Abstract
Balantidium coli human infection predominantly occurs in tropical and subtropical regions in the world. Human case is extremely rare in China. This report details a case of B. coli infection in a 68-year-old man in China, who presented with history of abdominal pain, tenesmus, diarrhea with blood and was diagnosed as B. coli-caused dysentery. Our case indicates possible occurrence of Balantidium coli-related disease in cooler climates. This case is presented not only because of its rarity but also for future references.
-
Key words: Balantidium coli, dysentery, China
INTRODUCTION
Balantidium coli is considered the largest protozoon and the only ciliated protozoon known to infect humans and nonhuman primates [
1]. However, human infection with
B. coli is uncommon despite its potential for worldwide distribution [
1], which predominantly occurs in tropical and subtropical regions [
2]. To our knowledge, only 18 single-case reports of human infections with
B. coli have been found in English literature in limited countries from 2001 until now (
Table 1). As for China, very few human
B. coli infections have been detected and it is rarely seldom for Chinese clinicians or laboratory technicians to consider
B. coli as a possible pathogen in patients with diarrhea or dysentery; however, here we report a case of intestinal balantidiasis in China, which indicates possible occurrence of
B. coli -induced diseases in cooler climates.
CASE DESCRIPTION
A 68-year-old man from Liulin County, Luliang City, Shanxi Province, North China (37°25′48.89″ N, 110°53′21.73″ E) was admitted to Emergency Department with complaints of a one-week history of abdominal pain, tenesmus, diarrhea with blood and mucus. He also reported a series of symptoms of anorexia, nausea, vomiting, muscular weakness and weight loss. An epidemiological investigation revealed that he was employed as a pig farmer for 4 months.
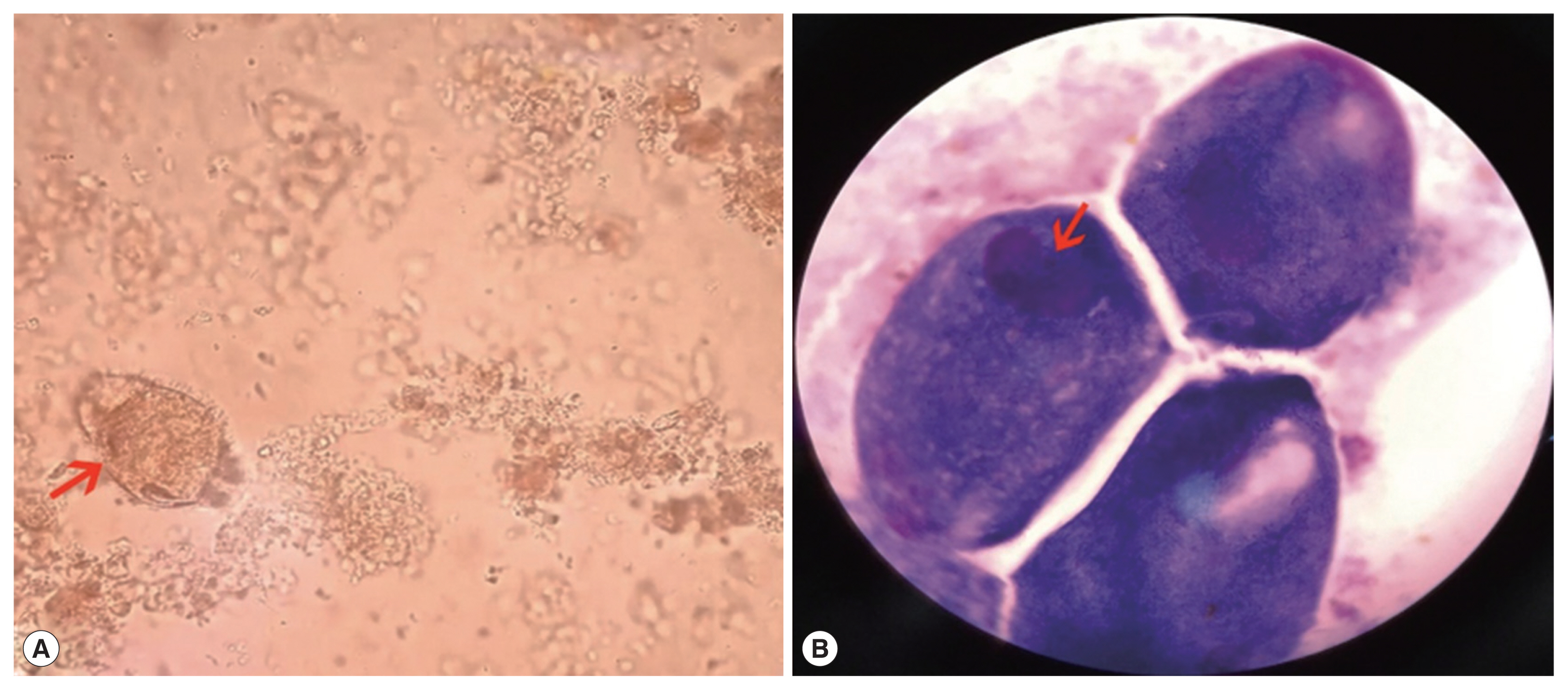
Routine blood testing upon admission displayed mild anemia (hemoglobin 111 g/L, reference interval 130–175 g/L). Serum potassium (2.94 mmol/L, reference interval 3.5–5.3 mmol/L), sodium (133.6 mmol/L, reference interval 137–147 mmol/L) and chloride (98.0 mmol/L, reference interval 99–110 mmol/L) were all outside normal limits. Stool occult blood testing was positive. Unpreserved bloody and mucus-containing stool was submitted to the laboratory. Microscopic observation in wet preparation demonstrated 4+ red blood cells and 4+ white blood cells per high power field. Uniformly covered with short cilia, some large oval trophozoites (approximately 50 μm by 80 μm) exhibiting rapid rotary-type motion were captured (
Fig. 1A). Two nuclei within the trophozoite were displayed in Wright-Giemsa stained smear, a smaller round micronucleus nestling against a larger kidney-shaped macronucleus (
Fig. 1B).
According to the result of morphological observation, the large active ciliated trophozoites were identified as
B. coli easily. Combining clinical manifestations, diagnosis of dysentery caused by
B. coli was soon established, which was further substantiated by the patient’s experience of working as a pig farmer because swine serves as the most important reservoir host for human infection with
B. coli [
1]. Once diagnosis was clear, oral metronidazole therapy for 2-weeks (750 mg 3 times daily) was administered to the patient which resulted in a full recovery. There were no further recurrences of
B. coli in stool after 6 months of follow-up.
DISCUSSION
The clinical manifestations of human infections with
B. coli can range from mild asymptomatic cases to cases of severe dysentery, which can even progress to life-threatening consequences [
1]. Theoretically, the symptoms of
B. coli-induced colitis may be confused with amebic colitis, hence
B. coli and
Entamoeba histolytica should be considered within a differential diagnosis of parasitic diarrhea or dysentery [
2], which is not difficult, in fact, because of their different sizes and modes of motion. Meanwhile, many extraintestinal sites of
B. coli disease have been reported, which can be seen from the results of cases review (
Table 1). It is worth mentioning that it should be careful to differentiate between
B. coli trophozoites and ciliated epithelial cells from pulmonary specimens [
20].
The life cycle of
B. coli consists of cysts or trophozoites. Trophozoites and cysts are both characterized by 2 nuclei. However, the micronucleus is usually not visible within the trophozoite or cyst in both stained preparations and on wet mounts [
20]. Surprisingly, the micronucleus in trophozoites was observed in Wright-Giemsa stained smear in our case. It is often difficult to distinguish motionless trophozoites from cysts. One important difference is that cilia are visible surrounding trophozoites but invisible in cysts form because cilia are contained within cysts wall [
20].
Laboratory diagnosis of B. coli-induced infection is relatively easy because of rapid spiraling motility and large size of trophozoites. Routine stool examinations, particularly wet-preparation examinations of fresh stools are of practical significance and permanent stained smear is not strictly necessary because B. coli are so large that they tend to stain very darkly, which is not conducive to observe the ciliate and internal structure. Some clearer images of trophozoite in Wright-Giemsa stained smear were lucky to be captured in this case.
In conclusions, the present case is a rare report of human infection caused by B. coli in China, which imply the likelihood of development of B. coli-induced human infections in cooler climates. The cases review since 2001 provides valuable data for the framework of human infections in B. coli worldwide.
Notes
-
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to thank Yuan Yao, Associate Professor in Shandong Medical College, for his help in identifying the parasite.
Fig. 1(A) Wet preparation demonstrating large trophozoite (arrow) (×400). (B) Wright-Giemsa staining demonstrating macronucleus and micronucleus within trophozoite (arrow) (×1,000).
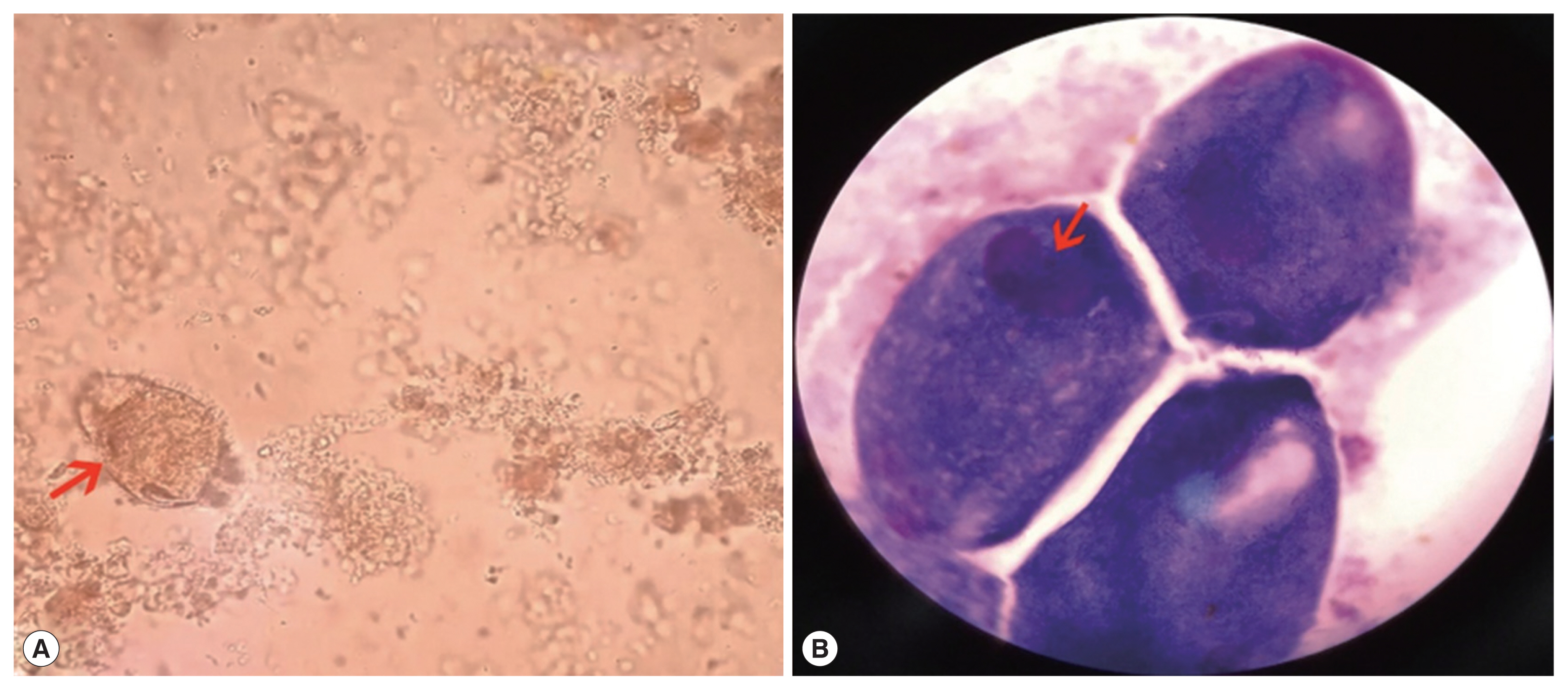
Table 1Literature reports of human infections caused by Balantidium coli (since 2001)
Table 1
|
Sex |
Age |
Country |
Detected specimen |
Year of publication |
Reference |
|
F |
71 |
Greece |
bronchial secretions |
2003 |
[3] |
|
M |
32 |
Venezuela |
stool |
2003 |
[4] |
|
M |
42 |
Canada |
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
2003 |
[5] |
|
F |
58 |
Greece |
bronchoalveolar lavage fluid |
2003 |
[6] |
|
F |
47 |
Turkey |
stool |
2004 |
[7] |
|
M |
54 |
France |
anatomic colon specimen |
2004 |
[8] |
|
F |
29 |
India |
urine |
2007 |
[9] |
|
M |
20 |
South Africa |
bronchial lavage fluid |
2010 |
[10] |
|
M |
56 |
Italy |
urine |
2010 |
[11] |
|
M |
60 |
India |
histological examination |
2013 |
[12] |
|
F |
72 |
India |
urine |
2013 |
[13] |
|
M |
23 |
France |
stool |
2013 |
[14] |
|
M |
68 |
India |
urine |
2014 |
[15] |
|
F |
55 |
India |
urine |
2014 |
[16] |
|
M |
37 |
India |
stool |
2016 |
[17] |
|
M |
48 |
India |
liver aspirate |
2016 |
[2] |
|
M |
22 |
India |
corneal scrapings, CL cleaning solution |
2016 |
[18] |
|
M |
60 |
India |
urine |
2016 |
[19] |
References
- 1. Schuster FL, Ramirez-Avila L. Current world status of Balantidium coli
. Clin Microbiol Rev 2008;21:626-638.
- 2. Kapur P, Das AK, Kapur PR, Dudeja M.
Balantidium Coli liver abscess: first case report from India. J Parasit Dis 2016;40:138-140.
- 3. Vasilakopoulou A, Dimarongona K, Samakovli A, Papadimitris K, Avlami A.
Balantidium coli pneumonia in an immunocompromised patient. Scand J Infect Dis 2003;35:144-146.
- 4. Cermeno JR, Hernandez De Cuesta I, Uzcategui O, Páez J, Rivera M, Baliachi N.
Balantidium coli in an HIV-infected patient with chronic diarrhoea. AIDS 2003;17:941-942.
- 5. Sharma S, Harding G. Necrotizing lung infection caused by the protozoan Balantidium coli
. Can J Infect Dis 2003;14:163-166.
- 6. Anargyrou K, Petrikkos GL, Suller MT, Skiada A, Siakantaris MP, Osuntoyinbo RT, Pangalis G, Vaiopoulos G. Pulmonary Balantidium coli infection in a leukemic patient. Am J Hematol 2003;73:180-183.
- 7. Yazar S, Altuntas F, Sahin I, Atambay M. Dysentery caused by Balantidium coli in a patient with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma from Turkey. World J Gastroenterol 2004;10:458-459.
- 8. Ferry T, Bouhour D, De Monbrison F, Laurent F, Dumouchel-Champagne H, Picot S, Piens MA, Granier P. Severe peritonitis due to Balantidium coli acquired in France. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2004;23:393-395.
- 9. Umesh S.
Balantidium coli on urine microscopy. Natl Med J India 2007;20:270.
- 10. Koopowitz A, Smith P, van Rensburg N, Rudman A.
Balantidium coli-induced pulmonary haemorrhage with iron deficiency. S Afr Med J 2010;100:534-536.
- 11. Maino A, Garigali G, Grande R, Messa P, Fogazzi GB. Urinary balantidiasis: diagnosis at a glance by urine sediment examination. J Nephrol 2010;23:732-737.
- 12. Dhawan S, Jain D, Mehta VS.
Balantidium coli: an unrecognized cause of vertebral osteomyelitis and myelopathy. J Neurosurg Spine 2013;18:310-313.
- 13. Bandyopadhyay A, Majumder K, Goswami BK.
Balantidium coli in urine sediment: report of a rare case presenting with hematuria. J Parasit Dis 2013;37:283-285.
- 14. Bellanger AP, Scherer E, Cazorla A, Grenouillet F. Dysenteric syndrome due to Balantidium coli: a case report. New Microbiol 2013;36:203-205.
- 15. Karuna T, Khadanga S. A rare case of urinary balantidiasis in an elderly renal failure patient. Trop Parasitol 2014;4:47-49.
- 16. Khanduri A, Chauhan S, Chandola I, Mahawal B, Kataria V. Balantidiosis: a rare accidental finding in the urine of a patient with acute renal failure. J Clin Diagn Res 2014;8:DD03-DD04.
- 17. Kumar M, Rajkumari N, Mandal J, Parija SC. A case report of an uncommon parasitic infection of human balantidiasis. Trop Parasitol 2016;6:82-84.
- 18. Hazarika M, Pai HV, Khanna V, Reddy H, Tilak K, Chawla K. Rare case of polymicrobial keratitis with Balantidium coli
. Cornea 2016;35:1665-1667.
- 19. Kaur S, Gupta A. Urinary balantidiasis: A rare incidental finding in a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Cytol 2016;33:169-171.
- 20. Garcia Lynne S. Diagnostic Medical Parasitology. 6th ed.. Washington, USA. John Wiley & Sons; 2016, pp 605-608.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- Development and application of a novel beta-tubulin genotyping tool reveals host-specific transmission cluster in Balantioides coli
Suhui Hu, Wen Zhang, Zhenzhen Liu, Junzhen Cheng, Qihao Zhang, Weifeng Qian, Min Zhang, Tianqi Wang, Wenchao Yan, Mehmet Aykur
PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.2025; 19(8): e0013426. CrossRef - The Presence of Potentially Pathogenic Protozoa in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) Sold in Markets in the Central Peruvian Andes
J. Raul Lucas, Daphne Ramos, S. Sonia Balcázar, Carlos Santos
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(2): 943. CrossRef - Balantidiasis in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Rayana Katylin Mendes da Silva, Laís Verdan Dib, Maria Regina Amendoeira, Camila Carvalho Class, Jessica Lima Pinheiro, Ana Beatriz Monteiro Fonseca, Alynne da Silva Barbosa
Acta Tropica.2021; 223: 106069. CrossRef - Identification of Zoonotic Balantioides coli in Pigs by Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) and Its Distribution in Korea
Jae-Won Byun, Jung-Hyun Park, Bo-Youn Moon, Kichan Lee, Wan-Kyu Lee, Dongmi Kwak, Seung-Hun Lee
Animals.2021; 11(9): 2659. CrossRef - Prevalence and risk factors of human Balantidium coli infection and its association with haematological and biochemical parameters in Ga West Municipality, Ghana
Enoch Aninagyei, Salifu Nanga, Desmond Omane Acheampong, Rita Mensah, Mercy Nelly Boadu, Henrietta Terko Kwansa-Bentum, Clement Okraku Tettey
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Balantidiasis: A Neglected Tropical Disease Used as a Study Model for a Holistic Approach to Sustainable Development in the Framework of Agenda 2030 Goals
Luca Nalbone, Filippo Giarratana, Ettore Napoli
Sustainability.2021; 13(22): 12799. CrossRef