Abstract
This study evaluated the potential repellent and acaricidal effects of 4 essential oils (clove, eucalyptus, lavender, and mint) against the Asian longhorned tick Haemaphysalis longicornis, a vector of various tick-borne diseases in medical and veterinary contexts. Selected for their potential repellent and acaricidal properties, the 4 essential oils were tested on adult and nymph H. longicornis ticks at different concentrations. The experiment assessed mortality rates and repellency, particularly during tick attachment to host skin. There was a significant increase (P<0.05) in tick mortality and repellency scores across all groups. At a 1% concentration, adult tick mortality ranged from 36% to 86%, while nymph mortality ranged from 6% to 97%. Clove oil exhibited notable efficacy, demonstrating high mortality rates of nymphs and adults. Clove oil also displayed strong repellency properties, with a repellency index of 0.05, surpassing those of mint, eucalyptus, and lavender oils. Clove oil showed the highest effectiveness in deterring nonattached adult ticks (90%) and nymphs (95%) when applied to skin. Clove oil was the most effective against adult and nymph ticks, achieving mortality rates of 86% and 97%, respectively, and led to the highest nonattachment rates when applied to skin. In conclusion, essential oils such as clove, eucalyptus, lavender, and mint oils present promising results for tick population control.
-
Key words: Comparative analysis, efficacy, essential oils
Introduction
Ticks are arthropods of the Acari subclass and are important vectors of various pathogens, posing significant threats to human and animal health worldwide [
1,
2]. Among numerous tick species,
Haemaphysalis longicornis has received particular attention due to its invasive nature and wide distribution across different continents [
3]. Ticks are major disease vectors that transmit pathogens to animals, ranking second only to mosquitoes. Their increasing prevalence has prompted interest in natural products, such as essential oils, for repellent and pesticide development. Ecofriendly acaricides have been developed using biodegradable vegetable products.
Recently, the global emergence and spread of tick-borne diseases have prompted the search for alternative and environmentally safe methods to control tick populations and reduce their impact on public and veterinary health. Natural essential oils have received attention as potential candidates for tick control, due to their bioactive properties and relatively low environmental impact. These oils contain active compounds such as eugenol, cineole, linalool, and menthol, which have demonstrated insecticidal and repellent properties against various ticks, mosquitoes, and flies [
4]. While previous research has explored the efficacy of individual essential oils against ticks, comparative analyses are still required to determine which oil offers the most effective and practical tick control solution. This study aimed to evaluate and compare the effect of clove, eucalyptus, lavender, and mint oils against
H. longicornis ticks in terms of mortality, repellency index (RI), and tick attachment to the host.
Despite their potential, few studies have investigated the in vivo or field repellent efficacy of essential oils against ticks. Understanding the potential acaricidal and repellent properties of these essential oils against
H. longicornis ticks could provide valuable insights for the development of novel and environmentally safe strategies to manage tick infestations and mitigate the risks associated with tick-borne diseases. Among the tested essential oils, clove, eucalyptus, lavender, and mint oils have shown potential as tick repellents and acaricides [
5]. Additionally, this research could have implications for public health, agriculture, and veterinary practices, contributing to overall efforts to safeguard both human and other animal populations from tick-related health hazards.
Materials and Methods
Ethics statement
All animals used in these experiments were housed in the Laboratory of Veterinary Parasitology of the College of Veterinary Medicine and Bio-Safety Research Institute, Jeonbuk National University (Jeonju, Korea). All animal studies and protocols complied with the Ethical Guidelines for the Use of Animals in Research and were approved by the Jeonbuk Animal Care and Use Committee (JBNU 2022-094).
Ticks and hosts
The Jeju strain of the hard tick
H. longicornis [
6] has been maintained in rabbits in our laboratory since 2003.
H. longicornis were reared at 27–28°C and 80–90% relative humidity. The 3 tick stages of larva, nymph, and adult were used in the study. To feed,
H. longicornis ticks were placed onto the dorsal surface sagittal to the vertebral column in the middle lumbar region of specific pathogen-free New Zealand White rabbits. A total of 16 rabbits were randomly assigned to 4 groups with 4 rabbits per group. Each group was tested for tick (adult and nymph) attachment following clove, eucalyptus, lavender, or mint oil application on the skin.
All the active ingredients used in this study, including clove oil (ALLE, Gimpo, Korea), mint oil (ALLE), lavender (Leciel, Seoul, Korea), and eucalyptus (Leciel), were commercially purchased. Solutions with varying concentrations (1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, and 0.125% v/v) were prepared by combining each essential oil with specific proportions of ethanol and water. As an example, the 1% solution consisted of 1% essential oil, 25% ethanol, and 77% distilled water. Similarly, the 0.5% solution contained 0.5% essential oil, 25% ethanol, and 77.5% distilled water, and so forth. The procedure involved the initial mixing of the essential oil with alcohol, followed by the addition of water for adequate blending. As a control, 25% ethanol was used.
Efficacy evaluation against ticks feeding on rabbits
We conducted the tick attachment assay on rabbit skin as described previously [
7]. Briefly, one day before the assay, rabbit hair at the tick attachment site was shaved properly. Two feeding chambers were affixed to each animal, positioned at least 4 cm apart. One chamber was placed cranially for acaricidal and repellent activity assessment, and the other, caudally, serving as the control (EtOH).
To replicate the test for each instar, a total of 25 rabbits were similarly infested, with nonsprayed feeding chambers used as controls for both the tested mineral oil acaricide and control solutions. Each feeding chamber contained either 10 adult ticks or 10 nymphs. Following a 24 h period after tick infestation, each chamber received a single application of 20 μl of the control solution or tested mineral oil acaricide by spraying, followed by the resealing of the chambers.
We conducted daily inspections after 24 h and collected dead or engorged ticks. On the 4th day post-tick infestation, the count encompassed both attached and nonattached ticks, marking the culmination of the study.
Repellency index assays
Experiments to determine the RI involved cutting filter paper (12.5 cm diameter) into halves, with one half treated with a corresponding essential oil with different dilution (1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, or 0.125%) in ethanol solution. Ticks were subjected to the assay following the procedure outlined by [
8] with minor adjustments. In brief, the experimental setup involved drawing 2 concentric circles (Lines A and B) on a Petri dish lid with 2.5 cm between them. Outside line B, a circular filter paper strip, 0.5 cm wide, was positioned. Subsequently, 100 μl of either the control substance (25% ethanol) or the essential oil diluted to 1% was applied to the filter paper and allowed to evaporate for 10 min. Following this, each Petri dish was placed on a moist circular filter paper inside a larger Petri dish.
Haemaphysalis longicornis adults and nymphs were tested individually in a paired design, with each tick being initially tested on the control dish and then on the dish with the essential oil. Each experiment involved up to 10 ticks. The ticks’ behavior was observed until they crossed line B, and the time spent between lines A and B was recorded. The RI [
9] was calculated using the formula RI=2G/(G+P). Here, G represents the percentage of larvae situated on disks treated with the essential oil and control (25% ethanol), while P indicates the percentage of larvae on the control leaf disks. The RI scale spans from 0 to 2, where RI=1 signifies a neutral effect, RI>1 indicates attraction, and RI<1 signifies repellency.
Mortality assay
The effect of different essential oil concentrations on the mortality of adult and nymph H. longicornis was also evaluated. To prepare the essential oil solutions, we followed the previously described method, obtaining concentrations of 0.125%, 0.25%, 0.5%, and 1.0% with total volumes of 100 μl each. For the experiments, we applied each solution to a 6 cm diameter filter paper using a micropipette and allowed the filter paper to dry under a ventilated hood. The treated filter paper was then attached to the inside of a cup lid with a 7-cm diameter using double-sided adhesive tape. Twenty H. longicornis adults were introduced into a transparent 300-ml plastic cup, and the lid with the treated filter paper was securely placed over its top opening. Following a 24-h exposure period, we recorded the number of live and dead H. longicornis nymphs and adults. Insect mortality was determined by observing the absence of leg or antennal movements, which indicated death. Each treatment concentration was replicated 10 times to ensure the reliability and accuracy of our results.
Statistical analysis
Study data was collected, and one-way ANOVA with a post hoc Tukey’s test was performed to examine the results and assess the differences among the various study groups, providing insights into the significance of the observed variations between the groups.
Results
The results of the RI of the clove, eucalyptus, lavender, and mint oils were evaluated at 4 different observation times on
H. longicornis adults (
Table 1). The RI values, representing the efficacy of each essential oil in repelling
H. longicornis adults at different time intervals, were calculated for each oil at 10, 20, 30, and 40 min after their application. The highest RIs among the tested essential oils were observed for eucalyptus oil and lavender oil, both reaching 0.60. The lowest RI value was detected for clove oil (0.05). Mint oil also displayed relatively low repellency, with an RI value of 0.15.
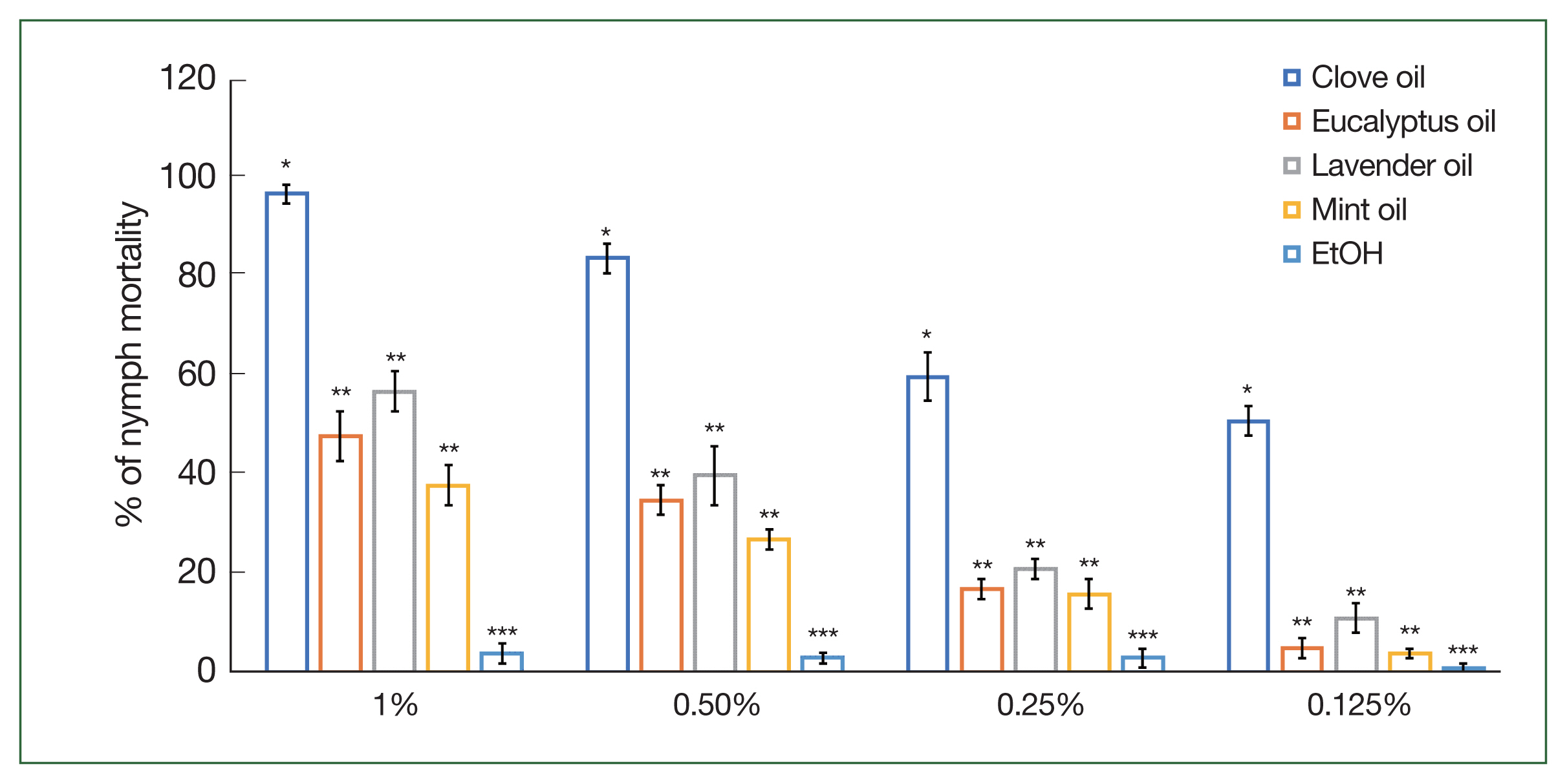
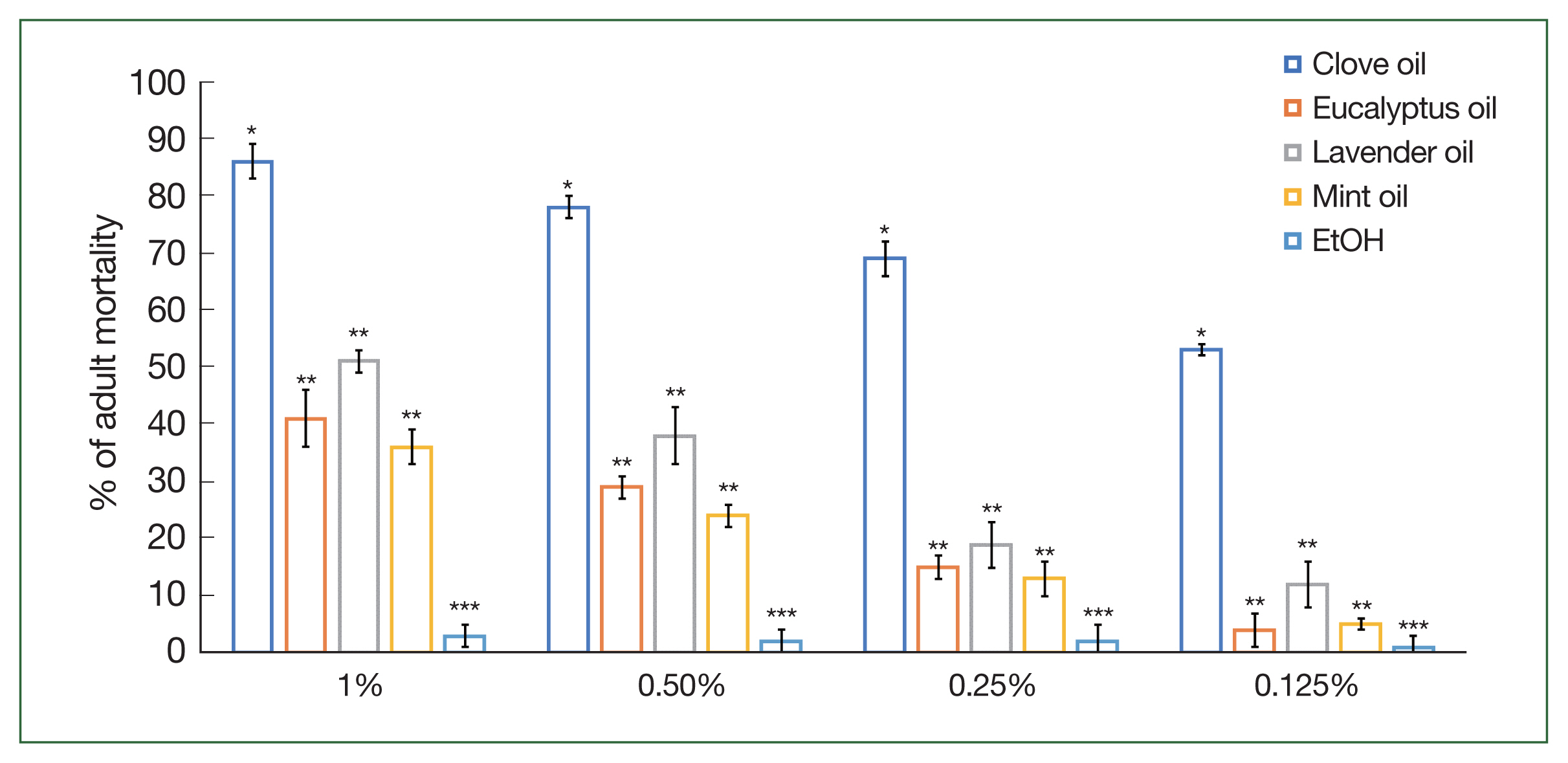
The mortality rates of
H. longicornis adults and nymphs were examined using various concentrations (1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, and 0.125%) of the 4 essential oils (
Figs. 1,
2). Clove oil exhibited the highest mortality percentages, with values of 86.0%, 78.0%, 69.0%, and 53.0% at concentrations of 1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, and 0.125%, respectively. Eucalyptus oil also displayed significant (
P<0.05) mortality effects, with percentages of 41.0%, 29.0%, 15.0%, and 4.0% at the respective concentrations. Lavender and mint oils demonstrated lower, yet considerable, mortality rates compared to clove and eucalyptus oils. For lavender oil, mortality percentages were 51.0%, 38.0%, 19.0%, and 12.0%, while for mint oil, mortality percentages were 36.0%, 24.0%, 13.0%, and 5.0% at the respective concentrations of 1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, and 0.125%. These findings highlight the potential of clove and eucalyptus oils as effective agents for
H. longicornis population control, with lavender oil and mint oil also showing promising results, albeit with slightly lower efficacy.
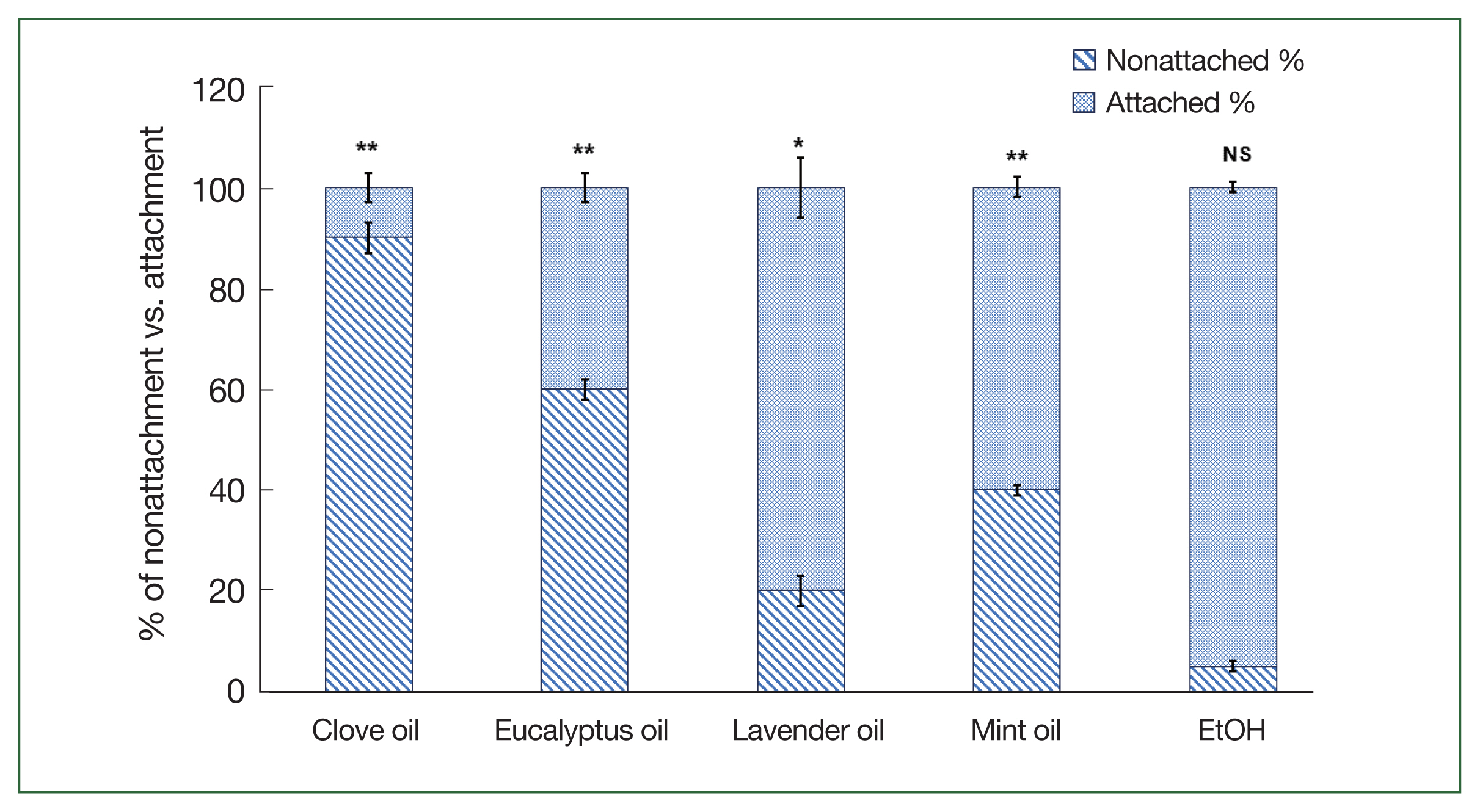
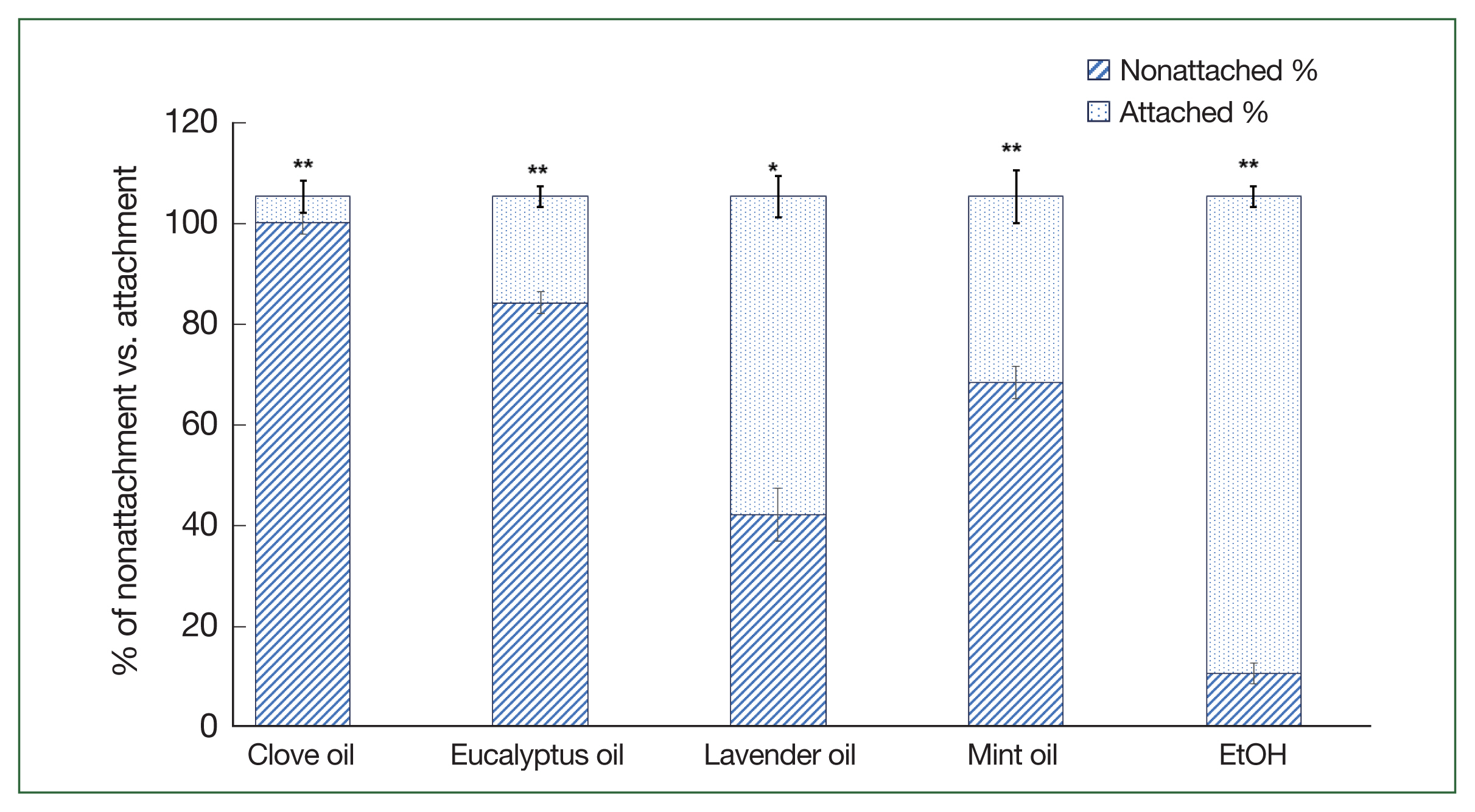
In this study, the application of various essential oils, including clove oil, eucalyptus oil, lavender oil, mint oil, and control (EtOH) at a concentration of 1%, yielded diverse outcomes in terms of preventing the attachment of adult and nymph
H. longicornis ticks to rabbit skin (
Figs. 3,
4). Among adult ticks, the rates of nonattachment were as follows: 90% for clove oil, 60% for eucalyptus oil, 20% for lavender oil, 40% for mint oil, and 5% for water oil. In contrast, for tick nymphs, the nonattachment rates were 95% for clove oil, 80% for eucalyptus oil, 40% for lavender oil, 65% for mint oil, and 10% for control (EtOH). These findings highlight the differences in effectiveness exhibited by the tested essential oils in retarding the attachment of
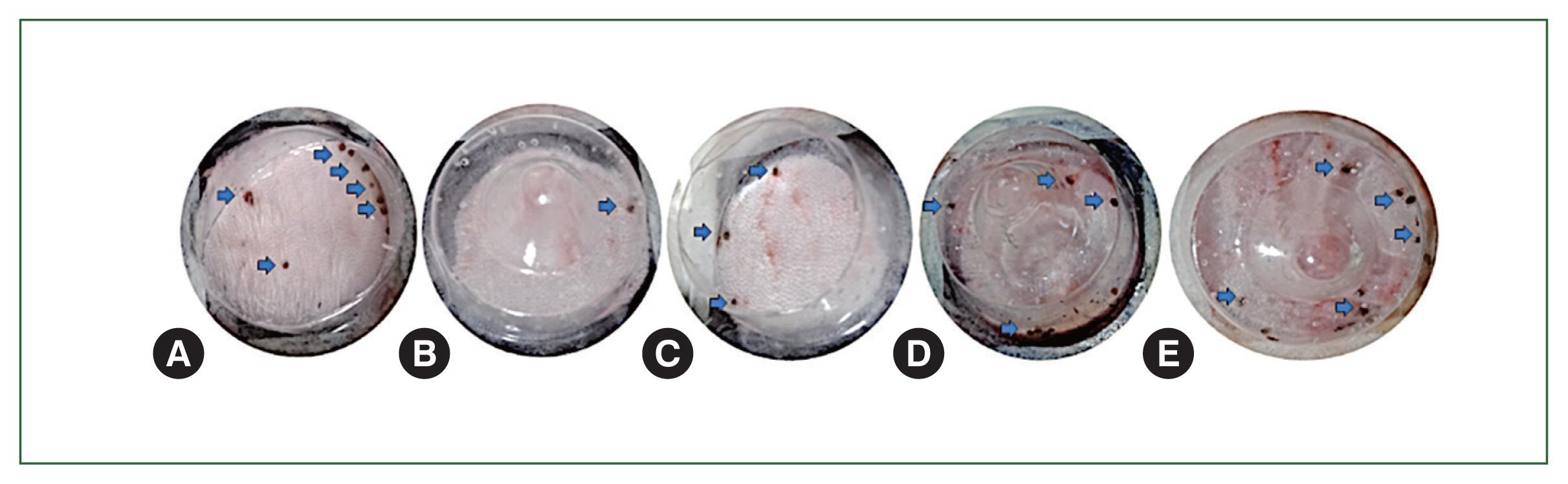
H. longicornis ticks to rabbit skin, and gross lesions were observed during the attachment (
Fig. 5). The statistical analysis indicated highly significant differences (
P<0.001) in both adult and nymph ticks when compared to the control group. These results emphasize the potential of these essential oils, especially clove and eucalyptus oils against nymphs, as promising agents for mitigating tick attachment, suggesting their utility in tick-bite prevention strategies.
Discussion
Ticks are the second most common vector of human disease following mosquitoes, and the prevalence of tick diseases is consistently increasing [
10]. In this study we used nymph and adult
H. longicornis, as it is the most common species in Korea [
11,
12]. We found that nymphs were more sensitive than adult
H. longicornis in terms of repellency, morbidity, and rabbit skin nonattachment following the application of clove, eucalyptus, lavender, and mint oils at different doses. Other previous studies have shown that
H. longicornis nymphs are more sensitive than adults to chemical treatments. Our previous study Islam et al. [
7] demonstrated that nymphs are more sensitive to histamine than adults, as their rate of detachment from the host was higher. Furthermore, juvenile ticks (larvae and nymphs) tend to be more susceptible to chemicals than adult ticks [
13].
Our study investigated the mortality rates of
H. longicornis adults and nymphs following exposure to varying concentrations of clove, eucalyptus, lavender, and mint essential oils. The mortality of adults and nymphs in all groups significantly increased, in a dose-dependent manner. Clove oil emerged as the most potent agent among the tested essential oils. Our study results are consistent with the findings of Xin et al. [
14], who conducted a similar investigation. They screened 20 essential oils for their acaricidal effects against
H. longicornis and found that cinnamon, clove, and chamomile oils exhibited the highest potency.
In our study, distinct mortality patterns were observed among different essential oils at a 1% concentration. Notably, clove oil exhibited the highest mortality rates for nymphs (97%) and adults (86%), while mint oil demonstrated the lowest rates, at 36% for nymphs and 38% for adults. The key active compound in clove oil, eugenol [
15], contributes to its efficacy, while mint oil relies on menthol and menthone [
16] for its effects. The mechanism by which clove oil exerts its acaricidal activity involves potential neurotoxic and cytotoxic actions [
17,
18], likely tied to the interaction of eugenol with tyramine and octopamine receptors. Nevertheless, the precise mode of action of mint oil remains unclear. Interestingly, research [
19] on the larvicidal effects of essential oils against
Aedes, Anopheles, and
Culex larvae reported the limited efficacy of methanol and menthone, highlighting the complexity of the effects of essential oils on arthropods.
In our investigation, we evaluated the RI of clove, eucalyptus, lavender, and mint essential oils against adult
H. longicornis ticks over 4 observation periods (
Table 1). RI values, signifying repellency potency, were obtained at 10, 20, 30, and 40 min postapplication. Eucalyptus and lavender oils exhibited the highest RI at 0.60 and were least effective, while clove oil showed the lowest RI at 0.05, highlighting its superior repellent efficacy. Notably, our findings align with those of a previous study [
20] evaluating the effects of 10 essential oils against star ticks (
Amblyomma americanum), which identified the ineffectiveness of the active ingredients of lavender oil in repelling ticks at the tested concentrations.
Various bioassay methods have been employed to assess tick-repellent efficacy. However, a solitary study has addressed the comparability of outcomes between diverse methods. Of specific importance is the comparison between bioassays conducted in artificial containers (in vitro) and those carried out using animal subjects (in vivo) when assessing the effectiveness of new potential unregistered active ingredients [
21]. Notably, in vitro methods are more frequently utilized for evaluating such ingredients. When ticks were experimentally attached to rabbits, nearly identical fatality patterns were observed. Previous in vivo studies have explored tick attachment through methods like pet line blanket-drag field assays [
22] or human skin assays [
23]. However, our study is the first one to investigate
H. longicornis attachment on rabbit skin in the presence of essential oils. In our research, mint oil exhibited the lowest mortality and repellent effects, while lavender oil displayed the lowest non-attachment in both nymph and adult
H. longicornis. The overall efficacy of clove oil in these circumstances stood at 95% for nymphs and 90% for adult
H. longicornis ticks within the specific experimental conditions. Thus, clove oil was identified as a promising acaricide and repellent for
H. longicornis ticks.
The outcomes of this study highlight the varying degrees of mortality, repellent efficacy, and host detachment induced by various essential oils at different concentrations. The results suggest that clove and eucalyptus oils hold significant potential as effective agents for H. longicornis population management. Furthermore, lavender and mint oils exhibited potential as alternative options, offering valuable insights for the development of environmentally safe and sustainable approaches to tick control. Further research into the mechanisms underlying the observed effects and for achieving the optimization of application methods could enhance the integration of these essential oils in tick management strategies. Future studies could explore the combination effects of these essential oils with various tick species in different life cycle stages.
Notes
-
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
-
Conceptualization: Islam MS
Data curation: Haque MS
Formal analysis: Islam MS, Haque MS
Funding acquisition: You MJ
Investigation: Islam MS, Haque MS
Methodology: Islam MS, Haque MS
Project administration: You MJ
Resources: Islam MS
Software: Islam MS, Haque MS
Supervision: You MJ
Validation: Islam MS, Haque MS
Writing – original draft: Islam MS, Haque MS
Writing – review & editing: You MJ
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries (IPET) through the Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs Convergence Technologies Program for Educating Creative Global Leaders, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (grant number: 320005-4).
Fig. 1
Haemaphysalis longicornis nymph mortality following the application of different concentrations (1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, and 0.125%) of clove, mint, eucalyptus, and lavender oils compared to control (EtOH). Each mortality value represents the mean of 3 values reported as a percentage with the standard error of the mean (SE). The same letters in superscript indicate no statistically significant differences. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences. Each time point represents the mean of 5 values reported as a percentage with the SE. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001.
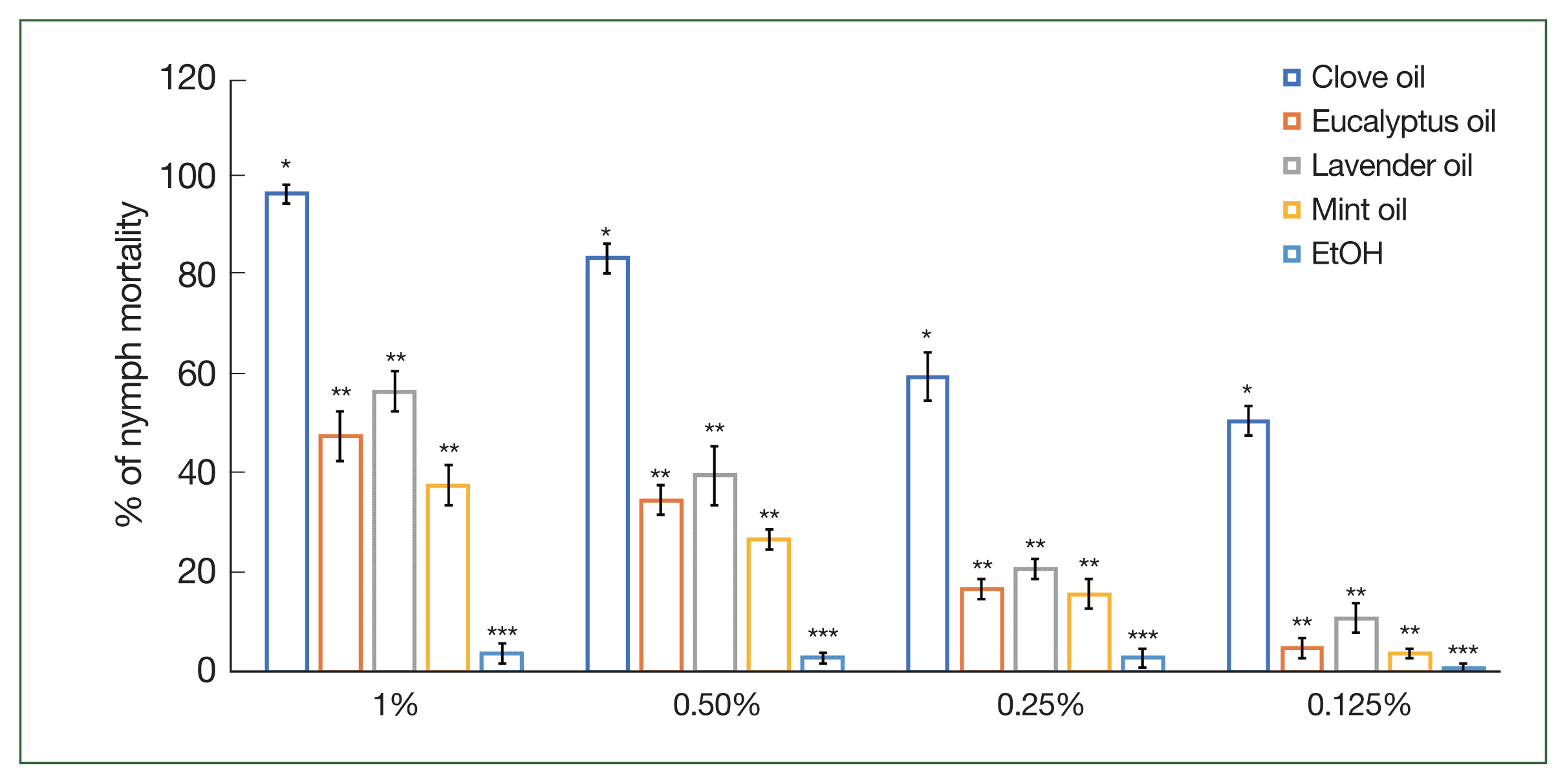
Fig. 2
Haemaphysalis longicornis adult mortality following the application of different concentrations (1%, 0.5%, 0.25%, and 0.125%) of clove, mint, eucalyptus, and lavender oils compared to control (EtOH). Each mortality value represents the mean of 3 values reported as a percentage with standard error of the mean (SE). The same letters in superscript indicate no statistically significant differences. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences. Each time point represents the mean of 5 values reported as a percentage with the standard error of the mean. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.
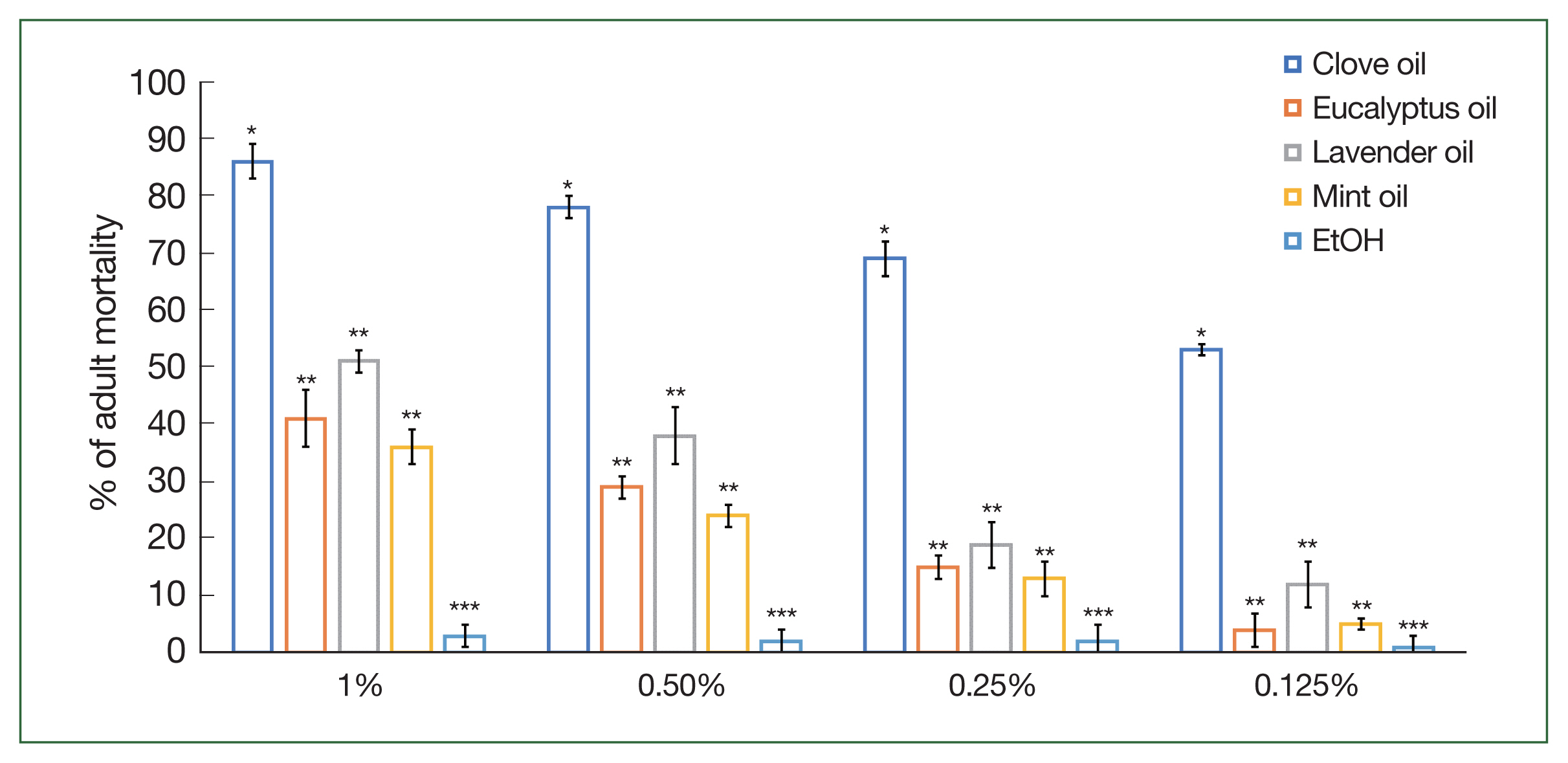
Fig. 3Comparison of attachment rates among adult H. longicornis following the application of clove, mint, eucalyptus, and lavender oils versus control. The % of ticks that were attached to rabbit skin was evaluated and expressed as a percentage for each group. Each time point represents the mean of 5 values reported as a percentage with the standard error of the mean. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
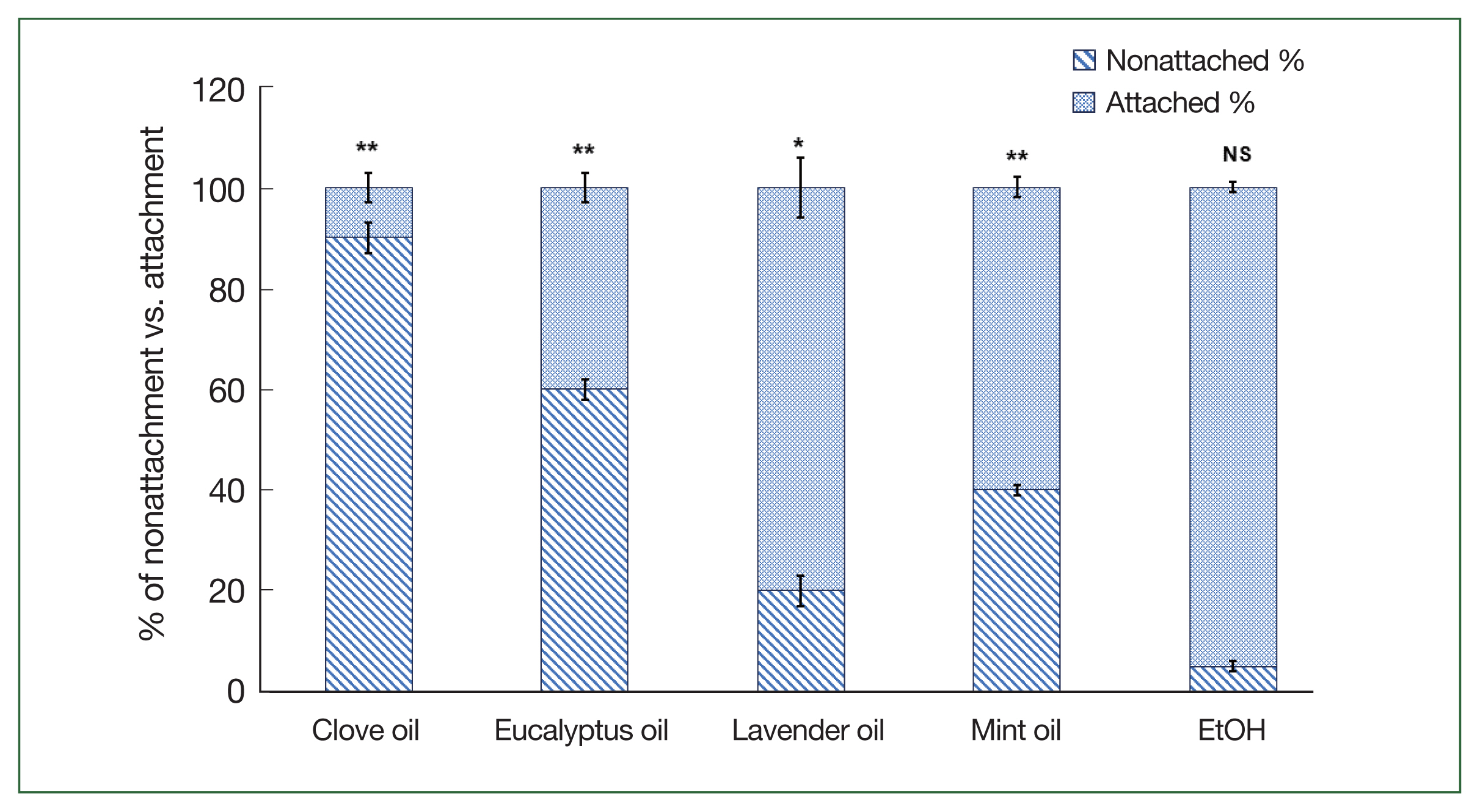
Fig. 4Comparison of attachment rates among nymph H. longicornis following the application of clove, mint, eucalyptus, and lavender oils versus control. The % of ticks that were attached to rabbit skin was evaluated and expressed as a percentage for each group. Each time point represents the mean of 5 values reported as a percentage with the standard error of the mean. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
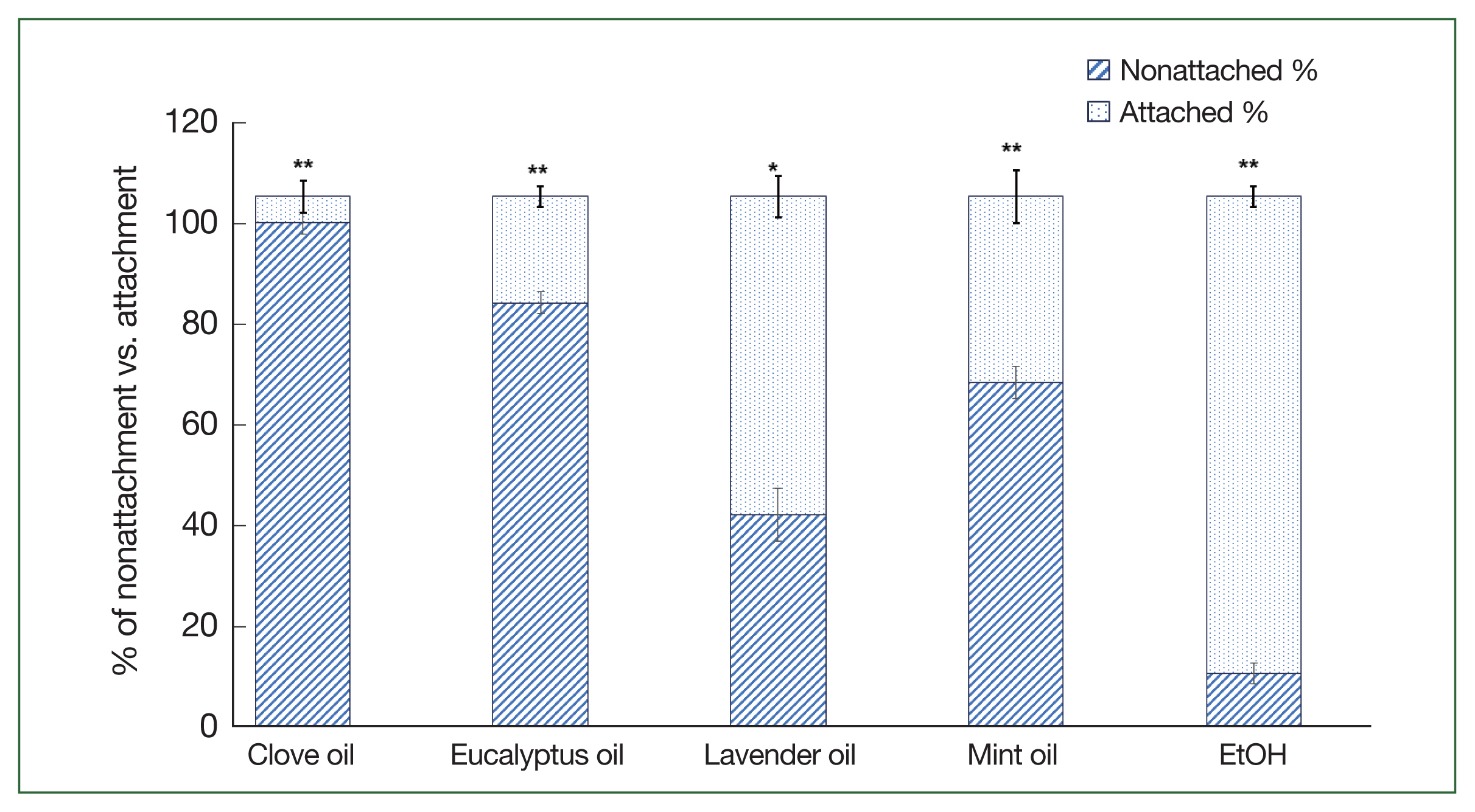
Fig. 5Gross lesions on rabbit skin upon the application of controls versus essential oils for tick attachment assessment. Adult female H. longicornis tick attachment on rabbit skin following the application of different essential oils. (A) Control, (B) clove oil, (C) mint oil, (D) eucalyptus oil, and (E) lavender oil. Arrows indicate tick attachment on rabbit skin.
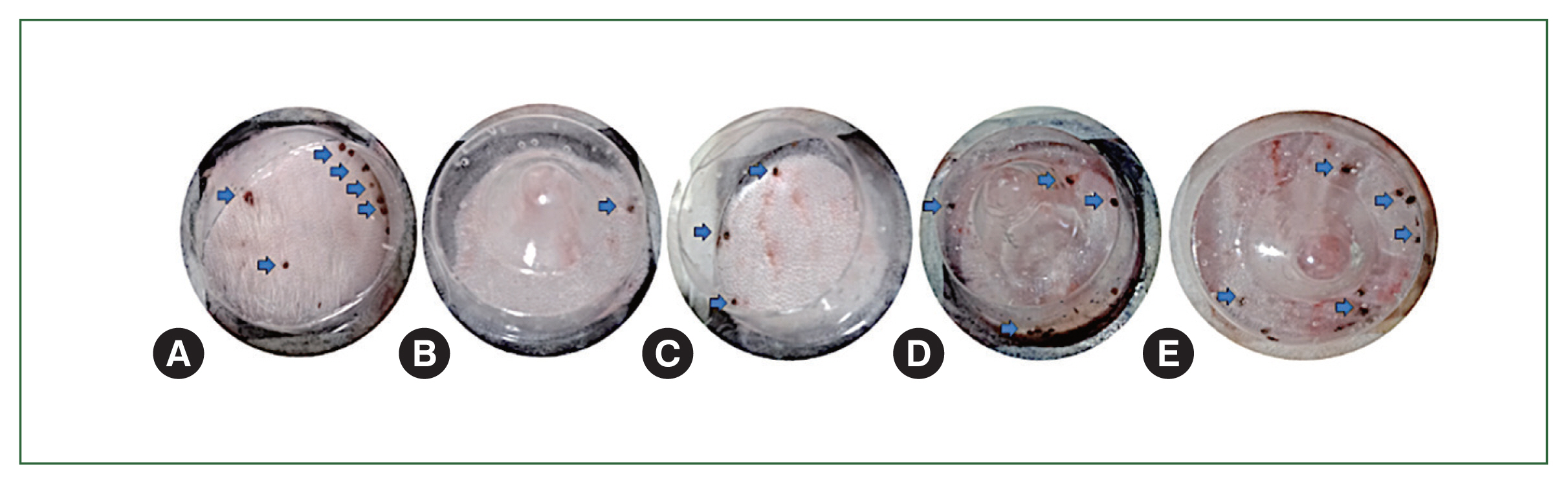
Table 1Repellency index (RI) of 1% clove oil, eucalyptus oil, lavender oil, and mint oil at 4 evaluation times on H. longicornis adults
Table 1
|
Oils |
Repellency index (RI), time (min) |
Effect |
|
10 |
20 |
30 |
40 |
|
Clove oil |
0.40 |
0.15 |
0.05 |
0.05 |
Repellent |
|
Eucalyptus oil |
0.60 |
0.30 |
0.30 |
0.20 |
Repellent |
|
Lavender oil |
0.60 |
0.50 |
0.40 |
0.40 |
Repellent |
|
Mint oil |
0.50 |
0.20 |
0.20 |
0.15 |
Repellent |
|
Control (ethanol) |
1.00 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
1.00 |
Nonrepellent |
References
- 1. Rizzoli A, Silaghi C, Obiegala A, Rudolf I, Hubalek Z, et al. Ixodes ricinus and its transmitted pathogens in urban and peri-urban areas in Europe: new hazards and relevance for public health. Front Public Health 2014;2:251. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2014.00251
- 2. de la Fuente J, Antunes S, Bonnet S, Cabezas-Cruz A, Domingos AG, et al. Tick-pathogen interactions and vector competence: identification of molecular drivers for tick-borne diseases. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2017;7:114. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00114
- 3. Estrada-Pena A, de la Fuente J. Host distribution does not limit the range of the tick Ixodes ricinus but impacts the circulation of transmitted pathogens. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2017;7:405. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00405
- 4. Coetzee D, Militky J, Venkataraman M. Functional coatings by natural and synthetic agents for insect control and their applications. Coatings 2022;12(4):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12040476
- 5. Selles SMA, Kouidri M, González MG, González J, Sánchez M, et al. Acaricidal and repellent effects of essential oils against ticks: a review. Pathogens 2021;10(11):https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10111379
- 6. Tirloni L, Islam MS, Kim TK, Diedrich JK, et al. Saliva from nymph and adult females of Haemaphysalis longicornis: a proteomic study. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:338. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-0918-y
- 7. Islam MS, Talha A, You MJ. Effects of histamine and antihistamine on the hard tick Haemaphysalis longicornis during blood sucking. Parasites Hosts Dis 2023;61(2):172-182. https://doi.org/10.3347/PHD.22068
- 8. Del Fabbro S, Fabbro SD, Nazzi F. From chemistry to behavior. molecular structure and bioactivity of repellents against Ixodes ricinus ticks. PLoS One 2013;8(6):e67832. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0067832
- 9. Santana MLG, Melo JPR, Camara C, Moraes MM, Araujo CA, et al. Lethal and sublethal effects of essential oils from Piper capitarianum Yunck and Piper krukoffii Yunck on Plutella xylostella L. An Acad Bras Cienc 2022;94(2):e20200072. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765202220200072
- 10. de la Fuente J. Controlling ticks and tick-borne diseases..looking forward. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2018;9(5):1354-1357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2018.04.001
- 11. Chae JB, Cho YS, Cho YK, Kang JG, Shin NS, et al. Epidemiological investigation of tick species from near domestic animal farms and cattle, goat, and wild boar in korea. Parasites Hosts Dis 2019;57(3):319-324. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2019.57.3.319
- 12. Lee JH, Park HS, Jang WJ, Koh SE, Park TK, et al. Identification of the Coxiella sp. detected from Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks in Korea. Microbiol Immunol 2004;48(2):125-130. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2004.tb03498.x
- 13. Williams H, Zoller H, Roepke RK, Zschiesche E, Heckeroth AR. Fluralaner activity against life stages of ticks using Rhipicephalus sanguineus and Ornithodoros moubata IN in vitro contact and feeding assays. Parasit Vectors 2015;8:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-0704-x
- 14. Xin R, Wang G, Qiu Z, Ma Q, Ahmad S, et al. Screening of essential oils with acaricidal activity against Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) and analysis of active components. Vet Parasitol 2022;307–308:109712. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2022.109712
- 15. Pramod K, Ansari SH, Ali J. Eugenol: a natural compound with versatile pharmacological actions. Nat Prod Commun 2010;5(12):1999-2006.
- 16. Schmidt E, Bail S, Buchbauer G, Stoilova I, Atanasova T, et al. Chemical composition, olfactory evaluation and antioxidant effects of essential oil from Mentha x piperita. Nat Prod Commun 2009;4(8):1107-1112.
- 17. Salman M, Abbas RZ, Israr M, Abbas A, Mehmood K, et al. Repellent and acaricidal activity of essential oils and their components against Rhipicephalus ticks in cattle. Vet Parasitol 2020;283:109178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2020.109178
- 18. Enan E. Insecticidal activity of essential oils: octopaminergic sites of action. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 2001;130(3):325-337. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1532-0456(01)00255-1
- 19. Amer A, Mehlhorn H. Larvicidal effects of various essential oils against Aedes, Anopheles, and Culex larvae (Diptera, Culicidae). Parasitol Res 2006;99(4):466-472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0182-3
- 20. Tabanca N, Wang M, Avonto C, Chittiboyina AG, Parcher JF, et al. Bioactivity-guided investigation of geranium essential oils as natural tick repellents. J Agric Food Chem 2013;61(17):4101-4107. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf400246a
- 21. Adenubi OT, McGaw LJ, Eloff JN, Naidoo V. In vitro bioassays used in evaluating plant extracts for tick repellent and acaricidal properties: a critical review. Vet Parasitol 2018;254:160-171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.03.008
- 22. Goode P, Ellse L, Wall R. Preventing tick attachment to dogs using essential oils. Ticks Tick Borne Dis 2018;9(4):921-926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ttbdis.2018.03.029
- 23. Luker HA, Salas KR, Esmaeili D, Holguin FO, Bendzus-Mendoza H, et al. Repellent efficacy of 20 essential oils on Aedes aegypti mosquitoes and Ixodes scapularis ticks in contact-repellency assays. Sci Rep 2023;13(1):1705. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-28820-9