Abstract
The positive rate of Clonorchis sinensis is the highest among intestinal parasites in the Republic of Korea (Korea). More than 1.2 million people were at risk of C. sinensis infection in Korea in 2012. An intensive control program is being implemented for residents of the 5 major river basins to reduce helminthic infections, including C. sinensis infection. This study evaluated the continuous intensive control program for parasitic diseases including clonorchiasis in areas near the 5 major river basins in Korea over the past 10 years (2011–2020). A total of 335,020 fecal samples (one sample per resident) prepared by the modified sedimentation technic were microscopically examined. Those who expelled helminth eggs were treated with anthelmintics through local health centers and re-examined 3 months later. The overall positive rate of helminths egg was 7.1%. The annual positive rates were dramatically decreased from 14.4% (2011) to 5.9% (2020). The egg positive rate was highest in C. sinensis (5.3%), followed by heterophyid flukes (1.5%) and Trichuris trichiura (0.2%). The prevalence of C. sinensis was significantly higher in males (7.6%) than in females (3.7%), and the highest in the 50–59 years (7.0%) age group. Our results are beneficial to establish prevention and control policies against helminthiases including clonorchiasis in endemic areas in this country.
-
Key words: Clonorchis sinensis, intestinal parasite, infection rate, endemic area
INTRODUCTION
Helminthic infections, including soil-transmitted and food-borne parasites, are widespread around the world, particularly in developing countries in tropical and subtropical regions. In 2010, 1.7 billion people were estimated to be infected with intestinal parasites including 438.9 million people with hookworm, 819 million people with
Ascaris lumbricoides, and 464.6 million people with
Trichuris trichiura [
1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that 1.5 billion people are infected with soil-transmitted helminths in 2020 [
2].
In 1971, the first nationwide survey was conducted to determine the status of intestinal parasite infection in Koreans. Thereafter, 8 surveys have been conducted at intervals of 5 to 8 years. From the 1970s to 1980s, parasitic infections in Koreans were mainly caused by soil-transmitted helminths, including
A. lumbricoides,
T. trichiura, and hookworms. In particular, the infection rate of
A. lumbricoides was extremely high in 1971 survey (54.9%), but decreased to 0.05% by 2004 and 0.03% by 2012. The reduction of these soil-transmitted helminthiases can be explained by the deworming and health prevention projects promoted by the government and related organizations for citizens [
3,
4].
Although the prevalence of soil-transmitted helminthiases was decreased significantly in 2004 survey, the prevalence of fish-borne parasitic diseases, caused by
C. sinensis and heterophyid flukes remained high, especially in river basins [
5–
8]. The egg positive rate of
C. sinensis was 4.6% in the first survey conducted in 1971, but decreased to 1.4% in the 6th survey conducted in 1992. However, the positive rate increased to 2.4% in the 7th survey in 2004. Although it decreased slightly in the 8th survey, it is higher than that reported in the 6th survey [
3].
C. sinensis infection is the most common parasitic infection in Korea [
9].
C. sinensis infection is particularly prevalent among people living in the basins of 5 major rivers, including the Han, Geum, Nakdong, Yeongsan, and Seomjin rivers [
10–
12]. The habit of eating raw fish is one of the reasons
C. sinensis is still endemic in these river basins. This habit, as part of popular and long-standing traditional eating patterns, has resulted in the ongoing transmission of
C. sinensis to humans [
13,
14].
C. sinensis infection provokes severe pathological changes in the biliary passage, including bile duct dilatation, ductal wall thickening, ductal inflammation, biliary mucosal hyperplasia, and biliary cirrhosis. Several studies have demonstrated carcinogenetic effects of clonorchiasis.
C. sinensis is classified as a group I biological carcinogen in 2009 by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) [
15]. Food-borne trematodiasis is also one of the neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) targeted by WHO. The present study aimed to evaluate the status of helminthic infections among the population in the 5 major river basins in the Korea from 2011 to 2020.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Institutional review board statement
Ethical approval was waived because this study was conducted to evaluate public welfare through a fact-finding survey (Infectious Disease Control and Prevention Act, Article 17 (1)).
Sampling strategy and study population
This study was conducted in regions endemic for clonorchiasis during the period between 2011 and 2020, including the Han, Geum, Yeongsan, Seomjin, and Nakdong river basins. The sampling regions were selected with the voluntary participation of the public health centers every year.
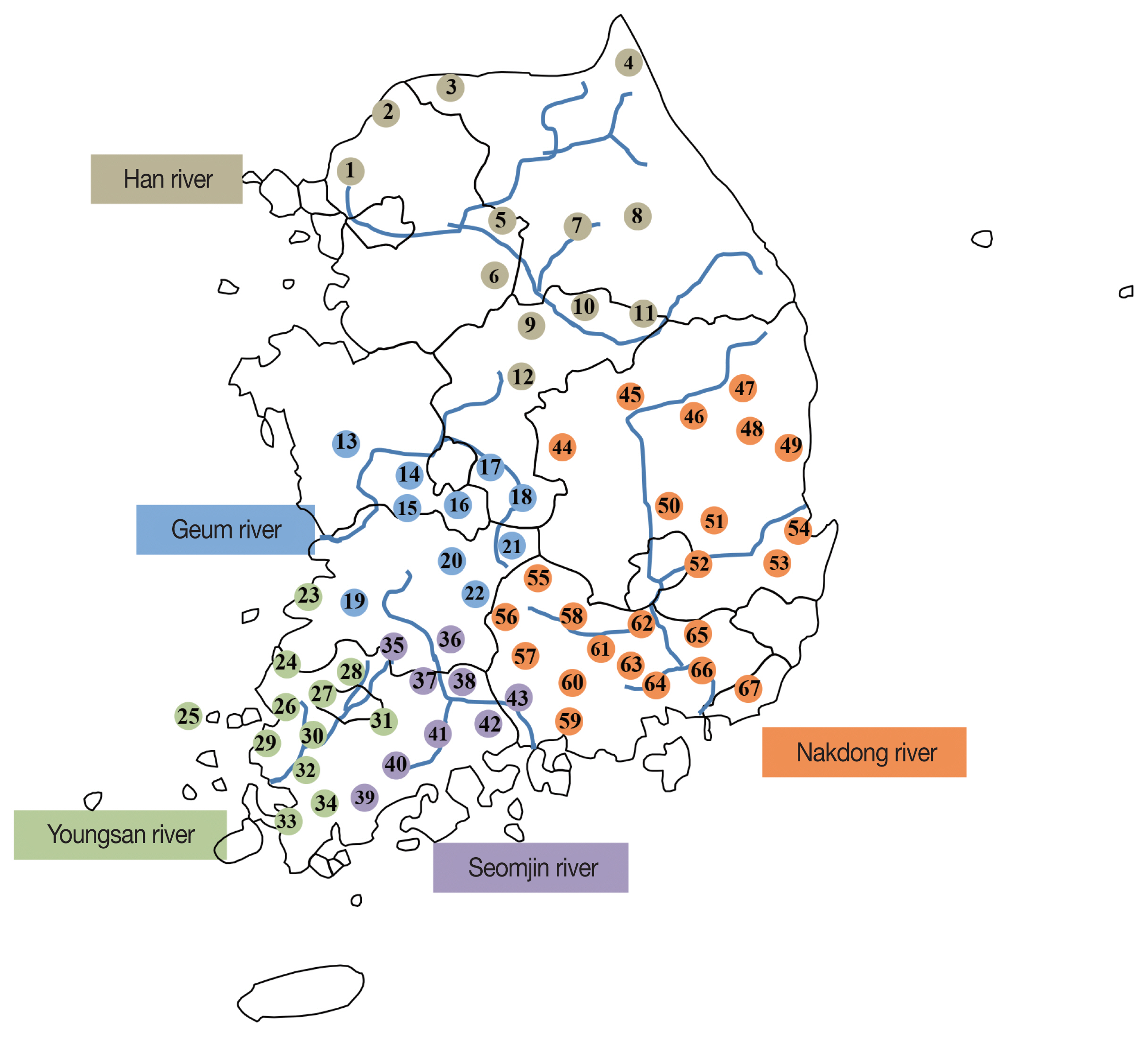
Fig. 1 summarizes the areas of the 5 major rivers and provinces.
The specimens were stored in a refrigerator until examination. The modified sedimentation technique using water instead of formalin was used to prepare specimens. The helminthic eggs and larvae, and protozoan cysts by microscopically detected. Further, we determined the number of helminth eggs per gram of feces (EPG). The EPG level was calculated based on a previous report with modification [
16,
17]. The infection levels were divided as follows: Group I (EPG 1–99), Group II (EPG 100–999), Group III (EPG 1,000–4,999), Group IV (EPG 5,000–9,999), and Group V (EPG>10,000).
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 28.0 (Chicago, Illinois, USA). Logistic regression was used to analyze statistically significant differences between years according to infection intensity. Statistical significance was set at P<0.05.
RESULTS
Infection rate of helminth parasites
Of 335,020 participants from 2011 to 2020, helminth eggs detected in 23,698 specimens. A total of 23,678 (7.06%) cases were positive for helminth eggs (
Table 1). The most commonly found parasitic eggs were fish-borne trematodes, such as
C. sinensis and heterophyids.
C. sinensis eggs were detected in 17,885 (5.3%) cases, which was significantly higher than that of other parasites. Heterophyids were detected in 4,892 cases, with a positive rate of 1.5%. The other detected helminth eggs and cysts included
T. trichiura,
Gymnophalloides seoi, and Echinostome species,
A. lumbricoides, hookworms,
Paragonimus westermani, Diphyllobothriid species, and
Taenia species had an infection rate of less than 0.2%. The prevalence of parasitic diseases decreased significantly during the survey period, from 14.4% in 2011 to 5.9% in 2020. In particular,
A. lumbricoides, hookworms,
P. westermani, Diphyllobothriid tapeworm species,
Taenia species were not detected in 2019 and 2020 during the survey.
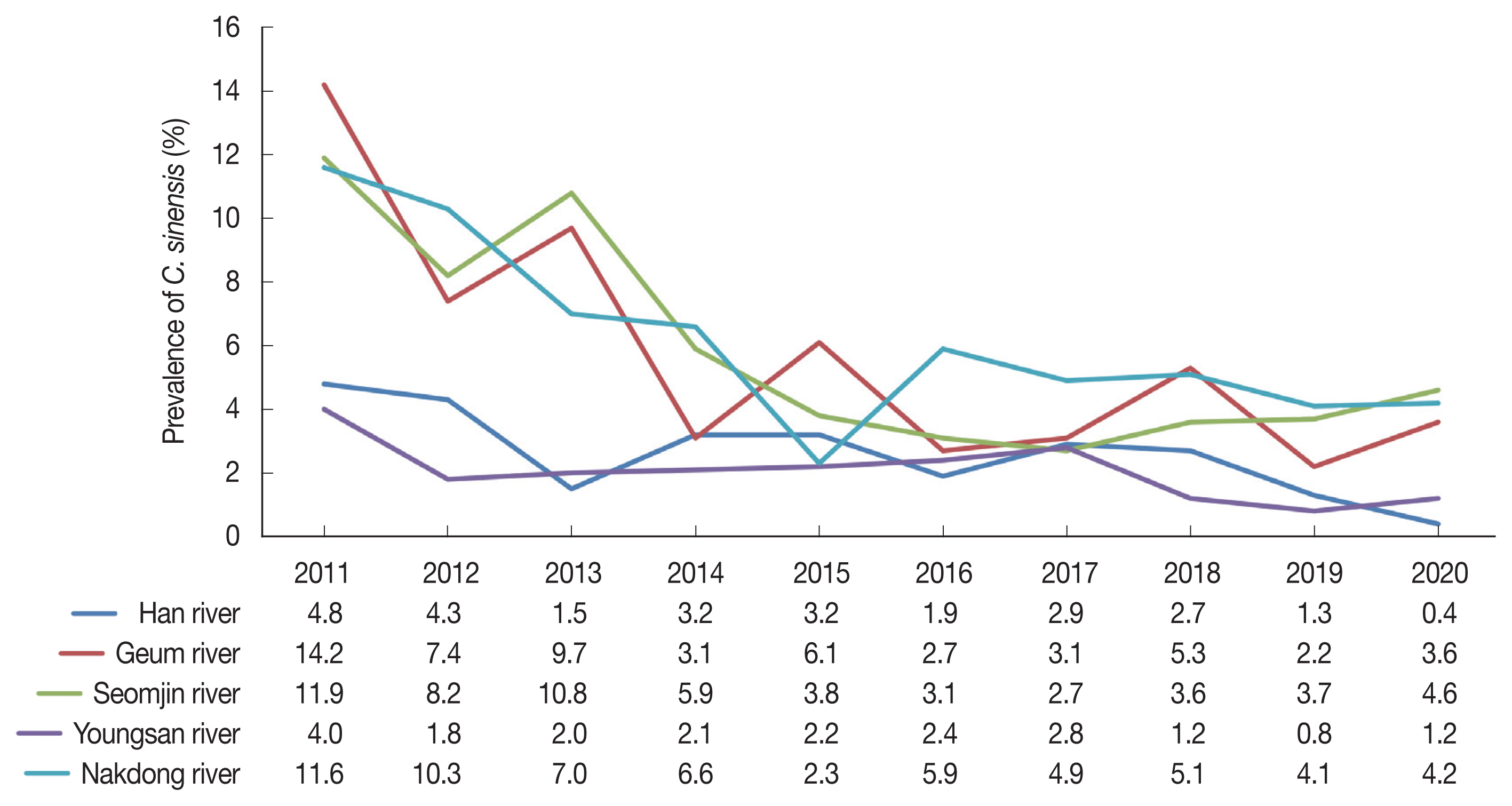
The infection rate of
C. sinensis decreased significantly from 11.1% in 2011 to 3.8% in 2020 in the river basins (
Table 1). In 2011, the prevalence of
C. sinensis was highest in Geum river (14.2%), followed by Seomjin river (11.9%), Nakdong river (11.6%), Han river (4.8%), and Youngsan river (4.0%). However, despite a significant decline in 2020,
C. sinensis infection rate was highest in Seomjin river (4.6%), followed by Nakdong river (4.2%), Geum river (3.6%), Youngsan river (1.2%), and Han river (0.4%) (
Fig. 2).
During the entire survey period,
C. sinensis positive rate in males (7.6%) was significantly higher than that in females (3.7%) (
Table 2). The positive rate for
C. sinensis was highest among those aged 50–59 years (7.0%), followed by those aged 60–69 years (5.9%), 40–49 years (5.9%), 70–79 years (4.5%), and 30–39 years (3.5%). Between 2019 and 2020, the highest positive rate was observed in individuals aged 60–69 years (4.2–4.3%) (
Table 3).
The intensity of infection was divided into 5 groups depending on the EPG value.
Table 4 shows that the intensity of infection decreased significantly below group III.
DISCUSSION
This study investigated the positive rate of helminth eggs through stool examination from 2011 to 2020, for residents in endemic areas who were exposed to risk of infection. We examined 335,020 inhabitants and found that 23,698 (7.1%) egg positive cases. We were able to identify 10 parasite species, the most common being C. sinensis.
In 1969, ascariasis was the most common parasitic disease, with an infection rate of 58.2% [
11]. Its rate was 55.9% in the first national survey done in 1971. However, the positive rate of ascariasis decreased to 0.3% in the 5th national survey in 1992 [
3], indicating that ascariasis was close to elimination. Korea was certified for eradication of soil-transmitted helminthiasis by WHO in 2001 [
18]. In this study, we detected only 12 cases of roundworm infection and 4 cases of hookworm infection during the study period. This result is consistent with previous reports [
3], and is attributed to the active and steady fecal examination for parasite eggs and anti-helminthic treatment conducted as part of the parasite disease prevention project led by the government [
19].
The infection rate of
C. sinensis was 1.9% in the 8th national survey in 2012. Considering the fact that the
C. sinensis infection rate in the endemic area declined from 8% in 2012 to 3.8% in 2020, the nationwide infection rate is expected to reach less than 1% in 2020. The Korea Association of Health Promotion (KAHP) has been implementing an annual intestinal parasite infection survey with more than 100,000 people through health checkups, and the surveys after 2019 also showed that the infection rate of liver flukes was less than 1% [
20].
Even though soil-transmitted parasites have been eliminated, food-borne parasites, such as C. sinensis and heterophyid flukes, account for a large proportion of helminthic infections. These results suggest strongly that liver flukes should pay the most attention to parasite elimination in this country.
C. sinensis eggs develop into adults approximately 4 weeks after the consumption of infected freshwater fish. If untreated, they can survive for up to 30 years in the human body [
21]. The frequency of infection is high in elderly individuals who have a habit of eating raw freshwater fish [
22]. In this study, people in their 50s and 70s were the major high-risk groups. Further, males showed a higher infection rate than females, as they are expected to have a relatively high chance of eating freshwater fish [
23]. The positive rates of liver flukes based on the river basin in 1981 were 40.2% in Nakdong river, 30.8% in Yeongsan river, 17.3% in Seomjin river, 15.7% in Han river, and 12.0% in Geum river [
16]. However, these rates were dramatically decreased to 4.6% in Seomjin river, 1.2% in Yeongsan river, and 3.6% in Geumgang river in 2020, as evidence by this study. This difference appears to be the result of continuous collective management of clonorchiasis [
23]. In the future, the elimination of clonorchiasis is possible through continued implementation of such management projects for residents of these high-risk areas.
Parasite infection intensity is considered an indicator of pathogenicity. To calculate the infection intensity, the EPG was determined. Although C. sinensis infection continued in Korea, the intensity of infection was found to have decreased. To eliminate clonorchiasis in this country, the control intervention should continuously focus on raw fish-eating population especially men over 50 in the residual endemic communities along the Nakdong river, Seomjin river, and Geum river.
Notes
-
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank person in charge of the health center who participated in the sample collection. This work was supported by a grant from the Korea Centers for Diseases Control and Prevention, Republic of Korea (KCDC 4800-4847-311).
Fig. 1The surveyed areas for fecal examination in residents by 5 major rivers in the Republic of Korea (2011–2020). 1. Paju-si, 2. Yeoncheon-gun, 3. Cheorwon-gun, 4. Goseong-gun, 5. Yangpyeong-gun, 6. Yeoju-si, 7. Hoengseong-gun, 8. Pyeongchang-gun, 9. Chungju-si, 10. Jecheon-si, 11. Danyang-gun, 12. Goesan-gun, 13. Cheongyang-gun, 14. Gyeryong-si, 15. Nonsan-si, 16. Geumsan-gun, 17. Okcheon-gun, 18. Yeongdong-gun, 19. Jeongeup-si, 20. Jinan-gun, 21. Muju-gun, 22. Jangsu-gun, 23. Buan-gun, 24. Yeongwang-gun, 25. Shinan-gun, 26. Hampyeong-gun, 27. Jangseong-gun, 28. Damyang-gun, 29. Muan-gun, 30. Naju-si, 31. Hwasun-gun, 32. Yeongam-gun, 33. Haenam-gun, 34. Gangjin-gun, 35. Sunchang-si, 36. Namwon-si, 37. Gokseong-gun, 38. Gurye-gun, 39. Jangheung-gun, 40. Boseong-gun, 41. Suncheon-si, 42. Gwangyang-si, 43. Hadong-gun, 44. Sangju-si, 45. Yecheon-gun, 46. Andong-si, 47. Yeongyang-gun, 48. Cheongsong-gun, 49. Youngduk-gun, 50. Gunwi-gun, 51. Yeongcheon-si, 52. Gyeongsan-si, 53. Gyeongju-si, 54. Pohang-si, 55. Geochang-gun, 56. Hamyang-gun, 57. Sancheong-gun, 58. Hapcheon-gun, 59. Sacheon-si, 60. Jinju-si, 61. Uiryeong-gun, 62. Changnyeong-gun, 63. Haman-gun, 64. Changwon-si, 65. Miryang-si, 66. Gimhae-si, 67. Busan metropolitan City.
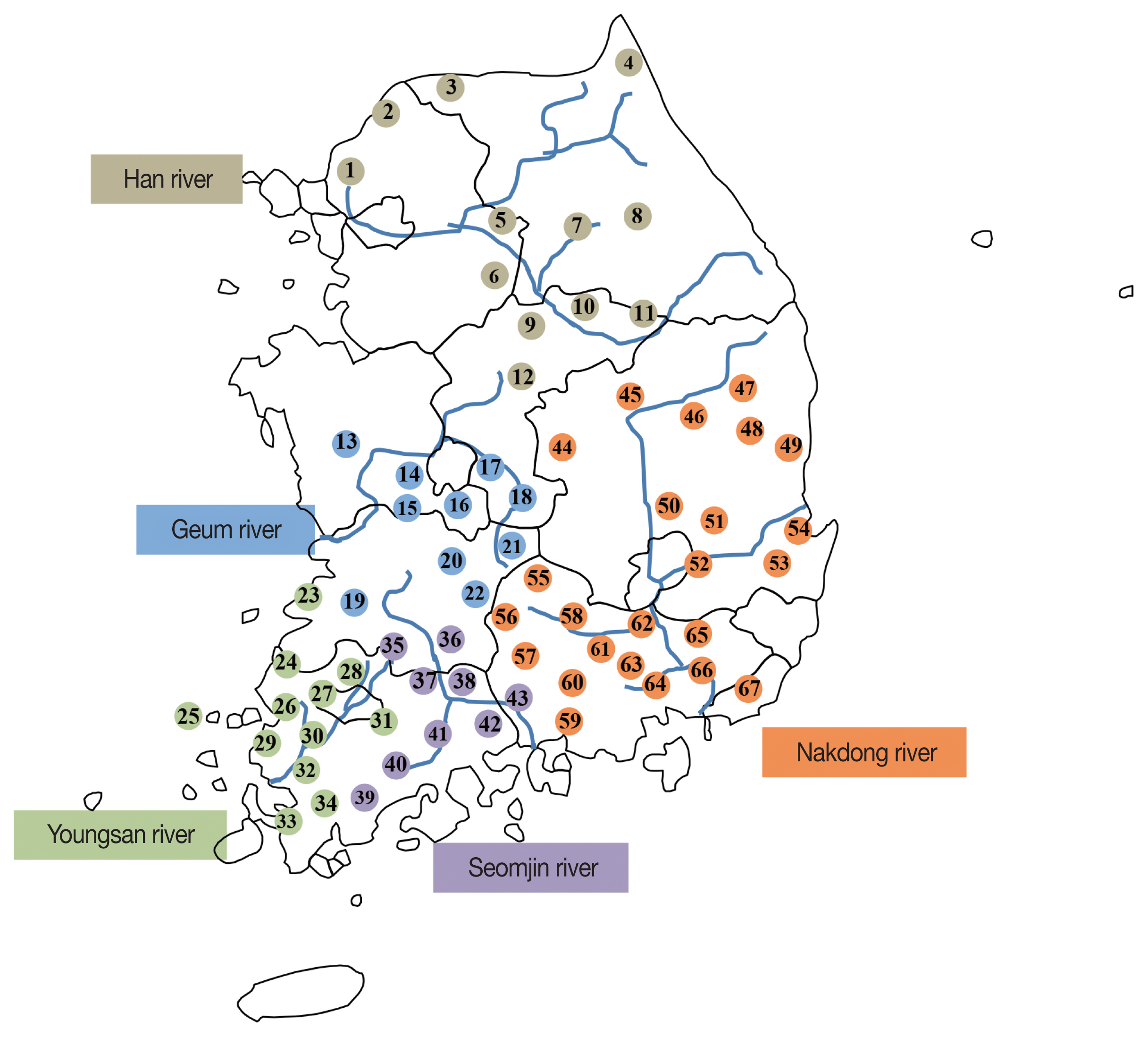
Fig. 2Changing patterns of clonorchiasis prevalence by the survey years and localities during 10 years in Korea. The value in each cell of table below the x-axis means the prevalence (%) of C. sinensis.
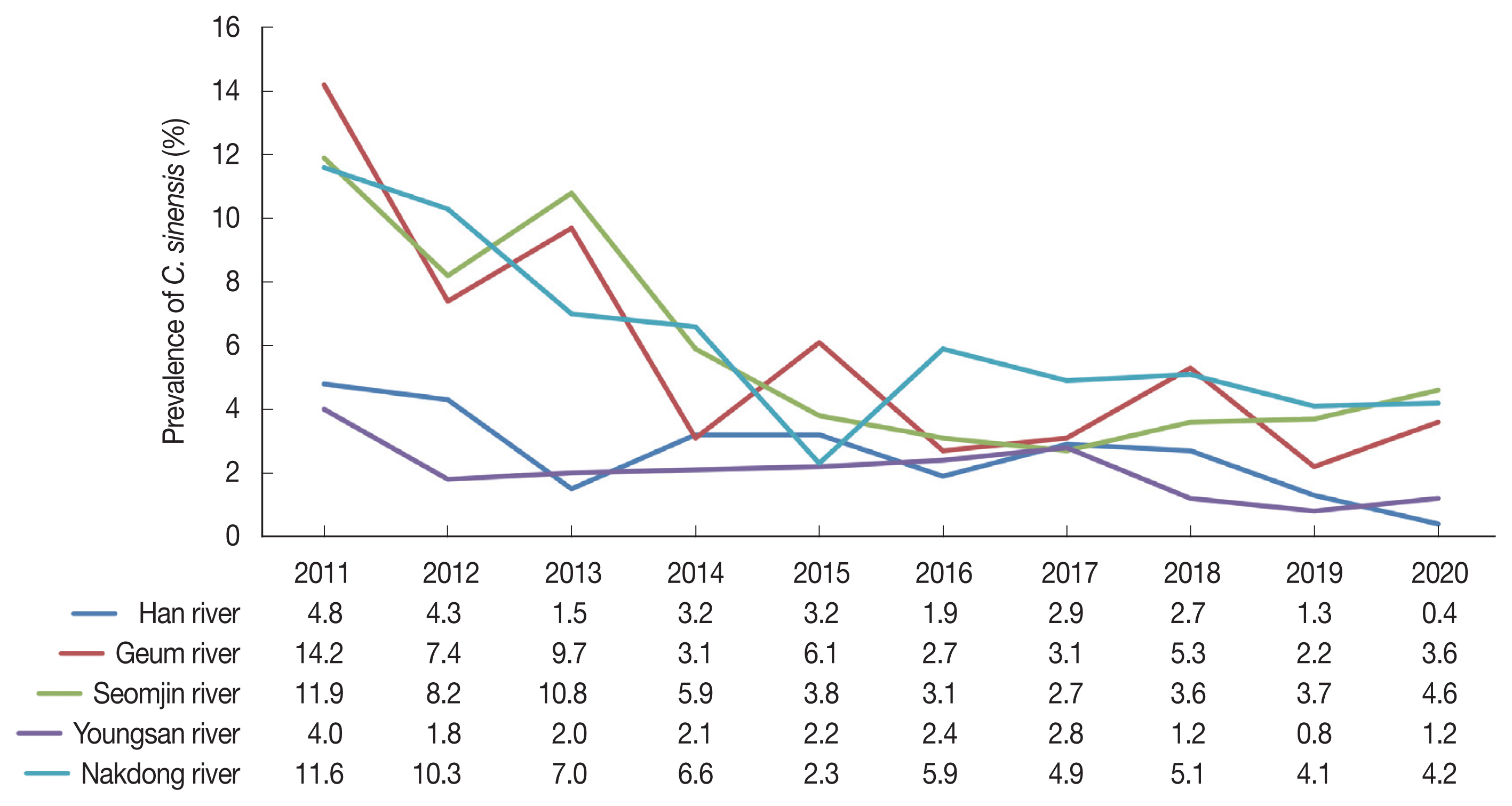
Table 1Prevalence (Egg positive rate) of helminths by the survey years (2011–2020) in Korea
Table 1
|
Year |
No. of Examined |
No. total positive (%) |
No. of cases positive for parasites (%) |
|
Cs |
Het |
Tt |
Gs |
Es |
Al |
Hw |
Pw |
Ds |
Ts |
|
2011 |
27,395 |
3,932 (14.4) |
3,049 (11.1) |
753 (2.7) |
107 (0.4) |
4 (0.01) |
3 (0.01) |
0 |
1 (0.004) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
2012 |
23,233 |
2,279 (9.8) |
1,867 (8.0) |
329 (1.4) |
49 (0.2) |
29 (0.12) |
2 (0.01) |
0 |
2 (0.01) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
2013 |
38,789 |
3,694 (9.5) |
2,950 (7.6) |
622 (1.6) |
69 (0.2) |
42 (0.11) |
2 (0.01) |
3 (0.01) |
1 (0.003) |
2 (0.01) |
1 (0.003) |
0 |
|
2014 |
41,139 |
2,682 (6.5) |
2,029 (4.9) |
555 (1.3) |
86 (0.2) |
6 (0.01) |
0 |
4 (0.01) |
0 |
1 (0.002) |
1 (0.002) |
0 |
|
2015 |
42,024 |
2,195 (5.2) |
1,778 (4.2) |
334 (0.8) |
69 (0.2) |
6 (0.01) |
4 (0.01) |
3 (0.01) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
2016 |
34,943 |
1,840 (5.3) |
1,419 (4.1) |
358 (1.0) |
44 (0.1) |
18 (0.05) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 (0.003) |
|
2017 |
38,648 |
1,927 (5.0) |
1,524 (3.9) |
319 (0.8) |
52 (0.1) |
28 (0.07) |
3 (0.01) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
2018 |
32,792 |
2,119 (6.5) |
1,351 (4.1) |
677 (2.1) |
63 (0.2) |
22 (0.07) |
1 (0.003) |
2 (0.01) |
0 |
0 |
3 (0.009) |
0 |
|
2019 |
30,415 |
1,528 (5.0) |
944 (3.1) |
505 (1.7) |
58 (0.2) |
21 (0.07) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
2020 |
25,642 |
1,502 (5.9) |
974 (3.8) |
440 (1.7) |
54 (0.2) |
33 (0.13) |
1 (0.004) |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Total |
335,020 |
23,698 (7.1) |
17,885 (5.3) |
4,892 (1.5) |
651 (0.2) |
209 (0.06) |
16 (0.005) |
12 (0.004) |
4 (0.001) |
3 (0.001) |
5 (0.001) |
1 (0.0003) |
Table 2Prevalence of clonorchiasis in the residents of Korea by the gender for 10 years
Table 2
|
Year |
Male |
Female |
|
|
|
No. examined |
No. positive (%) |
Prevalence (%) |
No. examined |
No. positive |
Prevalence (%) |
|
2011 |
11,917 |
1,747 |
14.7 |
15,478 |
1,302 |
8.4 |
|
|
2012 |
9,117 |
1,085 |
11.9 |
14,116 |
782 |
5.5 |
|
|
2013 |
16,138 |
1,647 |
10.2 |
22,651 |
1,303 |
5.8 |
|
|
2014 |
16,981 |
1,216 |
7.2 |
24,158 |
813 |
3.4 |
|
|
2015 |
17,076 |
1,071 |
6.3 |
24,948 |
707 |
2.8 |
|
|
2016 |
13,636 |
809 |
5.9 |
21,307 |
610 |
2.9 |
|
|
2017 |
14,475 |
842 |
5.8 |
24,173 |
682 |
2.8 |
|
|
2018 |
12,129 |
768 |
6.3 |
20,663 |
583 |
2.8 |
|
|
2019 |
10,851 |
503 |
4.6 |
19,559 |
441 |
2.3 |
|
|
2020 |
10,105 |
570 |
5.6 |
15,526 |
404 |
2.6 |
|
|
Total |
141,047 |
10,704 |
7.6 |
215,356 |
7,879 |
3.7 |
Table 3Prevalence of clonorchiasis during 10 years by age
Table 3
|
Year |
No. of egg positive/No. of examined (%) by age groups |
|
0–19 |
20–29 |
30–39 |
40–49 |
50–59 |
60–69 |
70–79 |
Over 80 |
|
2011 |
16/425 (3.8) |
15/274 (5.5) |
59/716 (8.2) |
266/1,953 (13.6) |
709/4,914 (14.4) |
832/7,230 (11.5) |
929/9,197 (10.1) |
208/2,526 (8.2) |
|
2012 |
1/199 (0.5) |
14/239 (5.9) |
18/486 (3.7) |
139/1,542 (9.0) |
439/4,212 (10.4) |
554/6,046 (9.2) |
584/8,446 (6.9) |
111/2,009 (5.5) |
|
2013 |
14/678 (2.1) |
10/375 (2.7) |
40/780 (5.1) |
181/2,441 (7.4) |
572/6,323 (9.0) |
747/9,328 (8.0) |
1,008/13,594 (7.4) |
230/3,788 (6.1) |
|
2014 |
1/439 (0.2) |
6/294 (2.0) |
19/695 (2.7) |
105/2,245 (4.7) |
472/6,920 (6.8) |
639/10,890 (5.9) |
605/14,617 (4.1) |
173/4,869 (3.6) |
|
2015 |
6/368 (1.6) |
4/303 (1.3) |
13/635 (2.0) |
79/1,882 (4.2) |
359/6,366 (5.6) |
598/11,479 (5.2) |
561/15,130 (3.7) |
158/5,842 (2.7) |
|
2016 |
1/225 (0.4) |
2/214 (0.9) |
14/506 (2.8) |
63/1,426 (4.4) |
268/4,802 (5.6) |
480/9,230 (5.2) |
436/12,840 (3.4) |
155/5,700 (2.7) |
|
2017 |
1/189 (0.5) |
3/275 (1.1) |
15/608 (2.5) |
63/1,520 (4.1) |
289/5,166 (5.6) |
517/10,200 (5.1) |
477/13,874 (3.4) |
158/6,798 (2.3) |
|
2018 |
1/304 (0.3) |
2/184 (1.1) |
14/409 (3.4) |
48/1,219 (3.9) |
262/4,231 (6.2) |
452/8,647 (5.2) |
426/11,753 (3.6) |
146/6,010 (2.4) |
|
2019 |
1/107 (0.0) |
3/157 (1.9) |
7/337 (2.1) |
23/823 (2.8) |
128/3,379 (3.8) |
343/8,165 (4.2) |
298/11,109 (2.7) |
140/6,323 (2.2) |
|
2020 |
0/117 (0.0) |
2/346 (0.6) |
5/373 (1.3) |
29/958 (3.0) |
139/3,287 (4.2) |
312/7,240 (4.3) |
340/8,615 (3.9) |
140/4,424 (3.2) |
|
Total |
44/3,249 (1.4) |
63/3,049 (2.1) |
216/6,235 (3.5) |
1,024/17,483 (5.9) |
3,857/54,734 (7.0) |
5,978/100,559 (5.9) |
6,064/133,461 (4.5) |
1,845/56,807 (3.2) |
Table 4Infection intensity of C. sinensis by EPG
Table 4
|
Grade |
Year |
P-value |
|
2011 |
2012 |
2013 |
2014 |
2015 |
2016 |
2017 |
2018 |
2019 |
2020 |
|
I |
2,613 |
1,577 |
2,646 |
1,780 |
1,608 |
1,253 |
1,337 |
1,199 |
840 |
830 |
0.000 |
|
II |
388 |
243 |
269 |
222 |
156 |
141 |
156 |
136 |
89 |
128 |
0.000 |
|
III |
42 |
43 |
32 |
24 |
13 |
20 |
17 |
13 |
15 |
14 |
0.002 |
|
IV |
3 |
3 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
0.250 |
|
V |
3 |
1 |
- |
1 |
- |
3 |
2 |
- |
- |
1 |
0.430 |
References
- 1. Pullan RL, Smith JL, Jasrasaria R, Brooker SJ. Global numbers of infection and disease burden of soil transmitted helminth infections in 2010. Parasites Vectors 2014;7:1-19. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-7-37
- 2. World Health Organization. Soil-transmitted helminth infections [Internet]; Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helminth-infections
- 3. Kim TS, Cho SH, Huh S, Kong Y, Sohn WM, Hwang SS, Chai JY, Lee SH, Park YK, Oh DK, Lee JK. A national survey on the prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in the Republic of Korea, 2004. Korean J Parasitol 2009;47:37-47. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2009.47.1.37
- 4. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National survey of the prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in Korea, the 8th report. Osong, Korea. Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention; 2013, (in Korean).
- 5. Hong SJ, Lee YH, Chung MH, Lee DH, Woo HC. Egg positive rates of Clonorchis sinensis and intestinal helminths among residents in Kagye-ri, Saengbiryang-myon, Sanchong-gun, Kyongsangnam-do. Korean J Parasitol 1994;32:271-273. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1994.32.4.271
- 6. Yu JR, Kwon SO, Lee SH. Clonorchiasis and metagonimiasis in the inhabitants along Talchongang (river), Chungwon-gun. Korean J Parasitol 1994;32:267-269. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1994.32.4.267
- 7. Joo CY, Chung MS, Kim SJ, Kang CM. Changing patterns of Clonorchis sinensis infections in Kyongbuk, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1997;35:155-164. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1997.35.3.155
- 8. Chai JY, Song TE, Han ET, Guk SM, Park YK, Choi MH, Lee SH. Two endemic foci of heterophyids and other intestinal fluke infections in southern and western coastal areas in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1998;36:155-161. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1998.36.3.155
- 9. Jeong YI, Shin HE, Lee SE, Cheun HI, Ju JW, Kim JY, Park MY, Cho SH. Prevalence of Clonorchis sinensis infection among residents along 5 major rivers in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2016;54:215-219. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2016.54.2.215
- 10. Hong ST, Fang Y. Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis, an update. Parasitol Int 2012;61:17-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2011.06.007
- 11. Seo BS, Rim HJ, Loh IK, Lee SH, Cho SY, Park SC, Bae JW, Kim JH, Lee JS, Koo BY, Kim KS. Study on the status of helminthic infections in Koreans. Korean J Parasitol 1969;7:53-70. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1969.7.1.53
- 12. Huh S, Huh SC. Intestinal parasitic infections of Korean Army soldiers in Whachon-gun, Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1993;31:293-294. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1993.31.3.293
- 13. Park MS, Kim SW, Yang YS, Park CH, Lee WT, Kim CU, Lee EM, Lee SU, Huh S. Intestinal parasite infections in the inhabitants along the Hantan river, Chorwon-gun. Korean J Parasitol 1993;31:375-378. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1993.31.4.375
- 14. Shin HE, Lee MR, Ju JW, Jeong BS, Park MY, Lee KS, Cho SH. Epidemiological and clinical parameters features of patients with clonorchiasis in the Geum river Basin, Republic of Korea. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis 2017;2017:7415301. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7415301
- 15. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. A review of human carcinogens Part B: biological agents. Lyon, France. International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2012.
- 16. Seo BS, Lee SH, Cho SY, Chai JY, Hong ST, Han IS, Sohn JS, Cho BH, Ahn SR, Lee SK, Chung SC, Kang KS, Shim HS, Hwang IS. An epidemiologic study on clonorchiasis and metagonimiasis in riverside areas in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1981;19:137-150. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.1981.19.2.137
- 17. Yu SH, Masanori K, Li XM, Xu LQ, Lan CG, Lin R. Epidemiological investigation on Clonorchis sinensis in human population in an area of South China. Jpn J Infect Dis 2003;56:168-171.
- 18. Executive Board. 107 World Health Organization Provisional Agenda of the Fifty-Fourth World Health Assembly [Internet]; Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/78662
- 19. Hong ST, Chai JY, Choi MH, Huh S, Rim HJ, Lee SH. A successful experience of soil-transmitted helminth control in the republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2006;44:177-185. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2006.44.3.177
- 20. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Infectious Disease Portal [Internet]; Available from: https://www.kdca.go.kr/npt/biz/npp/iss/parasitosisStatisticsMain.do
- 21. Na BK, Park JH, Hong SJ. Clonorchis sinensis and clonorchiasis. Acta Trop 2020;203:105309. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.actatropica.2019.105309
- 22. Kim C, So A, June KJ, Jung HY. A study on the prevalence of Clonorchis sinensis and the effects of educational program among residents in the basin of the Youngsan river, Korea. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs 2011;22:56-65. (in Korean)..
- 23. Lee SE, Shin HE, Lee MR, Kim YH, Cho SH, Ju JW. Risk factors of Clonorchis sinensis human infections in endemic areas, Haman-Gun, Republic of Korea: a case-control study. Korean J Parasitol 2020;58:647-652. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2020.58.6.647