Abstract
Genetic diversity of 18 Acanthamoeba isolates from ocean sediments was evaluated by comparing mitochondrial (mt) DNA RFLP, 18S rDNA sequences and by examining their cytopathic effects on human corneal epithelial cells versus reference strains. All isolates belonged to morphologic group II. Total of 16 restriction phenotypes of mtDNA from 18 isolates demonstrated the genetic diversity of Acanthamoeba in ocean sediments. Phylogenetic analysis using 18s rDNA sequences revealed that the 18 isolates were distinct from morphological groups I and III. Fifteen isolates showed close relatedness with 17 clinical isolates and A. castellanii Castellani and formed a lineage equivalent to T4 genotype of Byers' group. Two reference strains from ocean sediment, A. hatchetti BH-2 and A. griffini S-7 clustered unequivocally with these 15 isolates. Diversity among isolates was also evident from their cytopathic effects on human corneal cells. This is the first time describing Acanthamoeba diversity in ocean sediments in Korea.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba, diversity, 18S rDNA, genotype, ocean sediment, kerato-pathogenicity
INTRODUCTION
Acanthamoeba spp. are opportunistic protozoan parasites that have adapted to live in a variety of environments, e.g., soil, air, fresh water, ocean sediment, wild animals and humans (
Marciano-Cabral et al., 2003). Some species of the genus had been known to cause serious human infections, such as, the sight-threatening eye disease, i.e.,
Acanthamoeba keratitis, in healthy humans, especially in contact lens wearers (
Moore et al., 1987) and life-threatening granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE) in immuno-compromised individuals (
Martinez and Visvesvara, 1997;
Helton et al., 1993).
Although much research has been conducted on environmental isolates of
Acanthamoeba since the medical importance of this genus was described, only 4 isolates have been reported in ocean sediments, namely,
A. griffini (
Sawyer, 1971),
A. hatchetti (
Sawyer et al., 1977),
A. stevensoni (
Sawyer et al., 1993) and
A. jacobsi (
Sawyer et al., 1992). Two of these strains,
A. griffini, and
A. hatchetti, have been reported to be associated with human diseases (
Ledee et al., 1996;
Simitzis et al., 1979). In Korea,
Acanthamoeba isolates have been collected and identified from soil, hospital cooling tower water, and contact lens cases (
Kong et al., 1995;
Chung et al., 1996;
Kong and Chung, 1996;
Chung et al., 1998;
Kong et al., 2002), and some of these isolates have been found to be either the same or species closely genetically related to clinical isolates (
Chung et al., 1996,
1998;
Kong et al., 2002).
In the present research, we evaluated the genetic diversity of Acanthamoeba isolates from ocean sediments and assessed their possible kerato-pathogenicities with their mitochondrial DNA RFLP, 18S ribosomal DNA (rDNA) sequence analysis, and by examining their cytopathic effects on human corneal epithelial cells.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Acanthamoeba isolation and axenization
One gram samples of ocean sediments from 2 different beaches (Soonchun and Gangjin, Jeollanam-do, Korea) were loaded onto 1.5% agar plates covered with heat inactivated
Escherichia coli (free of plasmid, ATCC 25922, Washington D.C., U.S.A.). The plates were incubated at 25℃ and examined for the presence and growth of
Acanthamoeba under an inverted microscope daily for 1 week. Cysts were cloned on new agar plates, and cyst sizes and the number of arms were morphologically grouped according to Pussard and Pons (
1997). A piece of agar plate covered with the cysts of a clone was treated with 0.1 N HCl for 24 hr, and after washing with distilled water, agar plates containing many cysts were placed in Proteose peptone-Yeast extract-Glucose medium and incubated at 25℃.
The mtDNAs of
Acanthamoeba isolates were extracted as described by Yagita and Endo (
1990). Briefly, trophozoites harvested at the end of the logarithmic growth phase were washed with phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) 3 times at 2,000 rpm for 5 min. Pellets were resuspended in 100 µl of chilled TEG buffer (25 mM Tris-HCl, 10 mM EDTA, 50 mM Glucose, pH 8.0) and incubated on ice for 5 min. Amoebae were lysed by adding 200 µl of chilled fresh 1% sodium dodecyl sulfate solution in 0.2 N NaOH, and gently mixing by inversion, and then incubated on ice for 5 min. Then, 150 µl of 3 M chilled potassium acetate buffer (60 ml of 5 M potassium acetate, 11.5 ml of glacial acetate, 28.5 ml distilled water, pH 6.0) was added to the suspension and mixed by inverting the tube. After incubation on ice for 15 min, mixtures were centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 15 min at 4℃. Collected supernatant fluids were mixed with equal volumes of phenol saturated with 10 mM Tris-1 mM EDTA (pH 8.0) and centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 5 min at 4℃ (some times this step was repeated). Collected supernatants were added to an equal volume of phenol/chloroform (1:1) solution and centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 5 min at 4℃. The mtDNA was precipitated by adding 1 ml of absolute ethanol and 40 µl of 3 M sodium acetate solution and by incubating at -70℃ for at least 15 min. After centrifugation at 15,000 rpm for 20 min at 4℃, DNA precipitates were washed twice with 70% chilled ethanol. Isolated DNA samples were vacuum dried and dissolved in 15-25 µl of TE buffer (5 mM Tris-HCl. pH 8.0, 1 mM EDTA) or distilled water and stored at -20℃ until required.
The mtDNAs of Acanthamoeba isolates were digested with 1-6 units of restriction enzymes at 37℃ for 2 hr in 20 µl reaction volumes with the buffers specified for respective restriction enzymes (EcoR I, Bgl II, Cla I & Sca I; Promega, Madison, Wisconsin, U.S.A.). Digested DNA was electrophoresed in 0.7% agarose gel at 4 V/cm for 1-2 hr. Ethidium bromide stained gels were observed and photographed under a UV transilluminator. Hind III digests of λ phage were used as size markers.
Extraction of chromosomal DNA
Amoebae harvested at the end of the logarithmic growth phase were washed with cold PBS 3 times and boiled in 0.1 ml of 0.1 N NaOH at 100℃ for 3 min. Supernatants were collected after centrifugation at 2,000 rpm for 2 min at room temperature and mixed with 0.2 ml of distilled water. An equal volume of phenol was added to the solution and vortexed for 1 min. The mixture was centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 5 min at 4℃ twice, and aqueous phases were centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 5 min again with 300 µl of phenol/chloroform (1:1) solution. Nuclear DNA was precipitated by adding 600 µl of cold absolute ethanol and 30 µl of 3 M sodium acetate (pH 5.2) and then incubating at -70℃ for 15 min and centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 20 min at 4℃. DNA samples were then washed with 70% ethanol, vacuum dried, dissolved in 30-50 µl of ultra pure water, and stored at -20℃ until required.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of the small subunit ribosomal RNA coding DNA (ssu rDNA) and its sequence analyses
PCR primer sequences originated from the sequence of ssu rRNA of
A. castellanii Neff strain reported by Gunderson et al. (
1986). The sequences used were 5'-CCGAATTCGTCGACAACCTGGTTGATCCTGCCAGT-3' and 5'-GGATCCAAGCTTGATCCTTCTGCAGGTTCACCTAC-3'. A 50-µl PCR premix (Bioneer, Seoul, Korea) was used for ssu rDNA amplification by PCR. PCR was performed in 50 µl containing 1.25 U
Taq polymerase (SUPER BIO, Seoul, Korea), 0.1-1.0 ng DNA, 200 µM dNTPs, 1.5 mM MgCl
2 and 0.5 µM primer. PCR reactions were performed using an initial 3 min at 94℃, 30 amplication cycles (94℃ for 1 min, 60℃ for 1 min, 72℃ for 2.5 min), and a final elongation step of 10 min at 72℃. The presence and sizes of all amplification products were determined by agarose gel electrophoresis and ethidium bromide staining. Amplified DNAs from the 18 ocean sediment isolates were ligated into the T/A cloning vector pGEM-T easy System I (Promega) and forwarded to Macrogen Co. (Seoul, Korea) for sequence analysis.
Nucleotide sequences were compared with those of
Acanthamoeba strains available in Genbank using BLAST (
Altschul et al., 1990). Clustal X (
Thompson et al., 1997) was used for pairwise alignments and for calculating percentage sequence dissimilarities. Intron sequences in ssu rDNA were excluded in this analysis. A phylogenetic tree was reconstructed using the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic average (UPGMA) using Phylip version 3.5 (
Clark, 1992:
Felsenstein, 1993). In total 41 isolates were used in this study. Other
Acanthamoeba 18S rDNA sequences used in this study were 18
Acanthamoeba isolates from the infected corneas of Korean patients, and a sequence data of these in GenBank are under the following numbers: strain KA/E1, AF005996; KA/E2, AF005998; KA/E3, AF005997; KA/E4, AF349045; KA/E5, AY148954; KA/E6, AF349044; KA/E7, AY148955; KA/E8, AY148956; KA/E9, AF316546; KA/E10, AY148957; KA/E11, AY148958; KA/E12, AF316545; KA/E13, AY148959; KA/E14, AY148906; KA/E15, AY148961; KA/E16, AY148962; KA/E17, AY148963; KA/E18, AY148964. One
A. castellanii Castellani isolate (U07413), 2 ocean sediment isolates
A. hatchetti BH2 (AF019068) and
A. griffini S-7 (U07412),
A. astronyxis Ray and Hayes (AF019064) of morphological group I, and
A. healyi OC-3A (AF019070) isolate morphological group III were used as outgroup.
The sequence data reported in this paper have been deposited at GenBank and are available under the following reference numbers: strain KA/MSS1, AY172999; KA/MSS2, AY173013; KA/MSS6, AY173014; KA/MSS7, AY173015; KA/MSS8-1, AY173000; KA/MSS8-2, AY173001; KA/MSG1, AY173002; KA/MSG3, AY173003; KA/MSG4, AY173004; KA/MSG10, AY173005; KA/MSG12, AY173006; KA/MSG15, AY173007; KA/MSG16, AY173008; KA/MSG18, AY173009; KA/MSG23, AY176047; KA/MSG26, AY173010; KA/MSG27, AY173011; KA/MSG29, AY173012.
Culture of human corneal epithelial cells
Human corneal epithelial (HCE) cells were obtained from the Department of Biochemistry at Kyungpook National University School of Medicine and were cultured in DMEM/F12, 15% fetal bovine serum, 5 µg/ml insulin and 10 ng/ml human EGF. Cells were incubated at 37℃ in 5% CO2.
Assay of cytopathic effects
Trophozoites of 18 Acanthamoeba isolates were incubated with HCE cells for 36 hr at 37℃, 5% CO2 in a 24-well plate. Wells with monolayer of HCE cells were added 1 x 105 cells of respective amoebae. After incubation, wells were washed with warm PBS and stained with Giemsa (Merck, Germany), and cells remaining in wells were washed with PBS and solubilized in 0.4 ml of 5% sodium dodecyl sulfate in PBS. Optical densities (ODs) of 0.1 ml aliquots of solubilized cells were measured at 590 nm in a 96-well plate and checked with a microplate reader. Percentage CPE (cytopathic effect) was calculated using the following formula : % CPE = 100-[((OD of experimental well-OD of amoebae alone)/OD control cells alone) × 100]. Assays were performed in triplicate.
RESULTS
Morphologies of the Acanthamoeba isolates
All 18 isolates obtained from ocean sediments in this study exhibited the morphological characteristics of
Acanthamoeba group II (
Pussard and Pons, 1977). Mean cyst diameters ranged from 12.8 to 21.8 µm and the average number of arms from 4.3 to 7.3 (
Table 1).
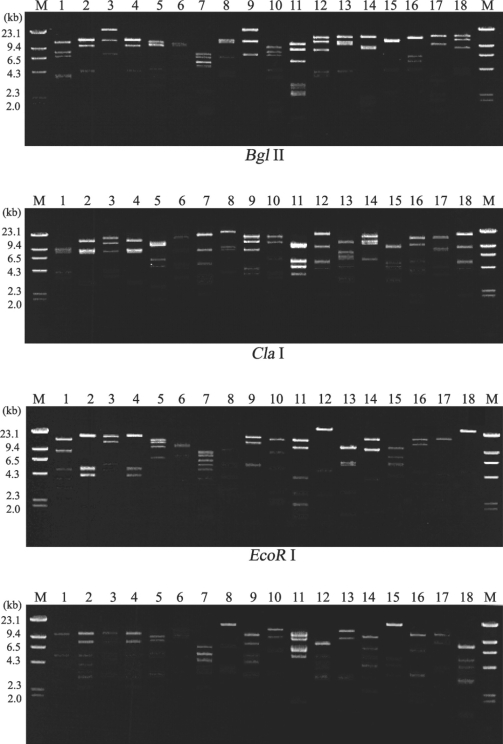
Fig. 1 shows 16 different restriction phenotypes of mtDNA RFLP emerged from the 18
Acanthamoeba isolates.
Acanthamoeba KA/MSS2 and KA/MSS7, KA/MSG15 and KA/MSG29 showed identical mtDNA RFLP patterns for all restriction enzymes applied in this study. However, the remaining 14 isolates had no common bands.
DNA sequence heterogeneity
The ssu rDNAs of the 18 isolates were all approximately 2,300 bp except for those of KA/MSS2, KA/MSS6, KA/MSS7 and KA/MSG23, which had an additional 969 bp, 959 bp, 967 bp and 1,276 bp intron, respectively. A BLAST search of nucleic acid sequences present in GenBank revealed that KA/MSS2, KA/MSS6 and KA/MSS7 introns most resembled the group I intron of A. griffini. A similar search found that the KA/MSG23 intron was not similar to any reported group I introns.
Including KA/MSS1, KA/MSG12 and KA/MSG27, sequence similarities between the 18 isolates ranged from 84.2% to 99.7%, and excluding KA/MSS1, KA/MSG12 and KA/MSG27, sequence similarities ranged from 95.8% to 99.7%.
Phylogenetic analysis
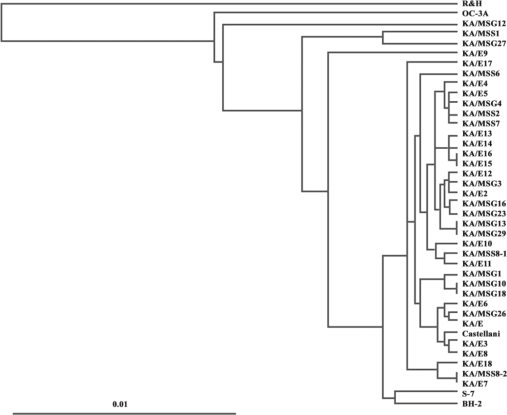
A phylogenetic tree constructed based on the determined sequence similarities is presented in
Fig. 2. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the 18 isolates were distinct from morphological groups I and III. With the exceptions of KA/MSS1, KA/MSG12, and KA/MSG27, 15 isolates belonged to the same lineage as 16 clinical isolates from Korean keratitis patients.
A. castellanii Castellani, and 2 ocean sediment isolates
A. hatchetti BH-2 and
A. griffini S-7 clustered unequivocally with these 15 isolates.
Further analysis of tree topology revealed the presence of several lineages of ocean sediment and clinical isolates: KA/MSS1 and KA/MSG27 (99.5% sequence similarity), KA/MSS2 and KA/MSS7 (99.5% sequence similarity), KA/MSG15 and KA/MSG29 (99.7% sequence similarity), KA/MSG16 and KA/MSG23 (99.1% sequence similarity), KA/MSG10 and KA/MSG18 (99.7% sequence similarity), KA/E7, KA/ME18, and KA/MSS8-2 (sequence similarities of 98.4% to 99.7%), KA/E2, KA/E12, and KA/MSG3 (sequence similarities of 98.9% to 99.6%), KA/E10, KA/E11, and KA/MSS8-1 (sequence similarities of 98.3% to 99.5%), KA/E6, KA/MSG26, and KA/E1 (sequence similarities of 98.3% to 99.2%), KA/MSS2, KA/MSS7, KA/MSG4, and KA/E5 (sequence similarities of 98.9% to 99.6%).
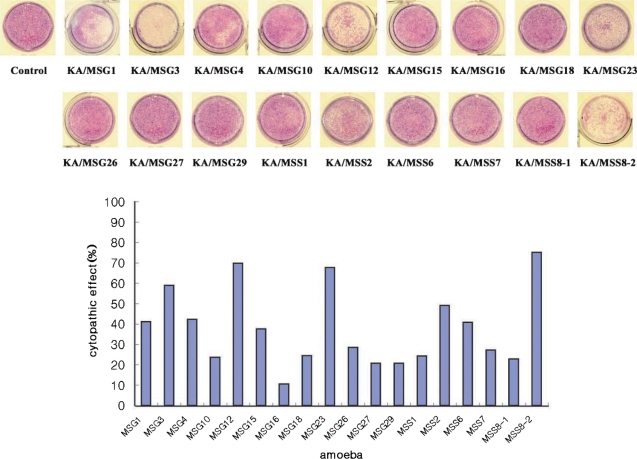
Cytopathic effects
Human corneal epithelial cells were lysed by the 18 Acanthamoeba isolates from ocean sediments. The cytopathic effect of KA/MSS8-2 was highest (75%) among these isolates. KA/MSG16 had the lowest cytopathic effect (10%). Isolates KA/MSG3, KA/MSG12, KA/MSG23, KA/MSS8-2 had cytopathic effects > 50%. Isolates KA/MSG1, KA/MSG4, KA/MSG15, KA/MSS2, KA/MSS6 had cytopathic effects ranging from 30% to 50%. Those with a cytopathic effect bellow 30% were KA/MSG10, KA/MSG16, KA/MSG18, KA/MSG26, KA/MSG27, KA/MSG29, KA/MSS1, KA/MSS7, and KA/MSS8-1.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, 18
Acanthamoeba isolates from ocean sediments obtained from Soonchun and Gangjin were analyzed morphologically and genetically by mtDNA RFLP and 18S rDNA sequence analysis. All isolates displayed the characteristic morphology of group II
Acanthamoeba (
Pussard and Pons, 1977). In a previous study of 18 cases of
Acanthamoeba-associated keratitis in Korea, all isolates exhibited group II morphology (Kim et al., unpublished data). In fact,
Acanthamoeba group II seems to predominate clinically, and in soil, and freshwater (
Stothard et al., 1998) and in the ocean sediments.
The phylogenetic tree reconstructed based on 18S rDNA sequence data of the 18 ocean isolates corresponded well with the morphological grouping of Pussard and Pons (
1977) who classified the members of genus
Acanthamoeba into 3 morphologic groups. KA/MSS1, KA/MSG12 and KA/MSG27 had larger cyst diameters than the other 15 isolates, and comparative sequence analysis revealed that the 18 ocean sediment isolates were distinct from
A. astronyxis of morphological group I and
A. healyi of morphological group III.
A total of 16 different restriction phenotypes of mtDNA of the 18 ocean isolates revealed the genetic diversity of
Acanthamoeba in sediments. KA/MSS2 and KA/MSS7 showed the same mtDNA RFLP patterns, and also exhibited morphological similarities based on their cyst diameters and arm numbers (
Table 1). KA/MSG15 and KA/MSG29 also had the same mtDNA RFLP patterns and were morphologically similar. KA/MSS6 showed the same mtDNA RFLP pattern as KA/E4, a clinical isolate from the infected cornea of a Korean patient. KA/MSG3 also showed the same mtDNA RFLP pattern as KA/E15 another clinical isolate (data not shown).
The 18S rDNA gene sequence analysis is a highly promising method for identifying and performing phylogenetic studies on the genus
Acanthamoeba (
Stothard et al., 1998;
Yu et al., 2004). Previous unpublished studies on molecular phylogeny and taxonomy of
Acanthamoeba (performed by TJB) indicated that isolates with < 1% sequence difference should be considered the same species (
Stothard et al., 1998). With the exceptions of KA/MSS1, KA/MSG12, and KA/MSG27, 15 isolates formed a lineage with 17 clinical isolates obtained from infected corneas in Korea. KA/MSS2 and KA/MSS7, KA/MSG15, and KA/MSG29 showed 99.5% and 99.7% sequence similarities, respectively, and the same mtDNA RFLP patterns. Based on these results, KA/MSS2, and KA/MSS7, KA/MSG15 and KA/MSG29 were identified as the same species.
Byers group in America differentiated
Acanthamoeba into 12 sequence types by 18S rDNA sequence analysis (
Gast et al., 1996;
Stothard et al., 1998). They reclassified
Acanthamoeba isolates belonging to T4, and found that the isolates were very closely related with nucleotide dissimilarities ranging from 0-4.4% and evolutionary distances of < 0.44%. They suggested that the various species previously assigned by morphological criteria might be reclassified as
A. castellanii complex, because the T4 sequence type included the type strain as the type species
A. castellanii Castellani (
Booton et al., 2004).
Nineteen of 20
Acanthamoeba isolates from beach sands were of genotype T4, which suggest that this is the most common genotype in this environment and that could be a potential source of
Acanthamoeba keratitis infection. The sequence type corresponding to
A. castellanii complex group of Chung et al. (
1998) by riboprinting. As indicated by our results, with the exception of KA/MSS1, KA/MSG12 and KA/MSG27, the other 15 ocean isolates formed a lineage with
A. castellanii Castellani and showed only 0.3% to 4.2% sequence dissimilarities among strains.
Although KA/MSG10 and KA/MSG18 were found to be genetically very closely associated each other with 99.7% 18S rDNA sequence similarity, their mtDNA RFLP were not identical. They had several common fragments. This finding can be explained by the fact that mtDNA evolves faster than the nuclear chromosomal DNA.
In conclusion, Acanthamoeba isolates from ocean sediments were found to be genetically diverse. Fifteen of 18 isolates were identified as A. castellanii complex based on 18S rDNA sequence analysis. Most of these isolates are suspected kerato-pathogens because 15 of the 18 isolates belonged to the same sequence type as most clinical isolates from infected cornea.
References
Fig. 1Agarose gel electrophoretic restriction fragment patterns of mitochondrial DNA from 18 strains of Acanthamoeba. Lane: 1, KA/MSS1; 2, KA/MSS2; 3, KA/MSS6; 4, KA/MSS7; 5, KA/MSS8-1; 6, KA/MSS8-2; 7, KA/MSG1; 8, KA/MSG3; 9, KA/MSG4; 10, KA/MSG10; 11, KA/MSG12; 12, KA/MSG15; 13, KA/MSG16; 14, KA/MSG18; 15, KA/MSG23; 16, KA/MSG26; 17, KA/MSG27; 18, KA/MSG29. M, Hind III digested λ phage DNA as a DNA size standard.
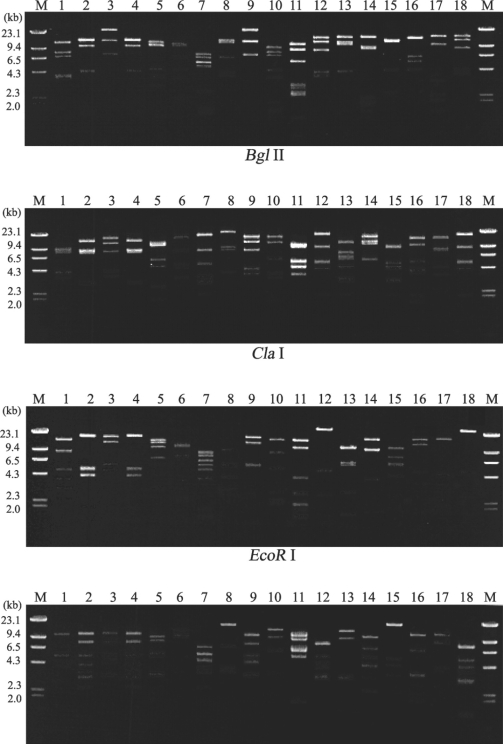
Fig. 2Dendrogram of 41 strains of Acanthamoeba using the UPGMA method using Phylip ver. 3.5 based on genetic divergence estimates.
Fig. 3Cytopathic effect of 18 isolated Acanthamoeba trophozoites on human corneal epithelial cells. A, KA/MSG1; B, KA/MSG3; C, KA/MSG4; D, KA/MSG10; E, KA/MSG12; F, KA/MSG15; G, KA/MSG16; H, KA/MSG18; I, KA/MSG23; J, KA/MSG26; K, KA/MSG29; L, KA/MSS1; M, KA/MSS2; N, KA/MSS6; O, KA/MSS7; Q, KA/MSS8-1; R, KA/MSS8-2; S, control. The control was cultured without Acanthamoeba trophozoites.
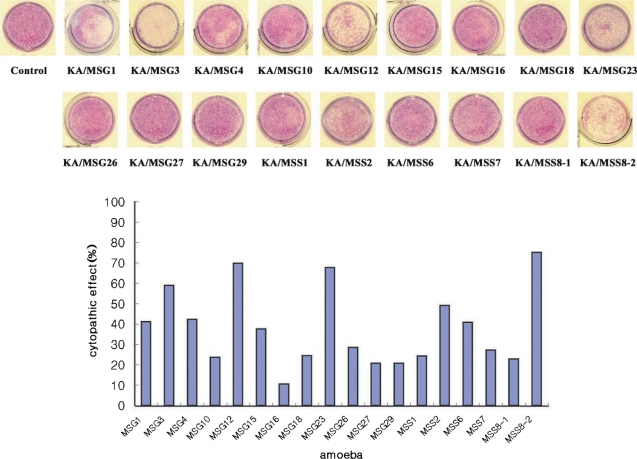
Table 1.Morphologies of Acanthamoeba strains analyzed in this study
Table 1.
|
Isolates |
Cyst diameter (μm) (range) |
No. of arms (range) |
|
KA/MSS1 |
17.5 (15.8-20.3) |
7.3 (6-8) |
|
KA/MSS2 |
16.0 (12.8-19.0) |
5.1 (4-6) |
|
KA/MSS6 |
14.5 (12.5-17.0) |
5.1 (4-6) |
|
KA/MSS7 |
16.0 (13.5-19.5) |
5.1 (4-6) |
|
KA/MSS8-1 |
16.5 (13.3-19.3) |
7.1 (5-8) |
|
KA/MSS8-2 |
15.0 (13.3-17.0) |
6.8 (6-8) |
|
KA/MSG1 |
15.3 (12.5-18.8) |
4.6 (4-6) |
|
KA/MSG3 |
15.3 (15.3-18.8) |
5.6 (4-7) |
|
KA/MSG4 |
15.0 (12.5-17.3) |
5.0 (4-6) |
|
KA/MSG10 |
15.0 (11.0-17.8) |
4.5 (3-6) |
|
KA/MSG12 |
21.8 (17.3-24.5) |
6.5 (6-8) |
|
KA/MSG15 |
12.8 (11.3-14.5) |
4.5 (4-5) |
|
KA/MSG16 |
15.3 (12.0-15.0) |
4.5 (4-6) |
|
KA/MSG18 |
16.0 (13.8-17.8) |
6.6 (5-9) |
|
KA/MSG23 |
16.5 (15.0-19.0) |
6.9 (5-10) |
|
KA/MSG26 |
15.3 (12.5-17.5) |
5.4 (4-6) |
|
KA/MSG27 |
17.3 (15.8-20.0) |
6.3 (5-8) |
|
KA/MSG29 |
13.3 (12.0-15.3) |
4.3 (4-5) |