Abstract
Livestock husbandry is vital to economy of the Tarim Basin, Xinjiang Autonomous Region, China. However, there have been few surveys of the distribution of ixodid ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) and tick-borne pathogens affecting domestic animals at these locations. In this study, 3,916 adult ixodid ticks infesting domestic animals were collected from 23 sampling sites during 2012–2016. Ticks were identified to species based on morphology, and the identification was confirmed based on mitochondrial 16S and 12S rRNA sequences. Ten tick species belonging to 4 genera were identified, including Rhipicephalus turanicus, Hyalomma anatolicum, Rh. bursa, H. asiaticum asiaticum, and Rh. sanguineus. DNA sequences of Rickettsia spp. (spotted fever group) and Anaplasma spp. were detected in these ticks. Phylogenetic analyses revealed possible existence of undescribed Babesia spp. and Borrelia spp. This study illustrates potential threat to domestic animals and humans from tick-borne pathogens.
-
Key words: Tick-borne pathogen, Tarim Basin, China
INTRODUCTION
Ticks are global obligate hematophagous ectoparasites of a wide variety of terrestrial vertebrates and significant vectors of diseases in humans, domestic animals, and wildlife [
1]. Tick-borne pathogens include various microorganisms, such as viruses, bacteria, and protozoans [
2,
3]. Approximately 119 tick species, including 100 species of Ixodidae and 19 species of Argasidae, have been identified in China [
4].
Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region is the largest province in China, covering more than 1/6 of the country’s territory; however, it is dominated by large areas of desert and mountain ranges [
5]. Forty-two species of ticks from 9 genera have been identified in Xinjiang; these represent more than one-third of the total tick species identified in China [
6]. More importantly, a high prevalence of tick-borne diseases has been reported in Xinjiang Autonomous Region [
5]. The Tarim Basin is an endorheic basin in Xinjiang that covers an area of approximately 1,020,000 km
2 [
1]. The name Tarim Basin is sometimes used synonymously to refer to the southern half of the province, or southern Xinjiang. The northern boundary of the Tarim Basin is the Tian Shan mountain range and the southern boundary is the Kunlun Mountains along the edge of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau [
7]. Various landscapes of the Tarim Basin harbor of high mountains, valleys, plains, the Gobi Desert, and additional characteristics [
8]. A previous survey of ticks from livestock conducted in northern Xinjiang indicated that the tick population was altered in response to climate change [
5]. The climate of the Tarim Basin is drier than that of northern Xinjiang. The Tarim Basin is one of the most highly erodible areas in China, and the Taklimakan Desert covers 64% of this region [
9]. Very low level of precipitation in the region inhibits plant growth and minimizes the habitable area for animals and humans [
10]. In the Tarim Basin, 90% of the humans and animals inhabit oases that are supplied by run-off water from the surrounding mountains. This has the effect of concentrating humans and livestock around peripheral oases, the most important ecosystem in the area, which constitutes 4–5% of the total land cover of the Tarim Basin [
11].
Until now, there have been few specific studies of ticks infesting domestic animals in these oases. However, little is known regarding tick-borne diseases of great medical significance, particularly zoonotic diseases, in this area. The current study investigated the associations between ticks and domestic animals in the Tarim Basin. In addition, molecular techniques were used to assess the presence of tick-borne pathogens.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sampling area and tick sampling and identification
From 2012 to 2016, we collected 3,916 ixodid tick specimens from 23 sampling sites in oases around the Tarim Basin, namely the Awat, Hejing, Hetian, Kargilik, Luntai, Minfeng, Poskam, Pishan, Qiemo, Qira, Shufu, Shanshan, Tuokexun, Xinhe, Xayar, Yarkand, Yanqi, Artux, Makit, Wensu, Tumxuk, Kuqa, and Aral counties (
Fig. 1A). These counties are mainly regions of livestock husbandry. The livestock reared in these regions are primarily autochthonous. Most of the sheep (approximately 95%) are Kazakh, Chinese Merino, Hu, and Altay breeds. The cattle are mainly Xinjiang Brown, Holstein, and Kazakh breeds. The dogs are mainly Kazakh Tobet, a breed commonly used to protect livestock herds. During this 5-year survey, most sampling sites (17/23), including farms in the Awat, Hejing, Hetian, Kargilik, Luntai, Minfeng, Poskam, Pishan, Qiemo, Qira, Shufu, Shanshan, Tuokexun, Xinhe, Xayar, Yarkand, and Yanqi counties, were surveyed only once. Three sampling sites in the Artux, Makit, and Wensu counties were surveyed twice. The sampling site in the Tumxuk county was surveyed 3 times, and the farm in the Kuqa county was surveyed 5 times. The sheep flock on the sampling site in Aral county was surveyed twice, and the dogs were surveyed 6 times.
We collected adult ticks from the body surfaces of livestock and dogs over 5 consecutive years. Data recorded for all specimens collected included their location, host, number of ticks collected and the date of collection, species, and sex (
Table 1). We grouped tick specimens according to location/host of collection, date of collection, and species. Ticks were collected from animals via tick sampling from the entire body of each animal, including sheep, cattle on 23 farms in 23 counties, and domestic dogs from farms in the Aral county. The collected ticks were kept alive until they were transferred to the laboratory of College of Animal Science, Tarim University. The collected ticks were counted and identified to species based on morphology according to standard morphological keys, and the identification was confirmed based on mitochondrial 16S and 12S rRNA sequences [
12–
14]. We utilized morphological characteristics, such as the anterior surface of the basis capituli flat, perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the hypostome, for morphological species identification. All specimens were preserved in 70% ethanol. All livestock we checked for ticks were grazed in the traditional manner, and all farm dogs were free-roaming. There was no evidence of the use of chemical acaricides prior to tick sampling.
We used 3 representative tick specimens from each specimen group for DNA extraction and mixed DNA templates of 3 ticks of each specimen group for molecular identification of tick species and screening of pathogens.
Ethanol-preserved tick samples were rinsed in distilled water, and then dried on filter paper. Total DNA was extracted using the DNeasy blood and tissue kit (Qiagen GmbH, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA was eluted in 80 μl elution buffer AE (provided with the kit) and stored at −80°C until tested.
Molecular identification of tick species
Partial sequences of 16S and 12S rRNAs were PCR amplified using the primers described in previous studies [
14]. PCR amplification was performed using GoTaq G2 Flexi DNA polymerase (Promega Corporation, Madison, Wisconsin, USA). The reaction master mix was prepared according to the manufacture’s protocol, and PCR conditions described in previous studies were applied [
15]. In brief, PCR reaction mixtures comprised 2 pmol of each primer, 200 μM of each deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP), 1×PCR buffer, 1 unit of Taq DNA polymerase, and 50–100 ng of sample DNA for each PCR in a 50-μl reaction.
Total DNA (including mitochondrial) extracted from H. asiaticum was used as a positive control. Sterile water included in the DNA extraction procedure was used as a negative control. PCR products were electrophoresed on a 1% agarose gel, stained with SYBR Safe DNA Gel Stain (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, California, USA), and visualized under ultraviolet light. DNA bands of the correct size were purified and sequenced by BGI Tech Solutions Co., LTD (Liuhe, Beijing, China).
Sequences of 12S rRNA of ticks obtained in this study are deposited in GenBank under accession Nos. MG645336–MG645377. Sequences of 16S rRNA of ticks obtained in this study are deposited in GenBank under accession Nos. MG 651923–MG651949.
Detection of DNA sequences of tick-borne pathogens
A total of 156 specimens were screened for tick-borne pathogens. Piroplasms were detected using primers PIRO-A and PIRO-B, which produce 423-bp band [
16].
Borrelia spp. were detected using a primer pair that targeted the flagellin gene [
17].
Anaplasma spp. were detected using 2 primer pairs that targeted msp4 and 16S rRNA [
14,
18].
Rickettsia spp. was detected using a set of primer pairs targeting 6 DNA fragments, including partial sequences of 17-kDa antigen, 16S rRNA, citrate synthase (gltA), surface cell antigen 1 (sca1), outer membrane protein A (ompA), and outer membrane protein B (ompB), as described previously [
19]. DNA bands of the correct size were purified and sequenced by BGI Tech Solutions Co., LTD. Representative DNA sequences of tick-borne pathogens are deposited in GenBank.
The reaction master mix was prepared according to the manufacture’s protocol, and PCR conditions described in previous studies were applied. All PCRs were run with positive and negative controls. Genomic DNA sequences of Babesia divergens, Rickettsia spp. [spotted fever group (SFG)], A. phagocytophilum, and Bo. garinii were used as positive controls. Sterile water included in the DNA extraction procedure was used as a negative control.
Sequence analysis
DNA sequences were assembled using Lasergene version 12.1 (DNASTAR) and edited in MEGA 5.0 [
20,
21]. Sequence alignments were performed using ClustalW within MEGA 5.0, using default parameters (open gap penalty=10.0, extend gap penalty=5.0) prior to checking via visual inspection. Genetic distances were calculated based on the K2P model for all pairwise comparisons in the matrix using MEGA5.0. Bootstrapping (1,000 replicates) was used to estimate variance. Pairwise deletion was used for gaps/missing data. Based on K2P distances, phylogenetic trees were constructed with the combined data sets of major tick genera and tick-borne pathogens using the neighbor-joining method, as described previously [
22]. For gltA, msp4, and groEL analyses, the sites of codon positions were tested.
RESULTS
Ticks collected and morphological identification
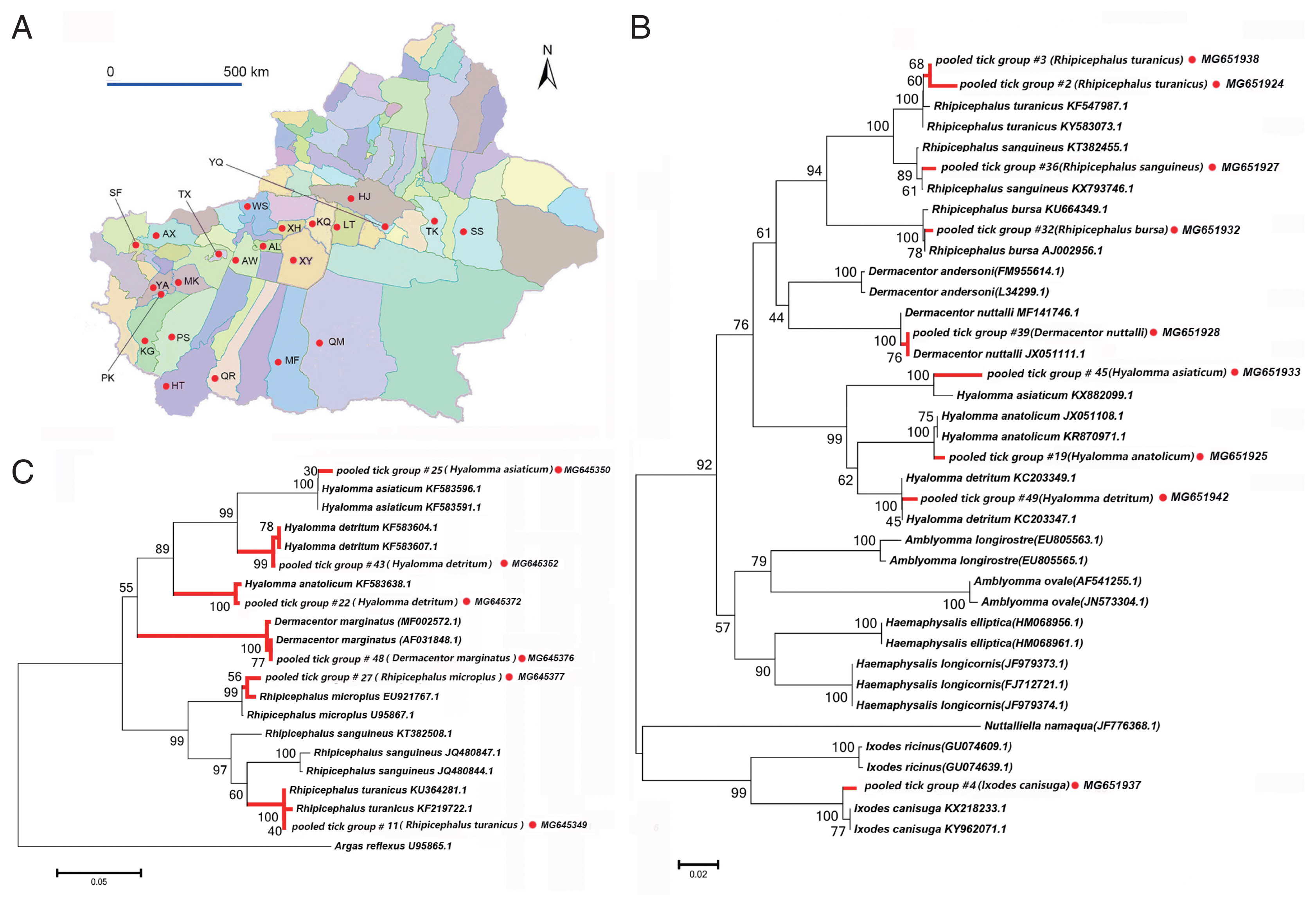
We collected 3,916 ticks of 10 species belonging to 4 genera from 23 sampling sites in the Tarim Basin (
Fig. 1A). These data are summarized in
Tables 1 and
2. We confirmed species identity via phylogenetic analysis using 16S (
Fig. 1B) and 12S rRNA (
Fig. 1C) sequences. All specimens belonged to the family Ixodidae. The species collected most frequently were
Rhipicephalus turanicus (n=2,224, 56.8%),
Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum (n=861, 22.1%),
Rh. bursa (n=231, 5.9%),
H. asiaticum asiaticum (n=205, 5.2%),
Rh. sanguineus (n=144, 3.7%),
H. detritum detritum (n=133, 3.4%),
Dermacentor marginatus (n=53, 1.4%),
D. nuttalli (n=37, 0.9%),
Rh. microplus (n=23, 0.6%), and
Ixodes canisuga (n=5, 0.1%), in that order. Notably, 5
I. canisuga females were collected from a farm dog in Xinjiang, supporting the existence of
I. canisuga in Xinjiang, as reported in a previous study [
23,
24].
Six PCR products, namely 17-kDa antigen, gltA, sca1, 16S rRNA, ompA, and ompB, were assessed within each tick pooled tick group to examine the presence of
Rickettsia spp. All PCR products of the correct size amplified from
Rickettsia spp. were sequenced, and the obtained sequences of
Rickettsia spp. obtained (
Fig. 2).
We detected DNA sequences of
Rickettsia spp. within SFG, such as
Ri. conorii, Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae, and
Ri. massiliae, in 11 of the 52 tick pooled tick groups (22.2%). This group included
Rhipicephalus spp. collected from 8 counties in the Tarim Basin. Five of the 11
Rickettsia spp. of SFG were confirmed as
Candidatus Ri. barbariae, one as
Ri. massiliae, 1 as
Ri. conorii, 1 as
Ri. raoultii, 1 as
Ri. sp. xinjiang02, and the remaining 2 as
Rickettsia spp. without clear species identification.
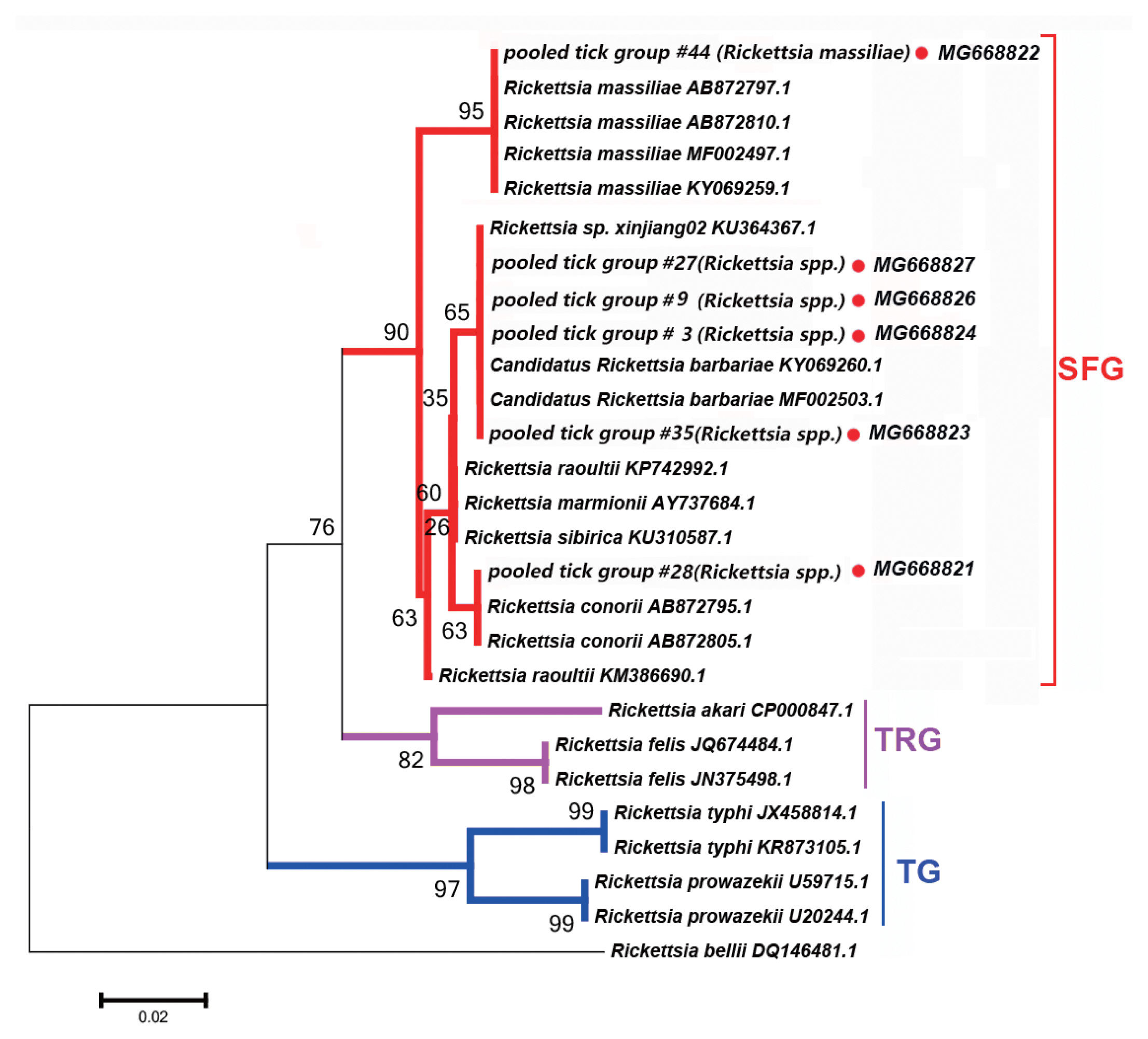
Fig. 2 depicts a phylogenetic tree based on the gltA sequences of the representative
Rickettsia spp.
Rickettsia sequences detected in this study were clustered with species within SFG, including
Ri. conorii (AB872795.1) and
Ri. massiliae (AB872810.1).
We detected Rickettsia spp. in Rh. turanicus, Rh. Bursa, and Rh. microplus ticks collected from the oases of the Makit, Tumxuk, Qiemo, Wensu, Qira, Aral, Minfeng, and Kuqa counties. We collected Rh. turanicus ticks from both sheep and cattle, Rh. bursa ticks from sheep, and Rh. microplus ticks from cattle.
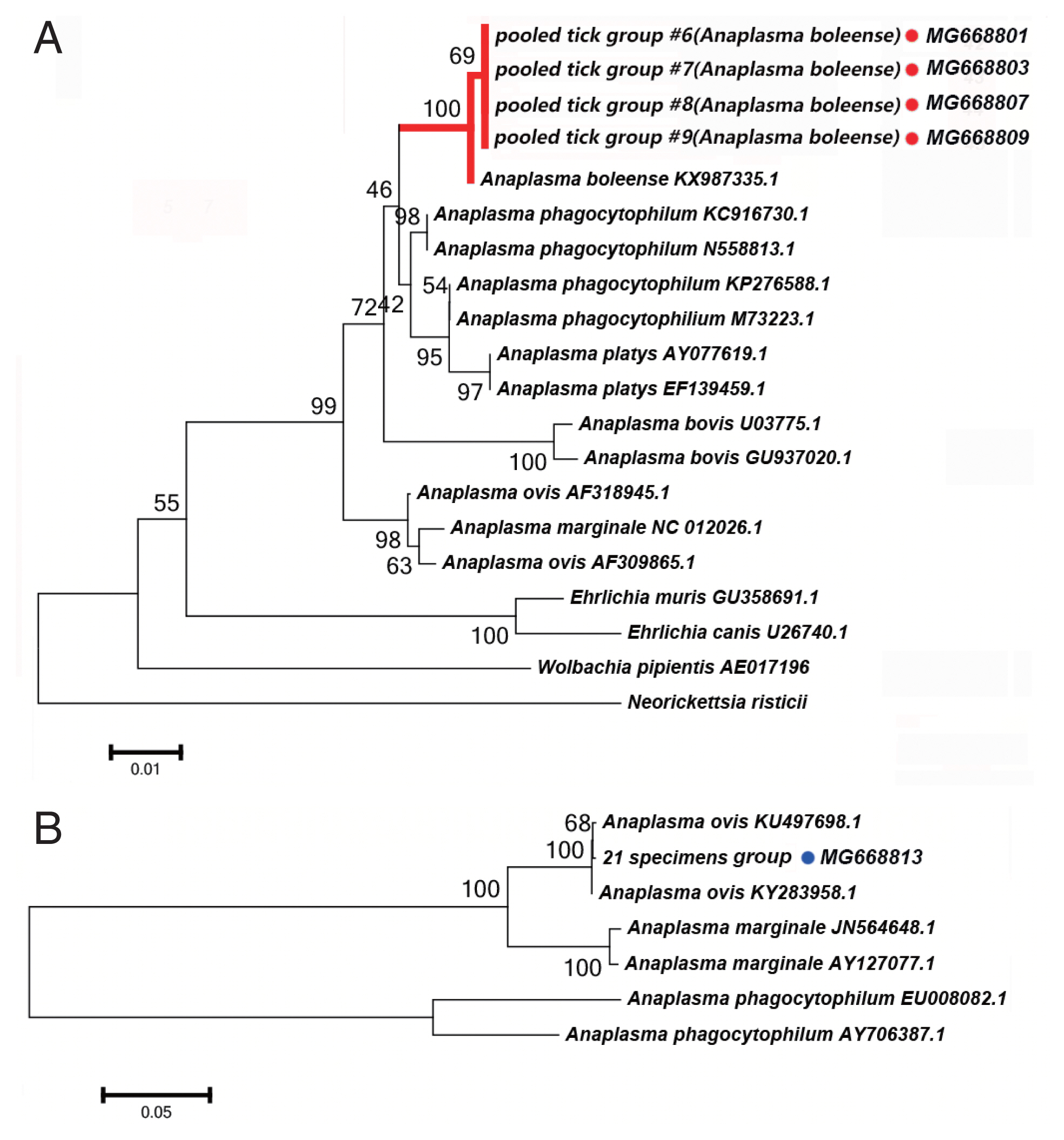
Anaplasma spp. Detectied
We detected DNA sequences of
Anaplasma spp. in 5 of the 52 tick pooled tick groups, which included
Rh. turanicus and
Rh. sanguineus ticks collected from the Aral and Kuqa counties. DNA sequence analyses of 4 amplicons from the Aral county revealed that they were identical to one another and shared 99% sequence identity with the 16S rRNA of
Candidatus Anaplasma boleense (KX987335.1), whereas the amplicon from the Kuqa county shared 99% sequence identity with msp4 of
A. ovis (KY283958.1).
Fig. 3A depicts a phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rRNA sequences of the representative
Ehrlichia/Anaplasma spp. The sequences acquired from the pooled tick groups #6 (
Rh. turanicus), #7 (
Rh. turanicus), #8 (
Rh. sanguineous), and #9 (
Rh. turanicus) belonged to the cluster corresponding to
Candidatus A. boleense.
Fig. 3B depicts another phylogenetic tree based on the msp4 sequences of the representative
Anaplasma spp. In this analysis, the sequence acquired from pooled tick group #21 (
Rh. turanicus) belonged to the cluster corresponding to
A. ovis.
We detected Candidatus Anaplasma boleense in both Rh. turanicus and Rh. sanguineus. Rh. turanicus ticks were collected from both sheep and dogs, and Rh. sanguineus ticks were collected from dogs. We detected A. ovis by PCR in Rh. turanicus ticks, which were collected from cattle.
Borrelia spp. Detected
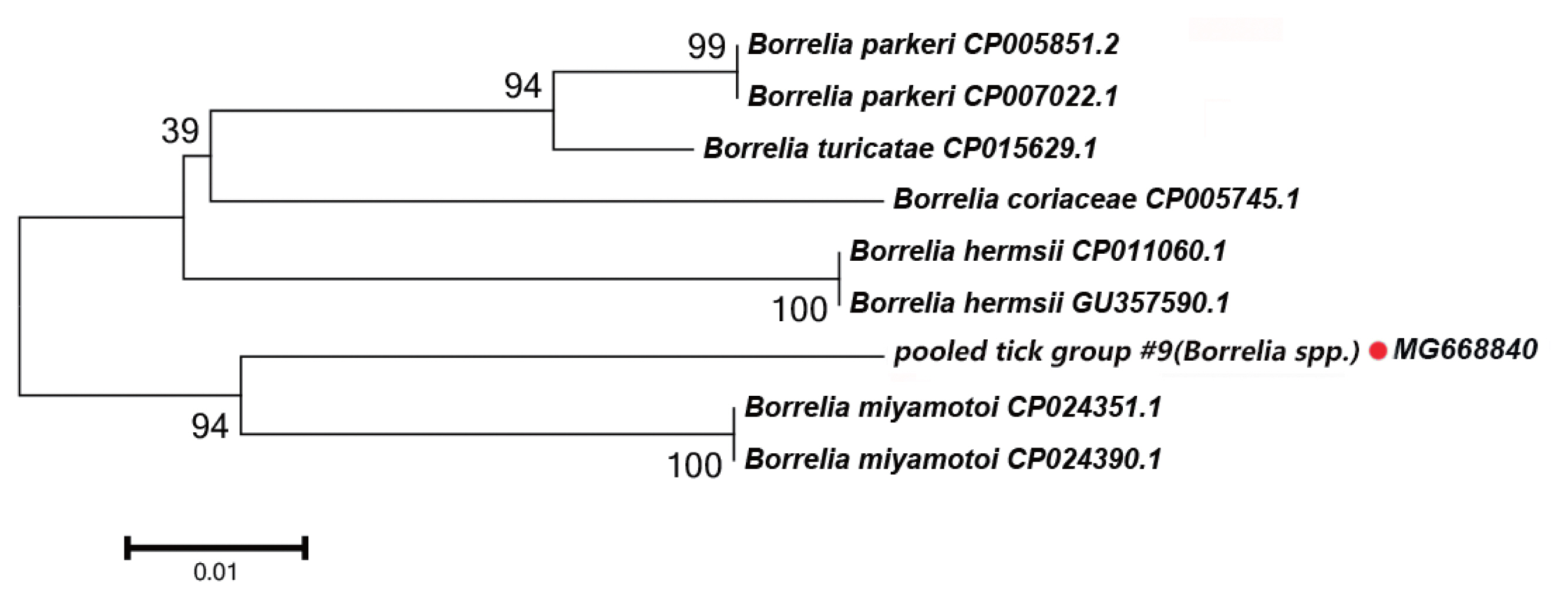
In this study, the groEL gene segment of
Borrelia spp. was detected in
Rh. turanicus collected from the Aral county; these ticks were collected from sheep. DNA sequence analysis of the amplicon revealed that it shared 94% sequence identity with the groEL gene of
Bo. miyamotoi (CP004217.2).
Fig. 4 depicts a phylogenetic tree based on the groEL sequences of the representative
Borrelia spp. The DNA sequence of the groEL gene amplified in this study formed a unique cluster within
Borrelia spp.
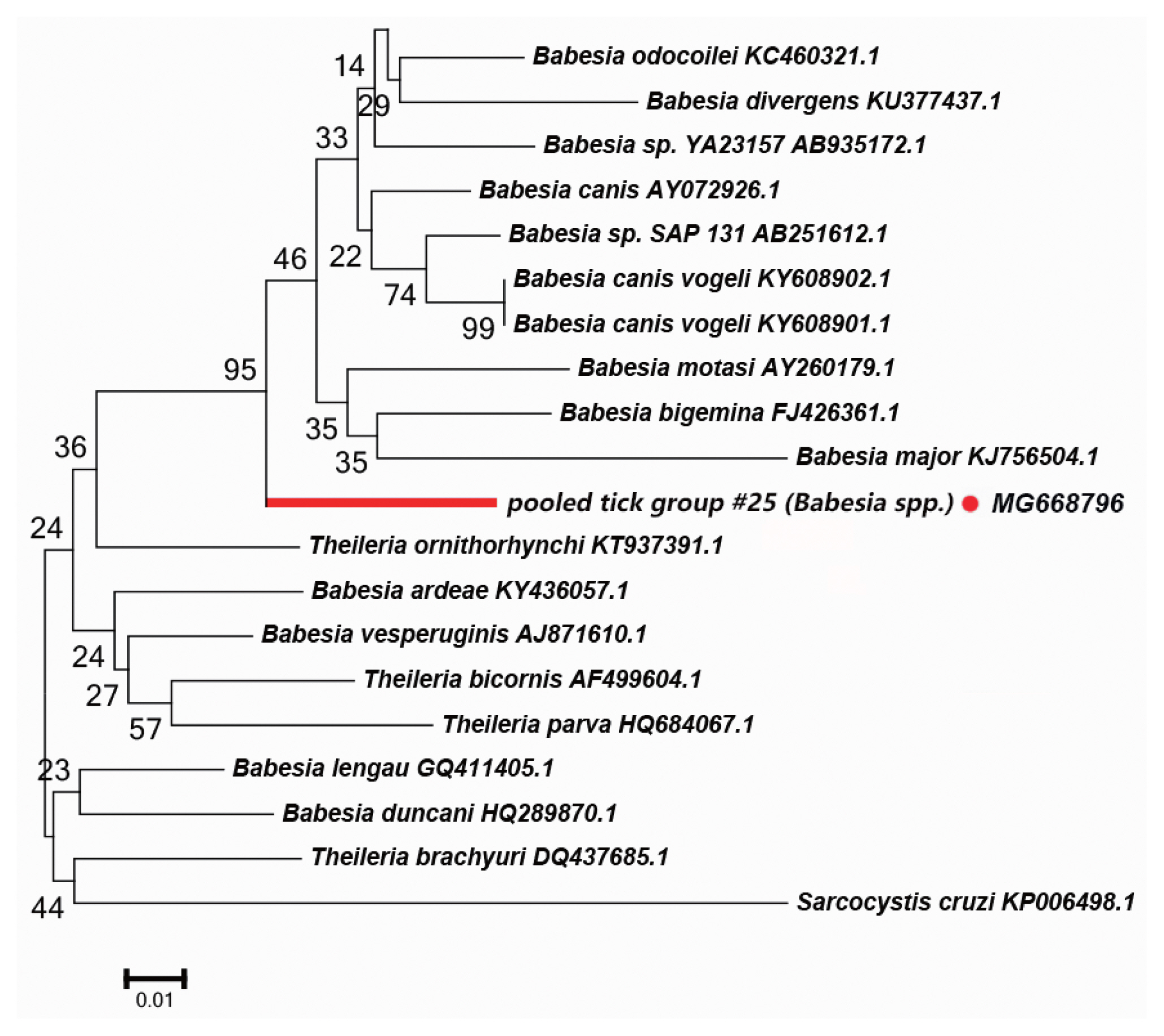
We detected a possibly undescribed
Babesia spp. in
H. asiaticum asiaticum collected from cattle in the Kuqa county. DNA sequence analysis of the amplicon revealed that it shared 91% sequence identity with the 18S rRNA sequence of a
Ba. canis vogeli isolate (KT323935.1).
Fig. 5 depicts a phylogenetic tree based on the 18S rRNA sequences of the representative
Babesia/Theileria spp. The DNA sequence of 18S rRNA amplified in this study formed a unique cluster within
Babesia/Theileria spp.
DISCUSSION
The survival, phenology, and biting activities of ticks are closely reliant on environmental conditions, including annual rainfall, atmospheric temperature and relative humidity, vegetation cover, altitude, and host availability [
5]. There is a dearth of study of disease transmission by ticks, and such studies necessitate ongoing active surveillance of the distribution of ticks in areas with specific desert environments, such as the Tarim Basin.
We identified 10 tick species from 4 genera associated with domestic animals from 23 study sites (
Fig. 1A). These species included
Rh. turanicus, H. anatolicum anatolicum, Rh. bursa, H. asiaticum asiaticum, Rh. sanguineus, H. detritum detritum, D. marginatus, D. nuttalli, Rh. microplus, and
I. canisuga, most of which have been reported in the study area. However, our findings are not entirely consistent with those of previous studies [
3]. We found
Rh. turanicus to be the most widespread tick species, although previous studies have described
Rh. turanicus as the second most abundant tick species in southern Xinjiang [
25]. We collected
Rh. turanicus from domestic animals in oases in 14 counties.
Rh. turanicus constituted 56.79% of the total number of ticks collected (2,224/3,916), and it was highly prevalent in various domestic hosts, including cattle, sheep, and dogs.
Rh. turanicus has been implicated as a vector of several human and veterinary pathogens, including
Rickettsia spp. of SFG,
Anaplasma spp.,
Borrelia spp. and West Nile virus [
26].
Rh. turanicus can infest people, and the risk of pathogens being transmitted from
Rh. turanicus to people should not be ignored [
27].
In Xinjiang,
I. canisuga was collected from a dog that had never traveled outside the region. We confirmed the morphological identification of
I. canisuga using molecular and phylogenetic methods. DNA sequence analysis of the amplicon revealed that the 16S rRNA sequences of the pooled tick group #4 shared 98.47% sequence identity with the 16S rRNA sequences of
I. canisuga from Hungary (KX218233.1). Precise distribution of
I. canisuga in Xinjiang requires further study. To date,
I. canisuga has been recorded in Xinjiang just once [
24]. There are several potential reasons for this. First,
I. canisuga is a common ectoparasite of carnivores; however, previous surveys in Xinjiang have always collected ticks from livestock and not from carnivores [
28]. Second, previous studies have revealed the proportion of
I. canisuga in some areas to be relatively rare [
29]. We identified 3 tick species from dogs and found that the proportion of
I. canisuga in these ticks was 4.42% (5/113). Our findings support previous reports of the presence of
I. canisuga in Xinjiang [
24].
In this study, we detected several pathogens in ticks from southern Xinjiang, including the
Rickettsia spp. of SFG and
Anaplasma spp. To screen for the
Rickettsia spp., we assessed 6 partial sequences of 17-kDa antigen, 16S rRNA, gltA, sca1, ompA, and ompB. Coinfections of multiple species of
Rickettsia in a single tick may occur [
30]. Tick-borne pathogens such as
Candidatus Anaplasma boleense,
Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae, and
Ri. massiliae have been reported in China [
31,
32], which were also detected in this study. However, it is noteworthy that possibly undescribed
Borrelia and
Babesia spp. were detected in this study.
In
Borrelia spp., the distribution of inter-specific K2P distances for groEL at the species level was between 1.8% and 9.7%. The groEL DNA segment that we detected could be correctly translated into a protein according to the Bacterial, Archaeal, and Plant Plastid Code, and it is nested within a novel phylogenetic group in the
Borrelia spp. clade (
Fig. 4). We speculate that the groEL DNA segment detected in this study belongs to an undescribed
Borrelia sp.; multilocus gene typing by targeting other genes should be performed.
In the
Babesia spp., the distribution of inter-specific K2P distances for 18S rRNA at the species level was between 0.8% and 14.4%. The 18S rRNA we detected was nested within in a novel phylogenetic group in the
Babesia spp. clade (
Fig. 5). Molecular evidence from recent studies has revealed the presence of some new
Babesia sp. [
33]. We speculate that the 18S rRNA segment we detected in this study belongs to an undescribed
Babesia sp; further study is required to confirm this.
In this study, 3,916 ixodid ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) from 10 species of 4 genera, which infest domestic animals, were collected from peripheral oases in the Tarim Basin. The study revealed that Rh. turanicus is currently the dominant ixodid species in this area. We rediscovered I. canisuga from Xinjiang after its first record 45 years ago. In addition to the tick-associated microorganisms, we detected some potential zoonotic pathogens, including Rickettsia spp. of SFG and Anaplasma spp. The analyses suggested the presence of some hitherto undescribed Babesia spp. and Borrelia spp. in ticks in the Tarim Basin. Some of the tick species we collected, such as Rh. turanicus and Rh. Sanguineus, may infest people, and they represent a potential risk of disease transmission from ticks to both livestock and people in the Tarim Basin.
Notes
-
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was funded by the Inner Mongolia Agricultural University High-level Talents Research Initiation Fund Project (NDYB2018-5), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31860698), the National key research and development program of China (No. 2016YFD0501100), and the open project of Key Laboratory of Tarim Animal Husbandry Science and Technology, Xinjiang Production & Construction Corps (No. HS201801).
Ethical treatment of animals was practiced in this study; however, the relevant document number is not available at Inner Mongolia Agricultural University. Permission was obtained from the farm owners before collection of the specimens.
Fig. 1A map of study area and tick species identification through phylogenetic analyses based on 12S and 16S rRNA. (A) The 23 surveyed counties in the peripheral oases around Tarim Basin are marked with red dots. (B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on partial 16S rRNA sequences of ticks, (C) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on partial 12S rRNA sequences of ticks. Bootstrap values are indicated at the nodes. Scale bar indicates degree of divergence represented by a given length of branch. Red dots indicate sequences acquired in this study. AL, Aral; AX, Artux; AW, Awat; HJ, Hejing; HT, Hetan; KG, kargilik; KQ, Kuqa; LT, Luntai; MK, Makit; MF, Minfeng; PS, Pishan; PK, Poskam; QM, Qiemo; QR, Qira; SS, ShanShan; SF, Shufu; TX, Tumxuk; TK, Tuokexun; WS, Wensu; XY, Xayar; XH, Xinhe; YQ, Yanqi; YA, Yarkand.
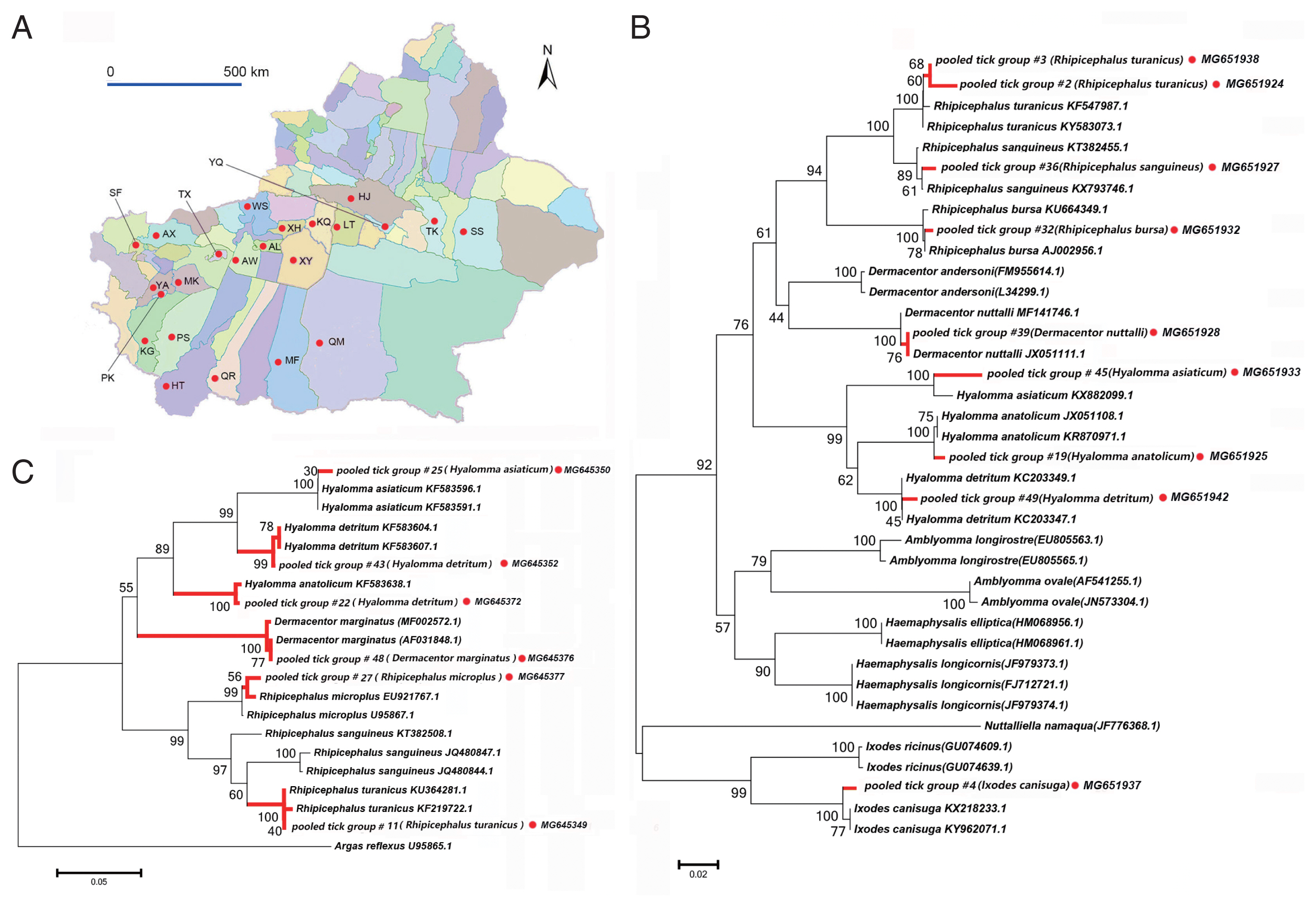
Fig. 2Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on partial gltA sequences of Rickettsia spp. in ixodid ticks. Bootstrap values are indicated at the nodes. scale bar indicates degree of divergence represented by a given length of branch. Red dots indicate sequences acquired in this study. SFG indicates a spotted fever group. TG indicates a typhus group. TRG indicates the transitional group of Rickettisa spp.
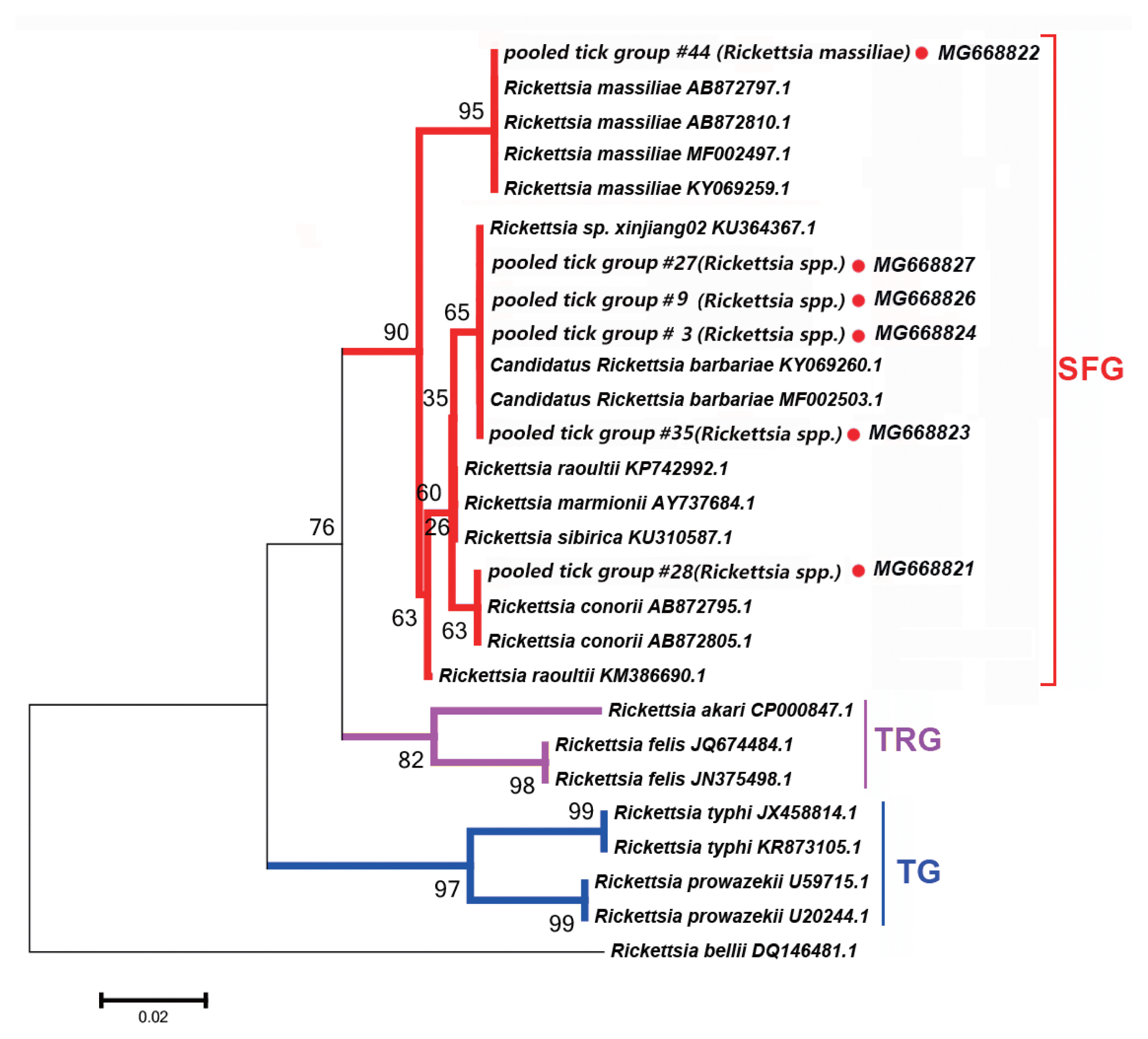
Fig. 3(A) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic analysis based on partial 16S rRNA sequences of Anaplasma spp. in ixodid ticks. (B) Neighbor-joining phylogenetic analysis based on partial msp4 sequences of Anaplasma spp. Bootstrap values are indicated at the nodes. Scale bar indicates degree of divergence represented by a given length of branch. Red and blue dots indicate the sequences acquired in this study.
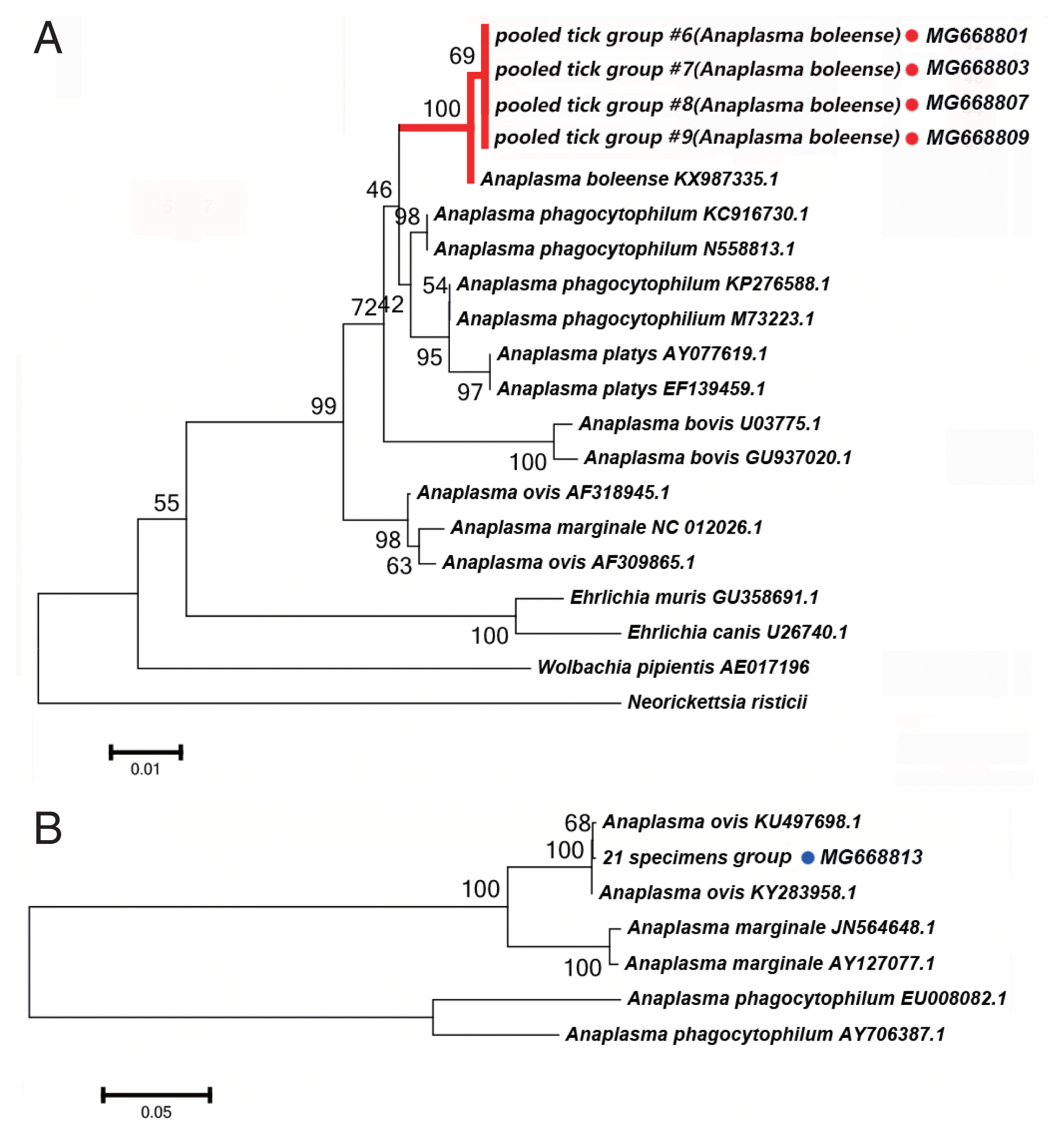

Fig. 4Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on partial groEL sequences of Borrelia spp. in ixodid ticks. Bootstrap values are on the nodes. Scale bar indicates degree of divergence represented by a given length of branch. Red dot indicates sequence acquired in this study.
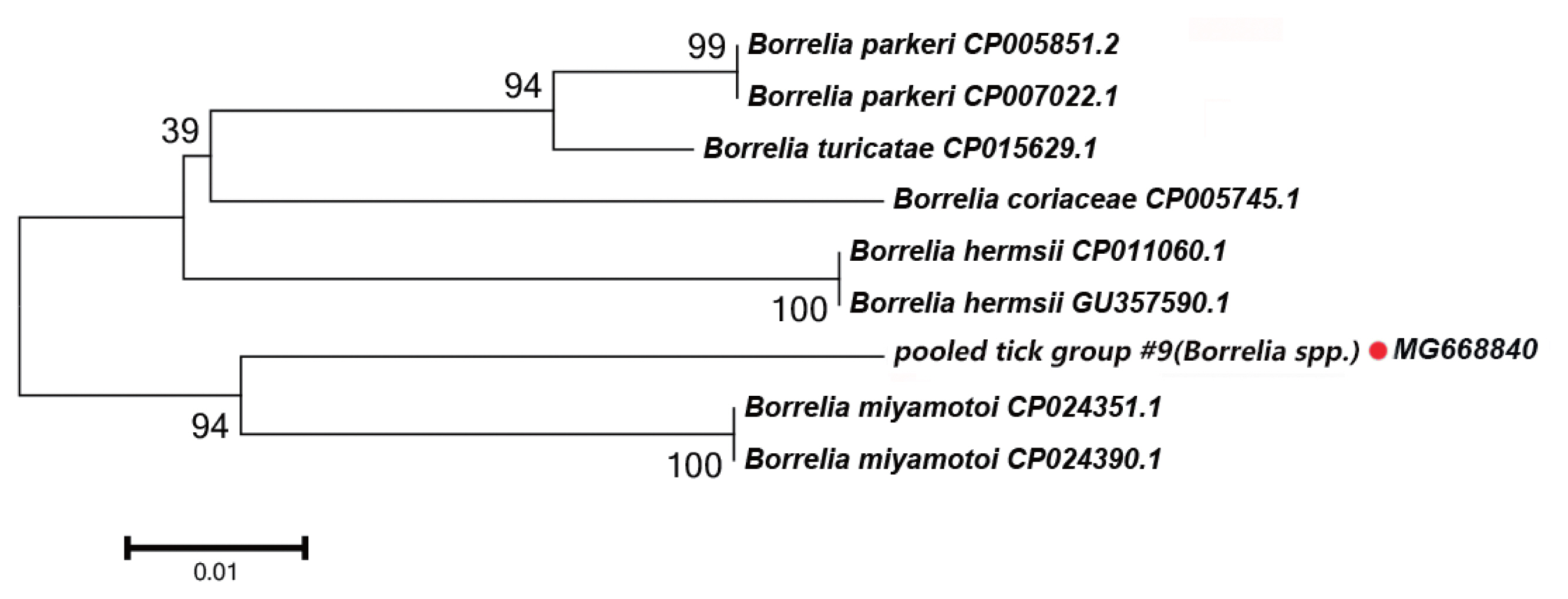
Fig. 5Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on partial 18S rRNA sequences of Babesia spp. in ixodid ticks. Bootstrap values are on the nodes. Scale bar indicates degree of divergence represented by a given length of branch. Red dot indicates sequence acquired in this study.
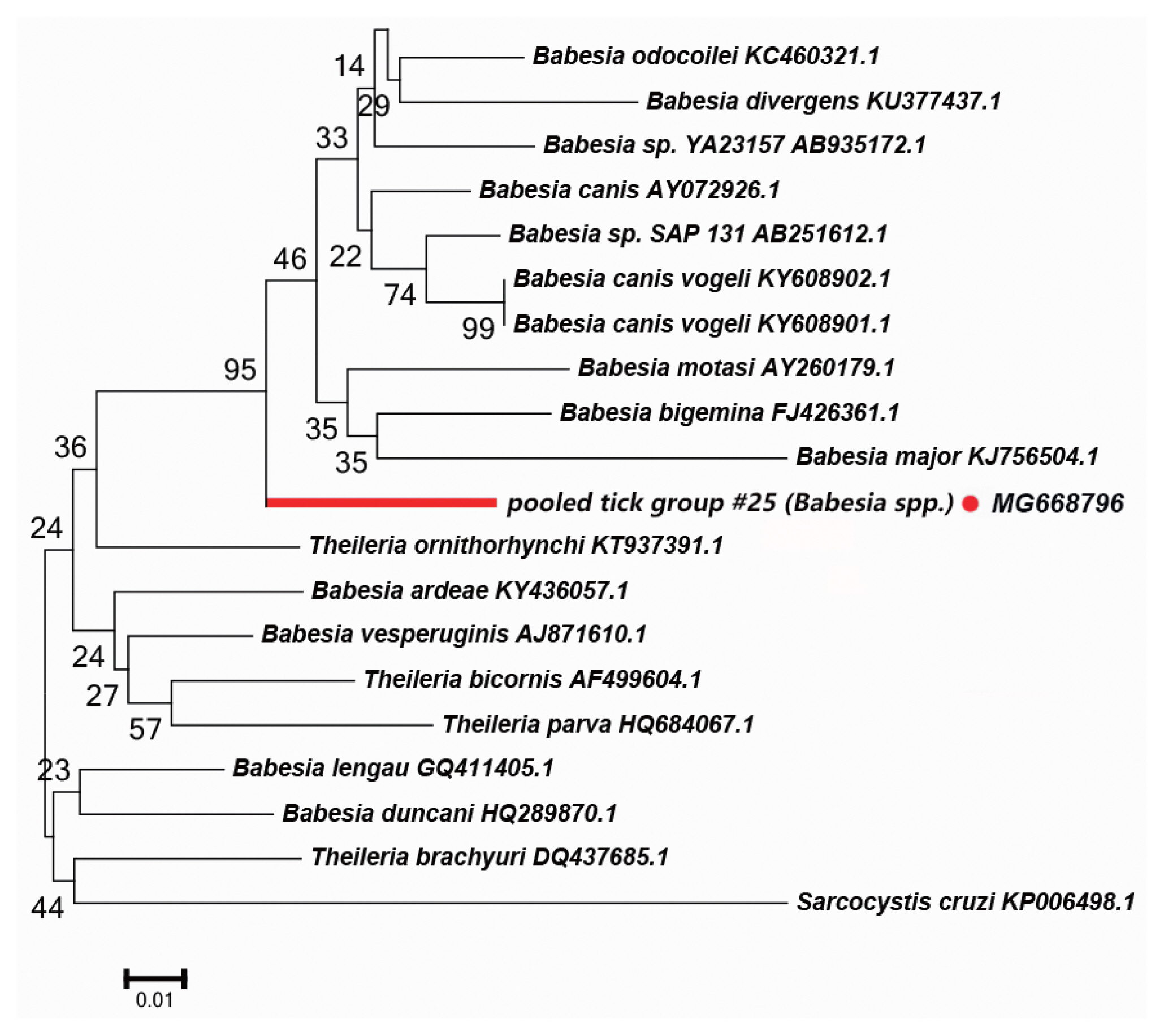
Table 1Counts of tick species collected from the sampling sites around Tarim Basin during 2012 and 2016
Table 1
|
No. of Sampling sites |
County |
Host |
Tick Species |
Tick No. |
Pooled tick group |
|
1 |
Aral (AL) |
Dogs |
R. turanicus
|
11 (9/2) |
1 |
|
|
Dogs |
R. turanicus
|
57 (37/20) |
2 |
|
|
Dogs |
R. turanicus
|
23 (8/15) |
3 |
|
|
Dogs |
I. canisuga
|
5 (0/5) |
4 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. sanuineus
|
111 (67/44) |
5 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
378 (278/100) |
6 |
|
|
Dogs |
R. turanicus
|
7 (6/1) |
7 |
|
|
Dogs |
R. sanguineous
|
3 (2/1) |
8 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
47 (27/20) |
9 |
|
|
Dog |
R. turanicus
|
7 (2/5) |
10 |
|
|
2 |
Artux (AX) |
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
203 (154/49) |
11 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
254 (130/124) |
12 |
|
|
3 |
Awat (AW) |
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
8 (2/6) |
13 |
|
|
Sheep |
H. anatolicum anatolicum
|
8 (0/8) |
14 |
|
|
4 |
Hejing (HJ) |
Sheep |
H. anatolicum anatolicum
|
15 (8/7) |
15 |
|
|
5 |
Hetian (HT) |
Cattle |
H. detritum detritum
|
35 (25/10) |
16 |
|
|
6 |
Kargilik (KG) |
Cattle |
R. turanicus
|
32 (10/22) |
17 |
|
|
7 |
Kuqa (KQ) |
Cattle |
H. anatolicum anatolicum
|
6 (0/6) |
18 |
|
|
Sheep |
H. anatolicum anatolicum
|
89 (12/77) |
19 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
94 (60/34) |
20 |
|
|
Cattle |
R. turanicus
|
4 (3/1) |
21 |
|
|
Sheep |
H. anatolicum anatolicum
|
89 (22/67) |
22 |
|
|
Cattle |
H. asiaticum asiaticum
|
38 (5/33) |
23 |
|
|
Cattle |
R. sanguineus
|
25 (10/15) |
24 |
|
|
Cattle |
H. asiaticum asiaticum
|
155 (24/131) |
25 |
|
|
8 |
LunTai (LT) |
Cattle |
H. anatolicum anatolicum
|
336 (281/55) |
26 |
|
|
9 |
Makit (MK) |
Cattle |
R. microplus
|
23 (8/15) |
27 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
5 (4/1) |
28 |
|
|
10 |
Minfeng (MF) |
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
8 (4/4) |
29 |
|
|
11 |
Poskam (PK) |
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
91 (64/27) |
30 |
|
|
12 |
Pishan (PS) |
Cattle |
H. detritum detritum
|
5 (4/1) |
31 |
|
|
13 |
Qiemo (QM) |
Sheep |
R. bursa
|
231 (136/95) |
32 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
254 (124/130) |
33 |
|
|
14 |
Qira (QR) |
Sheep |
H. detritum detritum
|
11 (7/4) |
34 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
3 (1/2) |
35 |
|
|
15 |
Shufu (SF) |
Sheep |
R. sanguineus
|
5 (4/1) |
36 |
|
|
16 |
ShanShan (SS) |
Sheep |
H. anatolicum anatolicum
|
271 (157/114) |
37 |
|
|
17 |
Tuokexun (TK) |
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
11 (11/0) |
38 |
|
|
18 |
Tumxuk (TX) |
Cattle |
D. nuttalli
|
37 (0/37) |
39 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
437 (274/163) |
40 |
|
|
Sheep |
H. anatolicum anatolicum
|
25 (25/0) |
41 |
|
|
Sheep |
H. anatolicum anatolicum
|
22 (0/22) |
42 |
|
|
19 |
Wensu (WS) |
Sheep |
H. detritum detritum
|
3 (0/3) |
43 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
37 (0/37) |
44 |
|
|
Sheep |
H. asiaticum asiaticum
|
12 (0/12) |
45 |
|
|
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
15 (15/0) |
46 |
|
|
Cattle |
R. turanicus
|
8 (8/0) |
47 |
|
|
20 |
Xayar (XY) |
Cattle |
D. marginatus
|
9 (2/7) |
48 |
|
|
21 |
Xinhe (XH) |
Sheep |
H. detritum detritum
|
22 (12/10) |
49 |
|
|
22 |
Yanqi (YQ) |
Sheep |
R. turanicus
|
230 (131/99) |
50 |
|
|
23 |
Yarkand (YA) |
Sheep |
H. detritum detritum
|
57 (26/31) |
51 |
|
Yarkand (YA) |
Cattle |
D. marginatus
|
44 (23/21) |
52 |
Table 2Summary of tick specimens collected in this study
Table 2
|
Hyalomma
|
Dermacentor
|
Rhipicephalus
|
Ixodes
|
|
|
|
|
|
H. detritum
|
H. anatolicum
|
H. asiaticum
|
D. marginatus
|
D. nuttalli
|
R. turanicus
|
R. sanguineus
|
R. bursa
|
R. microplus
|
I. canisuga
|
|
No. of ticks (♂/♀) |
133 (74/59) |
861 (505/356) |
205 (29/176) |
53 (25/28) |
37 (0/37) |
2,224 (1,362/862) |
144 (83/61) |
231 (136/95) |
23 (8/15) |
5 (0/5) |
|
|
Total number of ticks |
3,916 (2,222/1,694) |
|
|
No. of specimen group |
52 |
References
- 1. Mediannikov O, Fenollar F. Looking in ticks for human bacterial pathogens. Microb Pathog 2014;77:142-148.
- 2. Dietrich M, Gómez-Díaz E, McCoy KD. Worldwide distribution and diversity of seabird ticks: implications for the ecology and epidemiology of tick-borne pathogens. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 2011;11:453-470.
- 3. Yu Z, Wang H, Wang T, Sun W, Yang X, Liu J. Tick-borne pathogens and the vector potential of ticks in China. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:24.
- 4. Wu XB, Na RH, Wei SS, Zhu SJ, Peng HJ. Distribution of tick-borne diseases in China. Parasit Vectors 2013;6:119.
- 5. Wang YZ, Mu LM, Zhang K, Yang MH, Zhang L, Du JY, Liu ZQ, Li YX, Lu WH, Chen CF, Wang Y, Chen RG, Xu J, Yuan L, Zhang WJ, Zuo WZ, Shao RF. A broad-range survey of ticks from livestock in Northern Xinjiang: changes in tick distribution and the isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu stricto. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:449.
- 6. Chen Z, Yang X, Bu F, Yang X, Yang X, Liu J. Ticks (acari: ixodoidea: argasidae, ixodidae) of China. Exp Appl Acarol 2010;51:393-404.
- 7. Lu HF, Wang S, Jia D, Wang LS, Liu S. The Late Cenozoic Basin/Mountain Coupling Mechanics of the Tarim Basin and the Tianshan Mountains. Geol J Chin Univ 2005;4:493-503. (in Chinese)..
- 8. Feng Q, Jin H, Su Z. Desert evolution and climatic changes in the Tarim River basin since 12 ka BP. Sci China Ser D-Earth Sci 1999;42:101-112.
- 9. Pi H, Sharratt B, Lei J. Windblown sediment transport and loss in a desert-oasis ecotone in the Tarim Basin. Sci Rep 2017;7:7723.
- 10. Wang M, Wei W, Ruan Z, He Q, Ge R. Application of wind-profiling radar data to the analysis of dust weather in the Taklimakan Desert. Environ Monit Assess 2013;185:4819-4834.
- 11. Hao X, Li W, Deng H. The oasis effect and summer temperature rise in arid regions - case study in Tarim Basin. Sci Rep 2016;6:35418.
- 12. Karim S, Budachetri K, Mukherjee N, Williams J, Kausar A, Hassan MJ, Adamson S, Dowd SE, Apanskevich D, Arijo A, Sindhu ZU, Kakar MA, Khan RMD, Ullah S, Sajid MS, Ali A, Iqbal Z. A study of ticks and tick-borne livestock pathogens in Pakistan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2017;11:e0005681.
- 13. Lv J, Wu S, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Feng C, Yuan X, Jia G, Deng J, Wang C, Wang Q, Mei L, Lin X. Assessment of four DNA fragments (COI, 16S rDNA, ITS2, 12S rDNA) for species identification of the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Parasit Vectors 2014;7:93.
- 14. Kawahara M, Rikihisa Y, Lin Q, Isogai E, Tahara K, Itagaki A, Hiramitsu Y, Tajima T. Novel genetic variants of Anaplasma phagocytophilum, Anaplasma bovis, Anaplasma centrale, and a novel Ehrlichia sp. in wild deer and ticks on two major islands in Japan. Appl Environ Microbiol 2006;72:1102-1109.
- 15. Lv J, Wu S, Zhang Y, Zhang T, Feng C, Jia G, Lin X. Development of a DNA barcoding system for the Ixodida (Acari: Ixodida). Mitochondrial Dna 2014;25:142.
- 16. de Marco M, Hernandez-Triana LM, Phipps LP, Hansford K, Mitchell ES, Cull B, Swainsbury CS, Fooks AR, Medlock JM, Johnson N. Emergence of Babesia canis in southern England. Parasit Vectors 2017;10:241.
- 17. Park HS, Lee JH, Jeong EJ, Koh SE, Park TK, Jang WJ, Park KH, Kim BJ, Kook YH, Lee SH. Evaluation of groEL gene analysis for identification of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato. J Clin Microbiol 2004;42:1270-1273.
- 18. de la Fuente J, Atkinson MW, Naranjo V, Fernandez de Mera IG, Mangold AJ, Keating KA, Kocan KM. Sequence analysis of the msp4 gene of Anaplasma ovis strains. Vet Microbiol 2007;119:375-381.
- 19. Burland TG. DNASTAR’s Lasergene sequence analysis software. Methods Mol Biol 2000;132:71-91.
- 20. Anstead CA, Chilton NB. A novel Rickettsia species detected in Vole Ticks (Ixodes angustus) from Western Canada. Appl Environ Microbiol 2013;79:7583-7589.
- 21. Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 2011;28:2731-2739.
- 22. Tian ZC, Liu GY, Shen H, Xie JR, Luo J, Tian MY. First report on the occurrence of Rickettsia slovaca and Rickettsia raoultii in Dermacentor silvarum in China. Parasit Vectors 2012;5:19.
- 23. Yang XJ, Chen Z, Liu JZ. The valid genus and species names of ticks (Acari: Ixodida: Argasidae, Ixodidae) in China. J Hebei Norm Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 2008;32:529-533.
- 24. Teng K. Notes on some chinese ticks of the genus ixodes with descriptions of two new species (acarina: ixodidae). Acta Entomologica Sinica 1973;16:73-81.
- 25. Li B. Community constitution and distribution of ticks in the Tarim Basin. Chin J Vector Biol Control 2006;17:390.
- 26. Estrada-Pena A, Jongejan F. Ticks feeding on humans: a review of records on human-biting Ixodoidea with special reference to pathogen transmission. Exp Appl Acarol 1999;23:685-715.
- 27. Aktas M. A survey of ixodid tick species and molecular identification of tick-borne pathogens. Vet Parasitol 2014;200:276-283.
- 28. Najm NA, Meyerkayser E, Hoffmann L, Herb I, Fensterer V, Pfister K, Silaghi C. A molecular survey of Babesia spp. and Theileria spp. in red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) and their ticks from Thuringia, Germany. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2014;5:386-391.
- 29. Abdullah S, Helps C, Tasker S, Newbury H, Wall R. Ticks infesting domestic dogs in the UK: a large-scale surveillance programme. Parasit Vectors 2016;9:391.
- 30. Milhano N, de Carvalho IL, Alves AS, Arroube S, Soares J, Rodriguez P, Carolino M, Nuncio MS, Piesman J, de Sousa R. Coinfections of Rickettsia slovaca and Rickettsia helvetica with Borrelia lusitaniae in ticks collected in a Safari Park, Portugal. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2010;1:172-177.
- 31. Guo L, Jiang S, Liu D, Wang S, Chen C, Wang Y. Emerging spotted fever group rickettsiae in ticks, northwestern China. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2016;7:1146-1150.
- 32. Guo W, Tian J, Lin X, Ni X, Chen X, Liao Y, Yang S, Dumler J, Holmes E, Zhang Y. Extensive genetic diversity of Rickettsiales bacteria in multiple mosquito species. Sci Rep 2016;6:38770.
- 33. Jinnai M, Kawabuchi-Kurata T, Tsuji M, Nakajima R, Fujisawa K, Nagata S, Koide H, Matoba Y, Asakawa M, Takahashi K, Ishihara C. Molecular evidence for the presence of new Babesia species in feral raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Hokkaido, Japan. Vet Parasitol 2009;162:241-247.