Abstract
This experiment focused on MAPK activation in host cell invasion and replication of T. gondii, as well as the expression of CC chemokines, MCP-1 and MIP-1α, and enzyme, COX-2/prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) in infected cells via western blot, [3H]-uracil incorporation assay, ELISA and RT-PCR. The phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and p38 in infected HeLa cells was detected at 1 hr and/or 6 hr postinfection (PI). Tachyzoite proliferation was reduced by p38 or JNK MAPK inhibitors. MCP-1 secretion was enhanced in infected peritoneal macrophages at 6 hr PI. MIP-1α mRNA was increased in macrophages at 18 hr PI. MCP-1 and MIP-1α were reduced after treatment with inhibitors of ERK1/2 and JNK MAPKs. COX-2 mRNA gradually increased in infected RAW 264.7 cells and the secretion of COX-2 peaked at 6 hr PI. The inhibitor of JNK suppressed COX-2 expression. PGE2 from infected RAW 264.7 cells was increased and synthesis was suppressed by PD98059, SB203580, and SP600125. In this study, the activation of p38, JNK and/or ERK1/2 MAPKs occurred during the invasion and proliferation of T. gondii tachyzoites in HeLa cells. Also, increased secretion and expression of MCP-1, MIP-1α, COX-2 and PGE2 were detected in infected macrophages, and appeared to occur via MAPK signaling pathways.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK), chemokine, cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin E2
INTRODUCTION
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular apicomplexan protozoa, which induces severe congenital infections in newborns and an opportunistic infection in immunocompromised individuals. Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are crucial for maintenance of cells in many signaling pathways operant in a variety of stress responses. MAPKs constitute a family of serine/threonine protein kinases, which mediate fundamental biological process, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, as well as cellular responses to external signals. The MAPK family includes extracellular signal-related kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2), c-jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 MAPK. The MAPK pathways appear to be involved in the invasion processes of a variety of microorganisms.
The ability of
T. gondii to trigger early and specific phosphorylation of the cellular ERKs, p38 and JNK MAPKs, has been observed in previous studies (
Valere et al., 2003). The infection of human monocytes by
T. gondii results in an increase in MAPK activity, thereby implicating MAPK phosphorylation in signal transduction in cases of infection with this parasite. The MAPK inhibitors, SB203580 or SB202190 treatment applied to
T. gondii-infected fibroblasts resulted in a significant inhibition of intracellular tachyzoite replication (
Gomez-Marin et al., 1998). Activation of the ERK1/2 pathway appears to be involved in the mediation of the intracellular mycobacterial replication of
Mycobacterium avium strains (
Blumenthal et al., 2002).
Entamoeba histolytica profoundly induced ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation in neutrophils, and ERK1/2 activation was associated closely with ROS-mediated neutrophil apoptosis (
Sim et al., 2005). Cells infected with
Trichomonas vaginalis were associated with the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, p38 and JNK MAPKs, according to the results of western blotting (
Ryang et al., 2004). However, the activation of the MAPK pathway in the proliferation of
T. gondii has yet to be adequately characterized.
Chemokines are a subset of chemotactic polypeptides, and are key mediators of both leukocyte activation and chemotaxis. The CXC (cysteine-X-cysteine) chemokines are known to be involved in the recruitment and activation of neutrophils, and the CC (cysteine-cysteine) chemokine family has been identified as chemotactic factors for monocytes, dendritic cells, NK cells, and T cells (
Denney et al., 1999). Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) may contribute to the recruitment of monocytes and lymphocytes, and may participate in the control of
T. gondii infection and pathogenesis (
Brenier-Pinchart et al., 2000). The stimulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by the
T. gondii antigen has been shown to upregulate the expression of macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α) and MIP-1β gene transcripts (
Bliss et al., 1999). The ERK pathway, but not the p38 pathway, has been shown to be critical for the secretion of MCP-1 from human monocytes infected with
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (
Song et al., 2003).
T. gondii harbors molecules that induce the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines. However, the roles of CC chemokines, MCP-1 and MIP-1α in
T. gondii immunity have yet to be adequately characterized. In addition to chemokines, some lipids that appear to function as inflammatory mediators trigger specific aspects of inflammatory response when released by the cells. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is the enzyme which catalyzes the production of prostaglandins (PGEs) from arachidonic acid at inflammation sites.
Helicobacter pylori infection of a human gastric epithelial cell line upregulates mRNA and protein levels for COX-2, and stimulates the release of PGE
2. The
H. pylori water soluble proteins enhance COX-2 mRNA and protein expressions, and this action may be mediated via NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways (
Kim et al., 2000;
Kim et al., 2001). The secretion of PGE
2 upregulated in
Leishmania donovani infected human macrophages via a PKC-dependent induction of COX-2 (
Matte et al., 2001). A few reports have asserted that chemokine secretion or up-regulation of COX-2/PGE
2 and MAPK activation are related processes in cells infected with
T. gondii.
The objective of this study was to characterize the involvement of MAPK in invasion and proliferation of T. gondii tachyzoites. Also, the MAPK phosphorylation in T. gondii infected cells would be involved in secretion of CC chemokine, MCP-1, MIP-1α and COX-2/PGE2 expression.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Toxoplasma gondii
T. gondii (RH) was maintained via the serial passage of ICR mice (Daehan Biolink Co., Korea). Tachyzoites were harvested twice a week from the peritoneal fluids of infected mice. The peritoneal fluid was centrifuged for 5 min at 40 g and for 10 min at 650 g in order to remove any mouse peritoneal cells. The viability of the tachyzoites was assessed via trypan blue staining. The T. gondii tachyzoites were determined to be 95% viable.
Reagents and antibodies
Rabbit p44/42 MAPK polyclonal antibody (pAb), rabbit phospho-p44/42 MAPK pAb, rabbit p38 MAPK pAb, rabbit phospho-p38 MAPK pAb, rabbit JNK MAPK pAb, rabbit phospho-JNK MAPK pAb were obtained from Cell Signaling (Beverly, Massachusetts, USA). Anti-mouse IgG peroxidase-linked specific F(ab')2 fragment and [3H]-uracil (Amersham, Pharmacia Biotech, Uppsala, Sweden), PD98059, SB203580, SP600125, and NS-398 (Calbiochem, Fontenay sous Bois, France), scintillation cocktail (ICN Biomedical, California, USA), goat anti MCP-1 capture Ab and mouse anti-COX-2 Ab (Santa-Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, California, USA), anti-mouse MIP-1α monoclonal antibody (mAb), recombinant mouse MIP-1α Ab and biotinylated anti-mouse MIP-1α and Ab anti-mouse PGE2 Ab (R&D Systems, Abingdon, UK), recombinant mouse MCP-1 Ab, biotinylated hamster anti-mouse MCP-1 mAb (BD PharMingen, San Diego, California, USA) and mouse anti-actin Ab (Chemicon International, California, USA) were all purchased from the listed companies.
Cell culture and infection protocol
In this experiment, we utilized HeLa cells (human cervical cancer cells, from Yonsei University), RAW 264.7 cells (American Type Culture Center, Manassas, Virginia, USA), and mouse peritoneal macrophages from BALB/c mice (Hanyang University, Experimental Animal Center). The cells were cultured in 96-well plates or 6-well plates. The pellets were resuspended in RPMI 1640/10% FBS with penicillin (104 unit/ml) and streptomycin (104 µg/ml). The ratio of cell : tachyzoite was 1 : 5. HeLa cells and RAW 264.7 cells were subcultured in 250 ml culture flasks (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey, USA) with RPMI 1640/10% FBS at 37℃, in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2 at 2~3 day intervals.
One ml of 10% thioglycollate (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) was injected intraperitoneally into BALB/c mice prior to 3 to 4 days of cell collection. Murine peritoneal macrophages were harvested from peritoneal fluids, followed by 2 hr of cell culturing at 37℃, in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Murine peritoneal macrophages of 3 × 105 were seeded into 96-well plates (Becton Dickinson, Le Pont-De-Claix, France), and cultured for 15 hr in order to induce the formation of a cellular monolayer.
Western blot analysis
The activation of ERK1/2, p38, and JNK MAPKs in T. gondii-infected HeLa cells was observed at 1 hr and 6 hr PI via western blot. In order to observe the inactivation of MAPK in the cells, specific inhibitors of ERK1/2, p38, and JNK MAPK (PD98059, SB203580 and SP600125, 20 µM) were applied for 20 min before tachyzoite infection.
RAW 264.7 cells (1 × 106/well) were cultured for 6 hr in 6-well plates with RPMI 1640/10% FBS at 37℃, in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2. T. gondii tachyzoites were used to infect the cells for 1, 6, 18, and 24 hr, and COX-2 protein was detected via Western blotting. Mouse anti-COX-2 Ab (1 : 200) and mouse anti-actin Ab (1 : 1,000) were used as primary antibodies and ECL anti-mouse IgG peroxidase-linked sp. specific F(ab')2 fragment (1 : 200,000) was used as a secondary antibody. Specifically-bound peroxidase was detected using an ECL PLUS Chemiluminescence Detection System (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Uppsala, Sweden), and 1-5 min of exposure to High-performance chemiluminescence film (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech).
[3H]-uracil incorporation assay
Invasion and replication of
T. gondii tachyzoites were detected via [
3H] uracil incorporation assays (
Robert-Gangneux et al, 2000). HeLa cells (2 × 10
4) were infected with
T. gondii tachyzoites (cell : tachyzoite = 1 : 5 or 1 : 10) in 96-well culture plates for 1, 5, and 18 hr. [
3H]-uracil (1 µCi/ml) was added to the infected cells and incubated for an additional 2 hr. The precipitates were washed and transferred to filters using a cell harvester (Skatron Instruments, California, USA). After the filter was dried, 2 ml of scintillation cocktail was added, and radioactivity was counted in a β-scintillation counter (EG & G Wallac, Finland).
ELISA
Mouse peritoneal macrophages (3 × 105/well) were cultured overnight in 96-well plates with RPMI 1640/10% FBS at 37°C, in an atmosphere containing 5% CO2. The macrophages were infected with T. gondii (cell : tachyzoite = 1 : 5) for 6, 12, and 24 hr, with or without the application of 20 min of pretreatment with MAPK inhibitors (5 µM PD98059, 10 µM SB203580 and 20 µM SP600125). The levels of MCP-1 and MIP-1α in the supernatants were analyzed via sandwich-ELISA assays. Used antibody pairs were as follows: 4 µg/ml of goat anti-MCP-1 capture Ab (1 : 100) or anti-mouse MIP-1α mAb, recombinant-mouse MCP-1 Ab, recombinant-mouse MIP-1α Ab, biotinylated hamster anti-mouse MCP-1 mAb, 5 ng/ml of biotinylated anti-mouse MIP-1α Ab, and streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase conjugate (1 : 1,000). The assay was conducted in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions. All samples were analyzed in triplicate.
PGE2 levels were determined in the culture supernatants at 6, 18, 24, and 48 hr PI, using the ELISA kit (R&D Systems). The inhibitors of COX-2 (50 µM NS-398) and MAPKs (20 µM PD98059, 10 µM SB203580, 10 µM SP600125) were administered for 20 min. Supernatants were collected 48 hr after infection with the T. gondii tachyzoites, and the PGE2 levels were evaluated via ELISA, in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Reverse transcription (RT)-PCR
RAW 264.7 cells of 1 × 106/wells in 6-well plates with RPMI 1640/10% FBS were cultivated for 6 hr at 37℃, 5% CO2, and were infected with T. gondii tachyzoites for 1, 3, 6 and 18 hr. The RNA of the infected cells was extracted via an acid-guanidinine-phenol method. MIP-1α and COX-2 mRNA expression in the RAW 264.7 cells were assessed via RT-PCR.
The primer sequences and annealing temperature were as follows: for MIP-1α, (S) 5'-AACATCATGAAGGTCTCCACCAC-3', (AS) 5'-CATTCAGTTCCAGGTCAGTGATGT-3', 54℃, and for COX-2, (S) 5-ACACTCTATCACTGGCATCC-3', (AS) 5'-GAAGGGACACCCTTTCACAT-3', 55℃, and for β-actin, (F) 5'-CCAGAGCAAGAGAGGTATCC-3', (R) 5'-CTGTGGTGGTGAAGCTGTAG-3'. PCR was conducted via electrophoresis on 2% agarose gel with 1 µg/ml ethidium bromide.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as means ± SD for uracil incorporation assay and ELISA. The Mann-Whitney U-test was used for statistical analysis, and a P value lower than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
MAPKs were activated by T. gondii infection
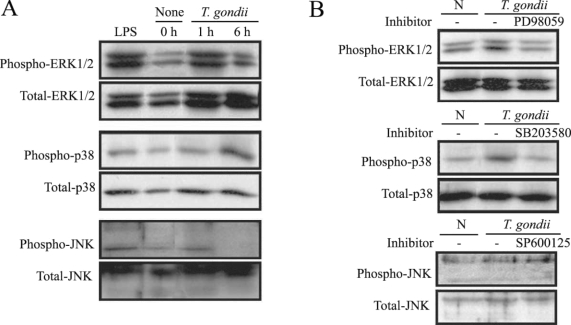
MAPK phosphorylation in HeLa cells after
T. gondii infection was observed at 1 hr and 6 hr via western blotting. ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation in the HeLa cells were noted at 1 hr and 6 hr PI, respectively. JNK MAPK activation was distinctly noted after 1 hr, and disappeared at 6 hr PI (
Fig. 1A). The effect of specific inhibitors of ERK1/2, p38, and JNK MAPKs on parasite invasion was assessed. Treatment of MAPK inhibitors, PD98059 and SB203580 showed downregulated MAPK phosphorylation during
T. gondii invasion (
Fig. 1B).
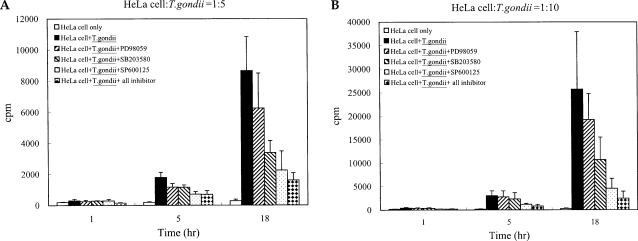
T. gondii tachyzoite proliferation in HeLa cells was assessed via [
3H]-uracil incorporation assay. Tachyzoite proliferation in the cells after treatment with MAPK inhibitors was also observed. Tachyzoite proliferation in infected HeLa cells was quantified as 305.0 ± 101.18 cpm and 8675.5 ± 2183.63 cpm at 1 hr and 18 hr, respectively. Parasite proliferation in the SB203580-treated cells was measured at 282.5 ± 24.85 cpm and 3386.8 ± 775.90 cpm after 1 hr and 18 hr of infection, respectively. Tachyzoite proliferation in the SP600125-treated cells was measured at 292.5 ± 84.98 cpm and 2256.8 ± 1228.96 cpm at 1 hr and 18 hr PI. Tachyzoite proliferation in mixed MAPK inhibitors was measured at 148.7 ± 28.06 cpm and 1612.5 ± 463.45 cpm at 1 hr and 18 hr after infection. Our results indicated that the replication of
T. gondii was suppressed at 18 hr of cultivation when treated with SB203580, SP600125 and mixed MAPK inhibitors (
Fig. 2).
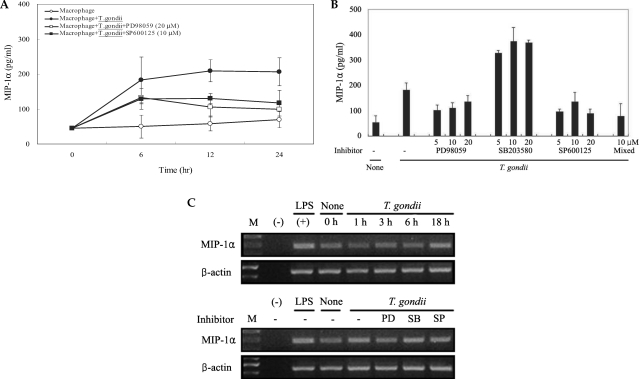
T. gondii infection induced abundant expression of MCP-1 and MIP-1α, which was reduced by treatment with MAPK inhibitors
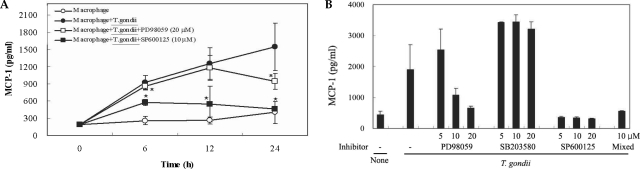
The levels of MCP-1 and MIP-1α in the culture supernatants of
T. gondii-infected mouse peritoneal macrophages were measured via ELISA. The levels of chemokines were increased between 6 hr and 24 hr after parasite infection. MCP-1 and MIP-1α secretion levels in the macrophages were reduced by PD98059 and SP600125, as well as the mixed MAPK inhibitors. However, the p38 inhibitor, SB203580, had no effects on MCP-1 and MIP-1α secretion after infection with
T. gondii (
Figs. 3A, 3B). MIP-1α mRNA levels were found to have increased at 18 hr PI, and were reduced as the result of treatment with PD98059 and SP600125 (
Fig. 4). Increased MIP-1α mRNA expression in
T. gondii-infected HeLa cells coincided with the secretion of MIP-1α protein (
Figs. 3,
4).
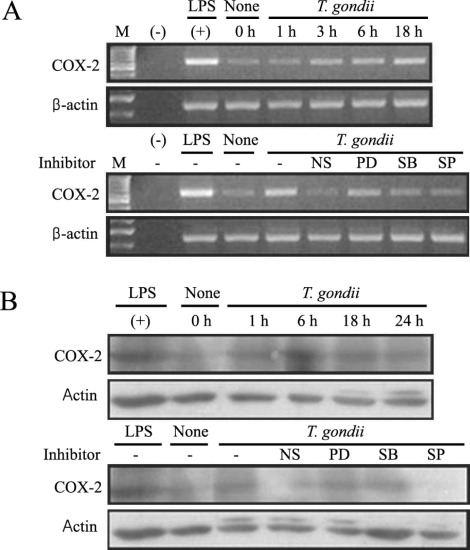
COX-2 mRNA and protein expression were upregulated in
T. gondii-infected RAW 264.7 cells at 18 hr and at 6 hr via RT-PCR and western blotting, respectively (
Figs. 5A, 5B). COX-2 mRNA was partially downregulated by the MAPK inhibitors, SB203580 and SP600125. COX-2 protein secretion levels peaked at 6 hr in the parasite-infected cells, and decreased gradually, and were completely suppressed by SP600125 (
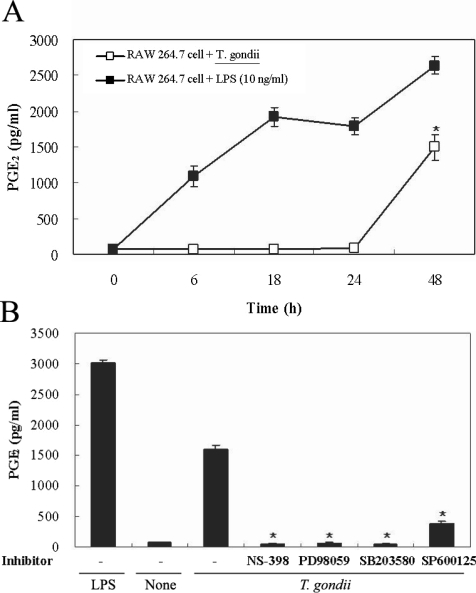
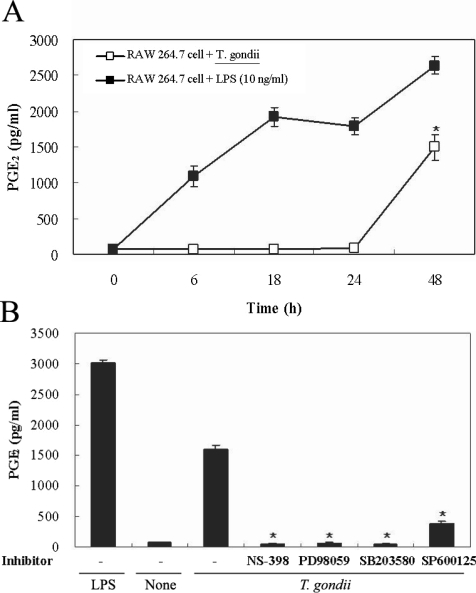
Figs. 5A, 5B). PGE
2 secretion from RAW 264.7 cells began to increase 24 hr after infection with
T. gondii (
Fig. 6A). PGE
2 secretion in infected RAW 264.7 cells was suppressed by the MAPK inhibitors, PD98059, SB203580, and SP600125 (
Fig. 6B).
DISCUSSION
Signal transduction of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways involves highly conserved cascades, and these processes are salient to several aspects of immune response (
Denkers et al., 2004). MAPKs phosphorylate selected intracellular proteins, including transcription factors that regulate gene expression. ERK1/2 is well-characterized MAPKs that are activated in response to growth stimuli. p38 and JNK MAPKs are referred to as stress kinases, and are activated by a host of stimuli, including heat shock, TNF-α, UV irradiation, and cytochalasin D (
Wada and Penninger, 2004). The infection of HeLa cells by
T. gondii resulted in an increase in MAPK phosphorylation, which has been implicated in signal transduction in this particular parasitic infection. In order to ascertain whether MAPKs function in cell invasion and the intracellular replication of
T. gondii, tachyzoite-infected HeLa cells, with or without specific MAPK inhibitors, were observed via western blot or [
3H] uracil incorporation assay. ERK and p38 MAPKs activations were observed in the infected cells at 1 hr and/or 6 hr after infection, and JNK activation was observed at 1 hr. The specific inhibitors, PD098059 and SB203580, prevented MAPK activation during
T. gondii infection. We observed that treatment with SB203580, SP600125 and mixed MAPK inhibitors in
T. gondii infected HeLa cells resulted in a suppression of tachyzoite replication (
Fig. 2). However, others have shown that
T. gondii replication appears independently of host p38 MAPK activation (
Gomez-martin et al., 1998). Macrophages exposed to live
T. gondii tachyzoites undergo ERK1/2, JNK and p38 MAPK activation (
Valere et al., 2003;
Denkers et al., 2004). The activity of ERK1/2, but not p38, is involved in the control of intracellular
Mycobacterium avium replication in human macrophages (
Blumenthal et al., 2002). SB203580 enhances
Leishmania donovani survival in human peripheral blood mononuclear macrophages (
Junghae and Raynes, 2002). In this experiment, ERK1/2, p38 and JNK MAPKs were involved in cell invasion of
T. gondii. However, p38 and JNK MAPK pathways were related with the replication of
T. gondii tachyzoites.
Chemokines are key inflammation mediators, and function principally as chemoattractants for leukocytes, recruiting monocytes, neutrophils, and other effecter cells from the blood to infection sites. In this experiment, the role of the chemokines in the mediation of inflammatory responses after
T. gondii infection and MAPK activation were evaluated via ELISA and RT-PCR. Elevated MCP-1 secretion by mouse peritoneal macrophages was demonstrated at 6, 12, and 24 hr after infection with
T. gondii tachyzoites. A suppression of MCP-1 secretion in infected peritoneal macrophages was observed in conjunction with treatment with PD98059, SP600125 and mixed MAPK inhibitors (
Fig. 3B). SB203580 was shown to inhibit
T. gondii proliferation, however, no inhibition of MCP-1 secretion was observed after tachyzoite infection (
Figs. 2,
3B). Increased MIP-1α secretion was observed 6 hr after the
T. gondii infection of macrophages, and evidenced a plateau 24 hr PI. MIP-1α secretion in infected cells evidenced a MCP-1 secretion profile; secretion was reduced as the result of treatment with PD98059, SP600125, and mixed MAPK inhibitors, but not with SB203580 treatment. The expression of MIP-1α mRNA in
T. gondii-infected macrophages was increased at 18 hr PI. The MIP-1α mRNA levels of macrophages infected with
T. gondii were shown to have been reduced after treatment with PD98059 and SP600125. MCP-1 secretion may contribute to the recruitment of monocytes and lymphocytes, and may also play a role in the control of
T. gondii infection as well as pathogenesis (
Brenier-Pinchart et al., 2000).
T. gondii-infected HeLa cells induced the activation of nuclear kappa B (NF-κB), and also effected an increase in the expression of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and MCP-1 mRNA (
Kim JM et al., 2001).
T. gondii infection of astrocytes and glioblastoma cells resulted in an increase in MCP-1 secretion (
Brenier-Pinchart et al., 2004). MCP-1 triggers tyrosine phosphorylation and the activation of the JAK/STAT3 pathway. MCP-1 stimulates ERK1/2 and stress activated protein kinase JNK and p38 (
Cambien et al., 2001;
Terra et al., 2004). MCP-1 mediated chemotaxis and transendothelial migration were diminished significantly by treatment with SB202190 and SB203580 (
Cambien et al., 2001). Uric acid-induced MCP-1 upregulation in vascular smooth muscle cells occurs in a p38 and ERK 1/2 MAPK-dependent manner (
Kanellis et al., 2003). Type I cytokine response induced by
T. gondii is a predictor for the upregulation of parasite-induced MIP-1 gene transcription (
Bliss et al., 1999). The CC chemokines, RANTES, MIP-1α and MIP-1β induced the microbicidal activity of
Trypanosoma cruzi via NO (
Villalta et al., 1998). In our experiment, the chemokines, MCP-1 and MIP-1α secretion were enhanced by
T. gondii infection via ERK1/2 and JNK MAPK pathways.
Induction of COX-2 expressions promotes inflammation with prostaglandins. Arachidonic acid within the cell membrane functions as a substrate for COX-2, which transforms it into eicosanoids. Two isoforms of COX have been identified. COX-1 is expressed in the majority of cells, and COX-2 is inducible and remains undetectable in unstimulated mammalian cells. COX-2, which is expressed abundantly in inflammation, is an enzyme that regulates prostaglandin synthesis. In as much as PGE
2 exerts immunosuppressive and vasodilator activities and enhances vascular permeability, it can be said to facilitate pathogenic invasion. The signal mechanisms involved in the upregulation of COX-2 remain unknown. The inhibition of COX-2 expression and/or its activity is a component of treatments for inflammatory diseases and tumor growth (
Tsatsanis et al., 2006). In the present study, we determined that MAPK activation was related to COX-2 expression and PGE
2 production in
T. gondii-infected RAW264.7 cells via RT-PCR, western blotting, and enzyme immunoassays. The expression of COX-2 mRNA in RAW 264.7 cells infected with
T. gondii was increased at 3, 6, and 18 hr. The specific inhibitors, SB203580 and SP600125 effected a marginal inactivation of COX-2 mRNA expression in infected cells. COX-2 secretion achieved a maximum level at 6 hr, and gradually decreased until 24 hr PI. COX-2 was suppressed by the JNK inhibitor, SP600125. The differential time course pattern of COX-2 mRNA expression (maximum at 18 hr) and COX-2 protein level (maximum at 6 hr) was presented. The secretion of PGE
2 from RAW 264.7 cells infected with
T. gondii increased rapidly at 24 hr PI, as determined. PGE
2 synthesis in parasite-infected cells was significantly suppressed by 3 MAPK inhibitors; PD98059, SB203580, and SP600125. MAPK inhibitors have been used to show that
Candida albicans selectively upregulates COX-2 via p38 MAPK. No involvement of JNK and ERK1/2 was observed (
Deva et al., 2003). An NF-κB inhibitor (PDTC), a ERK1/2 inhibitor (PD98059), and p38 inhibitor (SB203580) were shown to significantly suppress COX-2 gene transcription and PGE
2 synthesis in neutrophils treated with
H. pylori water extracts (
Kim JM et al., 2001). PGE
2 synthesis evidenced a significant increase in parallel with COX-2 expression, in cases in which cells were incubated in the presence of
L. donovani promastigotes or LPS (
Matte et al., 2001). SP600125, SB203580, and PD98059 suppressed IL-1 β-induced PGE
2 production and COX-2 expression in human chondrocytes (
Nieminen et al., 2005;
Nieminen et al., 2006). In this experiment, COX-2 secretions via JNK pathway and PGE
2 secretion via ERK1/2, p38 and JNK pathways were appeared, respectively.
In conclusion, the activation of MAPKs are involved in the invasion and proliferation of T. gondii tachyzoites in the host cells. Additionally, T. gondii induces the secretion of CC chemokines, MCP-1 and MIP-1α, as well as the expression of COX-2/PGE2 in the infected cells via MAPK signal pathways.
Notes
-
This work was supported by a Grant No. R01-2002-000-00422-0 from Korea Science and Engineering Foundation.
References
Fig. 1
T. gondii-induced phosphorylations of ERK1/2, p38 and JNK MAPK in HeLa cells were detected by western blot analysis. Proteins were extracted from HeLa cells, which were infected with T. gondii (cell : tachyzoite = 1 : 5). The specific inhibitors of MAPK, PD98059 (20 µM), SB203580 (20 µM) and SP600125 (20 µM) were applied for 20 min before infection. ERK1/2 MAPK activation at 1 hr PI and p38 MAPK activation at 1 hr and 6 hr were noted (A). Specific inhibitors of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK (PD98059 and SB203580) induced MAPK inactivation in T. gondii infected HeLa cells (B).
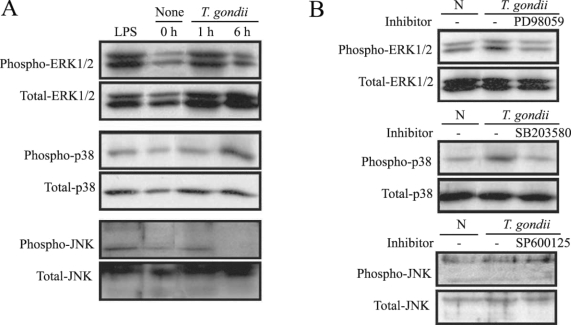
Fig. 2Replication of T. gondii tachyzoites in HeLa cell was detected by [3H]-uracil incorporation assay with or without specific MAPK inhibitors. After incubation, [3H]-uracil (1 µCi/ml) was added for 2 hr and [3H]-uracil incorporation was determined with a β-scintillation counter after cell harvesting. Treatment of SB203580 (10 µM), SP600125 (10 µM) and mixed MAPK inhibitors significantly suppressed tachyzoite replication in infected HeLa cells at 5 hr and 18 hr post infection. PD98059 (10 µM) did not significantly inhibit intracellular replication. Ratio of cell : tachyzoite = 1 : 5 (A) and 1 : 10 (B). *P < 0.05.
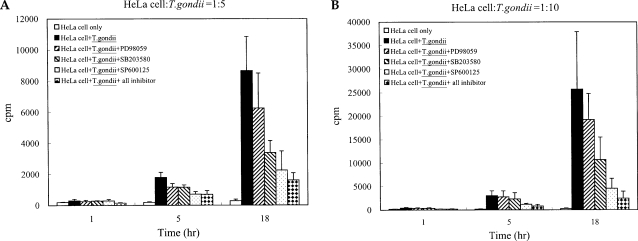
Fig. 3The time course of MCP-1 secretion in mouse peritoneal macrophages infected with T. gondii by ELISA (A). The macrophages were infected with T. gondii tachyzoite (•) or left untreated (◦) for 0, 6, 12 and 24 hr. The macrophages were pretreated with 20 µM PD98059 (▫) or 10 µM SP600125 (▪) for 20 min before infection. MCP-1 secretion levels of mouse macrophages were reduced by treatment with MAPK inhibitors (B). The macrophages were pretreated with ERK1/2 inhibitor (5 µM, 10 µM or 20 µM PD98059), p38 inhibitor (5 µM, 10 µM or 20 µM SB203580), JNK inhibitor (5 µM, 10 µM or 20 µM SP600125) or 10 µM mixed MAPK inhibitors for 20 min, and culture supernatants were obtained after 24 hr of infection. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 separate experiments. h = hour. None; mouse macrophages only, T. gondii; T. gondii infection. *P < 0.05.
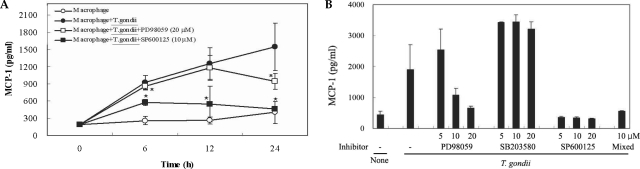
Fig. 4Time course of MIPP-1α secretion in mouse peritoneal macrophages infected with T. gondii via ELISA (A). The macrophages were cultured with T. gondii (•) or left untreated (◦) for 0, 6, 12 and 24 hr. The macrophages were pretreated with 20 µM PD98059 (▫) or 10 µM SP600125 (▪) for 20 min, and were infected with T. gondii. The MIPP-1α secretion levels of the macrophages were reduced by treatment with ERK1/2 or JNK MAPK inhibitors (B). The macrophages were pretreated with 5 µM, 10 µM or 20 µM PD98059, 5 µM, 10 µM or 20 µM SB203580, 5 µM, 10 µM or 20 µM SP600125, or 10 µM of all 3 MAPK inhibitors for 20 min, and were infected with T. gondii for 24 hr. MIPP-1α mRNA was upregulated in RAW 264.7 cells infected with T. gondii, according to the results of RT-PCR analysis (C). RNA was extracted from RAW 264.7 cells at 1, 3, 6, and 18 hr PI with T. gondii. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with 20 µM PD98059, 10 µM SB203580 or 10 µM SP600125 for 20 min, and were infected with T. gondii for 18 hr. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 separate experiments (A & B). h = hour. None (B); mouse macrophages only, T. gondii; T. gondii infection. *P < 0.05. None (C); RAW 264.7 cells only, PD; PD98059, SB; SB203580, SP; SP600125.
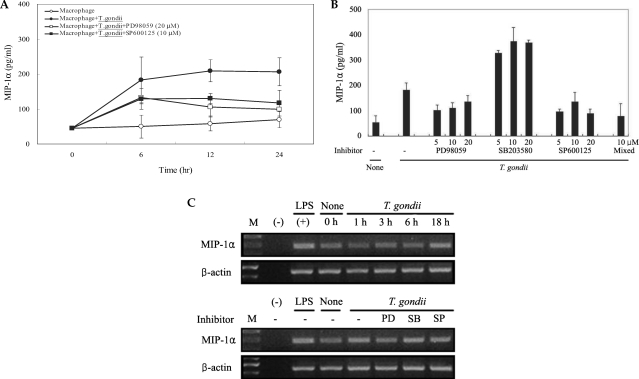
Fig. 5COX-2 mRNA expression was upregulated after T. gondii infection, according to the results of RT-PCR analysis (A). RAW 264.7 cells were infected with T. gondii for 1, 3, 6, and 18 hr, and total cellular RNA was extracted. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with 50 µM NS-398, 20 µM PD98059, 10 µM SB203580 or 10 µM SP600125 for 20 min, and were infected with T. gondii for 18 hr. COX-2 protein was upregulated in RAW 264.7 cells infected with T. gondii, according to the results of western blot analysis (B). Protein was extracted from RAW 264.7 cells at 1, 6, 18, and 24 hr postinfection with T. gondii. RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with 50 µM NS-398, 20 µM PD98059, 10 µM SB203580 or 10 µM SP600125 for 20 min, and were infected with T. gondii for 24 hr. (M); marker, (-); negative control, None; RAW 264.7 cells only, T. gondii; T. gondii infection, NS; NS-398, PD; PD98059, SB; SB203580, SP; SP600125.
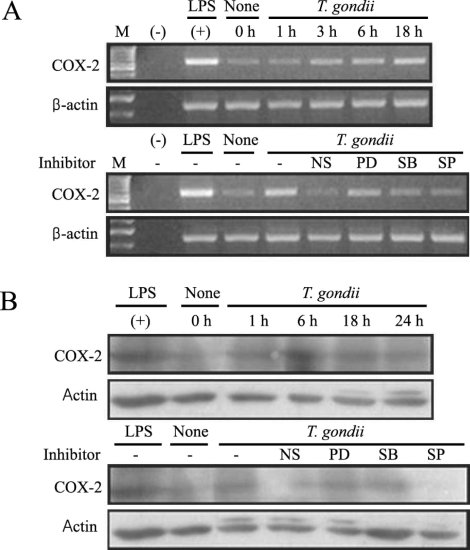
Fig. 6Time course of PGE2 synthesis in RAW 264.7 cells infected with T. gondii via ELISA. The RAW 264.7 cells were infected with T. gondii (▫) or LPS (▪) for 0, 6, 18, 24, and 48 hr, and the supernatant was used (A). The effects of MAPK inhibitors in RAW 264.7 cells infected with T. gondii (B). The RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with 50 µM NS-398, 20 µM PD98059, 10 µM SB203580, or 10 µM SP600125 for 20 min, and were infected with T. gondii for 48 hr. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD of 3 separate experiments. None; RAW 264.7 cells, T. gondii; T. gondii infection. *P < 0.05.