with 1,000 replicates.

Table 1Oligonucleotide primers used for detection of Rickettsia ompA, ompB and sca4
Table 1
|
Target gene |
Primer |
Nucleotide sequence (5′→3 ′) |
Product size (bp) |
PCR condition (°C/sec) |
|
|
Denaturation |
Annealing |
Extension |
Cycles |
|
ompA
|
190-70Fb
|
ATGGCGAATATTTCTCCAAAA |
645 |
94 |
50 |
72 |
40 |
|
RompA642Ra,b
|
ATTACCTATTGTTCCGTTAATGGCA |
|
30 |
30 |
45 |
|
|
190-3588F |
AACAGTGAATGTAGGAGCAG |
845 |
94 |
42 |
72 |
40 |
|
RompARm4433Ra,b,c
|
GAATTTAAGGTTACTATACCTTC |
|
30 |
30 |
50 |
|
|
|
ompB
|
RompB11F |
ACCATAGTAGCMAGTTTTGCAG |
1,892 |
94 |
50 |
72 |
40 |
|
RompB1902Ra
|
CCGTCATTTCCAATAACTAACTC |
|
30 |
30 |
120 |
|
|
RompBRm11Fc
|
RCCATAGTRGCCAGTTKTGCAG |
1,846 |
94 |
50 |
72 |
40 |
|
RompBRm1902Ra,c
|
CCGTMATTTCCAATAACTAACTC |
|
30 |
30 |
110 |
|
|
|
sca4
|
RrD928F |
ATTTATACACTTGCGGTAACAC |
1,758 |
94 |
45 |
72 |
40 |
|
RrD2685Ra
|
TTCAGTAGAAGATTTAGTACCAAAT |
|
30 |
30 |
110 |
|
|
RrDRm1826Ra,c
|
TCTAAATTCTGTTGCATCAAT |
|
|
|
|
|
Table 2Summary on tick species, stage and 17-kDa positive nPCR collected from 3 projected regions
Table 2
|
Province |
Species |
Stage |
No. of ticks (No. of tested pools) |
No. of 17-kDa PCR positive (%) |
|
Incheon |
H. flava
|
Larvaa
|
654 (24) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Nymphb
|
25 (6) |
2 (8.0) |
|
|
Adult (male)c
|
1 (1) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Adult (female)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
H. longicornis
|
Larvaa
|
1,080 (39) |
23 (2.1) |
|
|
Nymphb
|
12 (7) |
4 (33.3) |
|
|
Adult (male)c
|
6 (6) |
3 (50.0) |
|
|
Adult (female)c
|
3 (3) |
1 (33.3) |
|
I. nipponensis
|
Larvaa
|
3 (1) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Nymphb
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Adult (male)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Adult (female)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Chungcheong-do |
H. flava
|
Larvaa
|
127 (5) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Nymphb
|
74 (17) |
4 (5.4) |
|
|
Adult (male)c
|
2 (2) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Adult (female)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
H. longicornis
|
Larvaa
|
88 (3) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Nymphb
|
30 (7) |
2 (6.7) |
|
|
Adult (male)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Adult (female)c
|
1 (1) |
0 (0) |
|
I. nipponensis
|
Larvaa
|
12 (1) |
1 (8.3) |
|
|
Nymphb
|
11 (4) |
3 (27.2) |
|
|
Adult (male)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Adult (female)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Jeolla-do |
A. testudinarium
|
Larvaa
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Nymphb
|
1 (1) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Adult (male)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Adult (female)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
H. flava
|
Larvaa
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Nymphb
|
159 (36) |
2 (1.2) |
|
|
Adult (male)c
|
7 (7) |
1 (14.3) |
|
|
Adult (female)c
|
7 (7) |
0 (0) |
|
H. longicornis
|
Larvaa
|
30 (2) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Nymphb
|
473 (98) |
38 (8.0) |
|
|
Adult (male)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Adult (female)c
|
2 (2) |
1 (50.0) |
|
I. nipponensis
|
Larvaa
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Nymphb
|
6 (4) |
3 (50.0) |
|
|
Adult (male)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Adult (female)c
|
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Total (%) |
|
|
2,814 (284) |
88 (3.1) |
Table 3Summary on nPCR results of ticks tested for 3 rickettsial target genes, ompA, ompB and sca4
Table 3
|
Province |
Species |
No. of tested tick pools |
ompAa (%) |
ompBa (%) |
sca4a (%) |
|
Northwestern |
|
Incheon |
H. flava
|
2 |
0 (0) |
1 (50.0) |
1 (50.0) |
|
H. longicornis
|
31 |
20 (64.5) |
11 (35.4) |
15 (48.3) |
|
I. nipponensis
|
0 |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
Subtotal |
33 |
20 (60.6) |
12 (36.3) |
16 (48.4) |
|
H. flava
|
4 |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
|
Southwestern |
|
Chungcheong-do |
H. longicornis
|
2 |
2 (100.0) |
2 (100.0) |
2 (100.0) |
|
I. nipponensis
|
4 |
2 (50.0) |
0 (0) |
4 (100.0) |
|
Subtotal |
10 |
4 (40.0) |
2 (20.0) |
6 (60.0) |
|
Jeolla-do |
H. flava
|
3 |
3 (100.0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
|
H. longicornis
|
39 |
36 (92.3) |
29 (74.3) |
32 (82.1) |
|
I. nipponensis
|
3 |
3 (100.0) |
1 (33.3) |
3 (100.0) |
|
Subtotal |
45 |
42 (93.3) |
30 (66.6) |
35 (77.7) |
|
|
Total |
|
88 |
66 (75.0) |
44 (50.0) |
57 (64.7) |
References
- 1. Maurin M, Raoult D. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activity of levofloxacin against Rickettsia rickettsii, Rickettsia cornorii, ‘Israeli spotted fever group rickettsia’ and Coxiella burnetii
. J Antimicrob Chemoth 1997;39:725-730.
- 2. Shpynov SN, Fournier PE, Pozdnichenko NN, Gumenuk AS, Skiba AA. New approaches in the systematics of rickettsiae. New Microbes New infect 2018;23:93-102.
- 3. Mahara F. Rickettsioses in Japan and the far East. Ann NY Acad Sci 2006;1078:60-73.
- 4. Uchida T, Tashiro F, Funato T, Kitamura Y. Isolation of a spotted fever group Rickettsia from a patient with febrile exanthematous illness in Shikoku, Japan. Microbiol Immunol 1986;30:1323-1326.
- 5. Uchida T, Uchiyama T, Kumano K, Walker DH.
Rickettsia japonica sp. nov., the etiological agent of spotted fever group rickettsiosis in Japan. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1992;42:303-305.
- 6. Camer A, Masangkay J, Satoh H, Okabayashi T, Norizuki S, Motoi Y, Ueno H, Morita C. Prevalence of spotted fever rickettsial antibodies in dogs and rodents in the Philippines. Jpn J Infect Dis 2000;53:162-163.
- 7. Chung MH, Lee SH, Kim MJ, Lee JH, Kim ES, Kim MK, Park MY, Kang JS. Japanese spotted fever, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis 2006;12:1122-1124.
- 8. Gaywee J, Sunyakumthorn P, Rodkvamtook W, Ruang-areerate T, Mason CJ, Sirisopana N. Human infection with Rickettsia sp. related to R. japonica, Thailand. Emerg Infect Dis 2007;13:657-659.
- 9. Fournier PE, Dumler JS, Greub G, Zhang J, Wu Y, Raoult D. Gene sequence-based criteria for identification of new rickettsia isolates and description of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis sp. nov. J Clin Microbiol 2003;41:5456-5465.
- 10. Jiao Y, Wen B, Chen M, Niu D, Zhang J, Qiu L. Analysis of immunoprotectivity of the recombinant OmpA of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis
. Ann NY Acad Sci 2005;1063:261-265.
- 11. Mediannikov OY, Sidelnikov Y, Ivanov L, Mokretosova E, Fournier PE, Tarasevich I, Raoult D. Acute tick-borne rickettsiosis caused by Rickettsia heilongjiangensis in Russian Far East. Emerg Infect Dis 2004;10:810-817.
- 12. Rudakov N, Shpynov S, Fournier PE, Raoult D. Ecology and molecular epidemiology of tick-borne rickettsioses and anaplasmoses with natural foci in Russia and Kazakhstan. Ann NY Acad Sci 2006;1078:299-304.
- 13. Ando S, Kurosawa M, Sakata A, Fujita H, Sakai K, Sekine M, Katsumi M, Saitou W, Yano Y, Takada N, Takano A, Kawabata H, Hanaoka N, Watanabe H, Kurane I, Kishimoto T. Human Rickettsia heilongjiangensis infection, Japan. Emerg Infect Dis 2010;16:1306-1308.
- 14. Lee JH, Park HS, Jung KD, Jang WJ, Koh SE, Kang SS, Lee IY, Lee WJ, Kim BJ, Kook YH, Park KH, Lee SH. Identification of the spotted fever group rickettsiae detected from Haemaphysalis longicornis in Korea. Microbiol Immunol 2003;47:301-304.
- 15. Jang WJ, Choi YJ, Kim JH, Jung KD, Ryu JS, Lee SH, Yoo CK, Paik HS, Choi MS, Park KH, Kim IS. Seroepidemiology of spotted fever group and typhus group rickettsioses in humans, South Korea. Microbiol Immunol 2005;49:17-24.
- 16. Faccini-Martínez ÁA, García-Álvarez L, Hidalgo M, Oteo JA. Syndromic classification of rickettioses: an approach for clinical practice. Int J Infect Dis 2014;28:126-139.
- 17. Choi YJ, Jang WJ, Ryu JS, Lee SH, Park KH, Paik HS, Koh YS, Choi MS, Kim IS. Spotted fever group and typhus group rickettsioses in humans, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis 2005;11:237-244.
- 18. Choi YJ, Lee EM, Park JM, Lee KM, Han SH, Kim JK, Lee SH, Song HJ, Choi MS, Kim IS, Park KH, Jang WJ. Molecular detection of various rickettsiae in mites (acari: trombiculidae) in southern Jeolla Province, Korea. Microbiol Immunol 2007;51:307-312.
- 19. Moon BC, Jeong JH, Choi YJ, Kim JE, Seo HJ, Shin EH, Song BG, Lee SH, Park KH, Jang WJ. Detection and identification of the spotted fever group rickettsial agents from Haemaphysalis ticks in Jeju Island, Korea. J Bacteriol Virol 2009;39:317-327. (in Korean).
- 20. Kang SW, Doan HT, Choe SE, Noh JH, Yoo MS, Reddy KE, Kim YH, Kwon CH, Jung SC, Chang KY. Molecular investigation of tick-borne pathogens in ticks from grazing cattle in Korea. Parasitol Int 2013;62:246-282.
- 21. Liu H, Zhang X, Li Z, Wang Z, Song M, Wei F, Wang S, Liu Q. Characterization of rickettsiae in ticks in northeastern China. Parasit Vectors 2016;9:498.
- 22. Guo LP, Mu LM, Xu J, Jiang SH, Wang AD, Chen CF, Guo G, Zhang WJ, Wang YZ.
Rickettsia raoultii in Haemaphysalis erinacei from marbled polecats, China-Kazakhstan border. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:461.
- 23. Shin YC, Lee IY, Seo JH. Seasonal patterns of ticks in Pocheon and Cheolwon, Republic of Korea. Korean J Clin Lab Sci 2015;47:147-152. (in Korean).
- 24. Kim YS, Choi YJ, Lee KM, Ahn KJ, Kim HC, Klein T, Jiang J, Richards A, Park KH, Jang WJ. First isolation of Rickettsia monacensis from a patient in South Korea. Microbiol Immunol 2017;61:258-263.
- 25. Parola P, Paddock CD, Raoult D. Tick-borne rickettsioses around the world: emerging diseases challenging old concepts. Clin Microbiol Rev 2005;18:719-756.
- 26. Coburn JM, Chong ST, Kim HC, Chang NW, Calix LC, Resto K, Lee DJ, Johnson JL, Robbins RG, Klein TA. Tick surveillance in four southwestern provinces of the Republic of Korea during 2013. Syst Appl Acarol 2016;21:147-165.
- 27. Noh YT, Lee YS, Kim HC, Chong ST, Klein TA, Jiang Ju, Richards AL, Lee HK, Kim SY. Molecular detection of Rickettsia species in ticks collected from the southern provinces of Republic of Korea. Parasit Vectors 2017;10:20.
- 28. Peel MC, Finlayson BL, McMahon TA. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrol Earth Syst 2007;11:1633-1644.
- 29. Korea Meteorological Administration. Incheon metropolitan city, Normal year data (1981–2010) [Internet]; [Retrieved 8 December 2016]. Available from: http://www.weather.go.kr/weather/climate/past_cal.jsp