Abstract
To determine the status of Enterobius vermicularis infection among children living on western and southern coastal islands of the Republic of Korea, children (3-10 years) in 39 kindergartens and primary schools were examined using the cello-tape anal swab method, during July and August 2000. Of 1,661 children examined, 307 (18.5%) were found to be positive for E. vermicularis eggs. The highest infection rate (59.3%) was found in a kindergarten and a branch school of Shinyang primary school on Chujado, Jeju-do (Province). Remarkable differences in egg positive rates were observed in different localities. The egg positive rate for boys (21.3%) was significantly higher than that of girls (15.4%) (P = 0.02). However, positive rates were not significantly dependent on age. The results of the present study show that E. vermicularis infection is highly prevalent among pre-school and primary school children living on the western and southern coastal islands of the Republic of Korea, and indicate the need for efforts to control this infection.
-
Key words: Enterobius vermicularis, enterobiasis, prevalence, cello-tape anal swab, children, islands, Korea
INTRODUCTION
Enterobiasis is a nematode infection caused by the pinworm,
Enterobius vermicularis. Its principal mode of transmission is direct contact between infected and uninfected persons. For this reason, this infection is prevalent among primary school children who are easily exposed to overcrowded conditions and inadequate sanitation, and who actively contact each other (
Beaver et al. 1984;
Cook, 1994).
In the Republic of Korea,
E. vermicularis is a common human intestinal parasite among pre-school and primary school children (
Chai et al., 1976;
Lee et al., 2000;
Kim et al., 2003). Even though the national prevalence of soil-transmitted helminth infections has decreased remarkably, for example, only 0.05% of the general population were positive for
Ascaris lubmricoides in 2004 (
Ministry of Health and Welfare and Korea Association of Health Promotion, 2004). However, the same cannot be said for
E. vermicularis, for example, in two nation-wide surveys on the general population in 1997 and 2004, the egg positive rates of
E. vermicularis were unchanged at 0.6% (
Ministry of Health and Welfare and Korea Association of Health Promotion, 1997,
2004). Moreover, its prevalence among children is much higher than in the general population.
The patterns and prevalence of human helminth infections on coastal islands seem to be quite different from those of the inland (
Chai et al., 2001,
2004). For instance, intestinal trematodes including heterophyids and a gymnophallid are prevalent among residents of western and southern coastal islands, i.e.,
Heterophyes nocens (11.0%),
Gymnophalloides seoi (3.8%), and
Pygidiopsis summa (1.2%) (
Chai et al., 2004). Moreover, because of their geographical isolation, less medical attention has been paid to these areas, and with regard to
E. vermicularis infection, no surveys have been conducted. Therefore, the present survey was performed to determine the status of
E. vermicularis infection among children living on these off-shore islands of the Republic of Korea.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
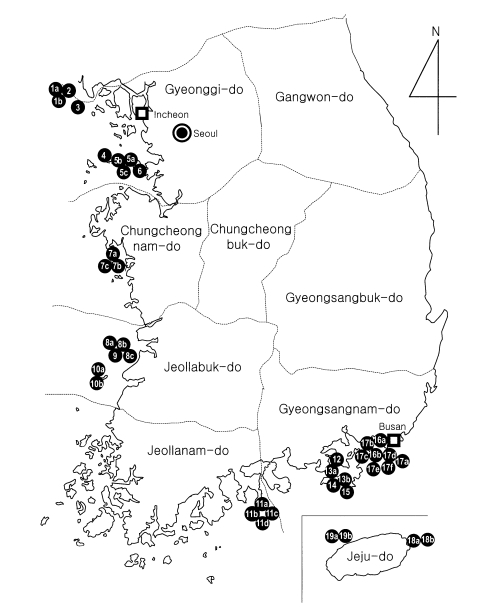
A total of 19 western and southern coastal islands in Gyeonggi-do, Incheon city, Chungcheongnam-do, Jeollabuk-do, Jeollanam-do, Gyeongsangnam-do, Busan city, and Jeju-do were involved in this study during July and August 2000, and a total of 39 kindergartens and primary schools were selected (
Table 1;
Fig. 1). After obtaining informed consent, 1,661 children (3-10 years old) in these schools were examined using the cello-tape anal swab technique (one smear per child), for the presence of
E. vermicularis eggs. Skilled laboratory technicians of the branch offices of the Korea Association of Health Promotion (KAHP) collected samples. Anal swabs were transported to the Department of Parasitology and Tropical Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, and examined using a light microscope. Results were analyzed with respect to locality, age, and sex using Fisher's exact test and the chi-square test.
RESULTS
A total of 307 (18.5%) of the 1,661 samples were positive for
E. vermicularis eggs. The egg positive rate ranged from 0% to 59.3% by location (
Table 1;
Fig. 1). The egg positive rate among boys (21.3%) was significantly higher than that among girls (15.4%) (
P = 0.02) (Tables
1,
2). No significant differences in egg positive rates according to age were observed in boys and girls (
Table 2).
DISCUSSION
It is of note that the detection of
E. vermicularis eggs from the peri-anal region means the termination of parasitism by the adult worms that produced these eggs (
Akagi, 1973;
Cho and Kang, 1975), and that such a finding does not necessarily mean that further worms are present in the intestine. Nevertheless, egg detection from the perianal region is significant, because egg positivity indicates a high probability of infection in the intestine (
Cho and Kang, 1975).
In the present study,
E. vermicularis infection was found to be prevalent in all ages from 3 to 10 years, and boys were more highly infected than girls. Children in this age group contact each other more frequently in kindergartens and primary schools than children of other ages, and are also exposed to unsatisfactory sanitary environments (
Chai et al., 1976;
Kim et al., 2003). Inadequate personal hygiene could also increase the risk of
E. vermicularis infection among children, particularly among boys. Other factors including playing on the floor, nail biting, a failure to wash hands before meals, and living in non-apartment dwellings have also been reported to be associated with the prevalence of enterobiasis (
Sung et al. 2001). In this respect, kindergarten- and school-based mass control activities are likely to be more effective than individual treatment.
Enterobiasis is a disease with usually mild symptoms such as, perianal itching and dermatitis; it is asymptomatic in most adults who have low worm burdens. However, in children, particularly who have heavy worm burdens, neurological symptoms including nervousness, restlessness, irritability, and distraction may occur, and these may influence child growth (
Beaver et al. 1984;
Cook, 1994;
Song et al. 2003). Rarely, ectopic infections in the pelvic area or urinary tract of women can occur (
Ok et al. 1999;
Tandan et al. 2002).
Effective chemotherapeutic regimens have been developed and used for decades; however, the control of enterobiasis is difficult because of frequent reinfection and a short life cycle (
Lohiya et al. 2000;
Lee et al., 2001). Repeated health education concerning improved personal hygiene and regular inspections and mass chemotherapy with appropriate anthelmintics are essentially required to control enterobiasis among children living on off-shore islands in the Republic of Korea.
Notes
-
This study was supported by a grant from Kangwon National University (2003).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We would like to express our appreciation to members of the Korea Association of Health Promotion for performing the cello-tape anal swabs.
References
- 1. Akagi K. Enterobius vermicularis and enterobiasis. Progress of Medical Parasitology in Japan 1973;5:229-279.
- 2. Beaver PC, Jung RC, Cupp EW. Clinical Parasitology. 1984, 9th ed. Philadelphia, USA. Lea & Febiger; pp 302-306.
- 3. Chai JY, Cho SY, Kang SY, Seo BS. Frequency distribution of Enterobius vermicularis in a highly endemic population. Korean J Parasitol 1976;14:103-108.
- 4. Chai JY, Park JH, Han ET, Shin EH, Kim JL, Hong KS, Rim HJ, Lee SH. A nationwide survey of the prevalence of human Gymnophalloides seoi infection on western and southern coastal islands in the Republic of Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2001;39:23-30.
- 5. Chai JY, Park JH, Han ET, Shin EH, Kim JL, Guk SM, Hong KS, Lee SH, Rim HJ. Prevalence of Heterophyes nocens and Pygydiopsis summa infections among residents of the western and southern coastal islands of the Republic of Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2004;71:617-622.
- 6. Cho SY, Kang SY. Significance of scotch-tape anal swab technique in diagnosis of Enterobius vermicularis infection. Korean J Parasitol 1975;13:102-114.
- 7. Cook GC. Enterobius vermicularis infection. Gut 1994;35:1159-1162.
- 8. Kim JS, Lee HY, Ahn YK. Prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis infection and preventive effects of mass treatment among children in rural and urban areas, and children in orphanages. Korean J Parasitol 1991;29:235-243.
- 9. Kim BJ, Lee BY, Chung HK, Lee YS, Lee KH, Chung HJ, Ock MS. Egg positive rate of Enterobius vermicularis of primary school children in Geoje island. Korean J Parasitol 2003;41:75-77.
- 10. Lee KJ, Lee IY, Im K. Enterobius vermicularis egg positive rate in a primary school in Chungchongnam-do (province) in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2000;38:177-178.
- 11. Lee KJ, Ahn YK, Ryang YS. Enterobius vermicularis egg positive rates in primary school children in Gangwon-do (province), Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2001;39:327-328.
- 12. Lohiya GS, Tan-Figueroa L, Crinella FM, Lohiya S. Epidemiology and control of enterobiasis in a developmental center. West J Med 2000;172:305-308.
- 13. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Association of Health Promotion. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in Korea. 1997, Seoul, Korea. Urim Inc.; The 6th report.
- 14. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Association of Health Promotion. Prevalence of intestinal parasitic infections in Korea. 2004, Seoul, Korea. Art Motion Inc.; The 7th report.
- 15. Ok UZ, Ertan P, Limoncu E, Ece A, Ozbakkaloglu B. Relationship between pinworm and urinary tract infections in young girls. APMIS 1999;107:474-476.
- 16. Song HJ, Cho CH, Kim JS, Choi MH, Hong ST. Prevalence and risk factors for enterobiasis among preschool children in a metropolitan city in Korea. Parasitol Res 2003;91:46-50.
- 17. Sung JF, Lin RS, Huang KC, Wang SY, Lu YJ. Pinworm control and risk factors of pinworm infection among primary-school children in Taiwan. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2001;65:558-562.
- 18. Tandan T, Pollard AJ, Money DM, Scheifele DW. Pelvic inflammatory disease associated with Enterobius vermicularis. Arch Dis Child 2002;86:439-440.
- 19. Yang YS, Kim SW, Jung SH, Huh S, Lee JH. Chemotherapeutic trial to control enterobiasis in schoolchildren. Korean J Parasitol 1997;35:265-259.
- 20. Yoon HJ, Choi YJ, Lee SU, Park HY, Huh S, Yang YS. Enterobius vermicularis egg positive rate of pre-school children in Chunchon, Korea (1999). Korean J Parasitol 2000;38:279-281.
Fig. 1Areas surveyed (•) for Enterobius vermicularis infection using the cello-tape anal swab technique on western and southern islands of the Republic of Korea.
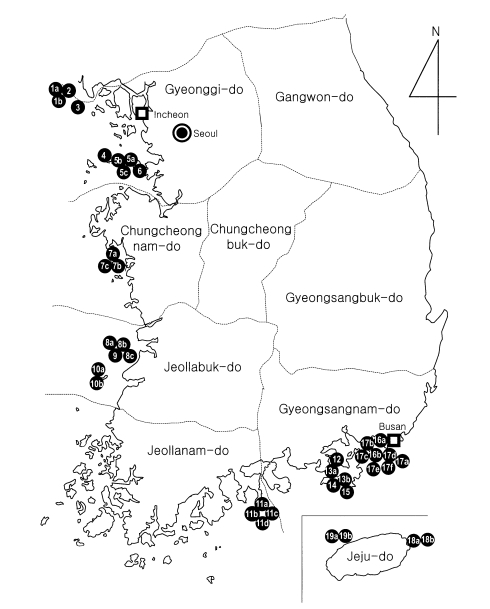
Table 1.Egg positive rates of Enterobius vermicularis among children living on different islands
Table 1.
|
Island codea)
|
Name of Island |
Name of kindergarten (K) or primary school (PS) |
No. children positive/No. examined (%)
|
|
Boys |
Girls |
Total |
|
Incheon city |
|
|
|
|
|
1a |
Baenyeongdo |
Bukpo (PS) |
11/51 (21.6) |
6/52 (11.5) |
17/103 (16.5) |
|
1b |
Baenyeongdo |
Baengnyeong (PS) |
9/41 (22.0) |
1/40 (2.5) |
10/81 (12.3) |
|
2 |
Daechungdo |
Daecheong (PS) |
1/17 (5.9) |
3/21 (14.3) |
4/38 (10.5) |
|
3 |
Yeonpyeongdo |
Yeonpyeong (PS) |
4/34 (11.8) |
1/25 (4.0) |
5/59 (8.5) |
|
4 |
Youngheungdo |
Yeongheung (PS) |
2/23 (8.7) |
4/21 (19.0) |
6/44 (13.6) |
|
Subtotal |
|
27/166 (16.2) |
15/159 (9.4) |
42/325 (12.9) |
|
Gyeonggi-do |
|
|
|
|
|
5a |
Daebudo |
Daenam (K & PS) |
2/42 (4.8) |
1/16 (6.3) |
3/58 (5.2) |
|
5b |
Daebudo |
Daebu (K & PS) |
8/55 (14.5) |
2/52 (3.8) |
10/107 (9.3) |
|
5c |
Daebudo |
Daedong (PS) |
1/14 (7.1) |
0/13 (0) |
1/27 (3.7) |
|
6 |
Jebudo |
Jebu Brb) (K & PS) |
1/25 (4.0) |
1/20 (5.0) |
2/45 (4.4) |
|
Subtotal |
|
12/136 (8.8) |
4/101 (4.0) |
16/237 (6.8) |
|
Chungcheongnam-do |
|
|
|
|
|
7a |
Anmyeondo |
Anmyeon (PS) |
18/63 (28.6) |
8/61 (13.1) |
26/124 (21.0) |
|
7b |
Anmyeondo |
Gonam (PS) |
11/33 (33.3) |
11/38 (28.9) |
22/71 (31.0) |
|
7c |
Anmyeondo |
Bangpo (PS) |
5/25 (20.0) |
4/24 (16.7) |
9/49 (18.4) |
|
Subtotal |
|
34/121 (28.0) |
23/123 (18.7) |
57/244 (23.3) |
|
Jeollabuk-do |
|
|
|
|
|
8a |
Shinsido |
Saesoonseon (PS) |
3/4 (75.0) |
0/6 (0) |
3/10 (30.0) |
|
8b |
Shinsido |
Seonyudo (PS) |
0/4 (0) |
0/4 (0) |
0/8 (0) |
|
8c |
Shinsido |
Shinsido (PS) |
0/4 (0) |
0/6 (0) |
0/10 (0) |
|
9 |
Munyeo |
Munyeo (PS) |
0/6 (0) |
0/3 (0) |
0/9 (0) |
|
10a |
Wido |
Wido (PS) |
3/18 (16.7) |
4/14 (28.6) |
7/32 (21.9) |
|
10b |
Wido |
Sikdo Br (PS) |
0/1 (0) |
0/5 (0) |
0/6 (0) |
|
Subtotal |
|
4/37 (10.8) |
7/38 (18.4) |
11/75 (14.6) |
|
Jeollanam-do |
|
|
|
|
|
11a |
Dulsando |
Dulsanchungang (K & PS) |
5/17 (29.4) |
6/23 (26.1) |
11/40 (27.5) |
|
11b |
Dulsando |
Daesin Br (PS) |
3/9 (33.3) |
4/14 (28.6) |
7/23 (30.4) |
|
11c |
Dulsando |
Dulsan (PS) |
9/31 (29.0) |
8/38 (21.1) |
17/69 (24.6) |
|
11d |
Dulsando |
Baekcho (PS) |
11/49 (22.4) |
8/31 (25.8) |
19/80 (23.8) |
|
Subtotal |
|
28/106 (26.4) |
26/106 (24.5) |
54/212 (25.4) |
|
Gyeongsangnam-do |
|
|
|
|
|
12 |
Kajodo |
Changho (PS) |
3/8 (37.5) |
1/10 (10.0) |
4/18 (22.2) |
|
13a |
Tongyeong |
Weonryang (PS) |
4/23 (17.4) |
6/25 (24.0) |
10/48 (20.8) |
|
13b |
Tongyeong |
Weonkwang (K) |
15/42 (35.7) |
6/40 (15.0) |
21/82 (25.6) |
|
14 |
Yeonhwado |
Yeonhwa (PS) |
2/11 (18.2) |
2/7 (28.6) |
4/18 (22.2) |
|
15 |
Bijindo |
Bijin (PS) |
2/7 (28.6) |
0/3 (0) |
2/10 (20.0) |
|
Subtotal |
|
26/91 (28.6) |
15/85 (17.6) |
41/176 (23.3) |
|
Busan city |
|
|
|
|
|
16a |
Nulchado |
Nulcha (PS) |
1/16 (6.3) |
0/10 (0) |
1/26 (3.9) |
|
16b |
Nulchado |
Nulcha (K) |
1/5 (20.0) |
0/9 (0) |
1/14 (7.1) |
|
17a |
Gadukdo |
Cheonga (K) |
2/15 (13.3) |
2/12 (16.7) |
4/27 (14.8) |
|
17b |
Gadukdo |
Daehang Br (PS) |
0/6 (0) |
0/4 (0) |
0/10 (0) |
|
17c |
Gadukdo |
Cheonsung Br (PS) |
0/6 (0) |
0/5 (0) |
0/11 (0) |
|
17d |
Gadukdo |
Cheinsung Br (K) |
1/6 (16.6) |
1/3 (33.3) |
2/9 (22.2) |
|
17e |
Gadukdo |
Soyang (K) |
0/4 (0) |
0/3 (0) |
0/7 (0) |
|
17f |
Gadukdo |
Cheonga (PS) |
4/20 (20.0) |
1/22 (4.5) |
5/42 (11.9) |
|
Subtotal |
|
9/78 (11.5) |
4/68 (5.9) |
13/146 (8.9) |
|
Jeju-do |
|
|
|
|
|
18a |
Udo |
Udo (PS) |
6/28 (21.4) |
3/14 (21.4) |
9/42 (21.4) |
|
18b |
Udo |
Yonpyung (K & PS) |
17/37 (45.9) |
9/33 (27.3) |
26/70 (37.1) |
|
19a |
Chujado |
Chuja (K & PS) |
8/50 (16.0) |
14/57 (24.6) |
22/107 (20.6) |
|
19b |
Chujado |
Shinyang Br (K & PS) |
14/17 (82.4) |
2/10 (20.0) |
16/27 (59.3) |
|
Subtotal |
|
45/132 (34.0) |
28/114 (24.5) |
73/246 (29.6) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
185/867 (21.3) |
122/794 (15.4) |
307/1,661 (18.5) |
Table 2.Age- and sex-prevalence of
Enterobius vermicularis infection among kindergarten and primary school children on 19 coastal islands
a)
Table 2.
|
Age |
No. children showing E. vermicularis eggs/No. examined (%)
|
|
Boys |
Girls |
Total |
|
3 |
3/12 (25.0) |
2/10 (20.0) |
5/22 (22.7) |
|
4 |
2/36 (5.6) |
4/27 (14.8) |
6/63 (9.5) |
|
5 |
12/43 (29.5) |
10/44 (22.7) |
22/87 (26.1) |
|
6 |
28/110 (27.9) |
9/83 (10.8) |
37/193 (19.2) |
|
7 |
26/131 (19.9) |
18/132 (13.6) |
44/263 (16.7) |
|
8 |
44/214 (20.6) |
34/208 (16.3) |
78/422 (18.5) |
|
9 |
39/171 (21.0) |
23/162 (14.2) |
62/333 (18.6) |
|
10 |
30/143 (21.0) |
20/119 (16.8) |
50/262 (19.1) |
|
Unknown |
1/7 (14.3) |
2/9 (22.2) |
3/16 (18.8) |
|
Total |
185/867 (21.3) |
122/794 (15.4) |
307/1,661 (18.5) |
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- The Incidence of Pinworm Enterobius Vermicularis Among School Children Aged 6-10
Ali Zbida, Mohammed Mftah Zayed, Salma Salem, Ekram Mustafa, Sumaya Ezulden, Aisha Mohammed, Munyah Abdullah, Wijdan Abdulbasset
Derna Academy Journal for Applied Sciences.2025; 3(1): 1. CrossRef - Pinworm (Enterobius Vermicularis) Infestation: An Updated Review
Alexander K.C. Leung, Joseph M. Lam, Benjamin Barankin, Alex H.C. Wong, Kin F. Leong, Kam L. Hon
Current Pediatric Reviews.2025; 21(4): 333. CrossRef - Enterobius vermicularis Infection in a Child Population with Evidence of Vulvovaginitis and Bacterial Coinfection in Girls in Oaxaca, México
Jaime Vargas-Arzola, Aristeo Segura-Salvador, Luis Alberto Hernández-Osorio, Nancy G. Santos-Hernández, Dolores G. Vidal-López, Adriana Moreno-Rodríguez, José A. De Fuentes-Vicente, Ranjan Kumar Mohapatra
Advances in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxyurose, trichocéphalose et ankylostomoses
F. Robert-Gangneux, B. Autier, C. Guiguen
EMC - Maladies infectieuses.2024; 41(3): 1. CrossRef - Positive rates for Enterobius vermicularis eggs among preschool children in Yeosu-si, Jeollanam-do, Korea (2017-2021)
Myoung-Ro Lee, Hee-Eun Shin, Seon-Ok Back, Young-Ju Lee, Jung-Won Ju, Chun Soon Park, Hee-Il Lee
Parasites, Hosts and Diseases.2023; 61(1): 84. CrossRef - Global prevalence of enterobiasis in young children over the past 20 years: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Elham Kia Lashaki, Azadeh Mizani, Seyed Abdollah Hosseini, Bentolhoda Habibi, Khadijeh Taherkhani, Amir Javadi, AliReza Taremiha, Samira Dodangeh
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2023; 14(6): 441. CrossRef - Pinworm infection in school children of four districts of Malakand region, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan
W. Khan, W. A. Panhwar, S. A. Mehmood, S. Ahmed, M. S. Ahmed, N. Khan, M. M. Khan, W. Akram, S. Ullah, Imran
Brazilian Journal of Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Enterobiasis and its risk factors in urban, rural and indigenous children of subtropical Argentina
Maria Romina Rivero, Carlos De Angelo, Constanza Feliziani, Song Liang, Karina Tiranti, Martin Miguel Salas, Oscar Daniel Salomon
Parasitology.2022; 149(3): 396. CrossRef - Enterobiasis among Yemeni children: a cross-sectional study
Abdulelah H. Al-Adhroey, Yahya A. Al-Ansi, Mohammed A. Al-Kholani, Abdulrahman H. Amer, Marwan M. Al-Khyat, Fadia H. Al Hubaishi, Radhwan H. Aziz, Ebrahim S. Al-Khateeb, Souad A. Al-Gabri, Tawfik M. Al-Gabri
Journal of Parasitic Diseases.2022; 46(3): 722. CrossRef - Is pinworm infection still a public health concern among children in resource-rich regions? Trends in pinworm infection prevalence and associated factors among children in Hualien County, Taiwan: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Yu-Chao Hsiao, Jen-Hung Wang, Chia-Hsiang Chu, Yu-Hsun Chang, Yung-Chieh Chang, Rong-Hwa Jan, Shao-Yin Chu, Shang-Hsien Yang, Jui-Shia Chen, Ming-Chun Chen
BMC Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef -
Enterobius vermicularis infections in Iraq
H. S. Al-Warid, A. Q. I. Alqaisi, I. M. Al Saqur, H. S. Al-Bahadely
Helminthologia.2022; 59(4): 364. CrossRef - Enterobius vermicularis Infection among Preschool Children: A 12-Year (2008-2019) Survey in Large Cities and Provinces of the Republic of Korea
Hyejoo Shin, Bong-Kwang Jung, Seungwan Ryoo, Sooji Hong, Taehee Chang, Jiyeon Park, Keon Hoon Lee, Jeonggyu Lee, Jae Young Park, Hoo-Gn Jeoung, Jae Hyun Cho, Jong-Yil Chai
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2021; 59(4): 421. CrossRef - Genetic variation of Enterobius vermicularis among schoolchildren in Thailand
K. Tomanakan, O. Sanpool, P. Chamavit, V. Lulitanond, P.M. Intapan, W. Maleewong
Journal of Helminthology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis infections and associated risk factors among schoolchildren in Nakhon Si Thammarat, Thailand
Pokkamol Laoraksawong, Pimyada Pansuwan, Supakrit Krongchon, Pongphan Pongpanitanont, Penchom Janwan
Tropical Medicine and Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The frequency of Enterobius vermicularis infection in children
from Wielkopolska Voivodeship
Marta Siekierska, Karolina Kot, Natalia Łanocha-Arendarczyk, Danuta Kosik-Bogacka
Diagnostyka Laboratoryjna.2018; 54(1): 5. CrossRef - Oxyurose, trichocéphalose et ankylostomoses
C. Guiguen, F. Robert-Gangneux
EMC - Maladies infectieuses.2018; 35(4): 1. CrossRef - Prevalence ofEnterobius vermicularisamong Children in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Mahmood Moosazadeh, Ghasem Abedi, Mahdi Afshari, Seif Ali Mahdavi, Fereshteh Farshidi, Elham Kheradmand
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2017; 8(2): 108. CrossRef - Prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis amongst kindergartens and preschool children in Mazandaran Province, North of Iran
Narges Afrakhteh, Zahra Marhaba, Seif Ali Mahdavi, Sahar Garoosian, Reyhaneh Mirnezhad, Mahsa Eshkevar Vakili, Haniye Ahmadi Shahraj, Behzad Javadian, Rozita Rezaei, Mahmood Moosazadeh
Journal of Parasitic Diseases.2016; 40(4): 1332. CrossRef - Prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis infection among preschool children, Babol, North of Iran
Seyed Ali Norbakhsh Amiri, Mohammad Taghi Rahimi, Seif Ali Mahdavi, Mahmood Moosazadeh, Omid Ramzani, Ali Farrokhi Koshk, Reza Rosbehan, Seyed Abolghasem Siyadatpanah
Journal of Parasitic Diseases.2016; 40(4): 1558. CrossRef - Paleoparasitological evidence of pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis) infection in a female adolescent residing in ancient Tehran (Iran) 7000 years ago
Niloofar Paknazhad, Gholamreza Mowlavi, Jean Dupouy Camet, Mohammad Esmaeili Jelodar, Iraj Mobedi, Mahsasadat Makki, Eshrat Beigom Kia, Mostafa Rezaeian, Mehdi Mohebali, Siamak Sarlak, Faezeh Najafi
Parasites & Vectors.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis Among Children in Kindergartens and Primary Schools in Iran: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Mahmood Moosazadeh, Ghasem Abedi, Mahdi Afshari, Seif Ali Mahdavi, Fereshteh Farshidi, Elham Kheradmand
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence ofEnterobius vermicularisamong preschool children in 2003 and 2013 in Xinxiang city, Henan province, Central China
Shuai Wang, Zhijun Yao, Yichen Hou, Dong Wang, Haizhu Zhang, Jingbo Ma, Luwen Zhang, Shiguo Liu
Parasite.2016; 23: 30. CrossRef - High Prevalence of <i>Enterobius vermicularis</i> Infection among Schoolchildren in Three Townships around Yangon, Myanmar
Jong-Yil Chai, Seung Koo Yang, Jae Won Kim, Soo-Lyoen Choi, Gyu-Young Song, Bong-Kwang Jung, Min-Jae Kim, Jaeeun Cho, Deok-Gyu Kim, Woon-Mok Sohn, Hoo-Gn Jeoung, Seon Cho, Jong-Bok Park, Sooji Hong, Thi Thi Htoon, Htay Htay Tin
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2015; 53(6): 771. CrossRef - Kindergarten Teacher’s Knowledge of Enterobiasis in Korea
Dong-Hee Kim, Hak-Sun Yu
Open Journal of Nursing.2014; 04(04): 330. CrossRef - Environmental Factors Related to Enterobiasis in a Southeast Region of Korea
Dong-Hee Kim, Min Kyoung Cho, Mi Kyung Park, Shin Ae Kang, Bo Young Kim, Sang Kyun Park, Hak Sun Yu
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2013; 51(1): 139. CrossRef - Impact of health education on the prevalence of enterobiasis in Korean preschool students
In-Soon Kang, Dong-Hee Kim, Hye-Gyung An, Hyun-Mi Son, Min Kyoung Cho, Mi-Kyung Park, Shin Ae Kang, Bo Young Kim, Hak Sun Yu
Acta Tropica.2012; 122(1): 59. CrossRef - Prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis among Preschool Children in Muan-gun, Jeollanam-do, Korea
Sung-Hee Hong, Young-Il Jeong, Jin-Hee Lee, Shin-Hyeong Cho, Won-Ja Lee, Sang-Eun Lee
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2012; 50(3): 259. CrossRef - Parasitic Prevalence in a Suburban School of Famaillá, Tucumán, Argentina
Julián Dib, Juana Oquilla, Silvia G. Lazarte, Silvia N. Gonzalez
ISRN Microbiology.2012; 2012: 1. CrossRef - Prevalence ofEnterobius vermicularisamong Preschool Children in Gimhae-si, Gyeongsangnam-do, Korea
Sang-Eun Lee, Jin-Hee Lee, Jung-Won Ju, Won-Ja Lee, Shin-Hyeong Cho
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2011; 49(2): 183. CrossRef - Comparison of Egg Positive Rates ofEnterobius vermicularisamong Preschool Children in Three Korean Localities
Sung-Hee Hong, Sang-Eun Lee, Young-Il Jeong, Won-Ja Lee, Shin-Hyeong Cho
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2011; 49(4): 441. CrossRef - Recent Advances in the Use of Anthelmintics for Treating Nematode Infections
Jong-Yil Chai
Infection and Chemotherapy.2011; 43(1): 26. CrossRef - Geographical aspects of enterobiasis in Estonia
Kalle Remm, Mare Remm
Health & Place.2010; 16(2): 291. CrossRef - Parents' Knowledge about Enterobiasis Might Be One of the Most Important Risk Factors for Enterobiasis in Children
Dong-Hee Kim, Hyun-Mi Son, Joo Young Kim, Min Kyoung Cho, Mee Kyung Park, Sin Ye Kang, Bo Young Kim, Hak Sun Yu
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2010; 48(2): 121. CrossRef - Changing Patterns of Human Parasitic Infection in Korea
Myoung-Hee Ahn
Hanyang Medical Reviews.2010; 30(3): 149. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis Among Japanese Expatriates Living in Developing Countries
Shinji FUKUSHIMA, Eiji MARUI, Atsuo HAMADA
Kansenshogaku Zasshi.2010; 84(1): 19. CrossRef - Prevalence of Enterobius vermicularis Infection among Preschool Children in Kindergartens of Taipei City, Taiwan in 2008
Tso-Kang Chang, Chien-Wei Liao, Ying-Chieh Huang, Chun-Chao Chang, Chia-Mei Chou, Hsin-Chieh Tsay, Alice Huang, Shu-Fen Guu, Ting-Chang Kao, Chia-Kwung Fan
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2009; 47(2): 185. CrossRef - Case-based estimation of the risk of enterobiasis
Mare Remm, Kalle Remm
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine.2008; 43(3): 167. CrossRef - Trends in parasitic diseases in the Republic of Korea
Eun-Hee Shin, Sang-Mee Guk, Hyo-Jin Kim, Soon-Hyung Lee, Jong-Yil Chai
Trends in Parasitology.2008; 24(3): 143. CrossRef - Transition of Parasitic Diseases in Korea
Soon-Hyung Lee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2007; 50(11): 937. CrossRef - Egg positive rate of Enterobius vermicularis among preschool children in Cheongju, Chungcheongbuk-do, Korea
Seokha Kang, Hyeong Kyu Jeon, Keeseon S. Eom, Joong-Ki Park
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2006; 44(3): 247. CrossRef