Abstract
Allyl isothiocyanate (AITC) is a natural product commonly used in food preservation and pharmaceutical applications. Toxoplasmosis, caused by the protozoan pathogen Toxoplasma gondii, is prevalent globally while the impact of AITC on toxoplasmosis is unclear. We explored the effect of AITC on acute toxoplasmosis. We infected C57BL/6 mice with T. gondii type I RH strain following AITC administration. On the 4th day after infection, which corresponds to the initial stage of infection, we collected serum for the determination of inflammatory cytokine levels. The mice serum of the AITC-administered group contained significantly lower levels of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, interferon-gamma, interleukin (IL)-23 subunit p19, IL-4, IL-6, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. The lifespan of the mice in the AITC-administered group was significantly reduced. In vitro experiments showed that AITC promoted the proliferation of intracellular T. gondii accompanied by the inhibition of IL-4, IL-1β, and IL-6 production in RAW264.7 macrophages. Our results showed that AITC facilitated T. gondii infection in the early stage by inhibiting the production of several inflammatory cytokines.
-
Key words: Toxoplasma gondii, acute toxoplasmosis, pathogen, inflammatory cytokine, allyl isothiocyanate
Due to its antimicrobial properties, allyl isothiocyanate (AITC), a natural substance abundantly present in horseradish, has gained attention for its application in food preservation and pharmaceuticals [
1]. Furthermore, AITC is effective in treating various cancer types [
2], and also acts as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent to treat many other diseases. Interestingly, AITC has been used to kill protozoan parasites, such as
Plasmodium berghei [
3] and
Trypanosoma brucei [
4].
Approximately one-third of the global population is infected with
Toxoplasma gondii, a protozoan parasite that invades and replicates in almost all nucleated cells [
5,
6]. Primary toxoplasmosis caused by
T. gondii infection typically manifests as a subclinical disease. However, people with weakened immune systems have a significantly higher risk of developing severe infection complications [
7]. During long-term chronic infections, the downregulation of inflammatory cytokines may lead to the transition from chronic to acute infection [
8]. Thus, maintaining the host’s immune balance is crucial for resisting
T. gondii infection.
Despite advancements in the understanding of T. gondii infection, the complexities of AITC’s interactions with this parasite and its implications for the host’s immune responses against T. gondii infection remain largely unexplored. Here, we aimed to address this critical knowledge gap by investigating the effect of AITC against T. gondii and its potential impact on the development of acute toxoplasmosis.
We purchased 8-week-old C57BL/6 female mice from the Guangdong Medical Laboratory Animal Center. All mice were housed in a specific pathogen-free environment at the Experimental Animal Center of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University. RH is a virulent strain of T. gondii. We used human foreskin fibroblasts (HFFs) to passage an RH strain that had been genetically modified to emit green fluorescence (RH-GFP). In all in vitro cell experiments, AITC was first diluted in DMSO and then further diluted to the specified concentration using the cell culture medium, ensuring that the final DMSO concentration was < 0.1%.
We investigated the effect of AITC on T. gondii infection using a mouse infection model. All animal experiments were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Pharmaceutical University (approval no: 00351890). Briefly, C57BL/6 mice were randomly allocated into 2 groups: the AITC group and the Vehicle group (n=8 per group). The AITC group received daily intraperitoneal injections of AITC (200 μl; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) at a dose of 5 mg/kg body weight. The Vehicle group received daily intraperitoneal injections of PBS (200 μl). On the third day after the first injection, all mice were infected with 5,000 fresh egressed RH-GFP tachyzoites that had been cultured in HFF cells. On the 4th day after infection, we collected blood samples from the tail vein of the mice to determine the serum levels of inflammatory cytokines and ascitic fluid for cell smears. The levels of serum inflammatory cytokines were measured using a RayPlex Mouse Inflammation Bead Array 1 kit (catalog no: FAM-INF-1-48, RayBiotech, Atlanta, GA, USA). Cell smears of the ascitic fluid samples were stained using a Wright–Giemsa stain kit (Baso, Guangdong, China). The mice were observed every 12 h until death.
For the in vitro experiments, RAW264.7 cells were seeded into 24-well cell culture plates containing coverslips. When they reached 70.0% confluency, they were inoculated with RH-GFP tachyzoites. After 4 h, T. gondii that had failed to infect the cells were washed away with PBS. Then we added fresh medium containing 5 μM AITC (AITC group) or no AITC (Vehicle group) to the cells. At 24 h after infection, we randomly chose 5 fields and photographed them using fluorescence microscopy. The relative size of the area of fluorescence was analyzed using ImageJ software and was proportional to the presence of T. gondii within the intracellular parasitophorous vacuoles (PV). Thus, the larger the fluorescence area, the higher the number of T. gondii in the PVs. Finally, the cells underwent Wright–Giemsa staining.
We also seeded RAW264.7 cells into 6-well plates. After 24 h, the cells were infected with RH tachyzoites. At 4 h after infection, the culture medium was replaced with a medium containing AITC. The cells were harvested 8 h after infection for RNA extraction using a Steady Pure Rapid RNA Extraction Kit (catalog no: AG21023, Accurate Biology, Hunan, China) followed by cDNA synthesis using a reverse transcription kit (catalog no: AG11728, Accurate Biology). The levels of gene expression were then analyzed using a qPCR assay kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China) and specific primers for interleukin (IL)-4 (NCBI gene ID: 16189, primers: 5′-ATGGATGTGCCAAACGTCCT-3′ and 5′-AAGCCCGAAAGAGTCT-CTGC-3′), IL-1β (NCBI gene ID: 16176, primers: 5′-TTCAAGGGGACATTAGGCAG-3′ and 5′-TGTGCTGGTGCTTCATTCAT-3′), and IL-6 (NCBI gene ID: 16193, primers: 5′-CAACGATGATGCACTTGCAGA-3′ and 5′-GTGACTCCAGCTTATCTCTTGGT-3′). β-actin (NCBI gene ID: 11461, primers: 5′-CTGGCTCCTAGCACCATGAA-3′and 5′-AGGGTGTAAAACGCAGCTCA-3′) was used as the reference gene.
Data were analyzed using SPSS 27.0 statistical software (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) and expressed as the mean±SEM unless otherwise indicated. Comparisons of the cytokine levels between the AITC and Vehicle groups were performed using independent sample t-test for normally distributed data and chi-square test and Mann–Whitney test for categorical data. The Kaplan–Meier method was used to generate survival curves using GraphPad Prism 10 software, and the Mantel–Cox log-rank test was used for survival analysis. P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
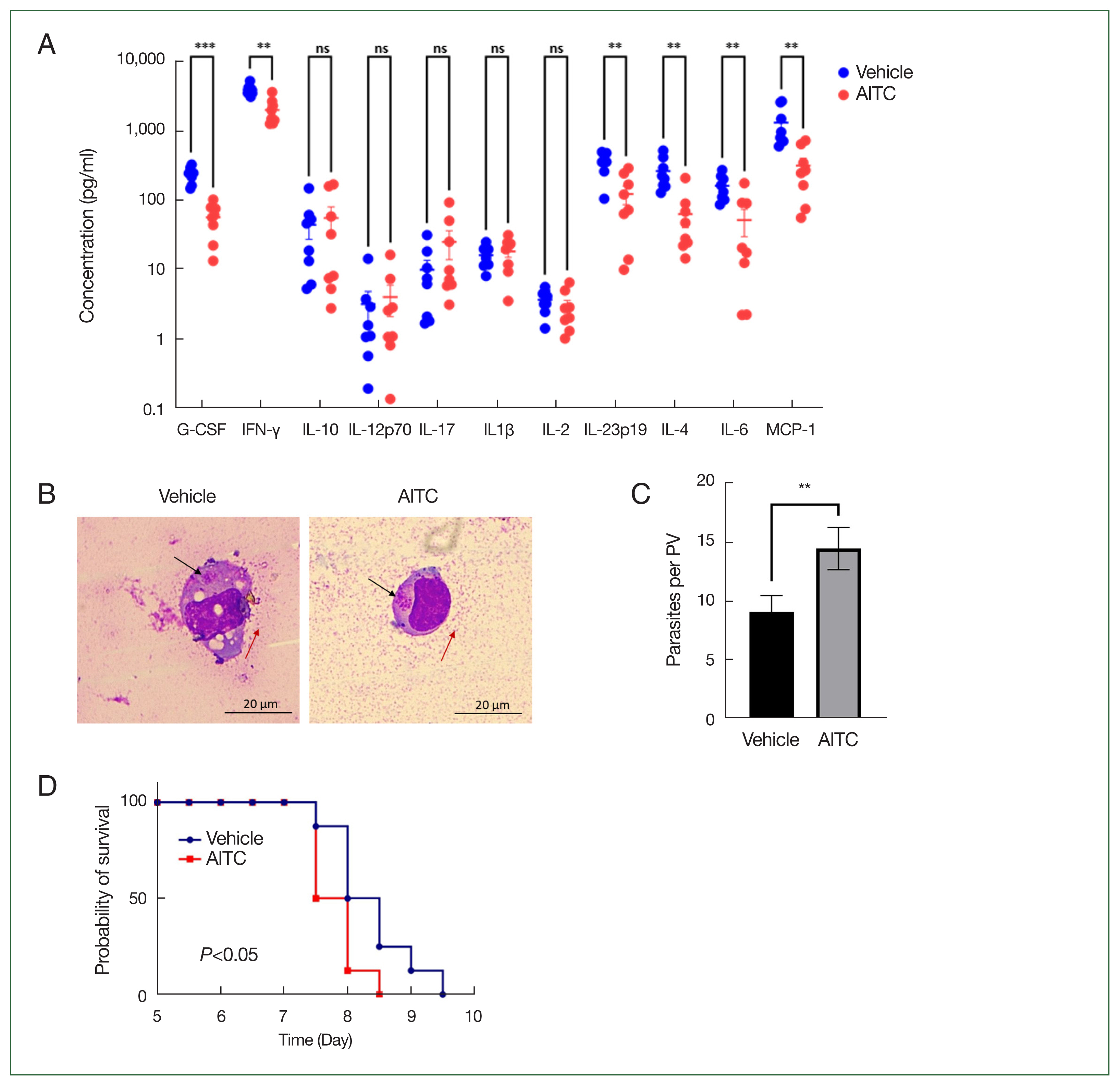
T. gondii type I RH strain infection in mice induces a strong immune response accompanied by the production of large amounts of inflammatory cytokines [
9], which help the host to resist
T. gondii infection. In this study, we treated C57BL/6 mice with AITC and infected them with
T. gondii strain RH. On the 4th day after infection, which corresponds to the initial stage of infection, we measured the levels of serum inflammatory cytokines (
Fig. 1A) and determined the number of
T. gondii within phagocytic cells in ascitic fluid (
Fig. 1B,C). The mean values of inflammatory cytokine levels in the Vehicle group were as follows: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), 236.72 pg/ml; interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), 3,933.67 pg/ml; IL-10, 43.61 pg/ml; IL-12 subunit p70 (IL-12p70), 3.13 pg/ml; IL-17, 9.81 pg/ml; IL-1β, 15.86 pg/ml; IL-2, 3.61 pg/ml; IL-23 subunit p19 (IL-23p19), 355.82 pg/ml; IL-4, 262.00 pg/ml; IL-6, 160.37 pg/ml; and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), 1,311.91 pg/ml. The mean values of inflammatory cytokine levels in the AITC group were as follows: G-CSF, 56.06 pg/ml; IFN-γ, 2001.48 pg/ml; IL-10, 54.84335 pg/ml; IL-12p70, 3.96 pg/ml; IL-17, 24.82 pg/ml; IL-1β, 18.02 pg/ml; IL-2, 2.87 pg/ml; IL-23p19, 121.88 pg/ml; IL-4, 62.37 pg/ml; IL-6, 51.25 pg/ml; and MCP-1, 314.14 pg/ml. G-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-23p19, IL-4, IL-6, and MCP-1 levels were significantly lower in the AITC group than in the Vehicle group (
Fig. 1A). These results suggested that AITC inhibited the production of several inflammatory cytokines induced by
T. gondii infection. Interestingly, the number of
T. gondii within phagocytes in the ascitic fluid samples was significantly increased in the AITC-treated group (
Fig. 1B, C). Survival analysis showed that mice in the AITC group succumbed to acute
T. gondii infection after 7.81 days compared with 8.38 days for mice in the Vehicle group (
Fig. 1D). The above results suggest that AITC downregulates the production of inflammatory cytokines and promotes acute toxoplasmosis.
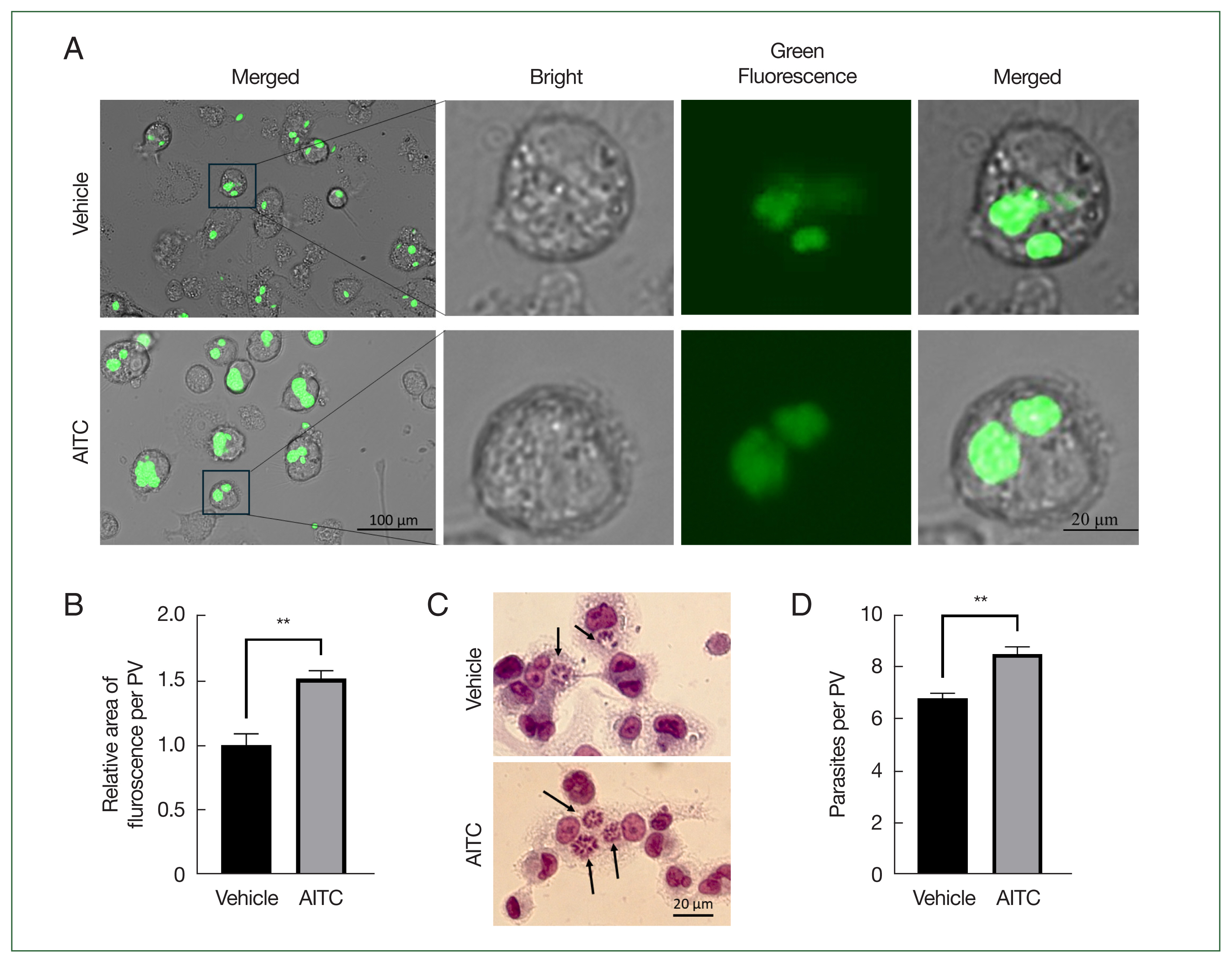
The infection of RAW264.7 cells (mouse macrophages) with
T. gondii leads to the release of multiple inflammatory cytokines [
10]. AITC has been reported to inhibit cytokine secretion in host cells, including macrophages, thereby altering the host’s immune profile [
11,
12]. The downregulation of inflammatory cytokines facilitates
T. gondii infection, converting chronic infections into acute infections [
8]. Thus, we designed a cell infection experiment involving
T. gondii-infected macrophages and treatment with 5 μM AITC [
12]. AITC notably stimulated
T. gondii proliferation in RAW264.7 cells (
Fig. 2). At 24 h after infection, the relative average fluorescent area of each PV in the AITC group was larger compared with that of the Vehicle group (
Fig. 2A, B). Wright–Giemsa staining further confirmed that the number of
T. gondii parasites within PVs in the AITC group was significantly higher than in the Vehicle group (
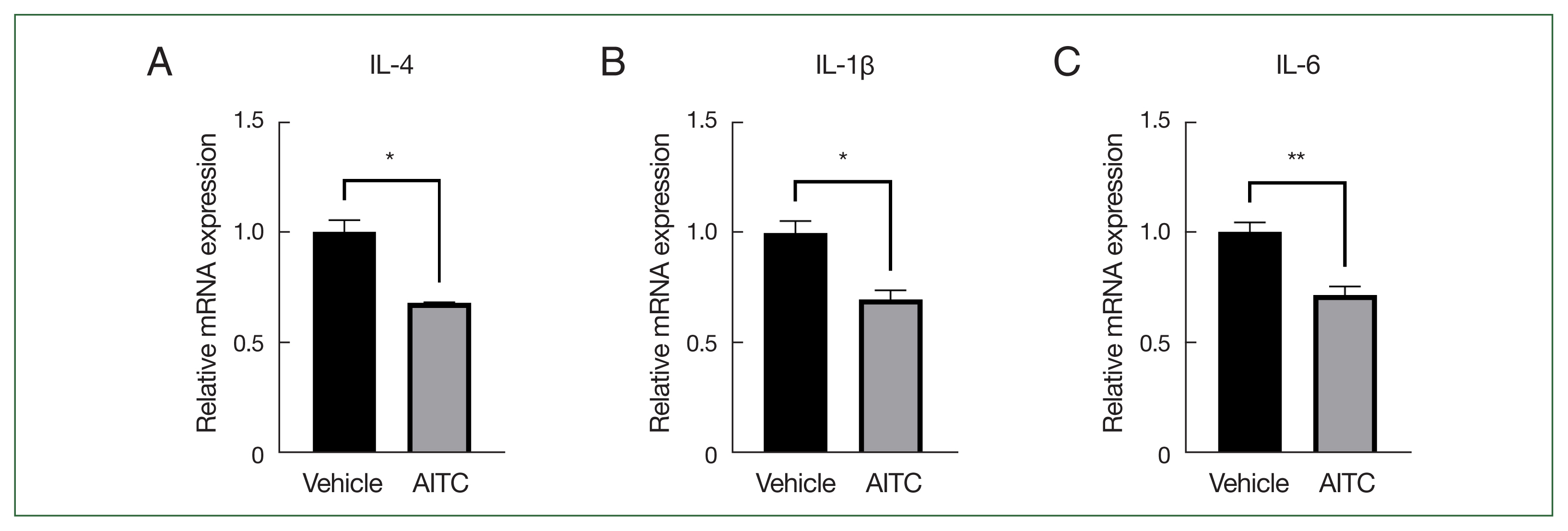
Fig. 2C, D). We also infected RAW264.7 cells with RH-GFP tachyzoites and treated them with AITC, revealing that AITC downregulated IL-4, IL-1β, and IL-6 production (
Fig. 3A–C). In summary, our findings indicate that AITC promotes intracellular
T. gondii proliferation in RAW264.7 cells, probably by inhibiting inflammatory cytokine production.
Although AITC has been widely studied in the field of medical research [
1], its potential impact on toxoplasmosis was unclear. Our results revealed that AITC promoted the growth of intracellular
T. gondii in immune cells, and mice treated with AITC exhibited a shorter lifespan during acute toxoplasmosis infection.
AITC and its derivatives have numerous health benefits. The direct effect of AITC on pathogenic microorganisms has been investigated in many studies. In a study focusing on the control of
Meloidogyne hapla in plants, the lowest AITC concentration was 100 mM [
13]. However, in studies involving mammals or mammalian cell lines, AITC concentrations are usually very low [
2,
11,
14]. Similarly, in experiments investigating the inhibition of malaria and trypanosome infections, the drug concentrations were also very low [
3,
4]. Therefore, to rule out the side effects caused by high doses of AITC, we used a low AITC concentration in our in vivo and in vitro experiments investigating the effect of AITC on
T. gondii infection. Interestingly, we found that AITC promoted acute
T. gondii infection. This differs from the previously reported inhibitory effects of AITC against other protozoan pathogens and may be attributed to the unique parasitic nature of
T. gondii, which invades the host cells and then forms PVs for protection against elimination.
During the initial stage of
T. gondii infection, the host responds by activating many immune cells accompanied by the production of inflammatory cytokines to eliminate the parasite. Anti-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-4 and IL-10) shield tissues from damage caused by inflammatory cytokines during infection, while proinflammatory cytokines promote
T. gondii clearance from the host. Neutrophils are highly mobile, rapidly migrating to sites of infection or inflammation. G-CSF helps to activate neutrophils, increasing their ability to phagocytose (engulf) and destroy invading pathogens [
15]. IFN-γ secreted by neutrophils assists the host in resisting
T. gondii infection. IL-23 is produced by certain immune cells, including dendritic cells and macrophages, in response to infection or inflammation [
16]. IL-23 and IL-12 play distinct roles in the immune system, and their interactions and coordinated actions are essential for mounting an effective immune response against pathogens [
9]. Additionally, IL-12 is involved in the response of natural killer cells and dendritic cells against
T. gondii infection [
17]. MCP-1 is produced by diverse cell types, such as macrophages and endothelial cells, in response to inflammatory signals. As a chemoattractant, it effectively attracts monocytes and other immune cells to the infection or inflammation site [
18]. IL-1β directly activates T-lymphocytes and macrophages, thereby enhancing IFN-γ production [
19]. IL-6 activates eosinophil cytotoxicity against
T. gondii, and IL-6 production during acute infection induces the secretion of specific proteins that inhibit parasite proliferation within the host [
19,
20]. However, AITC inhibits the secretion of IL-1β in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 cells [
12]. AITC administration was reported to reduce the production of host proinflammatory cytokines, including IL-1β and IL-6 [
11,
14]. Our study revealed that AITC inhibited the production of IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-4 in
T. gondii-infected RAW264.7 cells, accompanied by accelerated intracellular
T. gondii proliferation. Furthermore, AITC downregulated G-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-23p19, IL-4, IL-6, and MCP-1 production in
T. gondii-infected mice. Thus, the hindrance of inflammatory cytokine production by AITC may be one of the immune mechanisms by which AITC promotes acute
T. gondii infection.
Our study has some limitations. Since we focused solely on AITC among isothiocyanates, the potential role of other derivatives against T. gondii infection was not investigated. Second, only 1 strain of T. gondii was examined in this study. Finally, a chronic Toxoplasma infection model has not been implemented. Further research is warranted to address these limitations and delve deeper into the underlying mechanisms.
In conclusion, AITC promotes acute toxoplasmosis, which may be attributed to AITC interfering with the production of inflammatory cytokines by the host’s immune response. Our study sheds light on the impact of AITC on the development of acute toxoplasmosis, emphasizing the need for cautious consideration of its potential immunosuppressive effects when employed in the food and pharmaceutical domains. Immunocompromised patients with T. gondii infection should consider combining anti-Toxoplasma drugs, such as pyrimethamine, when consuming food or medications containing AITC. This approach would allow the benefit of AITC’s positive effects while mitigating its potential to promote Toxoplasma infection. Our findings highlight the potential negative impact of AITC on the immune response during T. gondii infection.
Notes
-
Author contributions
Conceptualization: Nam HW, Quan FS, Yang ZS
Data curation: Yang ZS
Formal analysis: Lin QM, Long HB, He JT,
Funding acquisition: Yang ZS
Investigation: Lin QM, Long HB, Yang ZS
Methodology: Lin QM, Long HB, He JT, Zhong Q, Liu XQ
Project administration: Yang ZS
Software: Lin QM, Long HB, He JT
Supervision: Nam HW, Yang ZS
Validation: Lin QM, Long HB, Zhang ZH
Visualization: Yang ZS
Writing – original draft: Lin QM, He JT, Yang ZS
Writing – review & editing: Lin QM, Zhang ZH, Yang ZS
-
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to this study.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou (grant no. 202103000051). We thank Professor Fang-li Lv from Sun Yat-Sen University for kindly providing RH-GFP and HFF cells.
Fig. 1Effect of AITC on acute Toxoplasmosis gondii infection in mice. (A) Representative cytokine levels in the serum of mice at 4 days after infection. (B) Cell smears of peritoneal fluid at 4 days after infection stained with the Wright–Giemsa stain. Representative images of infected phagocytes as confirmed by a hematology technician. RH-GFP tachyzoite in the PV of phagocytes (black arrow). The precipitated dye residue (red arrow). (C) Average number of tachyzoites per PV between the Vehicle and the AITC groups. (D) Representative survival curves of mice in the Vehicle and AITC groups (n=8 per group). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.

Fig. 2AITC promotes intracellular T. gondii proliferation in RAW264.7 cells. RAW264.7 cells were infected with RH-GFP tachyzoites. After 4 h of infection, the culture medium was replaced with fresh medium containing AITC. Further 24 h incubation, the cells were photographed using fluorescence microscopy and underwent Wright–Giemsa staining. (A) Representative fluorescence images. (B) Quantification of the relative fluorescence area within each PV in the cells using ImageJ software (n=3). (C) Cells were stained with Wright–Giemsa solution. Black arrow indicated T. gondii within the intracellular PV. (D) Number of T. gondii within the PV was counted and statistically analyzed (n=3). **P<0.01.

Fig. 3AITC inhibits inflammatory cytokine production in RAW264.7 cells. RAW264.7 cells were infected with RH-GFP tachyzoites. After 4 h of infection, the culture medium was replaced with fresh medium containing AITC. After 8 h of infection, the cells were collected for RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis. The relative mRNA expression levels of IL-4 (A), IL-1β (B), and IL-6 (C) in the 2 groups were determined by qPCR (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

References
- 1. Hoch CC, Shoykhet M, Weiser T, Griesbaum L, Petry J, et al. Isothiocyanates in medicine: a comprehensive review on phenylethyl-, allyl-, and benzyl-isothiocyanates. Pharmacol Res 2024;201:107107.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107107
- 2. Tarar A, Peng S, Cheema S, Peng CA. Anticancer activity, mechanism, and delivery of allyl isothiocyanate. Bioengineering (Basel) 2022;9(9):470.
https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9090470
- 3. Hashimoto T, Yoshioka S, Iwanaga S, Kanazawa K. Anti-malarial activity of allyl isothiocyanate and N-acetyl-S-(N-allylthiocarbamoyl)-l-cysteine. Mol Nutr Food Res 2023;67(21):e2300185.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.202300185
- 4. Steverding D, Michaels S, Read KD. In vitro and in vivo studies of trypanocidal activity of dietary isothiocyanates. Planta Med 2014;80(2–3):183-186.
https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1360262
- 5. Smith NC, Goulart C, Hayward JA, Kupz A, Miller CM, et al. Control of human toxoplasmosis. Int J Parasitol 2021;51(2–3):95-121.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2020.11.001
- 6. Marin-Garcia PJ, Planas N, Llobat L. Toxoplasma gondii in foods: Prevalence, control, and safety. Foods 2022;11(16):2542.
https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11162542
- 7. Dubey JP. Outbreaks of clinical toxoplasmosis in humans: five decades of personal experience, perspectives and lessons learned. Parasit Vectors 2021;14(1):263.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-021-04769-4
- 8. Yang J, Wang L, Xu D, Tang D, Li S, et al. Risk assessment of etanercept in mice chronically infected with Toxoplasma gondii. Front Microbiol 2018;9:2822.
https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02822
- 9. Sana M, Rashid M, Rashid I, Akbar H, Gomez-Marin JE, et al. Immune response against toxoplasmosis-some recent updates RH: Toxoplasma gondii immune response. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2022;36:3946320221078436.
https://doi.org/10.1177/03946320221078436
- 10. Yan K, Zhou H, Wang M, Li H, Sang R, et al. Inhibitory sffects of Inonotus obliquus polysaccharide on inflammatory response in Toxoplasma gondii-infected RAW264.7 macrophages. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2021;2021:2245496.
https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2245496
- 11. Caglayan B, Kilic E, Dalay A, Altunay S, Tuzcu M, et al. Allyl isothiocyanate attenuates oxidative stress and inflammation by modulating Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-kappaB pathways in traumatic brain injury in mice. Mol Biol Rep 2019;46(1):241-250.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4465-4
- 12. Wagner AE, Boesch-Saadatmandi C, Dose J, Schultheiss G, Rimbach G. Anti-inflammatory potential of allyl-isothiocyanate--role of Nrf2, NF-(kappa) B and microRNA-155. J Cell Mol Med 2012;16(4):836-843.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01367.x
- 13. Dahlin P, Hallmann J. New insights on the role of allyl isothiocyanate in controlling the root knot nematode Meloidogyne hapla. Plants (Basel) 2020;9(5):603.
https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9050603
- 14. Waz S, Matouk AI. Cardioprotective effect of allyl isothiocyanate in a rat model of doxorubicin acute toxicity. Toxicol Mech Methods 2022;32(3):194-203.
https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2021.1992064
- 15. Martin KR, Wong HL, Witko-Sarsat V, Wicks IP. G-CSF - a double edge sword in neutrophil mediated immunity. Semin Immunol 2021;54:101516.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2021.101516
- 16. McKenzie BS, Kastelein RA, Cua DJ. Understanding the IL-23-IL-17 immune pathway. Trends Immunol 2006;27(1):17-23.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2005.10.003
- 17. Mahmoudzadeh S, Nozad Charoudeh H, Marques CS, Bahadory S, Ahmadpour E. The role of IL-12 in stimulating NK cells against Toxoplasma gondii infection: a mini-review. Parasitol Res 2021;120(7):2303-2309.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-021-07204-w
- 18. Singh S, Anshita D, Ravichandiran V. MCP-1: function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int Immunopharmacol 2021;101(Pt B):107598.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107598
- 19. Chang HR, Grau GE, Pechere JC. Role of TNF and IL-1 in infections with Toxoplasma gondii. Immunology 1990;69(1):33-37.
- 20. Koo S, Marty FM, Baden LR. Infectious complications associated with immunomodulating biologic agents. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 2011;25(1):117-138.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hoc.2010.11.009
 , Hong-Bin Long1,†
, Hong-Bin Long1,† , Jun-Ting He2,†
, Jun-Ting He2,† , Zhi-hao Zhang1, Ho-Woo Nam3
, Zhi-hao Zhang1, Ho-Woo Nam3 , Fu-Shi Quan4
, Fu-Shi Quan4 , Qi Zhong1, Xu-Qing Liu1, Zhao-Shou Yang1,*
, Qi Zhong1, Xu-Qing Liu1, Zhao-Shou Yang1,*