Abstract
Ion channels are important targets of anthelmintic agents. In this study, we identified 3 types of ion channels in Ascaris suum tissue incorporated into planar lipid bilayers using an electrophysiological technique. The most frequent channel was a large-conductance cation channel (209 pS), which accounted for 64.5% of channels incorporated (n=60). Its open-state probability (Po) was ~0.3 in the voltage range of −60~+60 mV. A substate was observed at 55% of the main-state. The permeability ratio of Cl− to K+ (PCl/PK) was ~0.5 and PNa/PK was 0.81 in both states. Another type of cation channel was recorded in 7.5% of channels incorporated (n=7) and discriminated from the large-conductance cation channel by its smaller conductance (55.3 pS). Its Po was low at all voltages tested (~0.1). The third type was an anion channel recorded in 27.9% of channels incorporated (n=26). Its conductance was 39.0 pS and PCl/PK was 8.6±0.8. Po was ~1.0 at all tested potentials. In summary, we identified 2 types of cation and 1 type of anion channels in Ascaris suum. Gating of these channels did not much vary with voltage and their ionic selectivity is rather low. Their molecular nature, functions, and potentials as anthelmintic drug targets remain to be studied further.
-
Key words: single channel, cation channel, anion channel, substate, nematode
INTRODUCTION
In nematodes, ligand- and voltage-gated ion channels such as nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAchR), GABA receptors, glutamate-gated Cl
− channels, and large-conductance voltage- and Ca2
+- activated K
+ channels have been extensively studied as targets of major anthelmintics [
1–
4]. Additional channels including TRP channels were also identified from the analysis of the
Caenorhabditis elegans genome [
5].
Cholinomimetic anthelmintics including levamisole and pyrantel act on nAchR located in the muscle and induce a depolarizing block in muscle cells. Drugs such as piperazine act on the extrasynaptic, ionotropic GABA receptors in the
Ascaris suum (
A. suum) muscle cell bag. Macrocyclic lactones such as ivermectin act on the glutamate-gated Cl
− channel. Piperazine-like drugs and macrocyclic lactones induce muscle relaxation by Cl
− influx and resulting hyperpolarization of muscle cells. Buxton et al. [
6] further identified subtypes of nAchR that are the targets of important classical anthelmintics like levamisole and pyrantel, as well as novel anthelmintics like tribendimidine and derquantel.
In addition to ligand-gated ion channels, anthelmintics also target intrinsic voltage-gated membrane ion channels such as large-conductance Ca
2+-activated K
+ channels [
4,
7]. Indeed, the “resistance-busting” anthelmintic, emodepside, has a novel mode of action involving Slo-1-like K
+ current in adult
A. suum muscle [
8], and this channel is directly activated by emodepside [
9]. Buxton et al. [
10] further demonstrated that Slo-1 can be directly activated by diethylcarbamazine, which was previously considered to indirectly induce anthelmintic effects through activation of the innate, non-specific immune system, independent of the adaptive, antigen-specific, immune response [
11]. Recently, Verma et al. [
12] demonstrated that diethylcarbamazine directly activates TRP channels, including TRP-2, and increases Ca
2+ influx. The elevated intracellular Ca
2+ then activates the Slo-1 channel, and the resulting K
+ outflux hyperpolarizes the muscle cells in the filaria,
Brugia malayi. These findings elucidate mechanisms underlying the rapid onset and short-lasting therapeutic actions of diethylcarbamazine, which was previously an unresolved question.
Anthelmintics are still the first choice for the treatment and prophylaxis of nematode infection [
13] and new classes of “resistance-busting” anthelmintics (emodepside, monepantel, and derquantel) have been released into the market [
4,
14]. However, resistance to anthelmintic drugs is growing [
15,
16]. The search for targets of new anthelmintic candidates cannot be overlooked to combat resistance to the currently available anthelmintics. In search for novel ion channels, we screened the ion channels of
A. suum incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. This approach has been employed to characterize electrophysiological properties of single ion channels [
17,
18]. Using this method, we have previously identified single channels in the tissues of
Fasciola hepatica [
19,
20].
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Chemicals
Synthetic phospholipids—1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (PE), 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (PC), and 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-phosphoserine (PS)—were purchased from Avanti Polar Lipids (Alabaster, Alabama, USA). All other reagents were purchased from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, Missouri, USA).
Vesicle preparation
A. suum specimens were regularly and freshly obtained from a local abattoir in Suwon, Korea. Vesicle preparation was adapted from previous methods as follows [
18–
20]. After opening the cuticle, muscle tissue in the main body was dissected out and collected in 0.3 M sucrose buffer (10 mM HEPES, 0.2 mM EDTA, 3 mM NaN
3, pH 7.4 adjusted with 2 N NaOH) at 0–4°C. The tissue was homogenized and centrifuged as described previously. The microsomal fractions banding at the 10%/20%, 20%/30%, and 30%/40% sucrose interfaces were separately collected and pelleted at 100,000×g for 1 hr. The resulting pellets were re-suspended in 10% sucrose buffer and stored at −70°C until use.
Planar lipid bilayers and vesicle fusion
Channels were incorporated into planar lipid bilayers composed of PE:PC:PS (70:20:10) in decane (25 mg/ml) according to the methods reported previously [
19,
20]. The lipid solution was applied with a thin glass rod over the aperture (200 μm) of a polystyrene cup (0.6 ml; designated as the
trans compartment). The front compartment of the recording chamber (1.2 ml), to which the membrane preparation was added, was defined as the
cis compartment. Two compartments were filled with aqueous solutions containing 10 mM N-[2-hydroxyethyl]-piperazine-N′-[2-ethanesulfonic acid] (HEPES), adjusted to a pH of 7.4 with 1 M N-methyl d-glucamine (NMDG). Formation of the bilayer was visualized as reported previously. The final salt concentration was adjusted by adding 3 M KCl to the
cis compartment (200/0 mM KCl,
cis/trans). Small amounts of microsome solution (1–5 μl) were added to the
cis compartment and this suspension was continuously stirred with a small magnetic bar (1×3 mm) until fusion of microsomes into the bilayer was detected.
Currents were recorded at constant voltage with a bilayer amplifier (BC525A, Warner Instr. Co., Hamden CT, USA). The current was defined as positive when it flowed from cis to trans. The junction potential was adjusted prior to forming a bilayer. Electrical contacts were made through 2 Ag/AgCl electrodes. The other side of each electrode was suspended in 2 wells, which were filled with 0.5 M KCl. The 2 wells and cis/trans chambers were connected with a U-shape agar bridge filled with 3% agar in 0.2 M KCl and 1 mM EGTA solution. Currents were filtered at 500 Hz by an 8-pole Bessel filter and acquired at 2 kHz using a Digidata 1,200 data acquisition unit (Axon Instr. Co., Foster City, California, USA). The parameters analyzed were current amplitude, open state probability, and dwell-time distribution and its time constant, measured using pClamp software (Ver 6.0, Axon Instr. Co., Foster City, California, USA) for an analysis of a single-channel current.
The relative permeability of Cl
− to K
+ ions (P
Cl/P
K) was calculated from the measured reversal potentials using the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation [
17], as shown below:
where Vrev, PK, PCl, [K]o, and [Cl]i stand for the measured reversal potential, permeability of K+ and Cl− ions, and concentrations of trans K+ and cis Cl− ions, respectively. R, T, F, and z are the gas constant, absolute temperature, Faraday constant and ionic valence, respectively.
Statistical analyses
Experimental data were expressed as mean±standard error of the mean. The number of membranes tested and analyzed was represented by ‘n’. The statistical significance of data was determined using the independent Student t-test for the comparison of 2 means. P-values<0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.
RESULTS
We recorded 93 single-ion channels of
A. suum incorporated into the planar lipid bilayer. Most ion channels recorded were from the microsomes banded in the 20%/30% sucrose interface, although all the sucrose density gradient fractions were assayed for channel reconstitution. Among a total of 93 single-ion channels recorded, 74.3% were characterized as K
+-permeable channels and 25.7% as Cl
−-permeable channels based on the direction of current flow at 0 mV under a 200/0 mM KCl (
cis/trans) gradient. The cation channels were classified further into 2 groups by their conductance: large-conductance cation (209.3±42.4 pS, n=60) and small-conductance cation channels (55.3±2.6 pS, n=7;
Table 1).
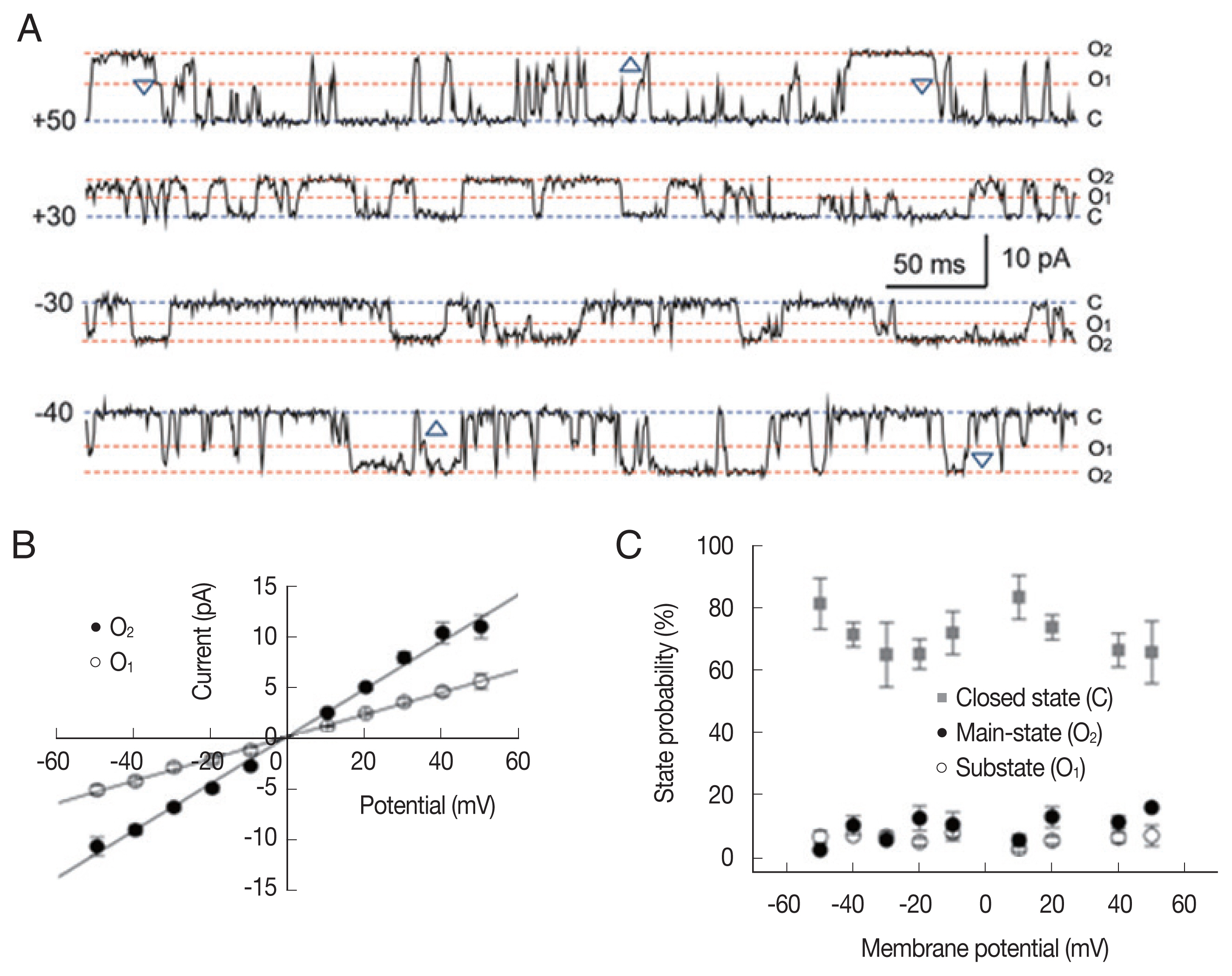
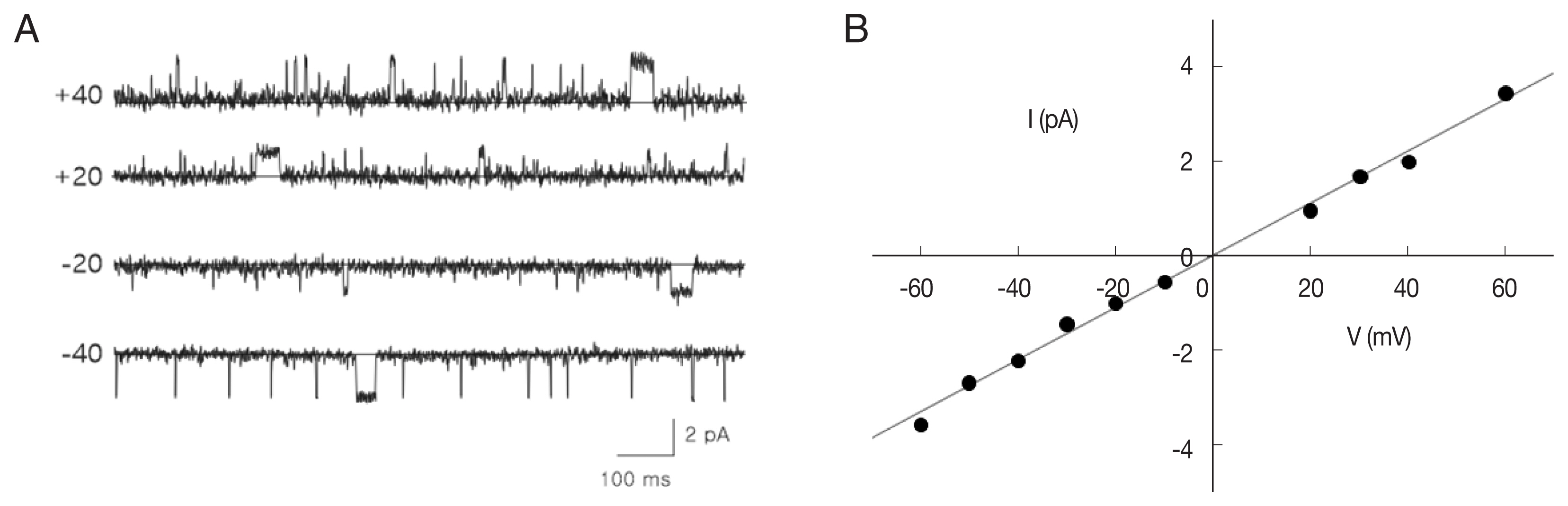
Fig. 1 shows representative single-channel traces and all-point histograms of a large conductance cation (LC) channel at +20 mV under a symmetrical condition (200/200 mM KCl). Interestingly, there was a substate at about 55% of the main-state (
Fig. 1A). The 2 conducting states appeared in isolation or in sequence: transition from substate to main-state (marked by △) or from main-state to substate (marked by ▽). In addition, the single cation channel with a conductance similar to the substate levels were never recorded throughout the whole experiments. These observations indicate that 2 conductance levels are not due to the incorporation of 2 identical channels nor 2 different cation channels [
21]. The current-voltage relations were linear in both the main-state and the substate (
Fig. 1B). The open-state probabilities (P
o) of main-state and substate were less than 0.2 and did not show any noticeable voltage dependence (n=8;
Fig. 1C).
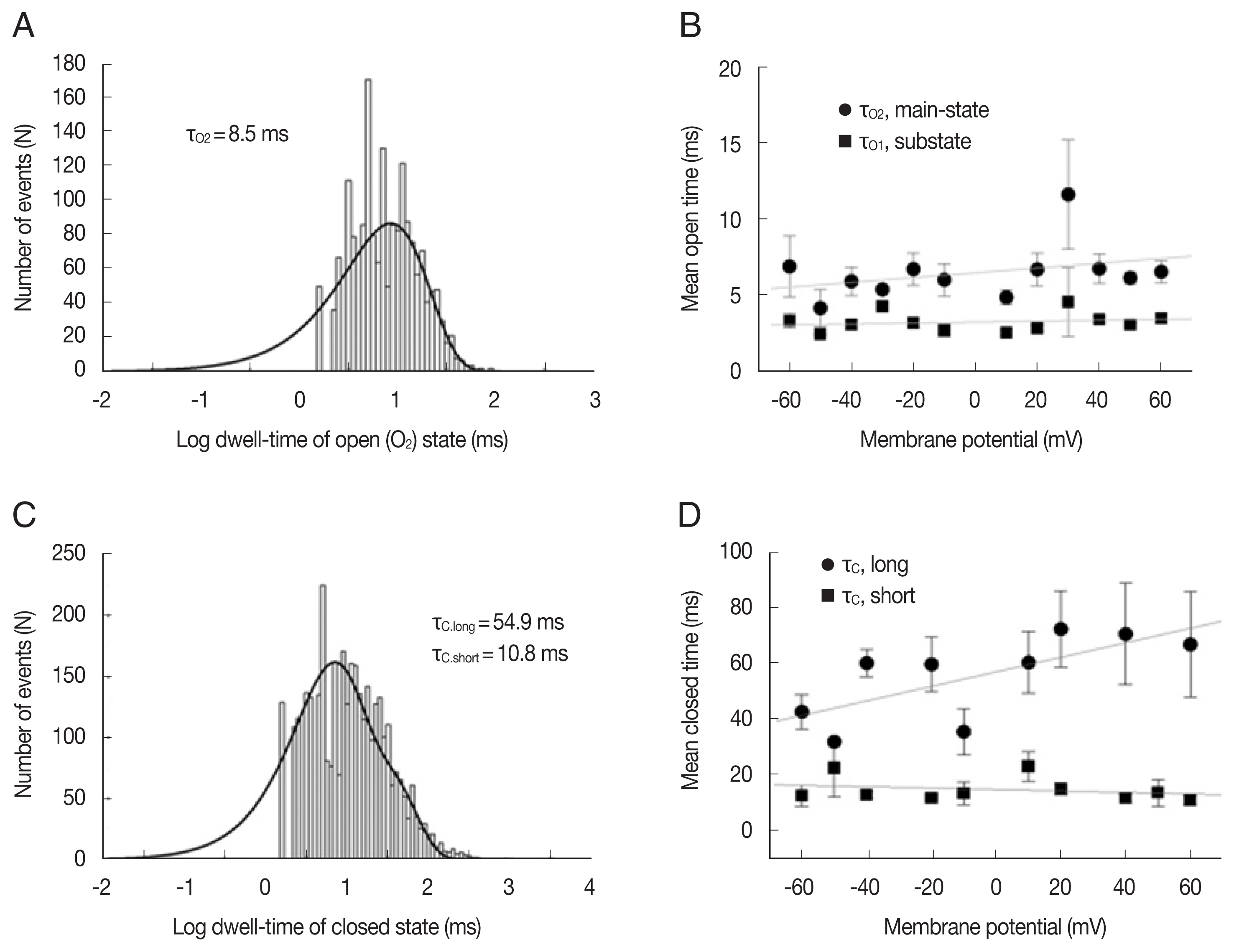
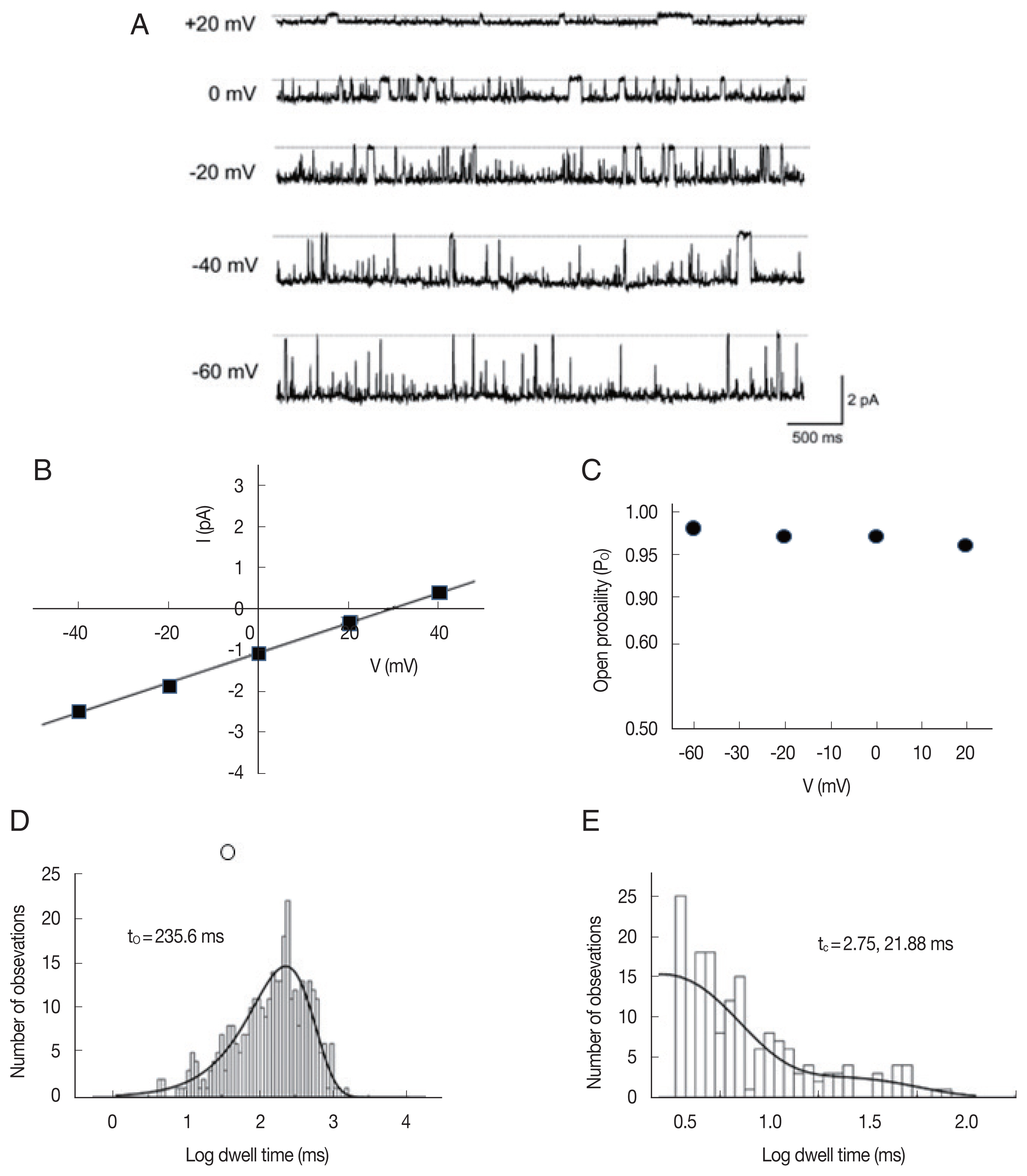
Fig. 2 shows the kinetic properties of the LC channels. The dwell time of the mean open time in both main-state and substate was fitted with 1 exponential curve using the maximum likelihood fitting method, respectively (
Fig. 2A). Channel gating was rather brief and the mean open times in main-state and substate were 5.02±0.4 and 3.2±0.1 ms at −40 mV, respectively (n=8). These mean open times did not show any remarkable voltage-dependence (
Fig. 2B). The mean closed times in both main-state and substate were fitted with 2 exponential curves using the maximum likelihood fitting method (
Fig. 2C). The short (t
c-short) and long mean closed time (t
c-long) were 8.16±0.3 ms and 67.1±6.7 ms (n=8) at −40 mV, respectively. The long closed times increased with voltage, whereas the short closed times decreased with voltage. These changes were rather small but noticeable. Hence, the difference between 2 closed times were more evident in more positive voltages (
Fig. 2D).
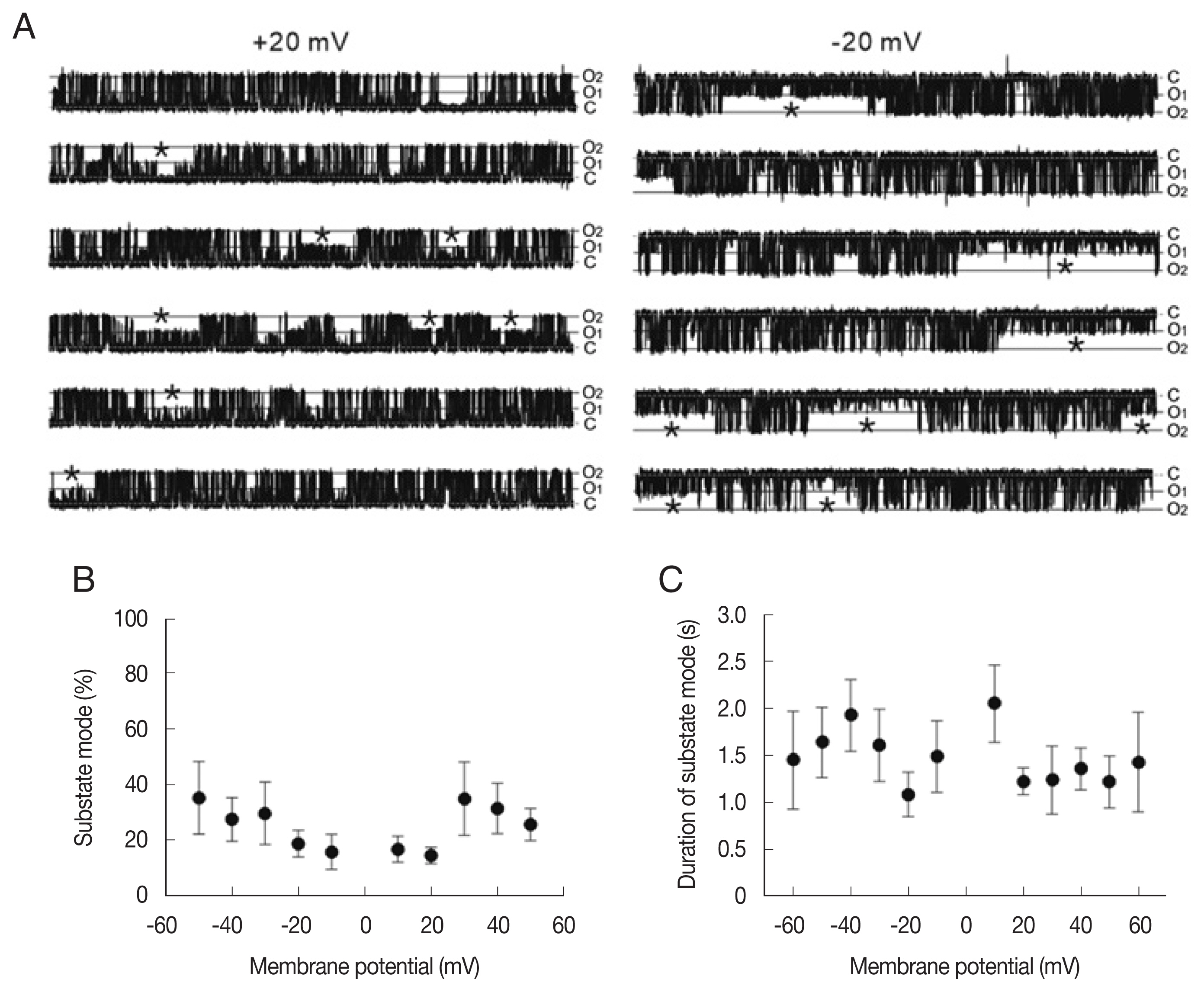
To analyze the state transition between the main-state (O
2) and substate (O
1) in the LC channel, we compared the portion and dwell time of the substate mode (marked by asterisk in
Fig. 3A) at different membrane potentials. As summarized in
Fig. 3B and C, the portion of the substate mode (ranging from 14% to 34%) was not significantly different at various membrane potentials (
Fig. 3B). The mean durations of the substate mode were 1–2 sec and do not show significant voltage dependence (
Fig. 3C).
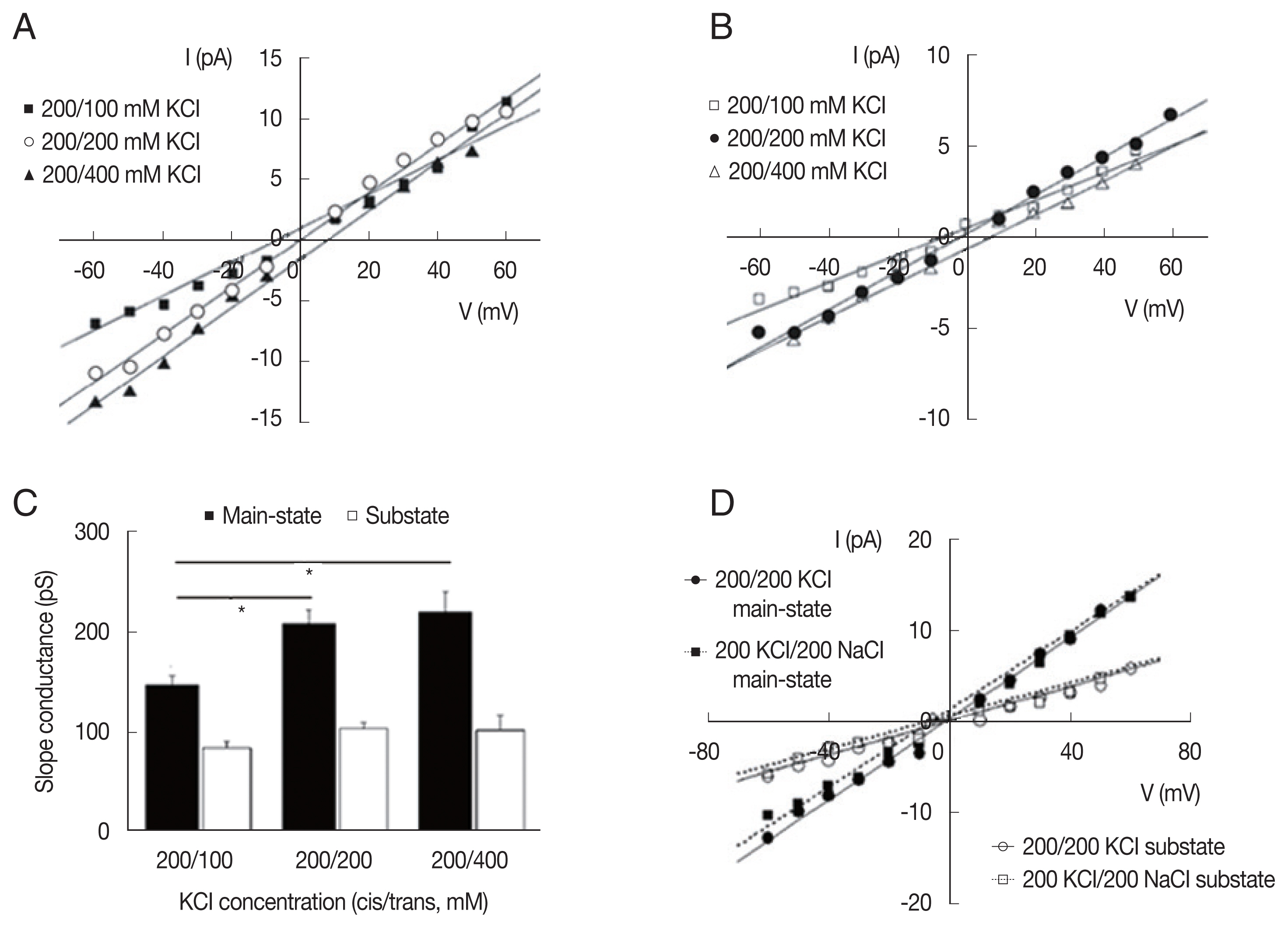
To investigate the ionic selectivity, we measured the reversal potentials of LC channel currents with different ionic compositions (
Fig. 4). Under asymmetrical 200/400 (
cis/trans) mM KCl conditions, the average reversal potentials were 6.47±3.77 and 6.94±3.05 and mV (n=4) in the main-state (O
2) and substate (O
1), respectively. P
Cl/P
K calculated by the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation from the reversal potential (in the Materials and Methods section) was 0.52±0.17 and 0.57±0.21 (n=4) in each state, respectively. Under 200/100 (
cis/trans) mM KCl conditions, the P
Cl/P
K values were 0.45±0.11 and 0.30±0.06 in the the main-state (O
2) and substate (O
1), respectively (n=4). As expected, the inward currents were smaller than the outward currents in 200/100 (
cis/trans) mM KCl (filled squares in
Fig. 4A), whereas the outward currents were smaller than the in outward currents in 200/400 (
cis/trans) mM KCl (filled triangles in
Fig. 4A). The same trend was also observed in the current-voltage relations of substate. Overall slope conductance of the main-state was smaller in the 200/ 100 (
cis/trans) mM KCl condition than in the 200/200 mM and 200/400 mM (
cis/trans) KCl conditions (
P<0.05 in both cases,
Fig. 4C).
To determine the cation selectivity, we compared the permeability of Na
+ with that of K
+. When KCl was substituted by NaCl on the
trans side, there are no significant shift in the reversal potentials of the current, indicating that the channel was only weakly selective for K
+ rather than Na
+. P
Na/P
K calculated from the reversal potentials under the bi-ionic condition (200 mM KCl/200 mM NaCl,
cis/trans) was 0.81±0.07 (n=2). The inward current in the bi-ionic condition was slightly smaller than that in symmetrical KCl condition, but there was significant amount of inward current under the bi-ionic conditions with 200 mM NaCl in the
trans chamber (
Fig. 4D). The latter indicates that Na
+ ions can pass through the channel. Consistent with the lack of significant changes in the reversal potential, the slope conductance of main-state and substate did not significantly differ between bi-ionic 200 mM KCl/200 mM NaCl conditions and symmetrical 200/200 mM KCl (
P>0.9 in both cases).
Small-conductance channels were identified in 7 of the 93 bilayers that showed single-channel activity.
Fig. 5A shows representative traces of a small-conductance cation channel at +40, +20, −20, and −40 mV under symmetric conditions (200/ 200 mM KCl). In contrast to the large-conductance cation channels, the small-conductance cation channels did not show any sub-conductance state. The current-voltage relations were linear (
Fig. 5B) and average slope conductance was 55.3±2.6 pS (n=3). Its gating and P
o did not meaningfully depend on the voltage, and the P
o was ~0.1 at positive and negative voltages. The chance of recording this type of channels was low, hence, we were not able to perform a further detailed analysis of the single-channel properties.
In 26 of the 93 bilayers that showed single-channel activity, we identified the third type of ion channels, which are more permeable to anions under a 200/0 mM KCl (
cis/trans) gradient at 0 mV.
Fig. 6A shows representative single-channel traces of such an anion channel recorded at various membrane potentials (−60 to +20 mV) under a 200/40 (
cis/trans) KCl gradient. The average slope conductance of the anion currents from the linear current-voltage relations (
Fig. 6B) was 39.0±0.7 pS (n=26). The reversal potential and P
Cl/P
K of the anion channel were 28.8±1.2 mV and 8.6±0.8 (n=26), respectively. As shown in
Fig. 6A, single-channel currents showed long-lasting openings at all tested potentials (−60 to +20 mV); therefore, the P
o of the anion channels was near 1 at the various voltage ranges (
Fig. 6C). The open- and closed-state dwell times were fitted with 1 and 2 exponential curves, respectively, by a maximum likelihood fitting method (
Fig. 6D, E). The mean open time was 221.5±29.7 ms (n=5) and the t
c-short and t
c-long at −40 mV were 3.23±1.4 ms and 28.4±3.0 ms (n=5), at −40 mV, respectively.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we characterized 3 types of ion channels from A. suum muscle incorporated into the planar lipid bilayers: 1) large-conductance cation (LC) channel characterized by large conductance (209±42.4 pS) and a substate; 2) small-conductance cation channel showing small conductance (55.3±2.6 pS); and 3) a group of anion channel highly selective for Cl− over K+. The properties of these ion channels appeared to be different from any other ion channels of A. suum reported previously.
In the present study, the LC channel was the most frequently observed type of single channels from the microsomal preparation of
A. suum tissue. The LC channel’s large conductance is comparable to Slo-1 or BK channels reported in various tissues [
18,
20,
22,
23]. However, the LC channel is likely to be different from Slo-1 channel. First, the sub-conducting state of the LC channel has not been reported from Slo-1 channel [
22,
24,
25]. Second, the LC channel activity and gating are little voltage-dependent (
Figs. 1–
3), whereas Slo-1 channel is voltage-dependent [
22,
24,
25]. Third, the LC channel’s permeability ratio of K
+ to Na
+ (pK/pNa) is much smaller than that of Slo-1 (1.25 vs. 5 [
20], 6.5 [
22]).
Ca2
+- sensitivity is one of the hall marks of the Slo-1 channels [
24,
25], but in the present study LC channel is recorded in the solution without adding any Ca
2+ and hence LC channel’s Ca
2+-sensitivity remains to be studied in the future. It is interesting that Slo-2 shows the substate [
26], although its frequency is much less than that of LC channel substate (
Figs. 1,
3). It is known that the voltage and Ca
+-sensitivity of Slo channel can vary by the different regulatory subunits [
25,
27]. Therefore, one cannot exclude the possibility that LC channel in
A. suum could be a member of Slo channel family with different regulatory subunits.
The LC channel looks like K
+ channel of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR K channel), showing a substate state in frog skeletal muscle [
28], and mammalian cardiac muscle [
29,
30]. The ionic selectivity of the substate is like that of the main-state in SR K channels. In the
A. suum muscle, the slope conductance of the sub-state reached ~50% of that of the main-state, which was between the 1/3 the value (50 vs. 150 pS) for the skeletal SR K channels and 2/3 of the value (100 vs. 160 pS) for cardiac SR K channels. However, the weak selectivity for K
+ over Na
+ (P
Na/P
K=~0.8) differentiated the LC channel of
A. suum from mammalian SR K channel (P
Na/P
K=0.5) [
29].
Comparable non-selective cation channels have been reported in
Schistosoma mansoni. Non-selective cation channels selective for Na
+ or K
+ over Cl
− represent an apparent ion channel with a conductance of 295 pS in the outer tegument of
S. mansoni [
31] and are equally permeable to Na
+ and K
+ (P
Na/P
K=0.7–1.1). However, this apparent ion channel conductance appears to result from cooperativity among several channels, with the unitary conductance for the channel averaging 95 pS. Another non-selective cation channel in
S. mansoni showed a 360 pS slope conductance of main-state with regular substate steps of 95 pS and a reversal potential near 0 mV [
32]. Despite their similar main-state conductance, the smaller substate conductance differentiated the LC channel of
A. suum muscle from the non-selective cation channels in
S. mansoni.
The conductance of small-conductance cation channels is similar to that of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channels. When activated by nicotine and levamisole, these channels showed 2 different conductance levels in patch clamp recordings: small-conductance (26 pS, N-type receptor channel) and large-conductance (38.8 pS, L-type receptor channel) conductance [
33]. However, the 2 channels are different because the large-conductance cation channels were active in the absence of acetylcholine. In addition, small-conductance cation channels did not show the flickering closures to a low sub-conductance state that have been described in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channels [
34].
Both glutamate and GABA could be inhibitory transmitters in invertebrates [
3,
35]. Although glutamate is a typical excitatory neurotransmitter in mammals, it gates chloride channels in different groups of invertebrates, including nematodes. For example, glutamate-gated chloride channels of 21 pS mediate the inhibitory action of motor neurons in
A. suum pharyngeal muscle [
36]. While they are not sensitive to mammalian GABA receptor antagonists such as bicuculline and picrotoxin, GABA receptors gating chloride conductance of ~10 pS and mediating muscle relaxation are the site of action of the anthelmintics piperazine and dihydroavermectin in
A. suum [
37,
38]. The observed conductance differences indicate that the anion channels in the present study differ from the GABA-gated channels of
A. suum. It is also noteworthy that a sub-conductance state was observed in the glutamate-gated chloride channels from
A. suum pharyngeal muscle [
36], but the anion channels in the present study did not show a substate.
Overall, we identified 3 types of cation channels: 2 cation and 1 anion channels in
A. suum tissue, which seemed different from the single-ion channels reported previously in terms of ion selectivity, slope conductance, and voltage dependence. All these channels showed little voltage dependence in gating, but active in the 10 mM HEPES solution, which is devoid of Ca
2+ or any intracellular modulators/metabolites such as ATP and cAMP. However, these channels will be exposed to and could be regulated by intracellular messengers or metabolites in
A. suum in vivo. In this case, they are likely to play as a linker for cellular metabolism to membrane excitability in
A. suum in vivo. A good example of such channel is ATP-sensitive K
+ channels which are regulated by intracellular nucleotides and phospholipids, and control membrane potentials of the various cells in the brain, heart, blood vessel and pancreas [
39]. The voltage dependence in gating the ATP-sensitive K
+ channel is further confirmed at the experimental conditions with different K
+ and intracellular modulators [
40]. Our observations on these channels incorporated into planar lipid bilayers are rather preliminary and limited to show the details of electrophysiological properties of these channels. Extensive further study is needed to understand their electrophysiological and molecular, physiological roles, and potentials as novel targets of anti-nematodal agents in animals and humans.
Notes
-
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant (2007-0054932 to PDR).
Fig. 1Single-channel properties of a large-conductance cation channel. (A) Representative current traces recorded under symmetrical 200 mM KCl conditions, filtered at 500 Hz, and digitized at 2 kHz. O2, O1, and C refer to the main-state, substate and closed state, respectively. Note the transitions from O2 to O1 (upward triangle) as well as from O1 to O2 (downward triangle). (B) Average current-voltage relation of the large-conductance cation channel was linear and its slope conductance was 235.5 and 110.4 pS in the main-state and substate, respectively. (C) Probability of closed state (gray square), main-state (filled circle), and substate (open circle).
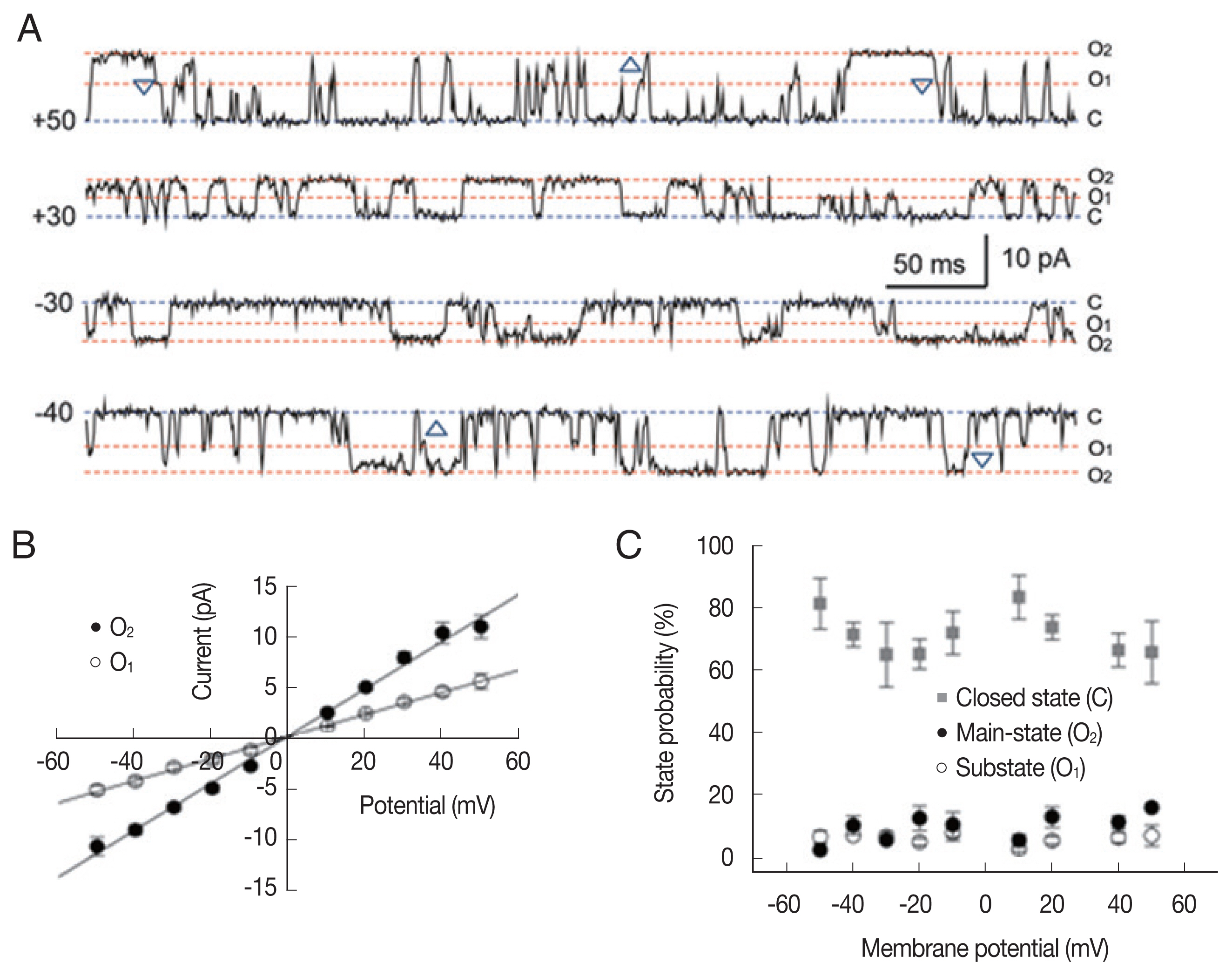
Fig. 2Kinetic properties of large-conductance cation channels from A. suum muscle. (A) Representative open dwell-time histogram in the main-state (O2) at −40 mV. The mean open dwell-time was fitted with 1 exponential curve (1,740 events for107 s). Solid lines were drawn by best-fit parameters. (B) Mean open times of main-state (O2) and substate (O1) at various voltages. (C) Representative closed dwell-time histogram at −40 mV. The mean closed dwell-time was fitted with 2 exponential curves (3,506 events for 107 s). Solid lines were drawn by best-fit parameters. τc,short and τc,long refer to the mean closed times of short and long duration, respectively. (D) Mean closed times at various voltages. Each symbol and bar represent mean±standard error from 2–10 channels. The solid lines in B and D represent the linear regression of voltage-dependence of dwell times and indicates that mean closed time of long duration (τc,long) increase about 20 ms per 100 mV.
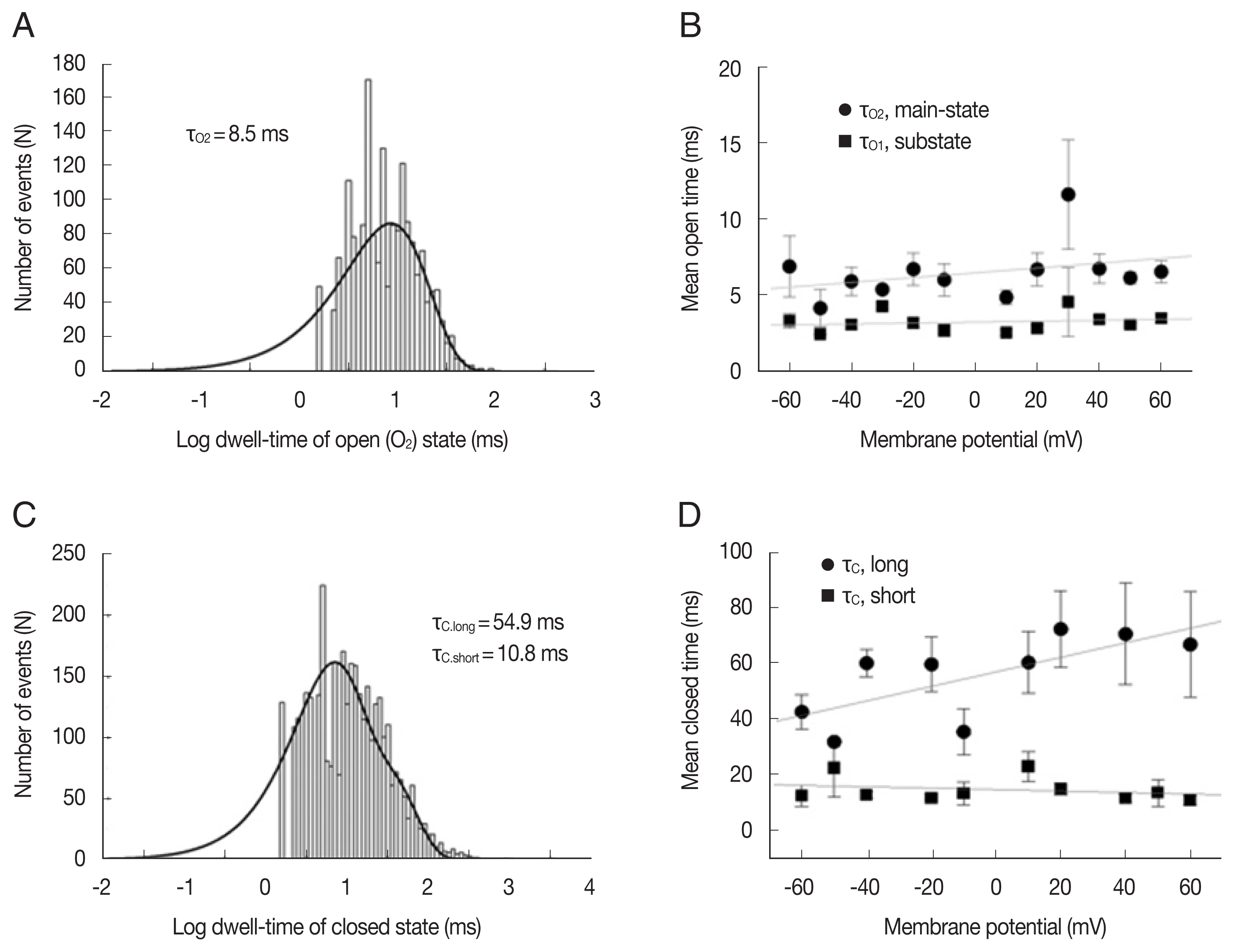
Fig. 3Sub-conductance state mode of large-conductance cation channels from A. suum muscle. (A) Representative single-channel traces showing 2 gating mode, main-state (O2) and substate (O1) recorded at +20 and −20 mV. Single-channel currents were recorded under symmetrical 200 mM KCl conditions. C, O2 and O1 refer to the closed, main-state and substate of the channel, respectively. Note the substate mode marked by asterisk (*). (B) All point histograms of the current records shown in A at +20 (top) and −20 mV (bottom). The peak of sub-conductance state occurred at 40 and 41% of the full state amplitude at +20 and −20 mV, respectively. (C) The proportion (B) and mean dwell time of the substate (C) at various membrane potentials.

Fig. 4Ion selectivity of large-conductance cation channels from A. suum muscle. Representative current-voltage curves obtained in different KCl compositions in the main-state (A) and substate (B). The reversal potentials were similar in main-state and substate at 3 different ionic compositions. (C) Summarized slope conductance of the main-state and substate in 200/100 mM, 200/200 mM, and 200/400 mM (cis/trans) KCl. Note that slope conductance of the main-state was smaller in the 200/100 (cis/trans) mM KCl condition than in the 200/200 mM and 200/400 mM (cis/trans) KCl conditions (P<0.05). (D) Representative current-voltage curves obtained under symmetric (200/200 mM KCl) and bi-ionic (cis/trans, 200 mM NaCl/200 mM KCl) conditions. I, membrane current in pA. V, membrane potential in mV.
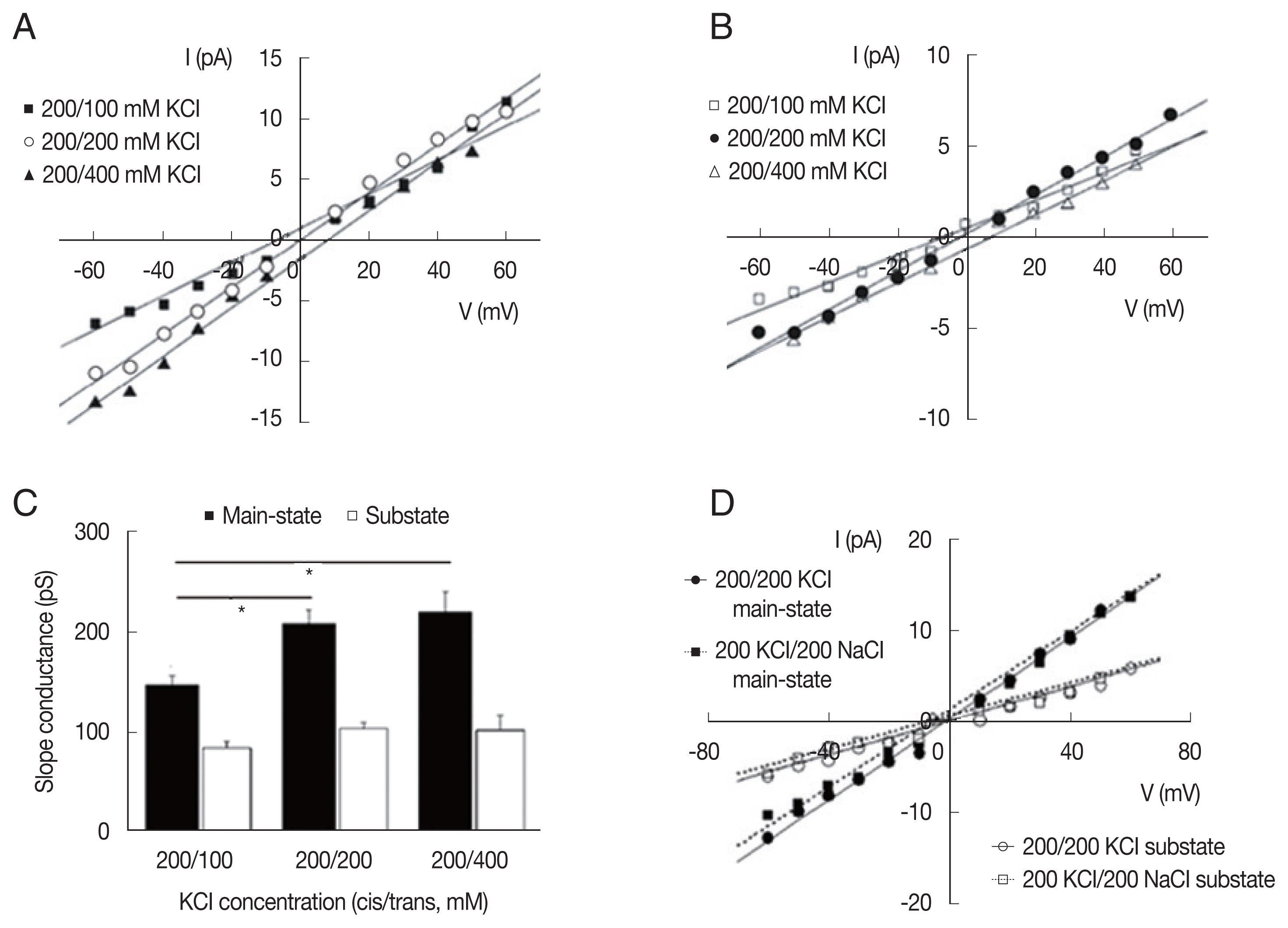
Fig. 5Small-conductance cation channel from A. suum muscle incorporated into a planar lipid bilayer. (A) Representative single-channel traces recorded at +40, +20, −20, and −40 mV. Currents were recorded at symmetrical 200 mM KCl conditions, filtered at 500 Hz, and digitized at 2 kHz. The horizontal lines denote the levels of closed state. Note that the open-state probabilities are not obviously different at positive and negative voltages. (B) Current-voltage relationship of the channel shown in (A). I, membrane current in pA. V, membrane potential in mV.

Fig. 6Single-channel properties of an anion channel from A. suum muscle incorporated into a planar lipid bilayer. (A) Representative current traces recorded at various membrane potentials at 200/40 mM (cis/trans) KCl solutions. Solid lines at each trace denote the closed states. (B) Current-voltage relationship of the channel shown in (A). Slope conductance and reversal potential were 36.5 pS and 29.6 mV, respectively. I, membrane current in pA. V, membrane potential in mV. (C) Open-state probabilities obtained at various membrane potentials as in (A). Dwell time histograms of open (D, event number=340) and closed (E, event number=158) states at −40 mV were fitted with 1 and 2 exponential curves, respectively. Solid lines were drawn by best-fit parameters. τo and τc indicate the mean open and mean closed times, respectively.
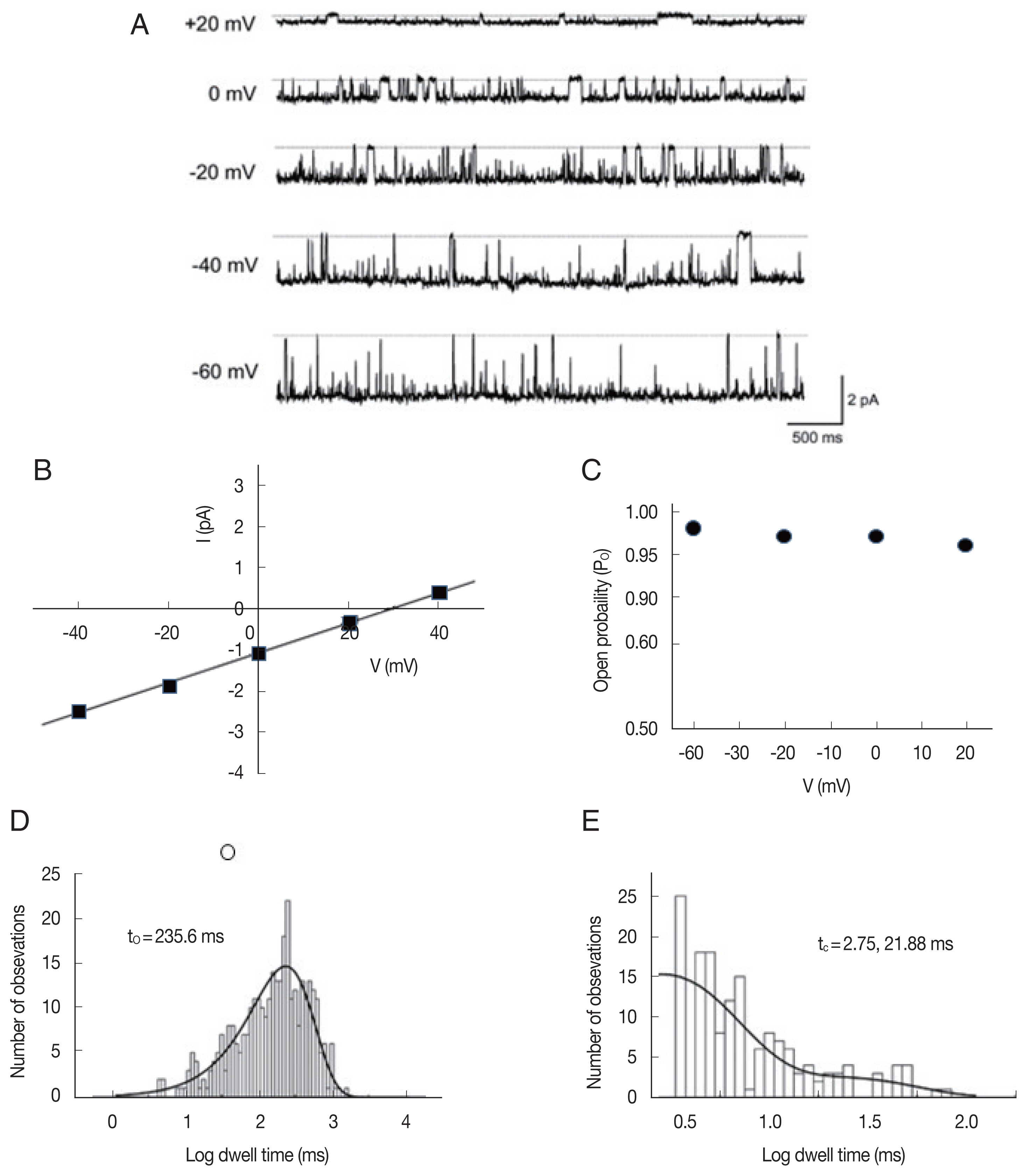
Table 1Single ion channels from A. suum incorporated into planar lipid bilayers
Table 1
|
Slope conductance (pS) |
No. of channels |
|
Cation channel |
|
Large-conductance |
209±42.4 |
60 |
|
Small-conductance |
55.3±2.6 |
7 |
|
|
Anion channel |
39.0±0.7 |
26 |
References
- 1. Martin RJ, Pennington AJ, Duittoz AH, Robertson S, Kusel JR. The physiology and pharmacology of neuromuscular transmission in the nematode parasite, Ascaris suum. Parasitology 1991;102(suppl):41-58. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000073285
- 2. Martin RJ, Valkanov MA, Dale VM, Robertson AP, Murray I. Electrophysiology of Ascaris muscle and anti-nematodal drug action. Parasitology 1996;113(suppl):137-156. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000077945
- 3. Robertson AP, Martin RJ. Ion-channels on parasite muscle: pharmacology and physiology. Invert Neurosci 2007;7:209-217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10158-007-0059-x
- 4. Martin RJ, Buxton SK, Neveu C, Charvet CL, Robertson AP. Emodepside and SL0–1 potassium channels: a review. Exp Parasitol 2012;132:40-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2011.08.012
- 5. Xiao R, Xu XZ. Function and regulation of TRP family channels in C. elegans. Pflugers Arch 2009;458:851-860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0678-7
- 6. Buxton SK, Charvet CL, Neveu C, Cabaret J, Cortet J, Peineau N, Abongwa M, Courtot E, Robertson AP, Martin RJ. Investigation of acetylcholine receptor diversity in a nematode parasite leads to characterization of tribendimidine- and derquantel-sensitive nAChRs. PLoS Pathog 2014;Jan. 30. 10:e1003870. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1003870
- 7. Blair KL, Geary TG, Mensch SK, Vidmar TJ, Li SK, Ho NF, Thompson DP. Biophysical characterization of a large conductance anion channel in hypodermal membranes of the gastrointestinal nematode, Ascaris suum. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 2003;134:805-818. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1095-6433(03)00014-x
- 8. Buxton SK, Neveu C, Charvet CL, Robertson AP, Martin RJ. On the mode of action of emodepside: slow effects on membrane potential and voltage-activated currents in Ascaris suum. Br J Pharmacol 2011;164:453-470. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01428.x
- 9. Kulke D, von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Miltsch SM, Wolstenholme AJ, Jex AR, Gasser RB, Ballesteros C, Geary TG, Keiser J, Townson S, Harder A, Krücken J. Characterization of the Ca2+-gated and voltage-dependent K+-channel Slo-1 of nematodes and its interaction with emodepside. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2014;8:e3401. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003401
- 10. Buxton SK, Robertson AP, Martin RJ. Diethylcarbamazine increases activation of voltage-activated potassium (SLO-1) currents in Ascaris suum and potentiates effects of emodepside. PLoS NeglTrop Dis 2014;8:e3276. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0003276
- 11. Maizels RM, Denham DA. Diethylcarbamazine (DEC): immunopharmacological interactions of an anti-filarial drug. Parasitology 1992;105(suppl):49-60. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000075351
- 12. Verma S, Kashyap SS, Robertson AP, Martin RJ. Diethylcarbamazine activates TRP channels including TRP-2 in filaria, Brugia malayi. Commun Biol 2020;3:398. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-020-01128-4
- 13. Idika IK, Okonkwo EA, Onah DN, Ezeh IO, Iheagwam CN, Nwosu CO. Efficacy of levamisole and ivermectin in the control of bovine parasitic gastroenteritis in the sub-humid savanna zone of southeastern Nigeria. Parasitol Res 2012;111:1683-1687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-012-3007-6
- 14. Epe C, Kaminsky R. New advancement in anthelmintic drugs in veterinary medicine. Trends Parasitol 2013;29:129-134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2013.01.001
- 15. Baiak BHB, Lehnen CR, Rocha RAD. Anthelmintic resistance of injectable macrocyclic lactones in cattle: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Bras Parasitol Vet 2019;28:59-67. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1984-296120180093
- 16. Rose Vineer H, Morgan ER, Hertzberg H, Bartley DJ, Bosco A, Charlier J, Chartier C, Claerebout E, de Waal T, Hendrickx G, Hinney B, Höglund J, Ježek J, Kašný M, Keane OM, Martínez-Valladares M, Mateus TL, McIntyre J, Mickiewicz M, Munoz AM, Phythian CJ, Ploeger HW, Rataj AV, Skuce PJ, Simin S, Sotiraki S, Spinu M, Stuen S, Thamsborg SM, Vadlejch J, Varady M, von Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Rinaldi L. Increasing importance of anthelmintic resistance in European livestock: creation and meta-analysis of an open database. Parasite 2020;27:69. https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2020062
- 17. Labarca P, Latorre R. Insertion of ion channels into planar lipid bilayers by vesicle fusion. Methods Enzymol 1992;207:447-463. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(92)07032-j
- 18. Park JB, Kim HJ, Ryu PD, Moczydlowski E. Effect of phosphatidylserine on unitary conductance and Ba2+ block of the BK Ca2+-activated K+ channel: re-examination of the surface charge hypothesis. J Gen Physiol 2003;121:375-397. https://doi.org/10.1085/jgp.200208746
- 19. Jang JH, Kim SD, Park JB, Hong SJ, Ryu PD. Ion channels of Fasciola hepatica incorporated into planar lipid bilayers. Parasitology 2004;128:83-89. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182003004232
- 20. Jang JH, Park JB, Kim SD, Lee SY, Hong SJ, Ryu PD. Property of large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels from Fasciola hepatica incorporated into planar lipid bilayer. Vet Parasitol 2012;186:281-288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2011.11.038
- 21. Fox JA. Ion channel subconductance states. J Membr Biol 1987;97:1-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869609
- 22. Latorre R, Vergara C, Hidalgo C. Reconstitution in planar lipid bilayers of a Ca2+-dependent K+ channel from transverse tubule membranes isolated from rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1982;79:805-9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.79.3.805
- 23. Davis SJ, Scott LL, Hu K, Pierce-Shimomura JT. Conserved single residue in the BK potassium channel required for activation by alcohol and intoxication in C. elegans. J Neurosci 2014;34:9562-9573. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0838-14.2014
- 24. Salkoff L, Butler A, Ferreira G, Santi C, Wei A. High-conductance potassium channels of the SLO family. Nat Rev Neurosci 2006;7:921-931. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn1992
- 25. González C, Baez-Nieto D, Valencia I, Oyarzún I, Rojas P, Naranjo D, Latorre R. K+ channels: function-structural overview. Compr Physiol 2012;2:2087-2149. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c110047
- 26. Yuan A, Santi CM, Wei A, Wang ZW, Pollak K, Nonet M, Kaczmarek L, Crowder CM, Salkoff L. The sodium-activated potassium channel is encoded by a member of the Slo gene family. Neuron 2003;37:765-773. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00096-5
- 27. Gonzalez-Perez V, Lingle CJ. Regulation of BK Channels by Beta and Gamma Subunits. Annu Rev Physiol 2019;81:113-137. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-022516-034038
- 28. Labarca PP, Miller C. A K+-selective, three-state channel from fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum of frog leg muscle. J Membr Biol 1981;61:31-38. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01870750
- 29. Tomlins B, Williams AJ, Montgomery RA. The characterization of a monovalent cation-selective channel of mammalian cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Membr Biol 1984;80:191-199. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868775
- 30. Hill JA Jr, Coronado R, Strauss HC. Potassium channel of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum is a multi-ion channel. Biophys J 1989;55:35-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82778-X
- 31. Day TA, Bennett JL, Pax RA. Schistosoma mansoni: patch-clamp study of a nonselective cation channel in the outer tegumental membrane of females. Exp Parasitol 1992;74:348-356. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-4894(92)90159-8
- 32. Robertson AP, Martin RJ, Kusel JR. A vesicle preparation for resolving single-channel currents in tegument of male Schistosoma mansoni. Parasitology 1997;115:183-192. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182097001273
- 33. Levandoski MM, Robertson AP, Kuiper S, Qian H, Martin RJ. Single-channel properties of N- and L-subtypes of acetylcholine receptor in Ascaris suum. Int J Parasitol 2005;35:925-934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2005.03.007
- 34. Auerbach A, Sachs F. Flickering of a nicotinic ion channel to a subconductance state. Biophys J 1983;42:1-10. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84362-8
- 35. Cully DF, Wilkinson H, Vassilatis DK, Etter A, Arena JP. Molecular biology and electrophysiology of glutamate-gated chloride channels of invertebrates. Parasitology 1996;113(suppl):191-200. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000077970
- 36. Adelsberger H, Scheuer T, Dudel J. A patch clamp study of a glutamatergic chloride channel on pharyngeal muscle of the nematode Ascaris suum. Neurosci Lett 1997;230:183-186. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(97)00512-0
- 37. Martin RJ, Pennington AJ. A patch-clamp study of effects of dihydroavermectin on Ascaris muscle. Br J Pharmacol 1989;98:747-756. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14602.x
- 38. Bascal Z, Holden-Dye L, Willis RJ, Smith SW, Walker RJ. Novel azole derivatives are antagonists at the inhibitory GABA receptor on the somatic muscle cells of the parasitic nematode Ascaris suum. Parasitology 1996;112:253-259. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000084845
- 39. Tinker A, Aziz Q, Li Y, Specterman M. ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels and Their Physiological and Pathophysiological Roles. Compr Physiol 2018;8:1463-1511. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c170048
- 40. Kurata HT, Rapedius M, Kleinman MJ, Baukrowitz T, Nichols CG. Voltage-dependent gating in a “voltage sensor-less” ion channel. PLoS Biol 2010;8:e1000315. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000315