Abstract
At the time of host attachment, ticks are very sensitive to histamine, but during rapid blood sucking they paradoxically require histamine. Using a rabbit model, we studied the effects of histamine and antihistamine during attachment and fast-feeding in different life stages of Haemaphysalis longicorns. We examined how they responded to histamine and antihistamine by analyzing the detachment rate, histology of feeding lesions, and post-feeding behavior. A significant difference (P<0.01) was found in the detachment rate between experimental and control treatments throughout the observation period. Ticks exhibited a higher detachment rate (30.1%) at 12 h after histamine application during attachment time and on antihistamine-treated skin (25.4%) at 96 h during fast-feeding. After feeding on histamine-treated rabbits, the fully engorged body weights of larvae and nymphs were 0.7±0.36 mg and 3.5±0.65 mg, respectively. An average increase in body weight of 0.6±0.05 mg and 3.2±0.30 mg was observed for larvae and nymphs compared to the respective control weights. Nymphs and adults engorged after antihistamine treatment had an average body weight of 1.3±0.54 mg and 54±0.81 mg, respectively. An average decrease in body weight was observed in antihistamine-treated H. longicornis compared with control nymphs (3.3±0.42 mg) and adults (174±1.78 mg). Skin biopsies were collected after treatment, and differential histopathological characteristics were found between the treatment and control groups. Tick-infested skin collected from rabbits in the antihistamine-treated group lacked erythrocytes in the feeding pool, indicating that antihistamine impaired tick fast-feeding stage.
-
Key words: Haemaphysalis longicornis, inflammatory mediator, blood sucking
Introduction
Tick feeding involves a complex series of 9 sequential stages [
1]. Host seeking and engagement with the host precede actual tick attachment and establishment of the feeding lesion. In the early phase of feeding, which lasts about 24 h post-attachment, ticks are sensitive to histamine [
2]. The skin is the main organ of the tick-host interface, playing a crucial role in the host’s response to tick infestation and in pathogen transmission by the vector. To feed, ticks must successfully overcome the host’s hemostasis, inflammation, and immune mechanisms [
3,
4].
Histamine is one of the major inflammatory mediators produced in response to tick infestation [
5]. In addition, histamine is thought to directly interfere with the normal feeding behavior of ticks [
6]. An in vitro study of the cattle tick
Boophilus microplus revealed that many larvae attached to bovine skin were induced to detach after infusion of a small amount of histamine into the attachment site [
2]. The same effect was found when histamine was injected below the larvae feeding on the cattle attachment site. The release of local histamine in the skin also causes the skin to itch, which could intensify grooming activities in tick-resistant hosts.
The feeding behavior of ticks during the attachment stage or the first 60–72 h is different from that in the fast-feeding stage or feeding stage after 60–72 h [
7]. Interestingly, histamine sensitivity is reduced after 3 days of attachment to the host [
2]. As the histamine-releasing factor induces histamine-release, histamine has a potential role in the late/rapid phase of tick feeding. Therefore, we hypothesized that histamine is essential during the fast-feeding stage of
H. longicornis ticks. If so, antihistaminic injection at this stage around the tick attachment site will either cause detachment of ticks or impair feeding.
In this study, a rabbit model was used to explore the role of histamine and antihistamine (chlorpheniramine maleate) during attachment and fast-feeding, respectively, of H. longicornis larvae, nymphs, and adults.
Materials and Methods
Ethic statement
All animals used in these experiments were housed in the Laboratory of Veterinary Parasitology, College of Veterinary Medicine and Bio-Safety Research Institute, Jeonbuk National University (Jeonju, Korea). All animal studies and protocols were compliant with the ethical principles of animal research and were approved by the Jeonbuk Animal Care and Use Committee (CBNU 2015–003).
Ticks and host
The Jeju strain of the hard tick
H. longicornis [
8] has been maintained in rabbits in our laboratory since 2003.
H. longicornis were reared at 27°C–28°C and 80–90% relative humidity. The three tick stages of larva, nymph, and adult were used in the study. To feed,
H. longicornis ticks were placed onto the dorsal surface sagittal to the vertebral column in the middle lumbar region of specific pathogen-free New Zealand White rabbits.
Sixteen rabbits were randomly assigned to 4 groups consisting of 4 rabbits per group. Two groups were injected with histamine at tick (larvae and nymph)-infested sites during the attachment stage. During the fast-feeding stage, the other 2 groups were injected with chlorpheniramine maleate at the attachment site of the tick (adult and nymph).
Tick attachment
Rabbit hair at the tick attachment site was clipped and shaved one day before transparent 1.25-inch-diameter plastic cups were attached to the rabbit with cement, one on each left and right lumbar sites. Each plastic cup received approximately 100 larvae, 50 adults, and 50 nymphs. The rabbits were sedated before tick attachment. Larvae and nymph attachment sites were used for histamine administration, while nymph and adult attachment sites were used for antihistamine administration.
Histamine and antihistamine injection
Intradermal histamine injections were administered (a dose of 20 μg) beneath the tick attachment at 12 h, 36 h, 48 h, and 60 h. In addition, Chlorpheniramine maleate (Huones Co., Seongnam, Korea) was administered (a dose of 200 μg) at 60 h, 72 h, 96 h, 108 h, and 120 h. After the histamine and antihistamine injections were completed, detached nymphs and adults (dead and alive) were collected, and live ticks were kept at 22°C in a 90% relative humidity chamber. For each rabbit, one of the 2 attachment sites was used as a control site that received no histamine or antihistamine injection.
For sedation, a combination of butorphanol (0.2 mg/kg), midazolam (0.5 mg/kg), and glycopyrrolate (0.01 mg/kg) was administered intramuscularly, as described previously [
9]. In addition, histamine dihydrochloride (Tokyo Chemical Industries, Tokyo, Japan) and chlorpheniramine maleate (Huones Co.) were diluted in PBS pH 7.5.
For histological evaluation, skin samples were collected from tick-infested rabbits (3 days post-infestation in histamine-treated rabbits and 6 days post-infestation in antihistamine-treated rabbits) and fixed in a 10% neutral buffered formalin solution. Afterward, fixed tissues were routinely processed [
10], embedded in paraffin, and then sectioned at 5-μm thickness using a microtome at room temperature. Tissue sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H & E) and examined under a microscope. Colored images were taken from H & E-stained skin sections using an Olympus BX51 microscope and Olympus DP72 camera equipped with DP2-BSW imaging software (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
The numbers of nymphs and adults in the dermis at the histamine or antihistamine-treated and non-treated sites were compared, and the significance was assessed using analysis of variance (ANOVA; P<0.05).
Results
Effect of histamine on larval and nymph attachment
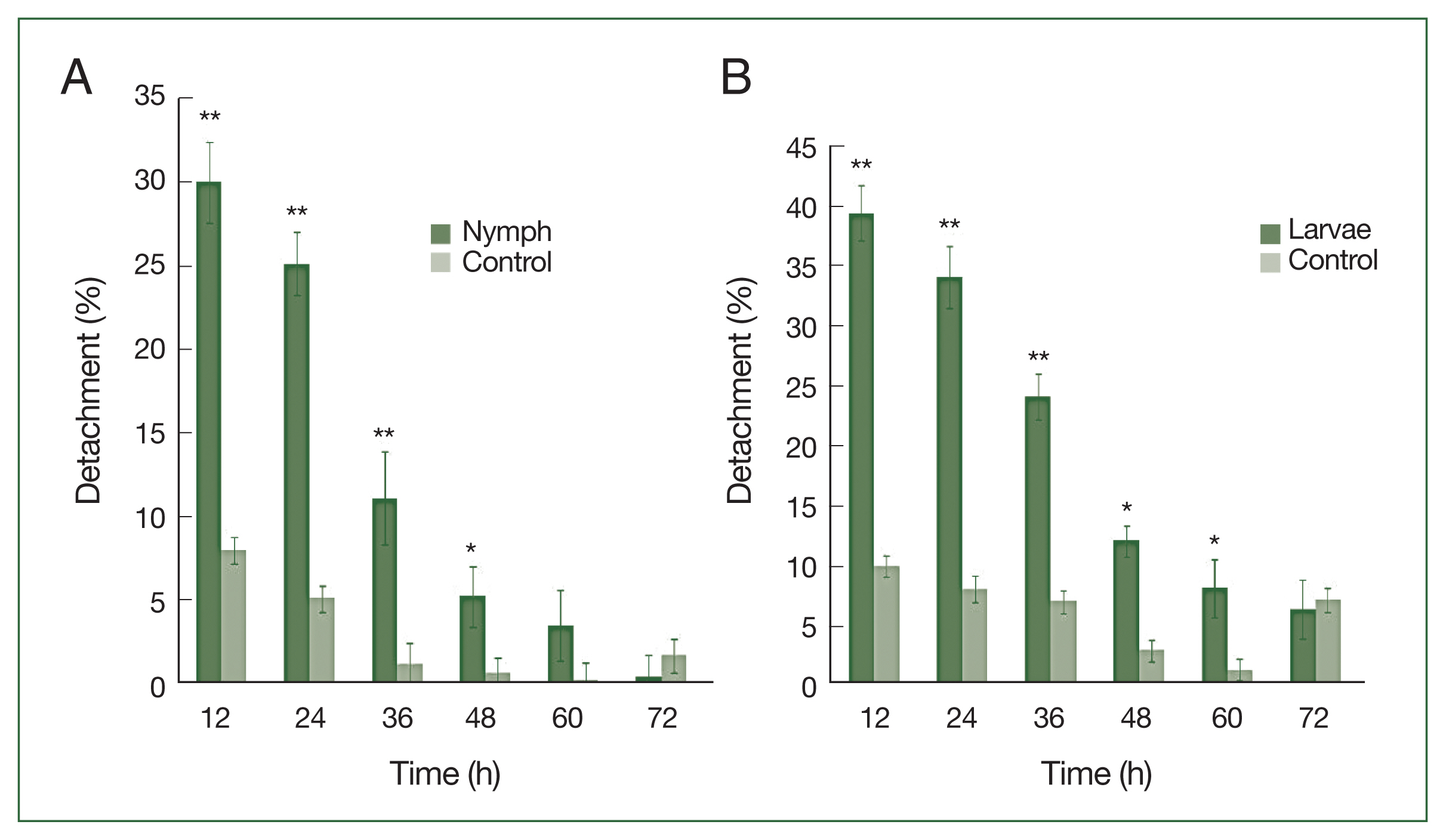
After 4 successive histamine injections in the rabbit skin, many larvae died; some of those still attached to the skin had not been fed. At the control site, all larvae were engorged (
Fig. 1A–D). A significant difference (
P<0.01) in the detachment rate between experimental and control treatments was observed from 12 to 48 h after histamine injection. The attachment of larvae had stabilized by 60 h at the histamine-treated sites, and very few ticks were detached. The highest detachment (39.5%) was 12 h after injection and decreased gradually. Nymphs were less sensitive than larvae to histamine. The highest nymph detachment (30.1%) was observed at 12 h after histamine injection (
Fig. 2A). Larvae showed more sensitivity to histamine than nymphs, and the highest larval detachment was observed at 12 h (39.5%;
Fig. 2B).
After feeding on histamine-treated rabbits, the average body weights of larval and nymphal ticks were 0.7±0.36 mg and 3.5±0.65 mg, respectively. Significant increases in body weight were observed for experimental larvae and nymphs compared with the controls (0.6±0.05 mg and 3.2±0.3 mg, respectively;
Table 1).
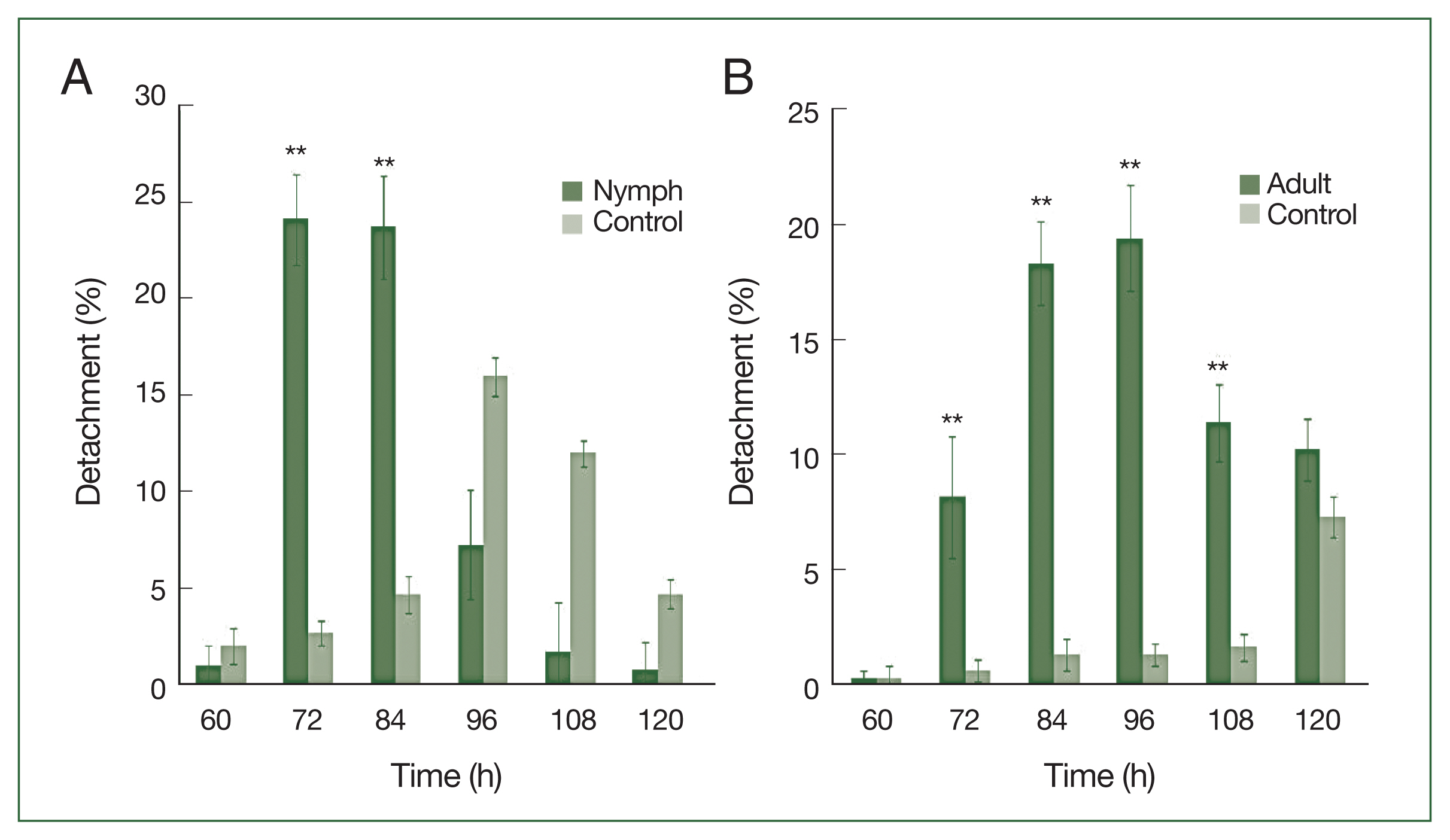
Nymphs were more sensitive than adults to antihistamine administration (
Fig. 3A). The highest nymph detachment was observed at 72 h after infestation (26.1%; after the first antihistamine administration). In the control group, tick detachment started after 96 h and most nymphs were engorged. During an infestation, most nymphs had engorged fully by the fifth day in the treatment group, whereas very few nymphs had engorged completely after 6 days at the control site. Most ticks that did not detach during antihistamine treatment were partially engorged and trapped in serous exudates. The highest detachment of adult ticks was observed at 96 h after infestation (19.4%), after the first antihistamine administration. A significant difference (
P<0.01) in the percentage of detachment (nymph and adult ticks) in antihistamine-treated and control groups was seen at 72 and 84 h after injection (
Fig. 3A, B).
The effects of antihistamine treatment during the fast-feeding stage on nymphs and adults are shown in
Table 1. Nymphs and adults weighed significantly less (
P<0.05) than control ticks. In the control group, the average body weight of the adult ticks after full engorgement and detachment was 174±1.78 mg, whereas in the antihistamine-treated group the average body weight was 54±2.17 mg. The average body weight of treatment and control group nymphs after treatment was 1.3±0.58 mg and 3.3±0.42 mg, respectively. The body weight of treated nymphs was significantly lower than that of controls (
P<0.05;
Table 1).
There were apparent gross signs of inflammation resulting from adult infestation of the skin of treated rabbits. In contrast, the skin reaction in control rabbits was minimal, with only mild diffuse hyperemia observed. A profuse wet exudate appeared early and then dried and formed crusts (
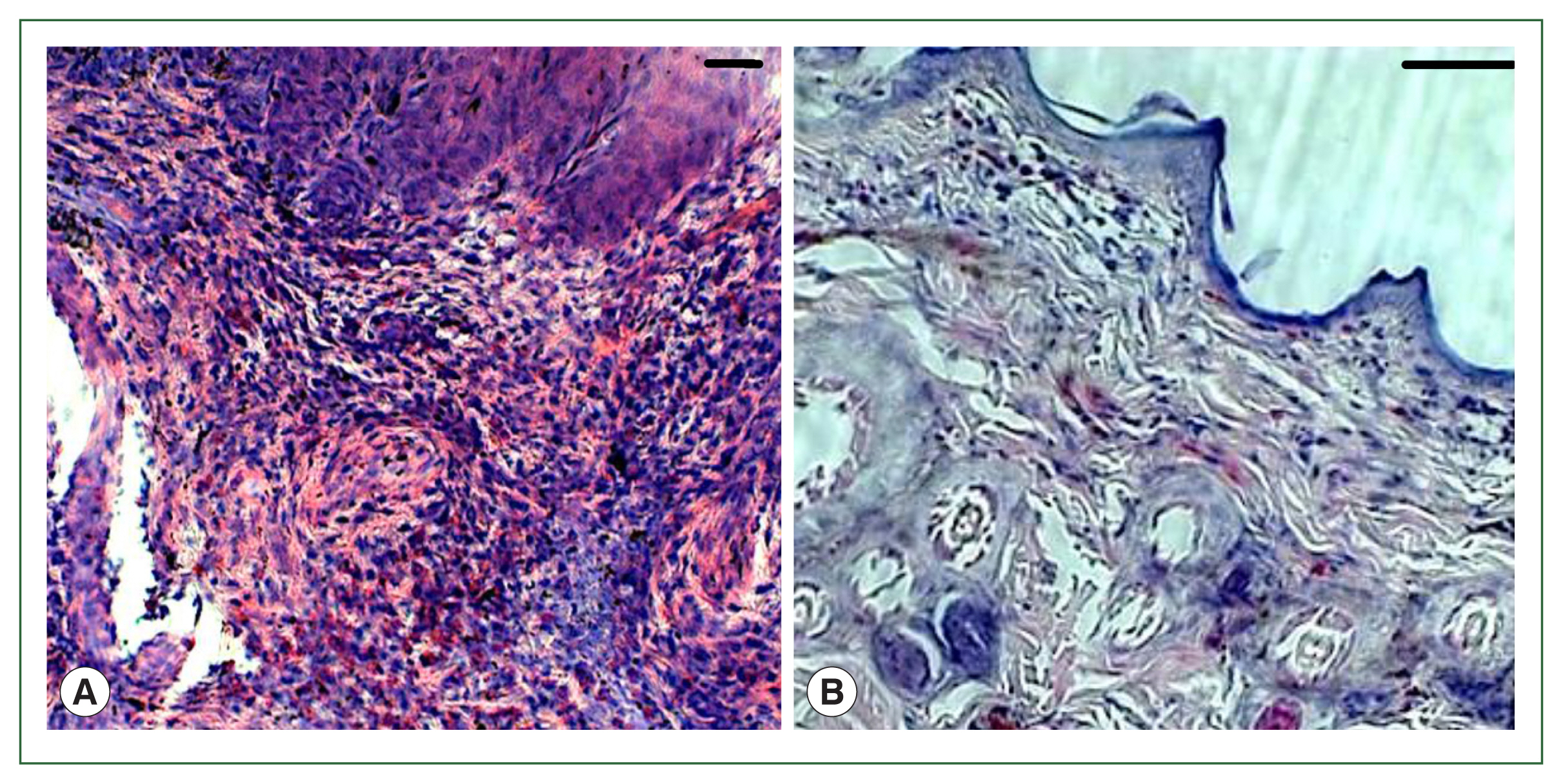
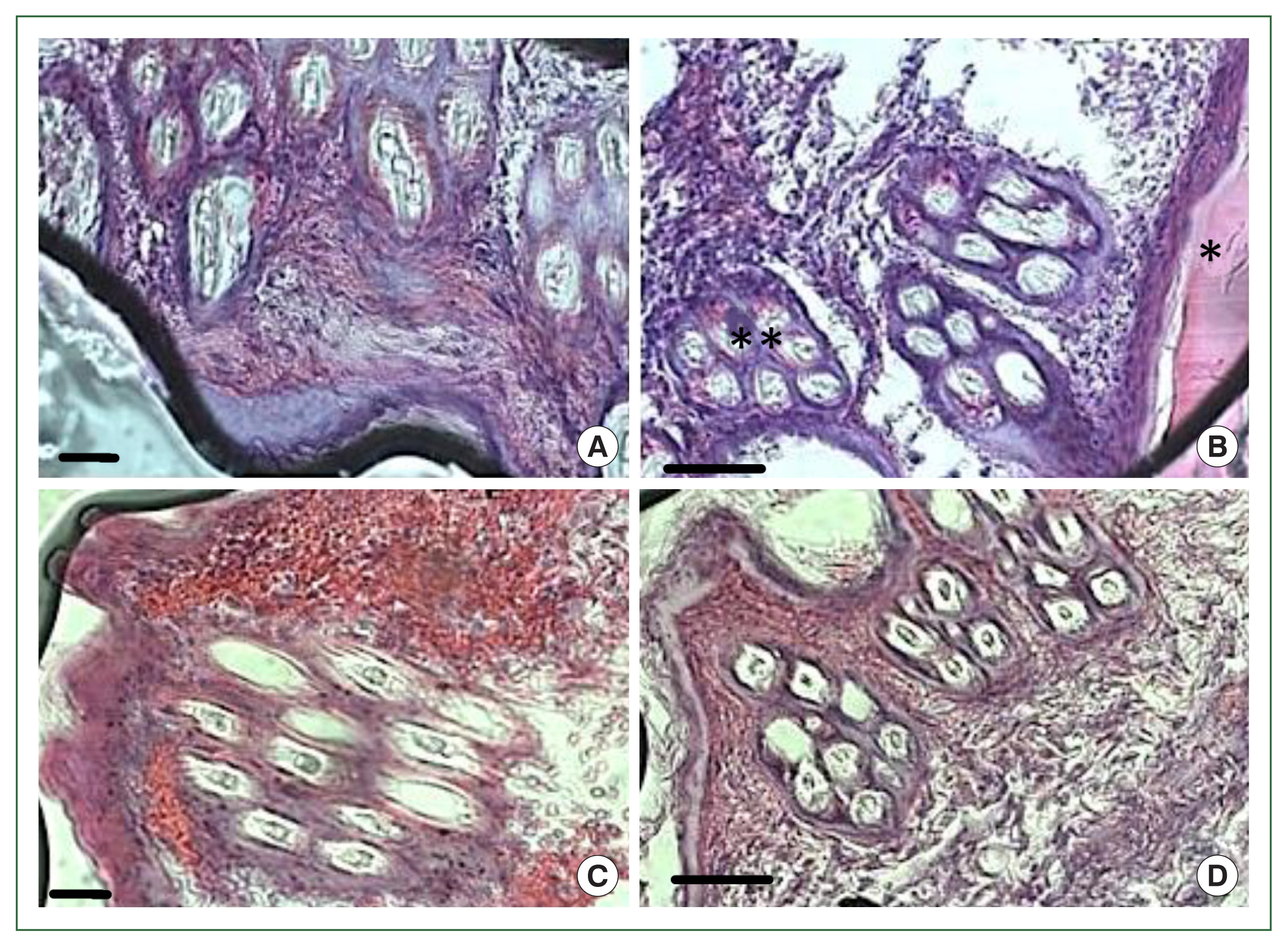
Fig. 1). No overt skin reactions were evident in the control rabbits. Superficial fluctuating edematous bullae appeared over the skin surface beneath the attached ticks in treated rabbits. The skin area over the histamine-treated area was crusty and hard, indicating that the superficial layers at the attachment sites had become necrotic. There was clear hyperplasia in the epidermis and dermis, and dense infiltrates with leukocytes in the treatment group. In addition, the epidermis was hyperplastic and projected into the dermis. Edema was evident throughout the dermis, and the inflammatory cell infiltrate at the tick attachment site was composed overwhelmingly of polymorphonuclear cells containing acidophilic granules in the cytoplasm and some mast cells, and a few basophils. Mast cells and basophils were rich in cytoplasmatic granules containing histamine (
Fig. 4A). Blood vessels appeared dilated, engorged with blood, and swollen with inflammatory cells. In control rabbits, lesions were not intense at attachment sites, consisted of a few granulocytes, and had a relatively low cell density compared to lesions in resistant rabbits. The epidermis and hair follicle epithelium were intact, with no signs of hyperplasia (
Fig. 4B).
In the antihistamine control group, erythrocyte extravasation was observed around the feeding pool, and erythrocytes were present inside the feeding pool (
Fig. 5A, B). In the antihistamine-treated group, erythrocyte extravasation was observed around the feeding pool, and erythrocytes were absent inside the feeding pool (
Fig. 5C, D).
Discussion
H. longicornis is widely distributed in East Asia and Australia, and transmits pathogens that cause deteriorative diseases in humans and animals [
11]. A comprehensive study of the effects of histamine and antihistamines on host parasitic interactions has yet to be performed in
H. longicornis. Histamine, which is secreted by host basophils and mast cells, affects ticks during feeding. Histamine mediates the itch response and promotes the recruitment of pro-inflammatory cells to the tick bite site to prevent tick attachment to the host's skin [
2,
5].
Ixodes ticks express several histamine-binding proteins (HBPs) to counteract the effects of histamine [
12,
13]. In our study, many
H. longicornis larvae and nymphs were detached after administration of histamine at the tick attachment sites. The findings support a direct role of histamine dihydrochloride in detachment rather than an indirect effect based on the inflammatory reaction.
Our previous proteomic study found that the lipocalin family of proteins is the major protein family expressed in the saliva of nymph and adult
H. longicornis [
8]. HBP belongs to the lipocalin family, suggesting that tick attachment in the early feeding stages is due to the production of HBPs.
H. longicornis larvae and nymphs eventually detached because the secreted
H. longicornis lipocalins could not counteract all the injected histamine. The secretion of a histamine-release factor (HRF) from tick salivary glands seems counterintuitive since such an activity would be detrimental to tick feeding. However, in this study, after treatment with histamine, fully engorged nymphs and larvae were found to have increased body weight compared with the control. This may be because of the secretion of HRFs, which might help increase the local concentration of histamine at tick feeding sites during the rapid feeding phase. HRF is known to bind to host basophils and induce histamine secretion; HRFs are also required for the fast-feeding stage of ticks [
14]. The increased histamine concentration might modulate vascular permeability to enhance blood flow to the tick feeding site, facilitating tick engorgement.
Tick feeding involves a complex series of 9 sequential stages [
1]. Host seeking and engagement precedes actual tick attachment and the establishment of the feeding lesion. Ticks imbibe very little blood during this early phase of feeding. At this early phase, early detachment of larvae and nymphs from cattle with high resistance [
2,
5] may be caused by histamine. About 60–72-h post-attachment, which includes the rapid feeding phase, tick sensitivity to histamine decreases significantly, and the tick becomes fully engorged [
2,
5]. During this new phase, the expression of HBP significantly decreases, and the expression of HRF increases. Evidence of greater histamine concentrations in the skin of tick-resistant animals comes from histological observation [
15]. In vitro, histamine-release experiments support our findings regarding tick detachment [
16]. Tick detachment was also found to be due to a hypersensitive reaction induced by tick antigens [
17]. The administration of an antihistamine was shown to protect the tick from host rejection in some highly resistant animals [
18]. It was found that nymphs of
H. longicornis were more sensitive than adults to treatment with a recombinant troponin I-like protein gene encoding 27 kDa and 30 kDa proteins (P27/30) of
H. longicornis [
19]. Our experiments demonstrated that nymphs are more sensitive to histamine than adults, as the detachment rate from the host was faster in nymphs. It has also been found that juvenile ticks (larvae and nymphs) are generally more sensitive to chemicals than adult ticks [
20].
At the tick attachment site, inflammatory cells were represented by polymorphonuclear cells, and acidophilic granules were also observed in the cytoplasm. In addition, mast cells and a few basophils were also noted. Mast and basophil cells are rich in cytoplasmic granules containing histamine, increasing vascular permeability [
21]. As mentioned, the most important action of histamine is to irritate, leading to the removal of ticks by host grooming [
6]. However, because our experimental animals were confined, grooming was impossible. In addition, the host rabbits studied in our experiment are not the natural hosts of
H. longicornis.
The results of the current study show that after an infestation with nymph and adult
H. longicornis ticks, chlorpheniramine maleate treatment resulted in a significantly higher number of detached ticks than the control treatment. In contrast, the mean weight of ticks after engorgement was significantly lower. Histamine acting via H1-receptors produces pruritis, vasodilatation, hypotension, flushing, headache, tachycardia, and bronchoconstriction. In addition, histamine increases vascular permeability and potentiates pain. Chlorpheniramine is a histamine H1 antagonist (or, more correctly, an inverse histamine agonist) of the alkylamine class. It competes with histamine for H1-receptor sites on effector cells of the gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels, and respiratory tract, thereby providing effective, temporary relief of sneezing, watery and itchy eyes, and runny nose due to hay fever and other upper respiratory allergies [
22,
23].
In our previous experiment, we found that the level of histamine in the blood plasma during the fast-feeding stage of
H. longicornis nymphs and adult ticks was elevated. Dai et al. [
14] also found a histamine-releasing factor during the fast-feeding stage of
Ixodes scapularis. When we treated nymphs and adult ticks with antihistamine during the fast-feeding stage from 60 h to 120 h, a significantly higher tick detachment from the host was observed compared to the control. In adults, the highest detachment occurred after 96 h, while in nymphs, it occurred after 86 h. In nymphs, the detachment rate after 72 h was higher than in adults, which may have been due to the shorter feeding period of nymphs [
24] and their earlier start of faster feeding. Sensitivity to histamine declined as tick detachment stabilized and other mediators such as bradykinin and serotonin were produced. In our experiments, we used an antihistamine to target histamine, as ticks are more sensitive to histamine than bradykinin and serotonin. Other mediators of inflammation, such as bradykinin, prostaglandin E2, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and dopamine, were shown to have little or no effect on tick behavior in vitro [
2].
Due to poor feeding, ticks fed for 120 h in the treatment group weighed significantly less than the control group ticks. We speculate that
H. longicornis secretes some factors during the fast-feeding stage that may help increase the local concentration of histamine at tick feeding sites. Increased histamine concentration may promote vascular permeability, enhance blood flow to the tick feeding site, and facilitate tick engorgement. Because of antihistamine injection at the fast-feeding stage, histamine was unavailable at the tick-biting site, thereby hampering feeding. Similarly, Dai et al. [
14] found that silencing histamine-releasing factor by RNA interference (RNAi) significantly impaired tick feeding and decreased the
B. burgdorferi burden in mice. Histopathology showed extravasation of erythrocytes but an absence of erythrocytes in the feeding pool in the antihistamine-treated group. In control rabbits, erythrocytes were present in the feeding pool. These results indicate that chlorpheniramine maleate inhibited blood flow to the feeding pool, and as a result, tick feeding was impaired.
In future experiments, we will need to decrease the variability in tick response in the experimental animals, which might have been due to variation in the of histamine injection, skin thickness, or other unknown factors. In addition, the minimum effective dose of histamine for the detachment of ticks has to be determined. Much of the intradermally-injected histamine might not have reached the larvae or nymphs, and the concentration of histamine around the mouthparts due to mast cell release is currently unknown. Determining if these results are consistent in all stages of H. longicornis when feeding on its natural hosts will also be important.
This study found that ticks failed to secure host attachment when they could not counteract the excess of histamine at the feeding site during the attachment stage. At the same time, attachment was also inhibited during the fast-feeding stage after antihistamine administration, indicating that the tick infestation response can be modulated through histamine treatment during the attachment stage and antihistamine treatment during the fast-feeding stage.
Notes
-
Author contributions
Investigation: Islam MS
Methodology: Islam MS
Resources: Islam MS
Supervision: You M
Visualization: Talha AFSM
Writing – original draft: Islam MS
-
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (IPET) through the Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs Convergence Technologies Program for Educating Creative Global Leader, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (grant number: 320005-4).
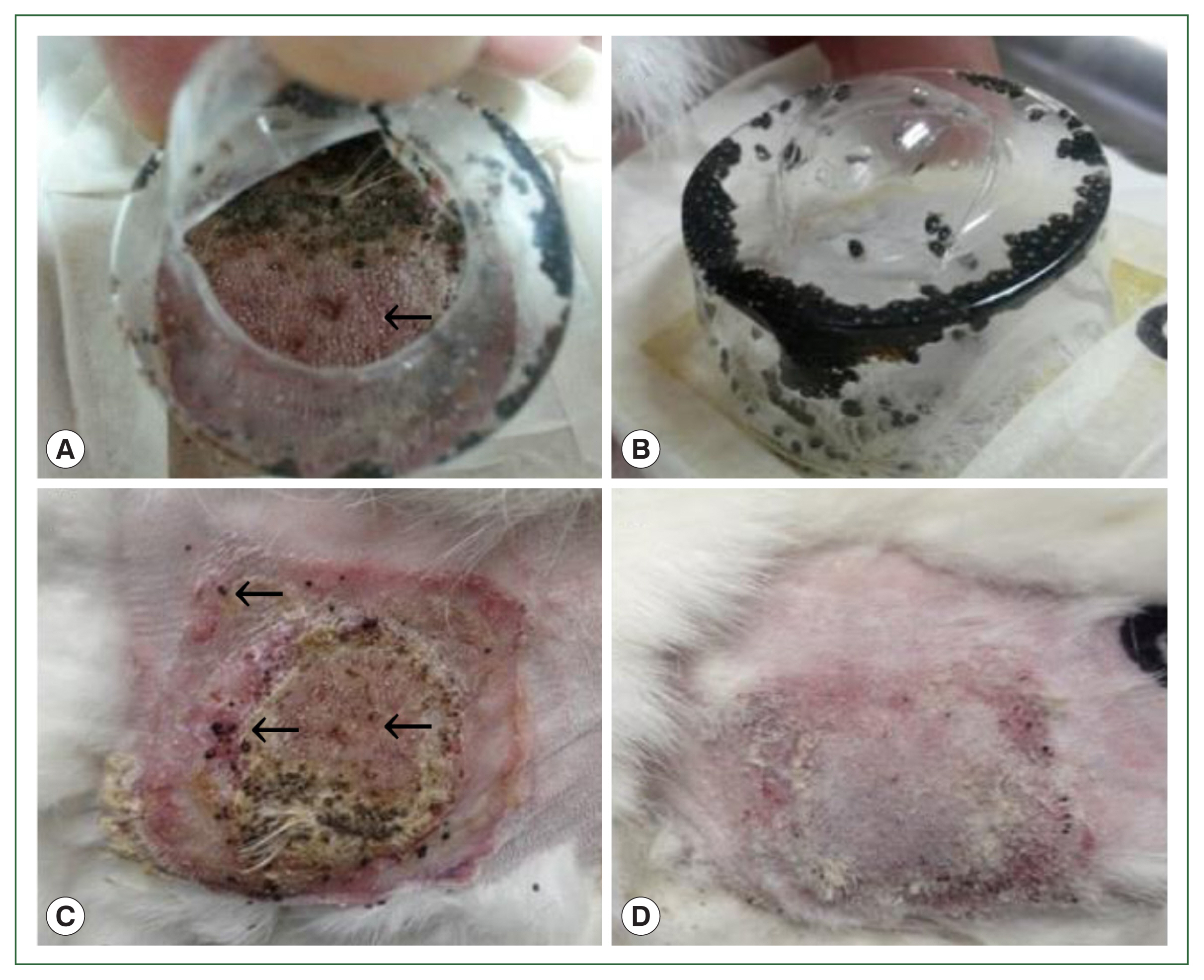
Fig. 1Gross lesions in histamine treatment versus control rabbits during tick attachment. The effect of histamine on the attachment of larval and nymphal H. longicornis to rabbits after 4 successive doses of histamine. Larvae detached from the injection site in the treatment group (A) and many died while some remained attached to the skin (C). At the control site, all larvae were engorged (B), and there were signs of recovery at the tick attachment sites (D).
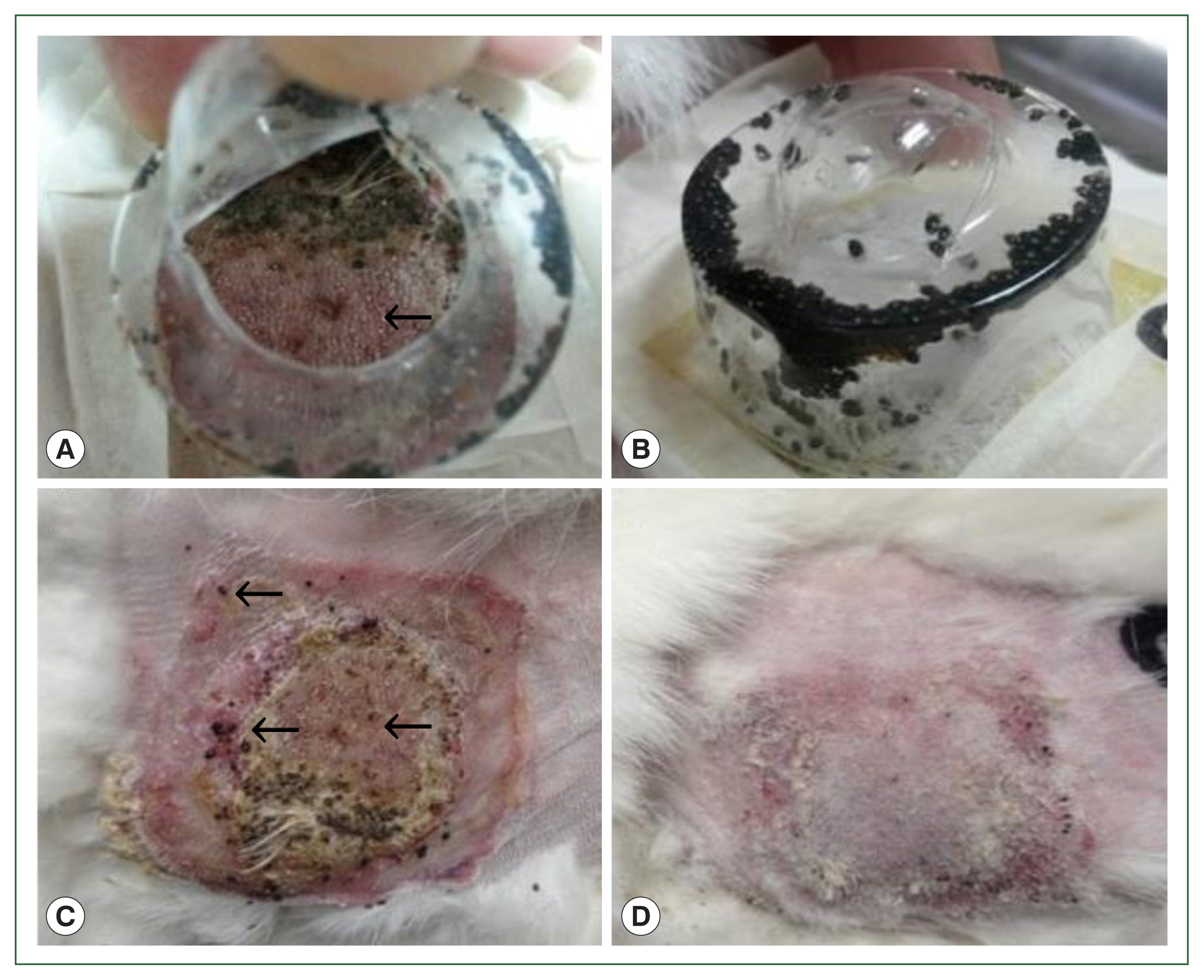
Fig. 2
H. longicornis nymph (A) and larval (B) detachment after treatment with histamine compared to control treatment. Each time point represents the mean of 3 values reported as a percentage with standard error of the mean (SEM). *P<0.05; **P<0.01.
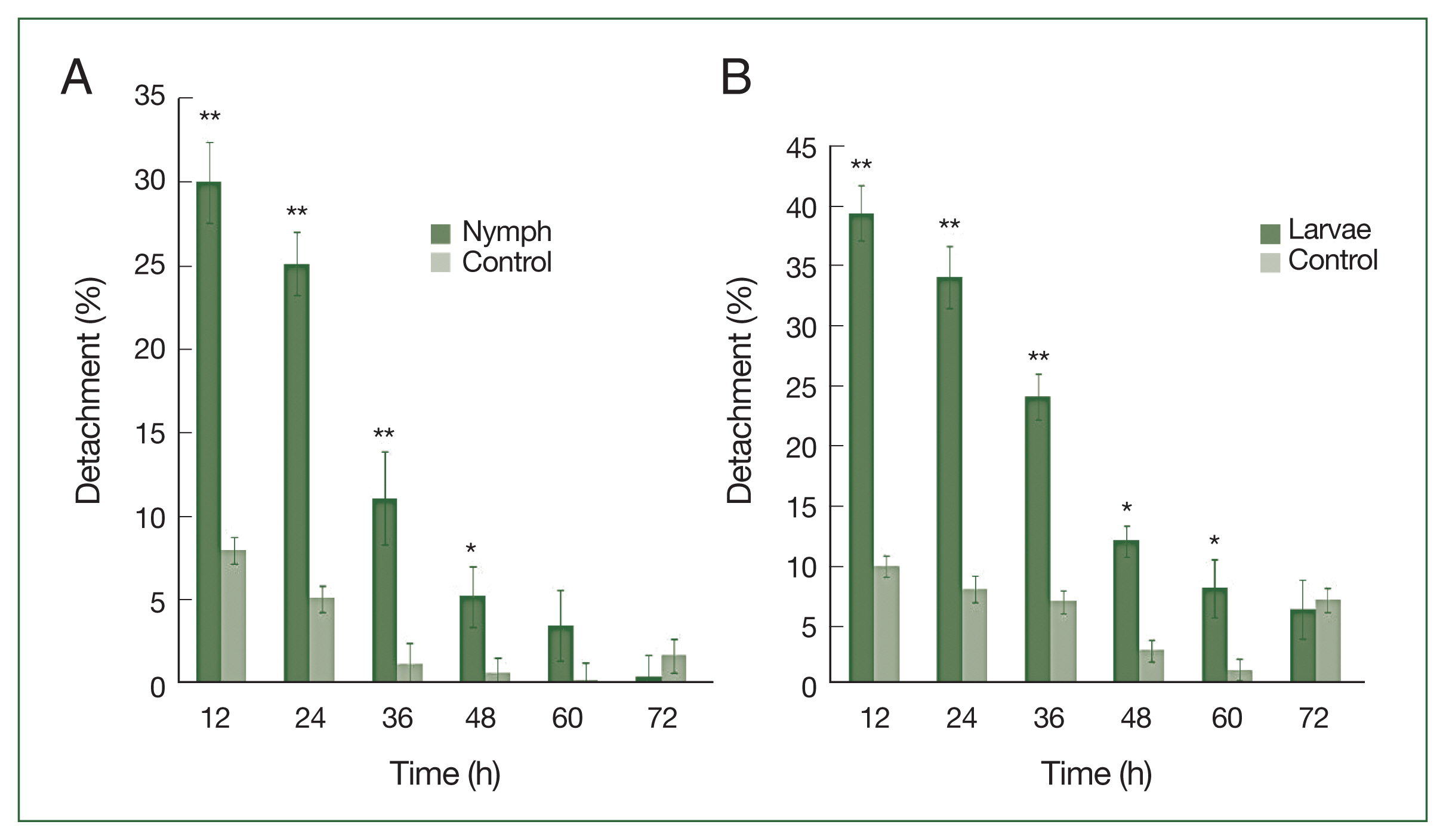
Fig. 3
H. longicornis nymph (A) and adult (B) detachment after treatment with an antihistamine compared to control treatment. Each time point represents the average expression level of three values and is reported as fold change±SEM. **P<0.01.

Fig. 4Histopathological features of rabbit skin in control versus histamine treatment groups. Tick-infested skin collected from rabbits in the histamine-treated group (A) showed clear signs of inflammation and a thickened epidermis layer. The control group showed fewer signs of inflammation and no thickening of the epidermis (B).
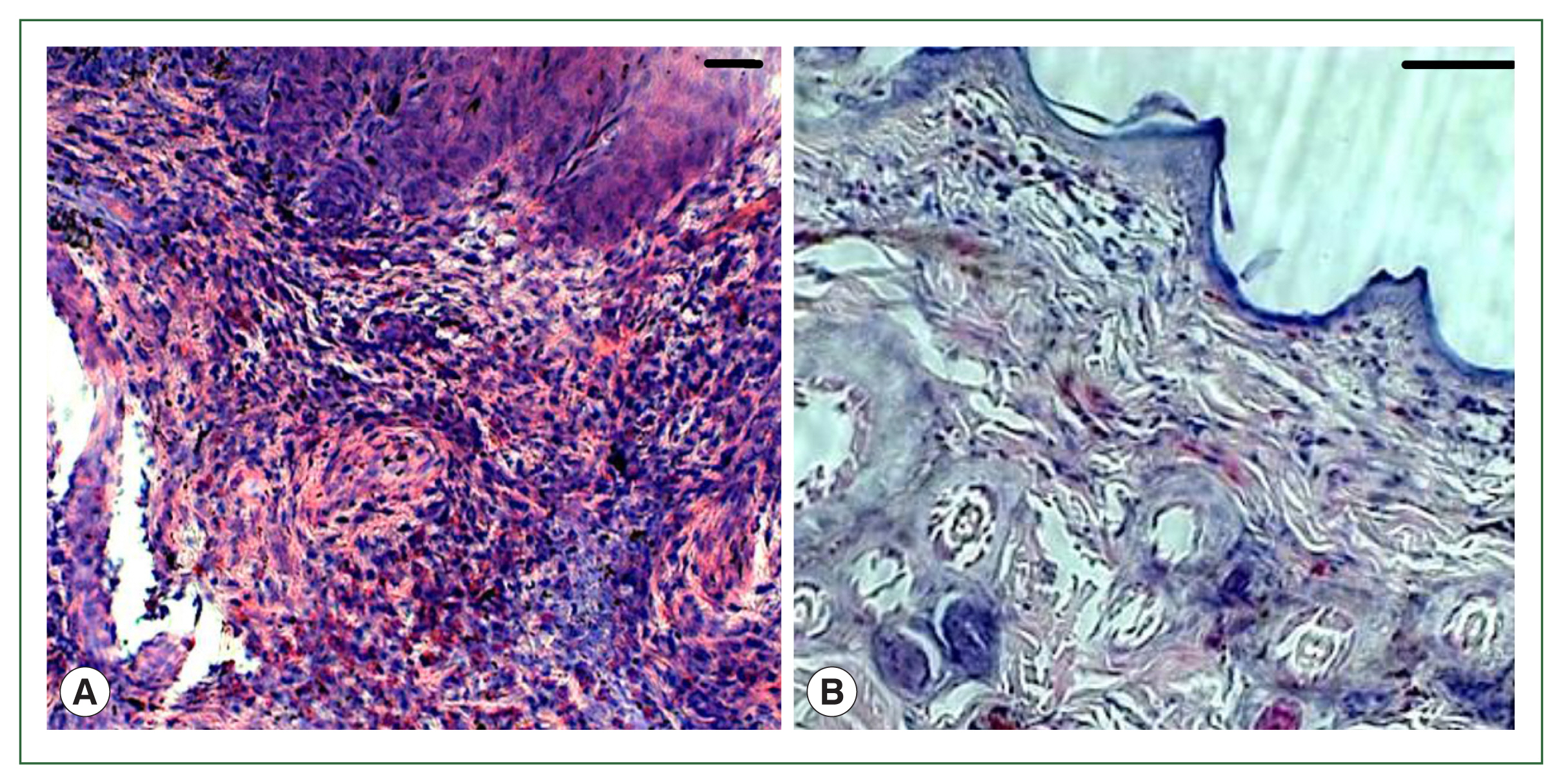
Fig. 5Histopathology of rabbit skin from the control versus antihistamine treatment group. Tick-infested skin collected from rabbits in the control group (A, B) indicating erythrocytes in the feeding pool. **cement; *feeding pool. Tick-infested skin collected from rabbits in the antihistamine-treated group (C, D) revealed no erythrocytes in the feeding pool. Bar=50 μm (A, C) and bar=100 μm (B, D).
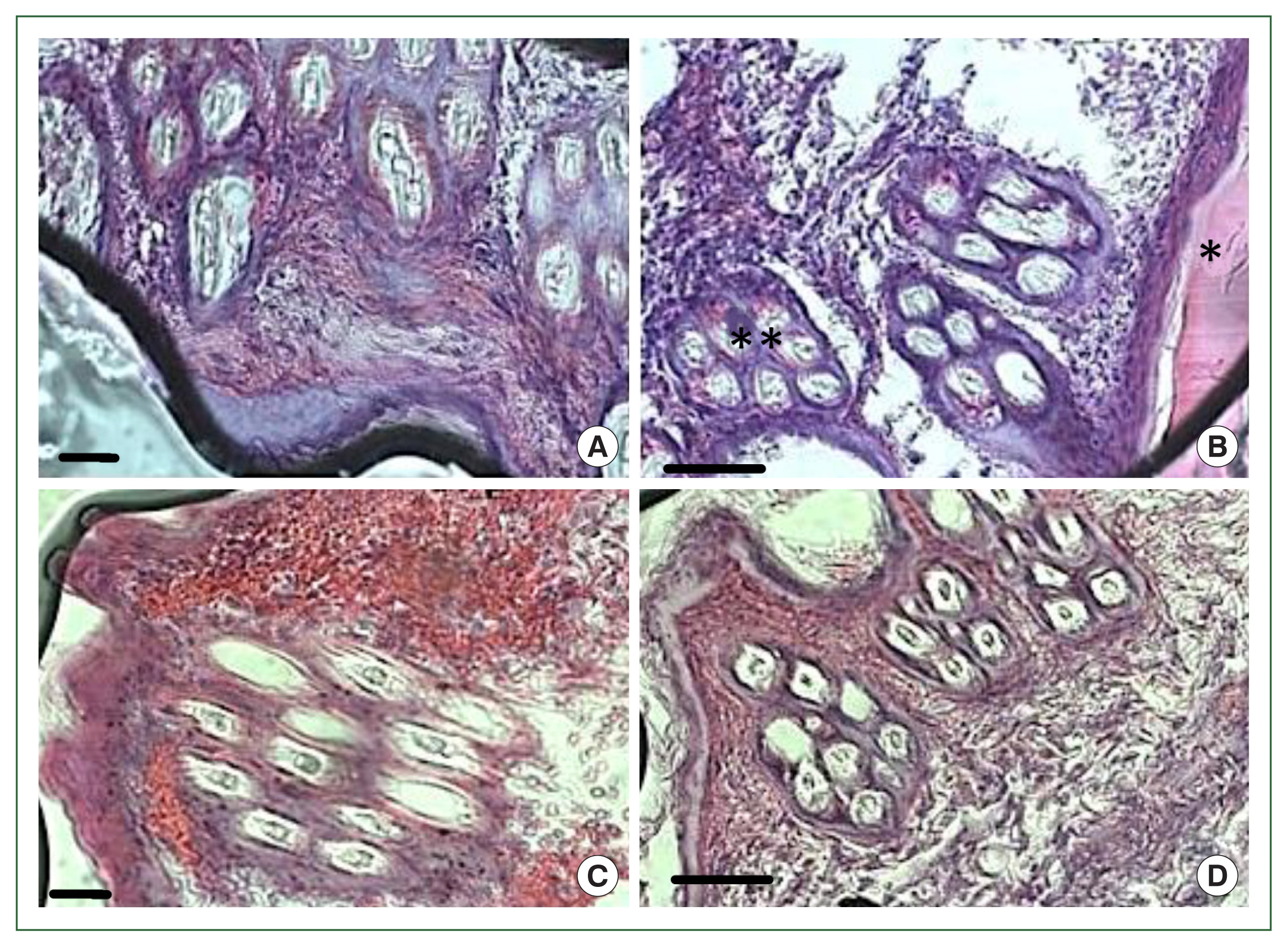
Table 1Engorged body weight of ticks after rabbit skin injected with histamine and antihistamine
Table 1
|
Engorged body weight (mg±SEM) |
|
|
Treatment |
Control |
|
Histamine treatment ticks |
|
Larva |
0.7±0.36 |
0.6±0.05*
|
|
Nymph |
3.5±0.65 |
3.2±0.30*
|
|
|
Antihistamine treatment ticks |
|
Nymph |
1.3±0.58 |
3.3±0.42**
|
|
Adult |
54±2.17 |
174±1.78**
|
References
- 1. Anderson JF, Magnarelli LA. Biology of ticks. Infect Dis Clin North Am 2008;22(2):195-215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idc.2007.12.006
- 2. Kemp DH, Bourne A. Boophilus microplus: the effect of histamine on the attachment of cattle-tick larvae--studies in vivo and in vitro. Parasitology 1980;80:487-496. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000000950
- 3. Francischetti IM, Sa-Nunes A, Mans BJ, Santos IM, Ribeiro JM. The role of saliva in tick feeding. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed) 2009;14(6):2051-2088. https://doi.org/10.2741/3363
- 4. Ribeiro JM, Alarcon-Chaidez F, Francischetti IM, Mans BJ, Mather TN, et al. An annotated catalog of salivary gland transcripts from Ixodes scapularis ticks. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 2006;36(2):111-129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2005.11.005
- 5. Paine SH, Kemp DH, Allen JR. In vitro feeding of Dermacentor andersoni (Stiles): effects of histamine and other mediators. Parasitology 1983;86(3):419-428. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000050617
- 6. Koudstaal D, Kemp DH, Kerr JD. Boophilus microplus: rejection of larvae from British breed cattle. Parasitology 1978;76(3):379-386. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000048241
- 7. Yeh MT, Bak JM, Hu R, Nicholson MC, Kelly C, et al. Determining the duration of Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) attachment to tick-bite victims. J Med Entomol 1995;32(6):853-858. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/32.6.853
- 8. Tirloni L, Islam MS, Kim TK, Diedrich JK, Yates JR 3rd, et al. Saliva from nymph and adult females of Haemaphysalis longicornis: a proteomic study. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:338. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-0918-y
- 9. Borkowski R, Karas AZ. Sedation and anesthesia of pet rabbits. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract 1999;14(1):44-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1096-2867(99)80026-7
- 10. Bancroft JD, Marilyn G. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques. 1st ed. Elsevier. Limited. London, UK. 2013, pp 168-173.
- 11. Fujisaki K, Kawazu S, Kamio T. The taxonomy of the bovine Theileria spp. Parasitol Today 1994;10(1):31-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/0169-4758(94)90355-7
- 12. Paesen GC, Adams PL, Harlos K, Nuttall PA, Stuart DI. Tick histamine-binding proteins: isolation, cloning, and three-dimensional structure. Mol Cell 1999;3(5):661-671. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80359-7
- 13. Mans BJ. Tick histamine-binding proteins and related lipocalins: potential as therapeutic agents. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2005;6(11):1131-1135. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1001205
- 14. Dai J, Narasimhan S, Zhang L, Liu L, Wang P, et al. Tick histamine release factor is critical for Ixodes scapularis engorgement and transmission of the lyme disease agent. PLoS Pathog 2010;6(11):e1001205. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1001205
- 15. Schleger AV, Lincoln DT, McKenna RV, Kemp DH, Roberts JA. Boophilus microplus: cellular responses to larval attachment and their relationship to host resistance. Aust J Biol Sci 1976;29(5–6):499-512. https://doi.org/10.1071/bi9760499
- 16. Kemp DH, Koudstaal D, Roberts JA, Kerr JD. Boophilus microplus: the effect of host resistance on larval attachments and growth. Parasitology 1976;73(1):123-136. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000051386
- 17. Willadsen P, Williams PG, Roberts JA, Kerr JD. Responses of cattle to allergens from Boophilus microplus. Int J Parasitol 1978;8(2):89-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7519(78)90003-6
- 18. Tatchell RJ, Moorhouse DE. The feeding processes of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus (Canestrini). II. The sequence of host-tissue changes. Parasitology 1968;58(2):441-459. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0031182000069468
- 19. You MJ. Immunization of mice with recombinant P27/30 protein confers protection against hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) infestation. J Vet Sci 2005;6(1):47-51.
- 20. Williams H, Zoller H, Roepke RK, Zschiesche E, Heckeroth AR. Fluralaner activity against life stages of ticks using Rhipicephalus sanguineus and Ornithodoros moubata in vitro contact and feeding assays. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-0704-x
- 21. Kumar V, Cotran RS, Robbins SL. Basic Pathology. 7th ed. Saunders. Philadelphia, USA. 2002.
- 22. Nicholson AN, Pascoe PA, Turner C, Ganellin CR, Greengrass PM, et al. Sedation and histamine H1-receptor antagonism: studies in man with the enantiomers of chlorpheniramine and dimethindene. Br J Pharmacol 1991;104(1):270-276. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12418.x
- 23. Chen X, Ji ZL, Chen YZ. TTD: therapeutic target database. Nucleic Acids Res 2002;30(1):412-415. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/30.1.412
- 24. Logan TM, Linthicum KJ, Kondig JP, Bailey CL. Biology of Hyalomma impeltatum (Acari: Ixodidae) under laboratory conditions. J Med Entomol 1989;26(5):479-483. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmedent/26.5.479