Abstract
Clonorchis sinensis is the most common fish-borne intestinal parasite in Korea. The aim of the present investigation was to survey the status of C. sinensis infection and analyze associated risk factors in residents of Haman-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do. A total of 5,114 residents from 10 administrative towns/villages voluntarily agreed to participate in the study, which comprised fecal examination, a questionnaire survey for risk factors, ultrasonography, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for cancer biomarker detection in the blood. We detected C. sinensis eggs in 5.3% of the subjects. By region, Gunbuk-myeon had the highest number of residents with C. sinensis eggs. The infection rate and intensity were higher in male than in female residents. Based on the risk factor questionnaire, infection was highly associated with drinking, a history of C. sinensis infection, and the practice of eating of raw freshwater fish. Extension of the bile duct, infection intensity, and cancer biomarker detection significantly correlated with the presence of eggs in the study population. In conclusion, the development of feasible, long-term control policies and strategies for the elimination of C. sinensis in Korea is still required.
-
Key words: Clonorchis sinensis, risk factor, freshwater fish, fish-borne trematode, Haman-gun, Korea
INTRODUCTION
Due to socio-economic development in Korea, soil-transmitted intestinal parasites, such as
Ascaris lumbricoides, reached the level of eradication in 1990; however, fish-borne parasites, such as
Clonorchis sinensis, remain a source of infection [
1]. According to the 8th Nationwide Survey for Intestinal Parasites (NSIP) in 2012, the intestinal parasite infection rate in Korea was 2.6% (approximately 1.3 million people), and the most common parasite was
C. sinensis, which accounted for infection of 1.9% of the population [
1]. The liver fluke
Clonorchis sinensis is a representative fish-borne parasite, which can be transmitted by eating raw freshwater fish infected with
C. sinensis metacercariae. The traditional and cultural practice of eating raw freshwater fish continues in modern-day Korea and is particularly common among residents living in river basins in the southern part of Korea. Chronic infection with
C. sinensis can parasitize the biliary tract for up to 20 years and cause digestive symptoms such as bloating, indigestion, and jaundice. In severe cases, it acts as a biological carcinogen and causes cholangiocarcinoma [
2]. According to the annual report of cancer statistics in Korea in 2016, the highest incidence of gallbladder and other biliary cancers in men from 2004 to 2013 was 18.3% in Haman-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do, followed by 15.9% in Miryang-si, and 15.7% in Changnyeong-gun [
3]. However, the risk factor analysis of
C. sinensis infection associated with biliary cancers are still lacking among the above prevalent villages.
The aim of the present study was to survey the status of C. sinensis infection and determine its associated risk factors among residents in Haman-gun.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Ethics statement
The investigations were approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Permit number KCDC-2017-02-02).
Study population
Given that the region had the highest incidence of gall bladder and other biliary cancers in the annual report of cancer statistics from 2016, we selected Haman-gun for our study. We enrolled 5,114 residents from 10 administrative towns/villages who voluntarily agreed to participate in the present investigation from March to August 2017. Blood and fecal samples which were obtained from all of 5,114 residents were submitted with questionnaires to the KCDC.
Feces sampling and examination
We acquired feces from the residents to diagnose C. sinensis infection. Of the sample, 1 g was pretreated for the modified formalin-ether method, to detect C. sinensis egg by microscopic examination, directly. The infection intensity per gram of feces (eggs per gram) was defined to determine the total C. sinensis egg count among the sediment.
Ultrasonography
Ultrasonography was performed on the upper abdomen of residents (n=156) with
C. sinensis eggs in their fecal samples to identify anatomical abnormalities such as biliary tract enlargement in the liver, in comparison with non-infected people (n=140) [
4].
We tested for the expression of the cancer biomarkers CA19-9, ferritin, and CYFRA 21-1, which are associated with biliary cancer, by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in residents that were positive and negative for
C. sinensis infection [
5–
6].
A questionnaire composed of 8 items related to risk factors for C. sinensis infection, such as the habit of eating raw freshwater fish, was filled out by an investigator in a local public health center through a direct interview with the residents. Any unanswered questions were treated as missing values. The stool test, questionnaire survey, ultrasonography, and cancer index test results were analyzed by t-test, chi-square analysis, logistic regression analysis, and linear-by-linear analysis with the SPSS v21.0 statistical program (SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA).
RESULTS
Sociodemographic characteristics of the participants
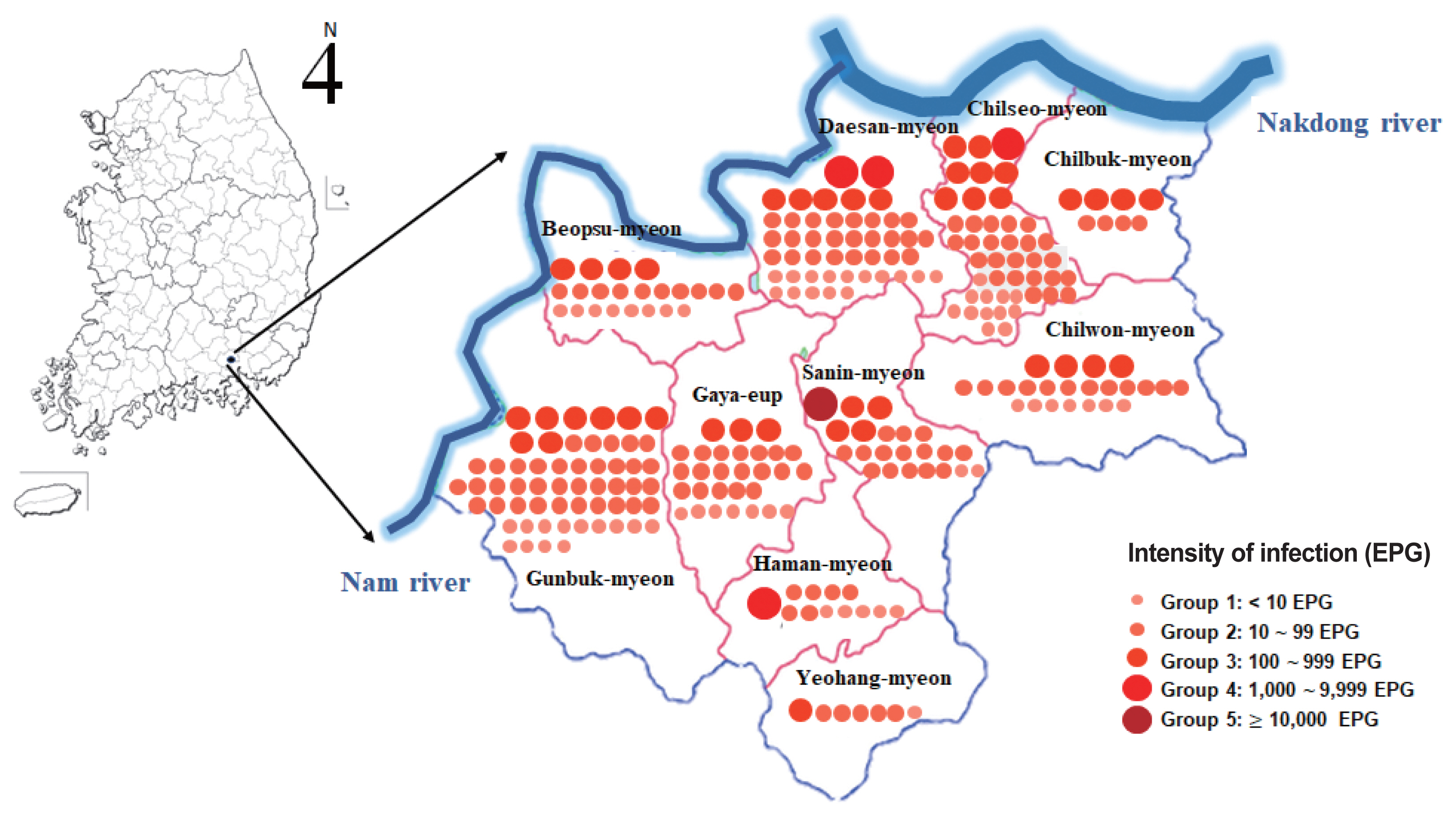
Inside the boundary of Haman-gun, the participation rate of Chilbuk-myeon (23.6%) was the highest in the region of the Nakdong River basin, that of Beopsu-myeon (13.9%) was the highest in the region of the Nam River basin, and that of Yeohang-myeon (19.9%) was the highest in the other areas (
Supplementary Table S1). Among the 5,114 residents, there were more female than male participants. Resident over the age of 60 accounted for more than 80% of the total cohort, and those of the 70 accounted for the largest 36.9% (
Table 1).
The overall
C. sinensis infection rate was 5.3% (270/5,114). By region, Gunbuk-myeon, which is located in the Nam River basin, had the highest infection rate with 8.5%, followed by Daesan-myeon with 7.0%. Among inland areas, Sanin-myeon had an infection rate of 5.7%, followed by 5.4% in Gaya-eup. In general, the infection rates were higher in regions adjacent to rivers than in inland regions. Chilbuk-myeon, which is in the Nakdong River basin, had an infection rate of 1.6%, which was the lowest among the regions represented (
Fig. 1).
More male residents were infected with
C. sinensis than female residents. In addition, the mean
C. sinensis infection intensity (224.6 eggs/g) in male residents was significantly higher than in female residents (
P<0.001,
Supplementary Fig. S1).
All subjects under the age of 30 (n=40) were identified as non-infected. The infection rate increased among residents over the age of 50, especially among those in 50 and 60 (
Table 1).
Liver fluke infection was highly associated with alcohol and tobacco use; the liver fluke infection rate was significantly higher among the resident in the group that drank alcohol 2–3 times/week than in other groups (
P<0.0001). Many residents among those infected with liver flukes had an infection history characterized by diagnosis with clonorchiasis (
P=0.024), and infection highly correlated with raw freshwater fish consumption in the past year (
P<0.0001). In addition, we observed a strong correlation between the symptoms of hepatitis and infection within the last 3 months (
P<0.002). However, there were no correlations between liver or biliary tract disease and infection among the participants or their families (
Table 2).
We analyzed 270 participants infected with
C. sinensis and 47 non-infected participants by ultrasonography. Among the infected residents, 84.7% had biliary dilatation, and the degree of intrahepatic biliary dilatation proportionally increased with the severity of infection (
Supplementary Fig. S2).
To ascertain the relationship between
C. sinensis infection and carcinogenesis, we estimated the positivity of the cancer biomarkers CA19-9, ferritin, and CYFRA 21-1 in the serum of residents. We found that 43.7% of infected resident were positive to single biomarker and 5.9% were positive to 2 or more biomarkers, which were significantly higher proportions than among non-infected residents (13.9% and 1.2%, respectively) (
P<0.0001,
Table 3).
DISCUSSION
In 2012, the total
C. sinensis infection rate in Korea was 1.9% [
1]. The population at high risk of
C. sinensis infection comprises resident who live on the banks of rivers, such as the Nakdong River and Yeongsan River, in the southern part of Korea and who eat raw freshwater fish [
1,
7,
8]. Although we surveyed for
C. sinensis infection during a similar period, the infection rate we detected in Haman-gun (5.3%) was higher than that in the Gyeongnam area (4.2%) in the NSIP, but lower than that in the Nakdong River basin (13.8%) in 2013 [
1,
7]. Residents living on the banks of both rivers in Haman-gun had a high risk of exposure to
C. sinensis infection because of the traditional practice of eating freshwater fish [
7,
8].
Male subjects had a higher infection rate and infection intensity than female subjects, likely due to repeated exposure to freshwater fish through various social activities such as the consumption of raw fish with alcohol. This may be one of the reasons for the high incidence of bile duct cancer in men in Haman-gun. In the previous literature on
C. sinensis infection, infection in males frequently occurred during the process of sharing freshwater fish, such as while handling or eating raw freshwater fish, that are infected with the metacercariae of
C. sinensis. However, women have a relatively low infection rate due to a low prevalence of eating raw freshwater fish; infections in women commonly occur due to exposure to metacercariae while cooking at home [
9,
10]. Also, in the present investigation, male residents were infected with
C. sinensis was higher than that of female residents. In addition, an intensity with
C. sinensis infection in male was significantly higher than in female residents, which this trend was showed in all towns and villages in Haman-gun. As regards of ages, egg positivity in fifties was the highest group in ages, followed 60 and over 70, suggesting that the habit of eating raw freshwater fish remains common in older inhabitants of the region.
Drinking is also a high-risk factor for infection in residents of Haman-gun. In particular, the infection rate was high in residents who drank alcohol 2–3 times/wk. Infection is, thus, likely related to the drinking culture that accompanies the consumption of raw freshwater fish [
7,
8].
The infection rate was high in the group that had a history of diagnosis with parasitic disease and eating raw freshwater fish in the previous year. It may be hard to eliminate C. sinensis infection in Korea due to the difficulty of recognizing some clinical symptoms, such as abdominal distention and jaundice in chronic infection, which are easily cured by administering an anthelmintic drug (Praziquantel), and due to repeated exposure to C. sinensis infection via eating raw freshwater fish.
Clonorchis sinensis invades the bile duct in the liver where it stimulates epithelial cells and causes thickening of the wall and expansion of the biliary tract, resulting in chronic inflammation and structural (pathological) deformation of the biliary tract, thereby increasing the long-term risk of developing biliary cancer [
2,
11,
12]. Ultrasonography is used to screen for chronic infection with
C. sinensis as it can reveal pathological deformation of the liver and biliary tract [
13,
14]. Consistent with previous reports, we found that 84.7% of those infected with
C. sinensis showed intrahepatic biliary dilatation.
Currently, there is no standard diagnostic method for cholangiocarcinoma. Furthermore, a diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma is beyond curative treatment. In recent years, many studies have identified diagnostic cancer-related metabolite biomarkers for cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma [
5,
6]. In this study, we analyzed the expression of 3 cancer biomarkers (CA19-9, ferritin, and CYFRA 21-1) in resident infected with
C. sinensis. We detected expression of 1 or more of these markers in resident infected with
C. sinensis, suggesting that a long-term follow-up on biliary cancer incidence in
C. sinensis-infected resident should be conducted. For detection of CCA, several serum makers, such as CA19-9, CA242, CYFRA21-1, MK-1, C-reactive protein, have been reported as a diagnostic and prognostic marker [
15,
16]. However, none of them alone show the sensitivity and specificity high enough to confirm CCA. In addition to these cancer markers, association studies of a various cancer biomarker candidates with infection should be performed in large populations in high-risk regions and in patients with cholangiocarcinoma. In the future, efforts will be needed to track the development of the infection into biliary cancer using cancer indicator tests, which will require the development of an early diagnosis method for biliary cancer. It will also be important to further investigate the link between progression and treatment, to address the potential health threats posed by
C. sinensis infection.
In conclusion, C. sinensis infection was highly prevalent among residents in Haman-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do. Infection highly correlated with alcohol and tobacco use, eating raw freshwater fish, and biliary tract expansion in the liver. We also detected cancer biomarker expression in infected residents. All residents infected with C. sinensis were prescribed praziquantel, educated on methods to prevent C. sinensis infection, and provided health checks in long-term follow-ups. As a long-term strategy, we recommend intensive campaigns to raise awareness and educate the population on the prevention of C. sinensis infection, focusing on high-risk endemic regions, to suppress the risk factors for C. sinensis infection.
Notes
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Table S1.
Sociodemographic characteristics of the Haman-gun residents participated in this study. The number of participating residents from 10 administrative towns/villages along rivers within Haman-gun
Supplementary Fig. 1.
Clonorchis sinensis egg positivity rate and eggs per gram of fecal matter displayed by gender. EPG,
eggs per gram of feces.
Supplementary Fig. 2.
Relationship between the intensity of Clonorchis sinensis infection and dilatation of the intrahepatic biliary tract. EPG, eggs per gram of feces.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Dr. Jeon, Byeong-Hak for statistical analysis for this investigation. This work was supported by funding from the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2017, 4837-311).
Fig. 1Distribution of residents positive for Clonorchis sinensis eggs in 10 administrative towns/villages in Haman-gun, Gyeongsangnam-do, Republic of Korea. Red dot represents a resident infected with C. sinensis. EPG, eggs per gram of feces.
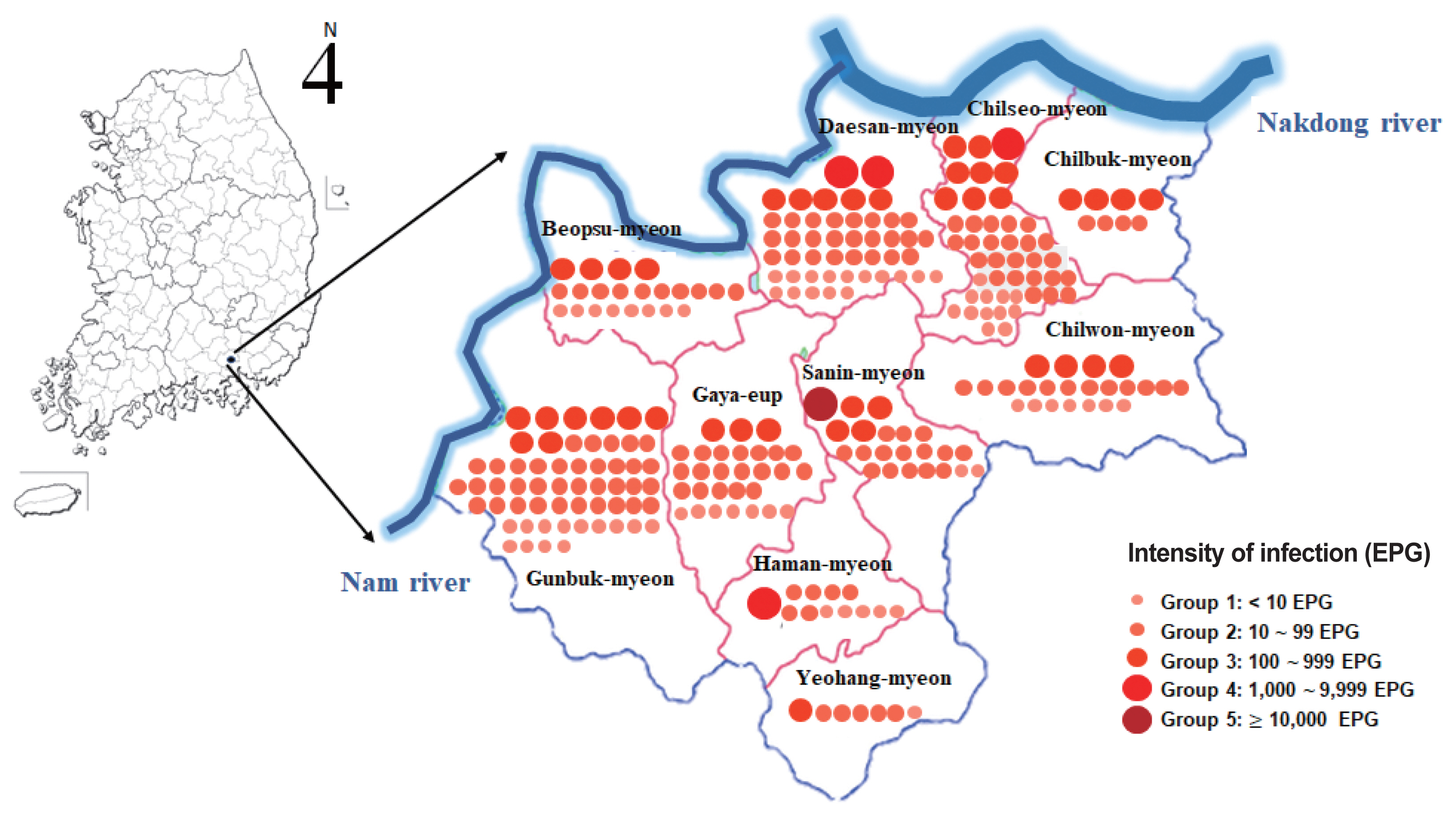
Table 1
Clonorchis sinensis egg positive rate of residents categorized by gender and age
Table 1
|
Group |
No. of residents |
No. of participants (%) |
No. of infected residents (%) |
Prevalence of eating raw fish (%) |
|
Male |
- |
1,729 (33.8) |
132 (7.63) |
64.8 |
|
|
Female |
- |
3,385 (66.1) |
138 (4.08) |
58.3 |
|
|
Age (yr) |
|
<30 |
19,410 |
40 (0.28) |
0 (0.00) |
35.0 |
|
30–39 |
8,144 |
89 (0.12) |
3 (3.37) |
50.6 |
|
40–49 |
10,844 |
221 (0.16) |
4 (1.81) |
48.9 |
|
50–59 |
11,851 |
593 (0.17) |
41 (6.91) |
63.6 |
|
60–69 |
8,773 |
1,251 (0.13) |
94 (7.51) |
63.5 |
|
>70 |
10,026 |
2,920 (0.15) |
128 (4.38) |
60.1 |
|
|
Total |
69,048 |
5,114 (1.00) |
270 (5.28) |
60.5 |
Table 2Correlation between Clonorchis sinensis egg positive rates and risk factors in Haman-gun, Republic of Korea
Table 2
|
Factor |
Clonorchis sinensis eggs |
Total |
OR (95% CI) |
P-value |
|
|
Positive (%) |
Negative (%) |
|
No. of alcoholic drinks/week |
|
|
|
|
|
|
None |
152 (4.1) |
3,530 (95.9) |
3,682 |
Ref |
|
|
1/week |
43 (6.4) |
627 (93.6) |
670 |
1.593 (1.123–2.258) |
0.0090*
|
|
2–3 times/week |
25 (7.1) |
327 (92.9) |
352 |
1.776 (1.146–2.751) |
0.0102*
|
|
4 times/week |
48 (14.2) |
290 (85.8) |
338 |
3.844 (2.720–5.432) |
<0.0001*
|
|
Subtotal |
268 (5.3) |
4,774 (94.7) |
5,042 |
|
|
|
|
No. of cigarettes/days |
|
|
|
|
|
|
None |
226 (85.0) |
4,372 (91.9) |
4,598 |
Ref |
|
|
10/day |
14 (5.3) |
192 (4.0) |
206 |
1.411 (0.807–2.467) |
0.2276 |
|
20/day |
20 (7.5) |
148 (3.1) |
168 |
2.614 (1.608–4.249) |
0.0001*
|
|
20+/day |
6 (2.3) |
45 (1.0) |
51 |
2.579 (1.089–6.109) |
0.0313*
|
|
Subtotal |
266 (5.3) |
4,757 (94.7) |
5,023 |
|
|
|
|
History of C. sinensis infection |
|
|
|
|
0.024**
|
|
No |
196 (4.9) |
3,768 (95.1) |
3,964 |
|
|
|
Yes |
62 (6.7) |
869 (93.3) |
931 |
|
|
|
Subtotal |
258 (5.3) |
4,637 (94.7) |
4,895 |
|
|
|
|
Eaten raw freshwater fish within the past year |
|
|
|
|
0.000**
|
|
No |
79 (3.9) |
1,940 (96.1) |
2,019 |
|
|
|
Yes |
191 (6.2) |
2,904 (93.8) |
3,095 |
|
|
|
Subtotal |
270 (5.3) |
4,844 (94.7) |
5,114 |
|
|
|
|
Experienced symptoms of hepatitis in the last 3 mo |
|
|
|
|
|
|
No |
222 (5.3) |
4,844 (94.7) |
5,114 |
|
|
|
Yes |
48 (3.7) |
1,247 (96.3) |
1,295 |
|
0.002**
|
|
Subtotal |
270 (5.3) |
4,844 (94.7) |
5,114 |
|
|
Table 3Detection of cancer markers in infected and non-infected residents
Table 3
|
Cancer markers detected (%) |
|
Subtotal |
1 |
2 or more |
Not detected |
|
Total (%) |
600 |
27.3 |
3.3 |
69.3 |
|
Infected residents |
270 |
43.7*
|
5.9*
|
50.4 |
|
Non-infected residents |
330 |
13.9 |
1.2 |
84.8 |
References
- 1. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National survey of the prevalence of Intestinal Parasitic Infections in Korea, the 8th Report. Osong, Korea. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. 2013, (in Korean).
- 2. Qian MB, Utzinger J, Keiser J, Zhou XN. Clonorchiasis. Lancet 2016;387:800-810. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60313-0
- 3. Korea Central Cancer Registry, National Cancer Center. Annual Report of Cancer Statistics in Korea in 2016. Ministry of Health and Welfare. 2018, (in Korean).
- 4. Choi MS, Choi D, Choi MH, Ji Z, Li Z, Cho SY, Hong KS, Rim HJ, Hong ST. Correlation between sonographic findings and infection intensity in clonorchiasis. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2005;73:1139-1144.
- 5. Malaguarnera G, Paladina I, Giordano M, Malaguarnera M, Bertino G, Berretta M. Serum markers of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Dis Markers 2013;34:219-228. https://doi.org/10.3233/DMA-130964
- 6. Banales JM, Iñarrairaegui M, Arbelaiz A, Milkiewicz P, Muntané J, Muñoz-Bellvis L, La Casta A, Gonzalez LM, Arretxe E, Alonso C, Martínez-Arranz I, Lapitz A, Santos-Laso A, Avila MA, Martínez-Chantar ML, Bujanda L, Marin JJG, Sangro B, Macias RIR. Serum metabolites as diagnostic biomarkers for cholangiocarcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 2019;70:547-562. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30319
- 7. June KJ, Cho SH, Lee WJ, Kim C, Park KS. Prevalence and risk factors of clonorchiasis among the populations served by primary healthcare posts along five major rivers in South Korea. Osong Public Health Res Perspect 2013;4:21-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2012.12.002
- 8. Shin HE, Lee MR, Ju JW, Jeong BS, Park MY, Lee KS, Cho SH. Epidemiological and clinical parameters features of patients with clonorchiasis in the Geum river basin, Republic of Korea. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis 2017;2017:7415301. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7415301
- 9. Vinh HQ, Phimpraphai W, Tangkawattana S, Smith JF, Kaewkes S, Dung DT, Duong TT, Sripa B. Risk factors for Clonorchis sinensis infection transmission in humans in northern Vietnam: a descriptive and social network analysis study. Parasitol Int 2017;66:74-82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2016.11.018
- 10. Park DS, Na SJ, Cho SH, June KJ, Cho YC, Lee YH. Prevalence and risk factors of clonorchiasis among residents of riverside areas in Muju-gun, Jeollabuk-do, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2014;52:391-397. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2014.52.4.391
- 11. The International Agency for Research on Cancer. Opisthorchis viverrini and Clonorchis sinensis. IARC, IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans 100B, A Review of Human Carcinogens: Biological Agents. Lyon, France. IARC. 2012, pp 341-370.
- 12. Bouvard V, Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Freeman C, Galichet L, Cogliano V. A review of human carcinogens--Part B: biological agents. Lancet Oncol 2009;10:321-322. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(09)70096-8
- 13. Chung BS, Lee JK, Choi MH, Park MH, Choi D, Hong ST. Single nucleotide polymorphisms of cytokine genes are associated with fibrosis of the intrahepatic bile duct wall in human clonorchiasis. Korean J Parasitol 2009;47:145-151. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2009.47.2.145
- 14. Choi D, Hong ST. Imaging diagnosis of clonorchiasis. Korean J Parasitol 2007;45:77-85. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2007.45.2.77
- 15. Wongkham S, Silsirivanit A. State of Serum Markers for Detection of Cholangiocarcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2012;13:17-27.
- 16. Wang B, Chen L, Chang HT. Potential diagnostic biomarkers for cholangiocarcinoma in serum and bile. Biomark Med 2016;10:613-619. https://doi.org/10.2217/bmm-2015-0062