Abstract
Acanthamoeba and Naegleria are widely distributed in fresh water, soil and dust throughout the world, and cause meningoencephalitis or keratoconjunctivitis in humans and other mammals. Korean isolates, namely, Naegleria sp. YM-1 and Acanthamoeba sp. YM-2, YM-3, YM-4, YM-5, YM-6 and YM-7, were collected from sewage, water puddles, a storage reservoir, the gills of a fresh water fish, and by corneal washing. These isolates were categorized into three groups based on the mortalities of infected mice namely, highly virulent (YM-4), moderately virulent (YM-2, YM-5 and YM-7) and nonpathogenic (YM-3). In addition, a new species of Acanthamoeba was isolated from a freshwater fish in Korea and tentatively named Korean isolate YM-4. The morphologic characters of its cysts were similar to those of A. culbertsoni and A. royreba, which were previously designated as Acanthamoeba group III. Based on experimentally infected mouse mortality, Acanthamoeba YM-4 was highly virulent. The isoenzymes profile of Acanthamoeba YM-4 was similar to that of A. royreba. Moreover, an anti-Acanthamoeba YM-4 monoclonal antibody reacted only with Acanthamoeba YM-4, and not with A. culbertsoni. Random amplified polymorphic DNA marker analysis and RFLP analysis of mitochondrial DNA and of a 18S small subunit ribosomal RNA, placed Acanthamoeba YM-4 in a separate cluster based on phylogenic distances. Thus Acanthamoeba YM-4 was identified as a new species, and assigned Acanthamoeba sohi. Up to the year 2002 in Korea, two clinical cases were found to be infected with Acanthamoeba spp. These patients died of meningoencephalitis. In addition, one case of Acanthamoeba pneumonia with an immunodeficient status was reported and Acanthamoeba was detected in several cases of chronic relapsing corneal ulcer, chronic conjunctivitis, and keratitis.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba, Naegleria, taxonomy, pathogenicity, phylogeny
INTRODUCTION
The small free-living amoebae,
Acanthamoeba and
Naegleria are widely distributed in fresh water, soil and dust throughout the world, and thus provide a potential source of meningoencephalitis and keratoconjunctivitis in humans and other mammals. Many aerobic amoebae have been cultured on plates from stool and tissue specimens, and thought to be related to disease.
Acanthamoeba was recognized as a contaminant in tissue cultures before and after the first report was issued to the effect that it could cause disease in experimental animals. Some amoebae from tissue culture were mistakenly identified as Ryan virus, or when cultured for longer durations as cytopathic viruses (
Chang and Owens, 1964;
Eldridge and Tobin, 1967;
Willaert, 1974).
Recent work on pathogenic free-living amoebae started when Culbertson and colleagues (
1958) tested a tissue culture, thought to contain a cytopathic organism (now identified as
A. culbertsoni) in brain sections and in tissue culture. Fowler and Carter (
1965) in Australia and Butt (
1966) in Florida first recognized primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAME) in humans and believed that the amoeba was the same or related to that examined by Culbertson. However, these are now considered to be
Naegleria infections. Human PAME was found, in retrospective studies, as early as 1937 near Richmond, Virginia (
dos Santos, 1970). Amoebae were also found in a museum specimen in England, in a brain preserved in 1909 (
Symmers, 1969), now the earliest known example of human PAME. Since then several hundred cases of central nervous system disease caused by
Acanthamoeba spp.,
Naegleria fowleri and
Balamuthia mandrillaris have been reported worldwide.
B. mandrillaris is an another opportunistic pathogen that causes granulomatous amoebic encephalitis in humans. This amoeba has yet to be isolated from nature.
Unfortunately, this amoebic disease is not well known, but clinical cases of acanthamoebic meningoencephalitis, pneumonia, and keratoconjunctivitis were reported prior up to 2002 in Korea. Naegleria and Balamuthia infections have not been reported.
TAXONOMIC POSITION
The taxonomy of the group including the pathogenic free-living amoebae was clarified and updated at the generic level by P. C. Page (
1967a), and a key was later published (
Page, 1976). The genus
Naegleria (Alexeieff 1912, emend Calkins 1913) belongs to the family Vahlkampfiidae, whereas the genus
Acanthamoeba (
Volkonsky 1931, emend
Page 1967b) was incorporated into the family Acanthamoebidae Sawyer and Griffin (
1975).
The genus
Acanthamoeba was established in 1931 (
Volkonsky, 1931), but until recently considerable confusion existed in the literature about its nomenclature and taxonomic status. In 1966, Pussard stated that spindle shape was an unsatisfactory feature for intergeneric differentiation, and rather considered the distinctive morphology of the cyst to be a decisive character at the generic level, and further recognized the genus
Acanthamoeba. In 1967, Page considered the presence of acanthopodia and the structure of the cyst to be sufficiently distinctive and concluded that the generic designations of
Acanthamoeba and
Hartmannella were justified because of their trophozoite and cyst characters. In 1975, Visvesvara and Balamuth identified clearly definable and demonstrable differences not only in the trophozoite and cyst stages of
Acanthamoeba and
Hartmannella but also in their nutritional requirements and serologic responses. Sawyer and Griffin created the family Acanthamoebidae in 1975, and Page designated the suborder Acanthopodina in the order Amoebida. However, Page separated
Acanthamoeba and
Hartmannella at the ordinal level by creating a new order, Acanthopodida, that includes the family Acanthamoebidae and placed
Hartmannella in the family Hartmannellidae, order Euamoebida.
On the basis of differences in the size and in the morphologic features of cysts, Pussard and Pons in 1977 recognized three groups within the genus. Although cyst characteristics make genus identification easy, differentiation at the species level is difficult. This is especially true for members of groups II and III that cannot always be differentiated by species on a morphologic basis alone. Moreover, species differentiation based on morphology alone may not always be correct, since the morphologies of cysts within a given species may vary according to culture conditions, as was shown for
A. castellanii by Stratford and Griffiths (
1978).
Dissimilarities between the protein banding patterns of an unknown strain and those of a described species might also be important. However, protein electrophoretic analysis is a very powerful tool for taxonomic investigations of protozoa, as large differences occur only between species and not within species (
Philippe et al., 1982;
Pernin et al., 1983). Tyndall et al. (
1979) detected isoenzyme differences of alkaline phosphatase and esterase in different
Acanthamoeba spp., and Dagett et al. (
1981) found that species identification based on cyst morphology does not correlate with identification based on zymograms obtained by starch gel electrophoresis. It became clear that isoenzyme analysis could be used as a strong aid for assigning
Acanthamoeba strains to species; however, different zymodemes may exist within a species, as was the case for the genus
Naegleria. Therefore, a different isoenzyme pattern must not be used as the sole criterion to establish a new species nor should morphological analysis be used in isolation (
De Jonckheere, 1983).
Efforts have been made to include other features in addition to morphology in the classification of
Acanthamoeba, such as isoenzyme profiles and restriction fragment length polymorphisms of mitochondrial DNA (
Bogler et al., 1983). Ribosomal DNA plasmid restriction maps of 10 strains and rDNA hybridization patterns of 61 additional strains have been used to assess inter- and intra-specific diversity and phylogenetic relationships in the
Naegleria (
Clark et al., 1989). Phylogenetic analysis of the rDNA data has also been used to elucidate the affinities of various
Acanthamoeba species (
Dagget et al., 1985). Later, De Jonckheere (
1987) and Page (
1988) accepted this rDNA classification with a few changes. Kong and Chung (
2002) described a riboprinting scheme for the identification of unknown
Acanthamoeba Korean isolates at the species level by using PCR-RFLP of small subunit ribosomal RNA gene using 4 kinds of restriction enzymes. In addition, interstrain polymorphisms of isoenzyme profiles and of Mt DNA RFLP patterns were observed among seven strains of
A. polyphaga and four strains of
A. castellanii (
Kong et al., 1995;
Chung et al., 1996;
Kong and Chung, 1996). Yu et al. (
1999) investigated the value of mitochondrial small subunit rRNA gene (mtSSU rDNA) PCR-RFLP as a taxonomic tool for
Acanthamoeba isolates with close relationships. Morever, mitochondrial riboprinting may have an advantage over nuclear 18S rDNA riboprinting because the mtSSU rDNAs do not seem to possess the introns found in the 18S genus of
Acanthamoeba that distort phylogenetic analysis. This approach may provide an alternative to the rDNA sequencing for the rapid identification of a new clinical isolate or for the identification of a large number of environmental isolates of
Acanthamoeba.
As a result, the most recent identification attempts have been based on morphologic, biochemical and molecular criteria, such as protein profiles, isoenzymes, antigens, and DNA restriction fragment-length polymorphism analysis.
In the present study, a new species of Acanthamoeba was isolated from a freshwater fish in Korea and tentatively named Korean isolate YM-4 (strain CDC-Fish-SK, Center for Disease Control, USA). The morphologic characteristics of its cysts were similar to those of A. culbertsoni and A. royreba, which were previously designated as Acanthamoeba group III. In the terms of the mortality of experimentally infected mice, Acanthamoeba YM-4 was found to be highly virulent. Moreover, the isoenzyme profile of Acanthamoeba YM-4 was similar to that of A. royreba, and an anti-Acanthamoeba YM-4 monoclonal antibody was found to react only with Acanthamoeba YM-4, and not with A. culbertsoni. Random amplified polymorphic DNA marker analysis and RFLP analysis of mitochondrial DNA and of 18S small subunit ribosomal RNA, placed Acanthamoeba YM-4 in a separate cluster based on phylogenic distances. Thus Acanthamoeba YM-4 was identified as a new species, and assigned Acanthamoeba sohi, in honor of Emeritus Professor Chin-Thack Soh of Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
MORPHOLOGY AND LIFE CYCLE
The generic characteristics of Acanthamoeba are reasonably distinct and they are readily recognized. However, identification at the species level is difficult because it is based on morphologic features that are not as clear, e.g., size and subtle morphologic differences in the cyst stage. Generic characters include the striking morphologic characters of the trophozoites and cysts. The amoebae are flat and irregular and project pointed, slender, and flexible micropseudopodia called acanthopodia. The cysts are polyhedral or convex with double walls, and consist of an outer ectocyst, and an inner endocyst. The two walls meet at several places, and pores or ostioles are evident at the wall junctions. Each pore is closed with plugs.
The two genera also differ in terms of the anatomy of the mitotic spindle.
Acanthamoeba exhibits standard mitosis with loss of the nuclear membrane and disappearance of the nucleolus. Amoebae generally lack centrioles, but some species of
Acanthamoeba contain centriolar equivalents (
Sawyer and Griffin, 1971). In
Naegleria, both the nucleolus and the nuclear membrane remain during mitosis.
The life cycle of
Acanthamoeba is comprised of two distinct stages, as motile vegetative trophozoites and as nonmotile resistant cysts. The sizes of trophozoites and cysts vary among species, and both trophozoite and cyst are characterized by a single nucleus that has a large, dense, centrally located nucleolus.
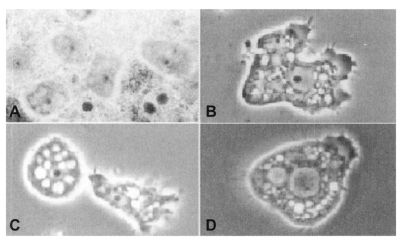
Acanthamoeba trophozoites, being approximately 10-45 µm, have an irregular appearance with spine-like pseudopodia. The cysts are polyhedral, about 20 µm or more in diameter, with a wall consisting of a stellate endocyst and a rippled ectocyst (
Fig. 1).
The trophozoites of
Naegleria commonly assume a monopodial form, and in size from 7 to 20 µm.
Naegleria cysts are generally uninucleate, round with a smooth wall, and 7 to 10 µm in diameter. A transient flagellate phase in
Naegleria may be induced on contact with water, or by other causes (
Fulton, 1970). The central nucleolus represents the diagnostic feature of amoebae of these genera in histopathologic sections. Its shape during locomotion permits a distinction to be made between
Acanthamoeba and
Naegleria trophozoites.
Acanthamoeba in locomotion is characterized by spiny acanthopodia and a slower locomotion without smooth anterior eruptions.
Naegleria has smooth contours and can move one to two lengths in a minute, with hemispherical eruptions alternating from side to side its advancing front.
Numerous vacuoles of three different structures, varying in size and shape, were observed to contain remnant degenerated food particles in
A. culbertsoni. A rough endoplasmic reticulum, some of which was associated with small vacuoles, was observed in the trophozoite of
N. fowleri. Mitochondria comprising typical cristae were abundantly distributed all over the cytoplasm in
A. culbertsoni and also in
N. fowleri (
Im et al., 1976). An ultrastructural study was undertaken to elucidate morphological differences between
N. fowleri trophozoites in the brain tissues of mice and in axenic culture medium. In amoebae from axenic culture, mitochondria were oval, round, and cylindrical in shape and stained darkly, whereas those of amoebae from mouse brain tissue were dumbbell shaped. However, the stain was not unique, but light and/or dark. The rough endoplasmic reticulum of amoebas in brain tissue was tubular, but in culture it was vesicular or tubular in shape. Empty vacuoles were demonstrated in amoebae from culture, while food vacuoles with myelinated structures were abundant in those obtained from brain tissue, suggesting a strong phagocytic process (
Ryu et al., 1984).
B. mandrillaris has a vegetative trophic stage and a dormant cyst stage. Its trophozoites measure 15-60 µm in diameter and are characterized by a round nucleus with a large, spherical, densely staining nucleolus. The nucleus may have more than one nucleolus in some cases and this feature distinguishes this amoeba from
Acanthamoeba, especially in tissue section (
Visvesvara and Stehr-Green, 1990;
Visvesvara et al., 1993). During the early stages of mitosis the nucleolus and the nuclear membrane both remain intact, but disappear as mitosis progresses. The nucleus is surrounded by abundant cytoplasm containing empty vacuoles, numerous mitochondria, ribosomes, and endoplasmic reticulum. The trophozoites form broad pseudopodia and move slowly. Occasionally, the amoebae produce finger-like pseudopodia and exhibit a spider-like walking movement across the floor of tissue culture cells on which they are feeding. The cyst is usually spherical and measures 6-30 µm in diameter, with a mean of 15 µm, and is usually uninucleate and possesses a layer of refractile granules beneath the inner cysts wall. Under the optical microscope they resemble
Acanthamoeba cyst with an outer wrinkled wall (the ectocyst) and an inner thin wall (the endocyst), but ultrastructurally they are tripartite with an additional thick, amorphous, fibrillar middle layer, the mesocyst (
Visvesvara et al., 1993).
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The real incidence of amoebic encephalitis is not precisely known. Up to August 2000, more than 120 cases of granulomatous encephalitis due to
Acanthamoeba spp. and more than 3000 cases of acanthamoebic keratitis had been reported. Many of those reports describe the clinical manifestations of eye infections caused by
Acanthamoeba, and suggest that such infections may be more prevalent than was previously recognized. More than 190 cases of meningoencephalitis due to
N. fowleri have been reported worldwide, and more than 85 additional reports of encephalitis due to
B. mandrillaris have been issued. The actual number is probably substantially higher, as diagnosis is usually made at autopsy, which is seldom done in many countries (
Ma et al., 1990).
Small free-living amoebae are distributed ubiquitously in nature, and thus accurate information on ecology and distribution in nature is particularly important since some species of free-living amoebae may cause disease in man and animals. Free-living amoebae have been isolated from a variety of habitats including fresh water ponds and lakes, domestic water supplies, hot springs and spas, swimming pools, aquaria, power plant thermal discharges, soil, sewage, sea water, ocean sediments, dust in air, and the cooling towers of electric and nuclear power plants. In humans they have been found in the noses and throats of patients with respiratory illness and in healthy individuals, and in bronchial secretions, ear discharges, and in stool samples from patients with diarrhea. Frequently, the source of infection was not identified but was presumed to be moist soil, dust or water. Pathogenic amoebae have been isolated from brackish and marine sediments, from a humidifier and from a dialysis apparatus. Cysts of
Acanthamoeba species can withstand drying, and thus transport by water and air is possible. A number of
Acanthamoeba sp. and
Naegleria sp. were isolated from the sewage, water puddles, a storage reservoir and the gills of a fresh-water fish in Korea (
Im and Shin, 2003).
Amoebae were taken by inoculating environmental samples onto agar plates. Samples were obtained from sewage, water puddles, a storage reservoir, the gills of a fresh water fish, and by corneal washing (
Table 1). The pathogenicity of these isolates was confirmed by experimental intranasal infection in mice (
Ahn and Im, 1984).
CHARACTERISTICS IN CULTURE AND PRESERVATION
Acanthamoeba spp. and
N. fowleri are usually isolated from non-nutrient agar plates coated with killed-
Escherichia coli by environmental sample inoculation. Unlike
Acanthamoeba spp. and
N. fowleri,
B. mandrillaris does not grow on agar plates covered with gram-negative bacteria (
Visvesvara et al., 1993), which are usually used for isolating free-living amoebae from nature. These amoebae grow well at 35-37℃ on monkey kidney cells or on human lung fibroblasts in fetal bovine serum. Bovee (
1963) found that the shapes and sizes of the trophozoites and cysts of
Acanthamoeba may be influenced by starvation, and thus, the nutritional status should be considered during culture.
According to the results of Costas and Griffiths (
1984), 36 distinct patterns of growth response are generated using numerical profiles, but it is possible to distinguish 37 strains of
Acanthamoeba within this total diversity of 20 sub-generic groups, which although not completely congruent morphologically distinguished species, are consistent with other nonmorphological characteristics. Seo et al. (
1992) successfully cryopreserved free-living amoebae in order to maintain them easily in the laboratory. The viability of trophozoites was higher when frozen by slow cooling (overall 0.7℃/min.) than by fast cooling (overall 1.3℃/min.). Glycerol and dimethylsulfoxide at a final concentration of 7.5% of each was used to cryopreserve free-living amoebae trophozoites. Survival rates were 2-39% after storage in liquid nitrogen for 60 days.
BIOCHEMISTRY
The specific and non-specific cytolytic activities of free-living amoebae have been emphasized by many researchers, even though their pathogeneses are not been well known. Several investigations have shown that pathogenic free-living amoeba will lyse various mammalian target cells. In addition, contact between amoeba and target cells would appear to be a pre-requisite for subsequent target cell damage, indicating that amoebic cell surface molecules have a role in the lytic event. To define the molecular nature of the amoebic lytic mechanism, Kim et al. (
1989) employed cytolytic assays to isolate and characterize lytic components that may participate in cytopathogenicity. A cytolytic substance was purified from
A. culbertsoni and turned out to be a 33,000 dalton protein by gel filtration and SDS PAGE. In addition, a secretory proteinase from
A. castellanii was observed to degrade IgA, IgG and IgM antibodies, interleukin-1α and IL-1β, also rapidly degraded endogenous protease inhibitors (
Na et al., 2002). A difference was noted between the cysteine proteinase activities of
A. culbertsoni and
A. royreba (
Kim et al., 1989). The amino acids essential for the intracellular proteinase reactivity of
A. culbertsoni trophozoites are serine and arginine, and serine and cysteine required for extracellular proteinase reactivity, as observed by gelatin-containing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (
Seo et al., 1991;
Rhim, 1997). Kong et al. (
2000) purified and characterized a serine proteinase secreted by
Acanthamoeba healyi, and suggested that it may play an important role in pathogenesis of granulomatous amoebic encephalitis by
A. healyi. Park et al. (
1993) purified a slightly cytotoxic substance of 17,500 daltons from
N. fowleri, and confirmed that cysteine and aspartic acid residues were responsible for its cytotoxic activity. Hadas and Mazur (
1993) found that cysteine proteinase is more active in pathogenic strains of amoeba, whereas serine proteinases are found in both pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains. Cysteine proteinases have also been shown to play important roles in the pathogenesis of parasitic protozoan infections (
North et al., 1990;
Mckerrow et al., 1992). It has been suggested that the cysteine proteinase found in the adult worms of
Schistosoma mansoni (
Chappel and Dresden, 1987),
Fasciola hepatica (
Rege et al., 1989), and
Clonorchis sinensis (
Park et al., 1995) hydrolyze hemoglobin and collagen, and play an important role in parasitic invasion and the acquisition of nutrients. These enzymes may play important roles in the metabolism, development, and survival of parasitic protozoans and thus they have been proposed as targets for the development of anti-protozoan agents.
The specific and non-specific cytolytic processes of free-living amoebae have been emphasized, and cytolytic ability related to hydrolysis by amoebic enzymes has also been reported in
Naegleria sp. Kim et al. (
1988) observed differences in hydrolases activity between
A. culbertsoni and
A. royreba. The hydrolases detected in trophozoite extracts and in culture media were; acid phosphatase, β-N-acetylgalactosaminidase, β-N-acetyglucosaminidase, α-mannosidase, neutral proteinase and acid proteinase, all of which were detected at a remarkably higher rate in
A. culbertsoni than in
A. royreba. Hydrolysis activities in
A. culbertsoni cultured with Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells were assayed according to culture time. The activities of acid phosphatase, β-N-acetylgalactosaminidase, β-N-acetyl glucosaminidase, α-mannosidase and acid proteinase in this pathogenic amoeba were higher in amoeba lysates than in culture media, but after 120 hours of cultivation these activities were higher in culture media than in amoeba lysates (
Fig. 2).
According to ultrastructural observations by Im et al. (
1976), the reaction product of acid phosphatase is present in aggregates in the membrane and within vacuoles, especially in large vacuoles. But the peroxidase reaction product was not observed in trophozoites of
A. culbertsoni and
N. fowleri.
Trophozoites undergo cellular differentiation into cysts during unfavorable condition. In order to understand the cellular differentiation involved, Park et al. (
2002) followed changes in the profiles of major proteins by 2D-PAGE, and of ubiquitinated proteins by immunoblotting. Fifty-one proteins present in the trophozoites of
A. castellanii were lost upon encystment, and a cyst-specific 33 kDa protein was identified as a subtilisin-like serine proteinase by N-terminal sequencing. On the other hand,
N. fowleri trophozoites may transform into flagellates in water at 45℃ (
Griffin, 1973).
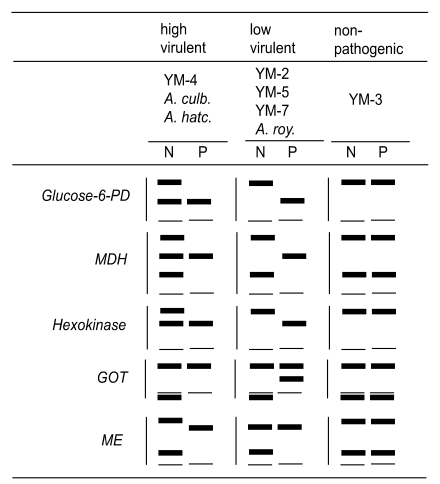
The zymodeme patterns of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), malate dehydrogenase (MDH), hexokinase (HK), glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT) and malic enzyme (ME), that were observed by starch gel electrophoresis, differred in the strains of free-living amoebae of
Acanthamoeba and
Naegleria. In spite of the polymorphic zymodemes, a slow band of G6PD and HK and an intermediate band of MDH were observed only in pathogenic
Acanthamoeba spp., which could be used as isoenzymatic makers to determine free-living amoebae virulence (
Han et al., 1982;
Kim et al., 1984;
Im et al., 1999). A considerable number of interstrain polymorphisms were observed in nine isoenzyme band patterns of the six isolates obtained from contact lens containers in Korea (
Shin et al., 1999).
IMMUNOLOGY
By SDS-PAGE, at least nine major protein bands (97, 81, 66, 53, 40, 39, 28, 25, and 23 kDa) were noticed in the lysate of
N. fowleri. As a result of EITB, immunized serum was reacted with major four bands (53, 40, 39 and 23 kDa) of
N. fowleri antigens. By EITB using infected sera, the 53 and 25 kDa bands were identified as major protein bands. In conclusion, the 23 and 25 kDa antigens were found to be specific for immunization and infection, respectively (
Shin et al., 1992).
Shin et al. (
2001b) cloned an antigen-related gene from a cDNA expression library of
N. fowleri by immunoscreening with sera obtained from mice that were either immunized or infected. The coding nucleotide sequence of the cloned gene, designated
nfa1, consisted of 357 bases. The deduced amino acid sequence of Nfa1 protein shares 43% identity with recombinant myohemerythrin protein, which exhibited strong immunoreactivity to infected, immune, and anti-Nfa1 sera. Nfa1 protein showed pseudopodiumspecific immunolocalization on a trophozoite of
N. fowleri (
Cho et al., 2003).
Protective immunity was developed effectively in mice immunized with i.p. injections of
N. fowleri trophozoites, and active or passive protective immunity against
N. fowleri infection was demonstrated in immunized mice and in mice born to immune mothers. However, the effectiveness of immunization was greatly impaired in terms of mortality in immune mice born to immune mothers when
N. fowleri or
A. culbertsoni was infected intranasally (
Im and Lee, 1985;
Lee et al., 1985). Ahn et al. (
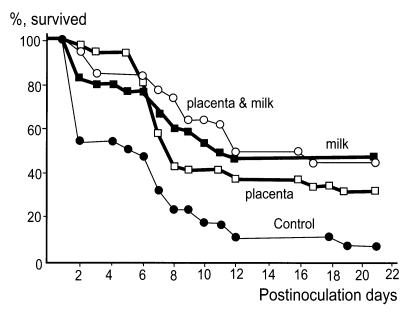
1986) studied the vertical transmission of immunity against
N. fowleri infection from dams to offspring in a murine model. Based on the results obtained, it was considered that maternal immunity is transferred to offspring through the placenta and/or milk. Moreover, vertical immunity transmission through milk is generally more powerful than that via the placenta (
Fig. 3).
According to the investigation of Kim et al. (
1986) on role of the thymus on protective immunity in mice, thymectomy and treatment with anti-thymocyte serum increased the mortality rate or shortened the survival of mice infected with
N. fowleri. They might have been due to the depression of T cell mediated immunity in the host. It was also observed that splenectomy has no influence on the development of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis in mice infected with
N. fowleri (
Shin et al., 1985). Overall, the results by Soh et al. (
1992) suggested that anti-
N. fowleri monoclonal antibodies administered before infection, reduce mortality and prolong survival in infected mice. The role of the passive cell-mediated transfer of immunity against experimental amoebic meningoencephalitis was studied in mice (
Im et al., 1988). Transplants of normal or immune splenocytes seem to alter the pattern of the amoebic meningoencephalitis development. Moreover, splenocytes transferred from immune mice reduced the mortality rate in the
N. fowleri infected mice versus mice receiving normal splenocytes or no splenocytes. The blastogenic response of splenocytes to both lipopolysaccharide and concanavalin A was elevated 7 days after infecting mice transinoculated with immune splenocytes. The serum antibody titers in the mice treated with immune splenocytes increased gradually from day 7 to day 20 after infection, suggesting that splenocytes transferred from immunized mice confer immunity against
N. fowleri infection.
Park et al. (
1987) observed changes in the blastogenic responses of splenic lymphocytes to
N. fowleri lysate and concanavalin A, the latter of which acts as a T-cell mitogen. The mean blastogenic response of splenocytes to
N. fowleri lysate was reduced, whereas that to concanavalin A was also reduced up to day 11 after infection. These results indicate that cell-mediated immunity to
N. fowleri lysate is impaired during the acute course of experimental amoebic meningoencephalitis in mice. In order to test lymphocyte function in
N. fowleri infected mice, the in vitro blastogenic response of splenocyte cultures to non-specific mitogens, concanavalin A or lipopolysaccharide was examined (
Im et al., 1987). For the first 14 days following
N. fowleri infection, the lymphoblastic transformation induced by concanavalin A was markedly reduced versus uninfected control mice, and blastogenic response to lipopolysaccharide remained depressed in infected mice up to 14 days after infection. These results suggest that cell-mediated immunity is suppressed during the acute course of experimental
Naegleria meningoencephalitis in mice. Lee et al. (
1989) observed differences in the cell-mediated immune responses in mice infected with
Naegleria spp. of different virulence; i.e., strongly virulent
N. fowleri, weakly virulent
N. jadini and non-virulent
N. gruberi. Variations in immune responses and changes of antibody titers were noted according to infection duration. In regard to delayed type hypersensitivity responses in
N. fowleri or
A. culbertsoni infected mice, an increase was noted, but these declined after 7 days (
Kim et al., 1990). The blastogenic response of splenocytes also increased after 10 days in the
N. fowleri infected group. These results indicate differences in cell mediated immunity and serum antibody titers in mice infected with three
Naegleria sp. strains of different virulence. The levels of splenocyte blastogenesis induced by concanavalin A and lipopolysaccharide showed increasing tendencies a week after
A. culbertsoni infection by intranasal inoculation in mice (
Im et al., 1989). The number of Ly2
+ and L3/L4
+ T lymphocytes in the
N. fowleri-infected mice were significantly increased 7 days after infection, and LR1
+ lymphocytes in infected mice tended to increase. Interleukin-2 was much suppressed on day 14, which may have resulted from an exhausted host immune response (
Kim, 1993;
Lyu et al., 1993). This indicates that cell mediated immunity after
N. fowleri infection acts on the host's protective immunity at around the 7th day postinfection.
In a test of the in vitro amoebicidal activity of C3H/HeJ mouse peritoneal macrophages, the intraperitoneal administration of silica (0.5 mg/0.5 ml) reduced the amoebicidal activity of macrophages. The level of interleukin-1β measured by ELISA, was highest in infected mice not treated with silica and lowest in treated infected mice. This showed that macrophages played a significant role in the defense mechanism against the development of experimentally induced
Acanthamoeba meningoencephalitis (
Lee et al., 1994). Myung et al. (
1988) observed the effect of zinc deficiency on immune response in mice immunized with
N. fowleri. In mice with zinc deficiency, the proliferative responses of splenocytes to concanavalin A and
N. fowleri lysate and the stimulation index to phytohemagglutinin were diminished after immunization, and the IgG level was reduced 5 weeks after immunization.
Shin et al. (
2001a) in a transmission electron microscopy (TEM) study, found that microglial cells cocultured with
A. culbertsoni trophozoites underwent a necrotic process, and that this was accompanied by lysis of the cell membrane. TEM of microglial cells cocultured with amoebic lysate showed that the membranes of the small cytoplasmic vacuoles and cell membranes were lysed. The amounts of TNF-α secreted from microglial cells cocultured with
A. culbertsoni trophozoites or lysate increased after 6 hours of incubation, and the amounts of IL-1β secreted from microglial cells cocultured with
A. culbertsoni trophozoites after 6 hours of incubation were similar to those secreted by the control group, but these amounts decreased during cultivation with
A. culbertsoni lysate. These results suggest that pathogenic
A. culbertsoni induces cytopathic effects in primary-cultured rat microglial cells, and that these effects are characterized by the necrosis of microglial cells and changes in the levels of secretion of TNF-α and IL-1β from microglial cells.
The natural killer cell activity of splenocytes and the recycling capacity of natural killer cells were observed by combining the
51Cr-release cytotoxicity assay and a single cell cytotoxicity assay against YAC-1 in
N. fowleri infected mice (
Lee et al., 1991). The cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells in infected ICR mice was significantly higher than that in non-infected mice during the period between 12 hours and 3 days after infection, and was highest on day 1. The target-binding capacity of natural killer cells in infected mice was no different from that in non-infected mice. Moreover, maximal killing potential and maximal recycling capacity were remarkably increased in infected mice. This observation indicated that elevated natural killer cell activity in mice infected with
N. fowleri was not due to the target-binding capacity of natural killer cells but due to the increased activity of natural killer cells and the increased recycling capacity of individual natural killer cells. Also the cytotoxicity of
N. fowleri against Chinese hamster ovarian cell was reduced in the presence of monoclonal antibody (
Ryu and Im, 1992). And, the cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells in
A. culbertsoni infected mice was significantly elevated from the 12th hour to the second day after infection, but on the 10th day, it was significantly suppressed. The target binding capacity and natural killer cell activity in infected mice was significantly increased 12 and 24 hours after infection, and maximal recycling capacity was not changed up to day 20 (
Hyun et al., 1992). Kim et al. (
1993) investigated natural killer cell activities in mice infected with pathogenic
A. culbertsoni and
N. fowleri, and non-pathogenic
N. gruberi. In all experimental mice, natural killer cell activities increased significantly on day 1 after infection and then remarkably declined. No difference was observed in the cytotoxic activity of natural killer cells in mice with respect to the inoculation doses of pathogenic strains. The target binding capacities of natural killer cells and the percentages of activated natural killer cells in mice infected with pathogenic strains were significantly increased on postinfection day 1, but no differences in the maximal recycling capacities of natural killer cells were observed in experimental mice.
MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
The primary sequences of nuclear DNA, RNA, and proteins that are available for
Acanthamoeba all indicate that the genus
Acanthamoeba is similar to those found in other organisms. Actin has the most highly conserved amino acid sequence found to date among
Acanthamoeba proteins. Calmodulin also is highly conserved, but its amino acid sequence is not complete. Profilin and myosin amino acid sequences have diverged significantly more than comparable sequences in other organisms, but in both cases sequences are more conserved in the N-terminal halves of the molecules. Data available to date support previous evidence (based on rRNA sequences) that
Acanthamoeba genes are at least as closely related to those of higher organisms (
Sogin, 1989). However, the mitochondrial genome of
Acanthamoeba deserves further study, whereas the RFLP data available for
Acanthamoeba may be useful both for the clinical identification of amoebae and for phylogenetic comparisons. Moreover, variations in nuclear gene DNA sequences among different strains of
Acanthamoeba may be useful for the development of oligonucleotide probes that can be used in clinical situations to identify isolates.
The Acanthamoeba genes considered are those of 5S, 5.8S and 18S rRNA, actin I, profilins Ia/b and II, myosin IB, IC and II, and calmodulin. Introns have been found in the actin and myosin genes. The location of the actin intron is unique, but many of the myosin introns occur at the same sites as introns in the myosin of other organisms. Sequence comparisons, especially of 5S and 5.8S rRNA and actin, support previous evidence, based primarily on 18S rRNA, that Acanthamoeba genes are at least as closely related to those of higher plants and animals as they are to various other protozoan genera. The functional organization of the nuclear rDNA transcription unit promoter region has been studied extensively. Restriction fragment length profile studies of mitochondrial DNA have revealed relatively high levels of overall sequence diversity, but information on the structure and function of individual genes is needed. Restriction site maps reflecting variations in RFLP patterns appear to have potential as tools for taxanomic studies of the Acanthamoeba.
Acanthamoeba has at least three actin genes (
Jantzen, 1981;
Nellen and Gallwitz, 1982), and the actins from many sources are highly conserved molecules of 374-375 amino acids. The actin I amino acid sequence of
Acanthamoeba is slightly more closely related to the cytoplasmic and muscle actins of mammals than it is to most other protists. Several isoforms of the small actin-binding protein profilin have been sequenced (
Ampe et al., 1985,
1988). The profilins of
Acanthamoeba have an actin capping activity that is not typically seen in other profilins (
Pollard and Cooper, 1986). Sequences similarities among the various profilins are highest in the N-terminal region corresponding to the 1st 34 amino acids of the
Acanthamoeba protein (
Byers et al., 1990).
One
Acanthamoeba myosin II heavy chain gene (M II) has been sequenced (
Hammer et al., 1987). Myosin II is the amoeba myosin most resembles muscle myosins. Two
Acanthamoeba myosin I heavy chain genes (MIB, MIC) have been sequenced, but more are likely to be found because three isoforms of myosin I protein have been purified (
Lynch et al., 1989). A recently sequenced gene of myosin I heavy chain from
Dictyostelium (
Jung et al., 1989) codes for a protein remarkably similar to
Acanthamoeba MIB and MIC. The evolutionary affinities of
Acanthamoeba myosins like those of higher life forms are evident from the locations of introns. Moreover, the calcium-binding regulatory protein calmodulin of
Acanthamoeba has been partially sequenced (Wylie and Vanaman, 1987).
Considering that the
Acanthamoeba have both highly phagocytic activity and tissue invasive behavior, it may be speculated that proteinases should be involved in their metabolic processes. Yun et al. (
1999) isolated a cysteine proteinase from
A. culbertsoni that has cathepsin L-like characteristics. Phylogenetic analysis based on the amino acid sequence of cysteine proteinase indicated that AcCP2 is closely related with papaya. Hong et al. (
2002) isolated a cDNA encoding a mammalian cathepsin L-like cysteine proteinase from
A. healyi, and identified a cDNA encoding a subtilisin-like serine proteinase of
A. healyi (
Hong et al., 2000).
The identification of the DNA amplicons representing differentially expressed mRNAs in the blood cells of mice infected with
A. culbertsoni was attempted using the differential display reverse transcriptionpolymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), which could be a prospective candidate for the development of a DNA probe for early diagnosis (
Park, 1996).
Phylogenetic analyses that included the sequence of a single nuclear small subunit ribosomal RNA gene (18S or ssu rDNA) from
B. mandrillaris suggested that this amoeba is closely related to
Acanthamoeba. Booton et al. (
2003) tested whether this is true for
Balamuthia. No variation in the nuclear rDNA sequences and low levels of variation in mitochondrial rDNA were found, and both gene sequences were consistent with a single genotype for
B. mandrillaris. The mitochondrial sequences of
B. mandrillaris are unique and should be useful for the development of genus-specific diagnostic probes.
MODE OF INFECTION
Pathogenic Naegleria have also been isolated from the nasal cavities of individuals with no history of water exposure, thus suggesting the possibility of airborne infection, and amoebae have been isolated from large numbers of throat swab culture, which is supported by findings of amoebic invasion of the nasal mucosa and olfactory nerves and olfactory bulb involvement. Acanthamoeba was detected and identified in the bronchial washings of a Korean patient with pneumonia, and Acanthamoeba infections have been demonstrated in both hard and soft lens wearers. Usually, almost all PAME patients have a history of swimming in a freshwater lake, pond, stream, hot spring, or swimming pool a few days before symptoms onset. The detection of N. fowleri in heated discharge water has been reported. Virulent strains are also found in lakes, and in any source of thermal discharge. Moreover, N. fowleri cysts produced in summer months may survive the winter and be capable of growth the following summer.
From epidemiological and experimental observations, it is apparent that infection results from organisms being taken into the nose in water. N. fowleri enters the nose and penetrates the olfactory mucosa and the cribriform plate and then travels via the olfactory nerves to the brain. Although the only known portal of entry for Naegleria is the olfactory neuroepithelium, Acanthamoeba species may enter through ulcerated or broken skin or the eye, and possibly through the lungs. Four Acanthamoeba species — A. culbertsoni, A. polyphaga, A. castellanii, A. astronyxis — and possibly others are known to cause disease in man.
Ahn et al. (
1979) observed the fate of free-living amoebae when inoculated into the oral cavity of mice, and when exposed in digestive juice ingredients. The amoebae survived ordinarily used food preservative concentrations. Pepsin with hydrochloric acid showed the strong amoebicidal action, suggesting that the inoculated amoebae might be destroyed in the stomach, and thus fail to propagate in the gastrointestinal tract or penetrate extra-intestinal organs. Acids, such as hydrochloric acid and vinegar showed a stronger amoebicidal action, which may explain why amoeba find the oral route more difficult than the nasal route penetrating the nervous system.
Invasion and penetration of
B. mandrillaris into the CNS probably arises by haematogenous spread from a primary focus of infection in the lower respiratory tract or skin (
Martinez and Visvesvara, 1997). The ulcerative skin lesions may serve as a portal of entry or may represent 'terminal' haematogenous infection dissemination.
PATHOLOGY
Tissue pathology
Tissue invasion by
Acanthamoeba species is relatively slow and tends to stimulate granuloma formation. In cases of
Acanthamoeba infection, gross findings were of purulent leptomeningitis brain edema and foci of necrosis in various locations both at the surface and in the deeper portions. Histopathologic findings were necrotizing chronic, granulomatous encephalitis with focal hemorrhages, multinucleated giant cells, large amoebic trophozoites, and smaller cysts (
Martinez et al., 1980). Both trophozoites and cysts were scattered throughout the lesions but the trophozoites were observed abundantly near the blood vessels at the margins of areas of acute inflammation and necrosis. Amoebae are readily distinguished by their large dense endosome, which is surrounded by a clear nucler halo, and abundant spongy cytoplasm that is often set off from the surrounding tissue by a clear space. The cysts are generally most numerous in granulomatous areas.
Chronic granulomatous lesions caused by Acanthamoeba elsewhere than in the brain have been reported in the skin, kidneys, liver, spleen, uterus, and prostate. The primary skin lesions caused by Acanthamoeba apparently remain focally, and show secondary invasion of the central nervous system. In a patient who died from amebic meningoencephalitis, a large superficial ulcer had developed early around the umbilicus. When the primary site of invasion is the skin, the period between exposure and the onset of central nervous system symptoms was several months to 1 year or longer, as was found in the Korean cases.
The lesions due to
Acanthamoeba invasion of the eye were primarily corneal ulcers, and keratoconjunctivitis and uveitis. The pathogenesis of acanthamoebic keratitis involves parasite-mediated cytolysis and phagocytosis of corneal epithelial cells and the induction of programmed cell death.
Acanthamoeba spp. can elaborate a variety of proteases that may facilitate cytolysis of the corneal epithelium, invasion of the extracellular matrix, and dissociation of the corneal stromal matrix (
Niederkorn et al., 1999). One boy who had waded in muddy water developed a sore throat of 3 weeks duration, followed by conjunctivitis and iritis of the left eye, followed by headache 1 week later and signs of meningoencephalitis. This patient died 3 weeks after presentation and abundant amoebae, tentatively identified as
A. castellanii, were found in brain sections. The left eye also was sectioned and revealed inflammation of the iris ciliary body, and vitreous, with necrosis of the ciliary body and the presence of
Acanthamoeba trophozoites (
Niederkorn et al., 1999).
Amoebic meningoencephalitis caused by N. fowleri is an acute infection of the brain and meninges. In humans, with extremely rare exceptions, the disease is rapidly fatal. Findings in Naegleria infection have been remarkably uniform, and are esswentially limited to the brain. Affected areas of the brain are soft, and the meninges are hyperemic and moderately purulent. The organisms are present in a relatively narrow zone within the gray matter beneath the ependymal and ventral surfaces where they frequently form clear lytic pockets. The olfactory bulbs are congested or hemorrhagic and necrotic. Histologic sections show amoebae throughout the affected gray matter, particularly near the subarachnoid space. Usually amoebae can be found in the exudate; they are most evident in perivascular tissues where inflammatory cells are scarce or absent. The main recognizable feature of the amoebae is its characteristic open nucleus with it's a large, dense, central endosome. Usually, there is a halo around the nucleus and a conspicuous space around the amoeba. Invasion of the skin and ear, and its presence in exudates from the vagina have also been reported.
B. mandrillaris produces multifocal, subacute chronic granulomatous encephalitis with trophozoites and cysts within the central nervous system, as well as cutaneous nodules, ulcerations and pneumonitis. Neuropathologically, the infection is characterized by brain edema and subacute necrotizing hemorrhagic encephalitis. A modest lymphocytic infiltrate is often present, depending on the immunological status of the host. This is usually composed of CD4 and CD8 T cells and B lymphocytes, together with a few plasma cells, macrophages and multinucleate giant cells. Amoebic trophozoites and cysts are usually present within perivascular spaces and within the necrotic CNS parenchyma. Focal chronic leptomeningitis may also be seen in the areas near the parenchymal lesions, and arteritis with trophozoites and cysts may be seen in the same areas. Pneumonitis, and ulcerative dermatitis with the presence of trophozoites and cysts have also been described (
Martinez and Visvesvara, 1997).
Pathology of Korean isolates
The recognition of the pathogenicity of all Korean isolates was determined by experimental infection into mice. Experimental animals such as out-bred mice were infected by the intranasal instillation of culture-grown trophozoites, which resulted in CNS disease and death.
Some of the Korean isolates caused a severe pathology and death in mice, and they clearly demonstrated the potentially pathogenic role of the so-called freeliving amoebae. Experimental meningoencephalitis was demonstrated in a murine model, infected intranasally with
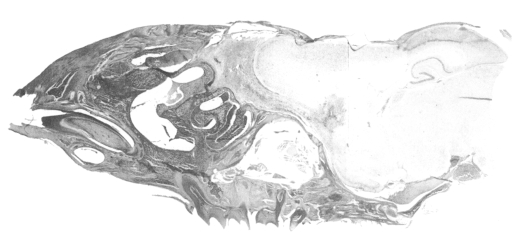
Acanthamoeba Korean isolates, and which resulted in death. The cerebral cortex, especially the olfactory lobes, of dead mice showed extensive inflammatory reaction and wide areas of necrotic tissue (
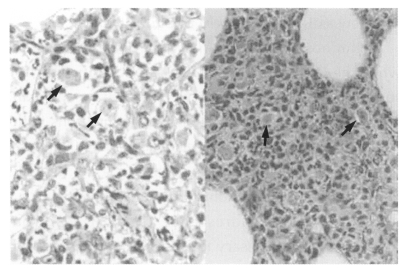
Fig. 4). Trophozoites were seen interspersed within brain tissue infiltrated by inflammatory cells (
Fig. 5). Lung tissue from dead mice showed extensive inflammatory reaction. Amoebae were successfully cultivated from the infected brain tissue after incubation in liquid medium.
For experimental infection, Korean isolate YM-4 was injected into mouse brain tissue through the occipital region (Hwang et al., 1980). The pathogenicity of the five Korean isolates of
Acanthamoeba sp. (YM-2, YM-3, YM-4, YM-5 and YM-7) was demonstrated by experimental infection intranasally in mice (
Im et al., 1999). According to the mortality of infected mice, Korean isolates could be categorized into three groups; highly virulent (YM-4), moderately virulent (YM-2, YM-5 and YM-7) and non-pathogenic (YM-3) (
Hwang et al., 1976) (
Fig. 6).
DETERMINATION OF PATHOGENICITY AND VIRULENCE
To determine the pathogenicity of free-living amoebae, the following trials have been reported. Three Korean isolates of
Acanthamoeba sp. from the environment were studied, and differences in isoenzyme profiles by strain investigated (
Im, 1990;
Im et al., 1999). The basic test used for confirming pathogenicity was via intranasal infection, which led to experimental amoebic meningoencephalitis.
Comparative ultrastructural cytochemistry with reference to the pathogenicity was undertaken in freeliving amoeba treated with concanavalin A and horseradish peroxidase. The electron density on the surface of cell membranes was marked increased in pathogenic strains of free-living amoeba, but not in non-pathogenic strains (
Chung et al., 1980).
The in vitro cytopathic effects of free-living amoebae on monolayer of CHO cells were examined by trypan blue dye-exclusion and
51Cr release measurements, in order to establish standards for the early determination of pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains of free-living amoebae (
Lee et al., 1986). In cytotoxicity tests against target CHO cells by pathogenic free-living amoebae, the dose-response curve and the number of CHO cells agreed with Michaelis-Menten kinetics, i.e., V = V
max × T/ K
max × T; where V is the number of dead target cells and T is the initial number of target cells. V
max (the number of target cells killed when T is infinity) and K
m (the number of target cells that produces one-half of V
max) were determined using the Lineweaver-Burk equation, 1/V = K
m/V
max × 1/T × 1/V
max, where 1/V is linearly related with 1/T. Using
A. culbertsoni as an effector, the hypothesis was proved, the pathogenicity of freeliving amoebae were determined, and the level of V
max or K
m might express the degree of pathogenicity (
Im, 1990).
In vitro cytopathic effects against tissue cell lines (CHO cells, Vero cells and HeLa cells), by trypan blue dye-exclusion testing and
51Cr release measurements, were performed in order to determine the pathogenicity of free-living amoebae (
Lee et al., 1986). In the cytotoxicity assays against CHO cells, Im et al. (
1999) observed that the virulence of brain-passaged
Acanthamoeba spp. was enhanced by brain passage in mice, and that it was relatively higher than in long term cultivated amoebae. Shin et al. (
2000a) observed cytotoxic effects of
Acanthamoeba spp. against CHO cells, (isolated from contact lens containers in Korea), they determined pathogenicity using crystal violet staining method and LDH release assay. Pathogenicity and virulence determinations of
Acanthamoeba spp., as determined by cytotoxicity in vitro against tissue cells did not correlate with the results of experimental meningoencephalitis in mice in some cases (
Table 3).
It was suggested that some rat microglial cells cocultured with pathogenic
A. culbertsoni undergo cytopathic changes which show the characteristics of apoptosis such as nuclear condensation and DNA fragmentation, but with weakly pathogenic
A. royreba, were not found to undergo any cytopathic change by Shin et al. (
2000b).
The pathogenicity of free-living amoebae could be determined by experimental infection into experimental animals. Mouse pathogenicity tests were conducted by inoculating approximately 5 × 104 amoebae intranasally into mice weighing 15 to 20 g under the secobarbital anesthesia. Mice were observed daily to record signs of disease and day of death. Brain and lung tissues were taken from dead or dying mice for histological examination and for further culture studies in axenic media.
Experimentally infected mice showed symptoms of disease, which consistently caused death, but some of animals survived for 25 days or more. In mice, experimental amoebic meningoencephalitis may be influenced by the inoculation dose of
N. fowleri trophozoites, mouse strain, and weight (
Ahn and Im, 1984), and by prednisolone pretreatment before infection (
Kim et al., 1985).
The zymodeme patterns of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), malate dehyrogenase (MDH), hexokinase (HK), glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT) and malic enzyme (ME) of
Acanthamoeba spp. were different for the Korean isolates. In spite of the polymorphic zymodemes, a slow band of G6PD and HK and an intermediate band of MDH were observed only in pathogenic
Acanthamoeba spp., which should be used as isoenzymatic markers for pathogenicity or virulence differentiation (
Im et al., 1999) (
Fig. 7).
Josephson et al. (
1977) found that pathogenic
Naegleria strains were the agglutinated by phytoagglutinin. Kim et al. (
1979) tried to visualize agglutination ability of free-living amoeba for pathogenicity determination. Concanavalin A-induced agglutination is related to the pathogenicity of
Naegleria sp., but not of
Acanthamoeba sp.
Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-4 was found to be agglutinated easily by 25 µg/ml of concanavalin A.
It was demonstrated that
Acanthamoeba and
Naegleria lost their virulence when cultured axenically for an extended time. The expressional changes in virulence related genes occur during the course of virulence restoration. Yun et al. (
2002) used northern blot hybridization to compare the expression patterns of genes isolated before and after virulence restoration after baby mouse brain passage of
N. fowleri. Among 480 randomly selected cDNA clones of
N. fowleri, four showed a constant level of expression during mouse brain passage, these encoded ribosomal protein, fumarase, malate dehydrogenase, and ubiquitin. Two clones were homologous to the genes of the high mobility group protein (HMG) and the 26S proteasome subunit. It was interesting that the expressions of these two genes were increased by successive mouse brain passages of
N. fowleri, which suggests that HMG protein and 26S proteasome of
N. fowleri may be involved in some biological adaptation processes of the amoeba in the host.
In order to identify the regulatory changes in the transcriptions of virulence related genes by brain passage, mRNA DD-PCR was performed. This enabled differentially transcribed mRNAs to be displayed after brain passages. One clone, amplified with an arbitrary primer of UBC #289 and oligo dT11-C primer, revealed highest homology to the amino acid sequences of UPD-galacatose lipid transferase of Erwinia amylovora, which is known to act as an important virulence factor.
Shin et al. (
2001b) and Cho et al. (
2003) cloned the
nfa1 gene from a cDNA library of pathogenic
N. fowleri by immunoscreening using immune and infection sera. This gene was found to have a coding nucleotide sequence consisting of 357 bases. Jung et al. (
2004) transfected the DNA of the
nfa1 gene into non-pathogenic
N. gruberi. The expressed DNA of the
nfa1 gene was observed by PCR from the genomic DNA of
N. gruberi transfected with pEGFP-C2/nfa1UTR. The
nfa1 and GFP gene were also identified by RT-PCR in transgenic
N. gruberi. This transgenic
N. gruberi was observed to be cytotoxic to CHO cells, and this
nfa1 gene of
N. fowleri may be associated with its pathogenicity.
It has been suggested that
Acanthamoeba may have a role in the transport of pathogenic microorganisms;
Legionella pneumophila (
Neumeister et al., 1997;
Berk et al., 1998;
Michel et al., 1998),
Mycobacterium avium (
Steinert et al., 1998) and
Chlamydia pneumoniae (
Essig et al., 1997). The growth of
L. pneumophila in
A. castellanii was found to be at least 100-fold more invasive for epithelial cells and 10-fold more invasive for macrophages than wild-types, and the
L. pneumophila entry gene
rtxA was observed to be involved in virulence (
Cirillo et al., 1994,
2001).
Acanthamoeba infection may complicate adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis (
Gajdatsy et al., 2000). And
Acanthamoeba keratitis may be present as a secondary or opportunistic infection in patients with herpetic keratitis (
Mathers et al., 1997), in patients infected with human immunodeficiency virus, rhinosinusitis (
Rivera and Padhya, 2002), osteomyelitis (
Selby et al., 1998) and sinusitis (
Kim et al., 2000).
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
Clinically, encephalitis caused by pathogenic freeliving amoebae is due to the presence of a single or multiple space-occupying lesions. The central nervous system disease caused by
Acanthamoeba occurs principally in immunosuppressed individuals, chronic alcoholics, or debilitated persons.
Acanthamoeba or any other free-living amoebae that causes subacute and/or chronic granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE), also causes a nonfatal, but nevertheless painful, vision-threatening infections of the human cornea,
Acanthamoeba keratitis. Infections due to
Acanthamoeba have also been reported in a variety of animals (
Ma et al, 1990).
Meningoencephalitis caused by Acanthamoeba may present as an acute suppurative inflammation of the brain and meninges, like that seen with N. fowleri. However, Acanthamoeba is generally reported to cause a more chronic form of meningoencephalitis which has frequently been observed in chronically ill and immunosuppressed patients. Therefore, the disease usually has a gradual onset and takes a prolonged chronic course. Some of the predisposing factors include diabetes, alcoholism, Hodgkin's disease, pregnancy, and steroid therapy. Symptoms at onset are a sore throat and fever followed by headache and other signs of meningeal irritation. Acute symptoms begin with a sore throat, a blocked or discharging nose and are frequently associated with parosmia, headache and fever. The illness progresses rapidly, with increased headache and pyrexia, vomiting, neck stiffness and mental confusion, culminating in coma and death within four to seven days.
The infection produced by N. fowleri occurs principally in immunocompetent children and young adults with a history of contact with fresh water. Infection is fulminating and nearly always fatal. Early symptoms of Naegleria infection include vague upper respiratory distress, headache, lethargy, and occasionally olfactory problems. The acute phase includes a sore throat, a stuffy blocked or discharging nose, and severe headache. Progressive symptoms include pyrexia, vomiting, and neck stiffness. Mental confusion and coma usually occur approximately 3 to 5 days prior to death.
B. mandrillaris produces encephalitis in the very young or in the very old. B. mandrillaris can infect healthy and immunosuppressed hosts of both sexes, and there may be no history of swimming or exposure to contaminated water. Encephalitis due to this amoeba usually runs a protracted insidious clinical course with an unknown incubation period, which is definitely longer than 10 days and may be several months.
CLINICAL CASES
Case reports have been numerous from the United States, Belgium, Czechoslovakia, England, Australia, New Zealand, India, Zambia, Nigeria, Germany, Netherlands and Korea. Up to October 1995, more than 200 cases of PAME due to
N. fowleri, and as many as 100 cases of GAE due to
Acanthamoeba spp. had been reported worldwide. Seven isolates of
B. mandrillaris were identified, including 5 from humans and 2 from animals (mandrill baboon, horse) (
Schuster and Visvesvara, 2001).
Several clinical cases had been reported up to 2002 in Korea, among which two cases infected with Acanthamoeba spp. died due to meningoencephalitis, and one case died of Acanthamoeba pneumonia with an immunodeficient status. Acanthamoeba was also detected in several cases of chronic relapsing corneal ulcer, chronic conjunctivitis, and keratitis.
Case 1: Ringsted et al. (
1976) first reported a
Acanthamoeba meningoencephalitis case in Korea. This case was of a 5-year-old boy who developed multiple subcutaneous, nontuberculous granulomas in many organs, and died of meningoencephalitis.
Case 2: Was of a 7-month-old girl with congenital immunodeficiency, in whom the diagnosis of
Acanthamoeba pneumonia was established by agar plate culture of bronchial washings. She had been ill for a month when she was admitted due to neonatal thrombocytopenia with respiratory difficulty, and was treated with γ-globulin and steroid. A chest X-ray showed diffuse alveolar consolidation on the left lung with interstitial haziness, which characterized acute respiratory disease syndrome. Laboratory tests showed that
Candida and
Mycoplasma antigens were negative, and
Pneumocystis carinii was not detected. All immunoglobulin levels (IgA, IgG and IgM) were below the normal range (
Im and Kim, 1998).
Case 3: Was of an immunosuppressed 7-year-old boy, in whom
Acanthamoeba trophozoites were observed by skin biopsy, followed by meningitis leading to death. About five days after a laceration in the region of the left eyebrow, a painful bean-sized nodule developed at the suture site and was treated with antibiotics and corticosteroid. The skin biopsy showed severe inflammatory cell infiltration. Trophozoites were scattered near blood vessels throughout the inflammatory zone (
Fig. 8). Skin nodules with tenderness then appeared all over his body surface. An examination of cerebrospinal fluid were clear, gram stain was negative, bacterial culture negative, India ink preparation negative, and organism on wet smear negative. A brain CT revealed calcific density in the left parietal lobe area and hypodensity in the left basal ganglia (
Im and Kim, 1998).
Cases 4-10,
Acanthamoeba keratitis cases: Cho et al. (
1992) firstly reported two cases of
Acanthamoeba keratitis and conjunctivitis in Korea. These patients had no history of contact lens wearing or eye injury. Cysts with calcofluor white staining were confirmed by dark-field fluorescent microscopy. Kim et al. (
1995) presented a contact lens wearing patient with a corneal ulcer. Double walled
Acanthamoeba cysts were detected, cultured on 1.5% non-nutrient agar, and identified by the Institute of Tropical Medicine, Yonsei University. This Korean isolate was named YM-7 (
Fig. 9). Chung et al. (
1996) presented two cases. A 16-year-old female wearing contact lenses was suffering from a severe corneal ulcer.
Acanthamoeba cysts were detected from the corneal scraping and confirmed by acridine orange staining. Isolate KA/E3 from this patient was observed to be close to
A. castellanii by riboprints. A 32-year-old male, who was not wearing contact lenses, had been complaining of eye pain and congestion. Isolate KA/E4 from a corneal scraping was confirmed to be
Acanthamoeba cysts by acridine orange staining.
The clinical details of the two keratitis cases were not reported (
Kong and Chung, 1998). These Korean isolates were named KA/E1 and KA/E2.
DIAGNOSIS
Prior to 1989, the identification of the causative agent of granulomatous amoebic encephalitis, in the absence of culture isolation or immunohistological assay, was based on the presence of amoebic cysts in tissue sections; since
N. fowleri does not produce cysts in tissue whereas
Acanthamoeba does. Hence many cases due to
Acanthamoeba were identified on the basis of cysts in tissue sections.
B. mandrillaris infections, diagnosed mainly at postmortem, have been identified in both immunocompromised and immunocompetent individuals. Isolation of
B. mandrillaris trophozoites and the production of specific serum for
B. mandrillaris were instrumental in the differentiation of
Balamuthia and
Acanthamoeba encephalitis (
Huang et al., 1999).
A patient's history of swimming in thermal or stagnant water several days prior to onset of symptoms of severe meningitis or meningoencephalitis should suggest a diagnosis of Naegleria infection. An immediate attempt should be made to detect and to isolate the amoebae from cerebrospinal fluid. Naegleria can be detected and identified in histopathologic sections by immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase methods. A firm diagnosis of Acanthamoeba infection depends on the detection and identification of the amoebae in cerebrospinal fluid in cases with a central nervous system infection, in scrapings from corneal lesions or cutaneous infections, or in cultures of materials from these sources.
The symptoms resemble those of fulminating bacterial meningitis, but an examination of cerebrospinal fluid shows a less purulent reaction, more numerous mononuclear cells, and higher protein and sugar levels. Amoebae are present in cerebrospinal fluid but are difficult to identify, and when motile may be confused with motile macrophages.
Cultivation on a 1.5% non-nutrient agar plate seeded with Escherichia coli is recommended for isolation of either Naegleria or Acanthamoeba from cerebrospinal fluid or from brain or other tissues. Because meningoencephalitis from Naegleria infection develops rapidly, in suspected cases with an elevated cell count, it is worthwhile culturing cerebrospinal fluid even if no amoebae are recognized in direct or wet mount examinations.
Serological tests can be useful for detecting the presence of circulating antibody against
Acanthamoeba or
Naegleria (
Im and Oh, 1978;
Im and Soh, 1978). However, species identification is not easy, because reliable diagnostic agents based on species-specific antibodies are not available. Considering the possibility of specific antibody production, Im et al. (
1983) developed a monoclonal antibody against
A. royreba. Ryu and Im (
1992) attempted to produce several clones secreting anti-
N. fowleri monoclonal antibodies that had demonstrated immunodiagnostic potential. An examination of sections of formalin-fixed tissues from cases of meningoencephalitis showed that indirect immunofluorescent staining or indirect immunoperoxidase staining should be useful in the localization and identification of amoebae. Tissue stains are also effective and cysts can be stained with iron hematoxylin, Giemsa, Gomori's methenamine silver, periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), or calcofluor white. In cases of presumptive pyogenic meningitis, the computerized tomographic appearance of basal arachnoiditis should alert the staff to possibility of acute PAM.
In terms of the detection of
Acanthamoeba, PCR using non-radioactive rDNA probes, which is a specific, rapid, sensitive, and safe-practical method, was developed by Lai et al. (
1994). This PCR procedure provides increased sensitivity and the direct detection of as few as 10
Acanthamoeba trophozoites.
A diagnosis of
Balamuthia encephalitis is made when the trophozoites and cysts are identified in tissues or the agent is isolated in culture. Brain and skin biopsies for culture and histologic examinations with hematoxylin and eosin or special stains like Gomori's methenamine silver and PAS are also useful. However, some immunohistological techniques, e.g., indirect immunofluorescence assay, or electron microscopy are necessary to identify
B. mandrillaris in tissue sections (
Denney, 1997). A serum antibody test that may be helpful in the diagnosis was developed for
B. mandrillaris infection (
Huang et al., 1999). Neuroimaging by CT and MRI of the head may also be helpful for diagnosis.
TREATMENT
The treatment of Acanthamoeba meningoencephalitis has not been largely successful. Granulomatous encephalitis due to Acanthamoeba sp. is unresponsive to chemotherapy. Treatments were credited with prolonging life in a fatal case and possibly saving life in another. The therapy of amoebic keratitis and uveitis likewise remain problematical. Acanthamoeba keratitis usually necessitates corneal grafting although topical anti-microbial therapy may be required for many months before surgery can be undertaken. Cysts of A. polyphaga are extremely resistant and abundant in corneal scrapings and sections from patients under treatment. Clinical observations suggest the beneficial effects of natamycin (primaricin) and rifampin and in a few cases keratoplasty has been successful.
Although sulfadiazine has been shown to protect mice from infection by pathogenic strains of
Acanthamoeba, it has proved useless in human cases. To be effective, treatment should be started early, but until a drug with specific activity against the organism suitable for use by a parenteral route and with the ability to reach therapeutic levels in brain tissue is found, successful treatment is unlikely. One patient in California was successfully treated with amphotericin B, miconazole and rifampin (
Ma et al., 1990). A synergistic effect was found between miconazole and amphotericin B in vitro; however, rifampin was ineffective. Amoebae may be sensitive in vitro to clotrimazole, pentamidine, polymyxin-B, 5-fluorocytosine, paromomycin, miconazole or acriflavine.
No satisfactory treatment for primary amoebic meningoencephalitis is known.
N. fowleri meningoencephalitis is usually fatal. However, a few patients have responded to amphotericin B administered both intravenously and intrathecally. A marked synergism between amphotericin B and tetracycline has been observed when cotreated to
N. fowleri infected mice (
Ma et al., 1990). Despite early and intensive treatment with amphotericin B, PAME is usually fatal. Nevertheless, amphotericin B remains the only known effective agent for the treatment of PAME (
Ma et al., 1990).
There is presently no known effective treatment for encephalitis due to
B. mandrillaris, though experimental studies indicate that the amoeba is sensitive to pentamidine isethionate, azithromycin, and clarithromycin (
Schuster and Visvesvara, 1998).
PROGNOSIS
In view of the demonstrated susceptibilities of Acanthamoeba species to various drugs in vitro and in experimental animals the outlook in cases diagnosed early would seem to be favorable. However, Naegleria menigoencephalitis is usually fatal within a week of onset, and survival depends on an early suspicion of infection. In addition, the prognosis of Balamuthia encephalitis is very poor.
PREVENTION
Recently these amoebae have been isolated from hot tubes, contact lens-care solutions, and intrauterine contraceptive devices. Many reports, together with the fact that
Acanthamoeba spp.,
N. fowleri, and
Hartmannella sp. can harbor pathogenic microorganisms such as
Legionella and/or
Mycobacterum indicate the public health importance of these amoebae. Since fatal
Acanthamoeba meningoencephalitis has occurred in chronically ill or debilitated patients or in those with an impaired immune system, caution in the use of immunosuppressive therapy is indicated. The recovery of
Acanthamoeba in nasal isolates and pharyngeal swabs from humans indicates human introduction of these organisms into swimming pool settings. Moreover, the genus
Acanthamoeba has been detected in a number of contact lens containers (
Lee et al., 1997). With the increasing reports of infection in soft contact lens wearers it is important to carefully consider the effectiveness of various contact lens disinfection systems. Wearers of contact lenses should receive precise instructions on lens care, in particular, about the risk of home-made non-sterile saline rinsing solutions.
Our incomplete recognition of human infections caused by free-living amoebae and the increasing number of reports on the isolation of free-living amoebae from natural sources suggest that caution should be exercised in the dumping of sewage and spoils. It was found that N. fowleri was widely distributed in streams and canals, and that it is associated with warm factory effluent. Heavy chlorination to 10 ppm failed to eradicate N. fowleri from a swimming pool, but salination to 0.7% resulted in negative cultures for a period of 5 months. The pathogenic Naegleria tolerates even higher temperatures up to 45-46℃. The only known preventable risk of infection is contact with stagnant or thermal water. General preventive measures include the public awareness of the potential hazards of contaminated water. It has been recommended that warm discharge water should not be used directly for sports or recreational purposes.
References
- 1. Ahn M, Im KI, Soh CT. Fate of free-living amoebas in the outer environment and in experimental host. Yonsei J Med Sci 1979;12:28-37.
- 2. Ahn MH, Im KI. Experimental meningoencephalitis by Naegleria fowleri in mice. Korean J Parasitol 1984;22:253-258.
- 3. Ahn MH, Min DY, Im KI, Lee KT. Experimental study on vertical transmission of immunity against Naegleria fowleri. Yonsei J Med Sci 1986;19:102-110.
- 4. Ampe C, Sato M, Pollard TD, Vandekerckhove J. The primary structure of the basic isoform of Acanthamoeba profilin. Eur J Biochem 1988;170:597-601.
- 5. Ampe C, Vandekerckhove J, Brenner SL, Tobacman L, Korn ED. The amino acid sequence of Acanthamoeba profilin. J Biol Chem 1985;260:834-840.
- 6. Berk SG, Ting RS, Turner GW, Ashburn RJ. Production of respirable vesicles containing live Legionella pneumophila cells by two Acanthamoeba spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 1998;64:279-286.
- 7. Bogler SA, Zarley CD, Burianek LL, Fuerst PA, Byers TJ. Interstrain mitochondrial DNA polymorphism detected in Acanthamoeba by re-striction endonuclease analysis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1983;8:145-163.
- 8. Booton GC, Carmichael JR, Visvesvara GS, Byers TJ, Fuerst PA. Genotyping of Balamuthia mandrillaris based on nuclear 18S and mitochondrial 16S rRNA genes. Am J Trop Med Hyg 2003;68:65-69.
- 9. Bovee EC. Studies concerning the effects of nutrition on morphology of amoebas. II. Acanthamoeba castellanii (Douglas) on abundant and starvation quantities. Am Midland Nat 1963;69:73-181.
- 10. Bovee EC. In Lee JJ, Hunter SH, Bovee EC eds, Class Lobosea Carpenter, 1861. An illustrated guide to the protozoa. 1985, Lawrence, Kansas. Society of Protozoologists; pp 158-211.
- 11. Butt CG. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis. N Engl J Med 1966;274:1473-1476.
- 12. Byers TJ, Hugo ER, Stewart VJ. Genes of Acanthamoeba: DNA, RNA and protein sequences (a review). J Protozool 1990;37:17S-25S.
- 13. Chang RS, Owens S. Patterns of "lipovirus" antibody in human populations. J Immunol 1964;92:313-319.
- 14. Chappell CL, Dersden MH. Purification of cysteine proteinases from adult Schistosoma mansoni. Arch Biochem Biophys 1987;256:560-568.
- 15. Cho HK, Moon YS, Lee HK, Park AJ, Cho SI. Acanthamoeba keratitis. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 1992;33:538-543.
- 16. Cho MS, Jung SY, Park S, et al. Immunological characterizations of cloned 13.1-kilodalton protein from pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2003;10:954-959.
- 17. Chung DI, Kong HH, Yu HS, Oh YM, Yee ST, Lim YJ. Biochemical and molecular characterization of a strain KA/S2 of Acanthamoeba castellanii isolated from Korean soil. Korean J Parasitol 1996;34:79-85.
- 18. Chung DI, Kong HH, Yu HS, Yun HC, Chun ES. Acanthamoeba keratitis 2 cases; Case report and characterization of the isolates. Program and Abstracts of the 38th Annual Meeting of The Korean Society for Parasitology. 1996. Korea: 35.
- 19. Chung KS, Yun DJ, Im KI, Soh CT. Study on the determination of free-living amoebae pathogenicity by ultrastructural cytochemical method. Yonsei J Med Sci 1980;13:72-81.
- 20. Cirillo JD, Falkow S, Tompkins LS. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in Acanthamoeba castellanii enhances invasion. Infect Immun 1994;62:3254-3261.
- 21. Cirillo SLG, Bermudez LE, El-Etr SH, Duhamel GE, Cirillo JD. Legionella pneumophilia entry gene rtxA is involvd in virulence. Infect Immun 2001;69:508-517.
- 22. Clark CG, Cross GAM, De Jonckheere JF. Evaluation of evolutionary divergence in the genus Naegleria by analysis of ribosomal DNA plasmid restriction patterns. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1989;34:281-296.
- 23. Costas M, Griffiths AJ. The esterases and acid-phosphatases of Acanthamoeba (Amoebida, Acanthamoebidae). Protistologica 1984;20:33-41.
- 24. Culbertson CG, Smith JW, Minner JR. Acanthamoeba: Observations on animal pathogenicity. Science 1958;127:1506.
- 25. Daggett PM, Brook DR, Nerad TA. Relationship among 31 strains of Acanthamoeba based upon nonmorphological characters. J Protozool 1981;28:22A.
- 26. Daggett PM, Lipscomb D, Sawyer TK, Nerad TA. A molecular approach to the phylogeny of Acanthamoeba. Biosystems 1985;18:399-405.
- 27. De Jonckheere J. Use of an axenic medium for differentiation between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Naegleria fowleri isolates. Appl Env Microbiol 1977;33:751-757.
- 28. De Jonckheere J. Differences in virulence of Naegleria fowleri. Pathol Biol 1979;8:453-458.
- 29. De Jonckheere J. Isoenzyme and total protein analysis by agarose isoelectric focusing and taxonomy of the genus Acanthamoeba. J Protozool 1983;30:701-706.
- 30. De Jonckheere J. In Rondanelli EG ed, Taxonomy. Amphizoic amoebae human pathology. 1987, Padua, Italy. Piccin Nuova Libraria; pp 25-48.
- 31. Denney CF, Iragui VJ, Uber-Zak LD, Karpinski NC, Ziegler EJ, Visvesvara GS. Amebic meningoencephalitis caused by Balamuthia mandrillaris: case report and review. Clin Infect Dis 1997;25:1354-1358.
- 32. Dos Santos JG. Fatal primary amebic meningoencephalitis: A retrospective study in Richmond, Virginia. Am J Clin Pathol 1970;54:737-742.
- 33. Eldridge AE, Tobin J OH. "Ryan virus". Br Med J 1967;10:299.
- 34. Essig A, Heinemann M, Simnacher U, Marre R. Infection of Acanthamoeba castellanii by Chlamydia pneumoniae. Appl Environ Microbiol 1997;63:1396-1399.
- 35. Fowler M, Carter RF. Acute pyogenic meningoencephalitis probably due to Acanthamoeba sp.: A preliminary report. Br Med J 1965;2:740-742.
- 36. Fulton C. Amebo-flagellates as research partners: The laboratory biology of Naegleria and Tetramitus. Methods Cell Physiol 1970;4:341-476.
- 37. Gajdatsy AD, Kosmin A, Barrett GD. Coexistent adenoviral keratoconjunctivitis and Acanthamoeba keratitis. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol 2000;28:434-436.
- 38. Griffin JL. Environmental sampling for pathogenic Naegleria. J Protozool 1973;20:497-498.
- 39. Griffiths AJ, Curnick L, Unitt MD, Wilcox SL. The use of physiological characterizations in the classification of five species of Acanthamoeba. J Gen Microbiol 1978;107:211-215.
- 40. Hadas E, Mazur T. Proteolytic enzymes of pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains of Acanthamoeba spp. Trop Med Parasitol 1993;44:197-200.
- 41. Hammer JA III, Bowers B, Paterson B, Korn ED. Complete nucleotide sequence and deduced polypeptide sequence of a nonmuscle myosin heavy chain gene from Acanthamoeba: evidence of a hinge in the rodlike tail. J Cell Biol 1987;105:913-925.
- 42. Han KS, Min DY, Soh CT. Study on isoenzyme patterns of free-living amoebae, Acanthamoeba species. Yonsei J Med Sci 1982;15:75-86.
- 43. Hong YC, Hwang MY, Yun HC, et al. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a mammalian cathepsin L-like cysteine proteinase from Acanthamoeba healyi. Korean J Parasitol 2002;40:17-24.
- 44. Hong YC, Kong HH, Ock MS, Kim IS, Chung DI. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a subtilisin-like serine proteinases (AhSUB) from Acanthamoeba healyi. Mol Biochem Parasitol 2000;111:441-446.
- 45. Huang ZH, Ferrante A, Carter RF. Serum antibodies to Balamuthia mandrillaris, a free-living amoeba recently demonstrated to cause granulomatous amebic encephalitis. J Infect Dis 1999;179:1305-1308.
- 46. Hwang HK, Yun DJ, Im KI, Soh CT. Experimental study on the pathogenicity of free-living amoebae. Yonsei J Med Sci 1976;9:182-194.
- 47. Hyun DK, Shin CO, Im KI. Natural killer cell activity in mice infected with Acanthamoeba culbertsoni. Korean J Parasitol 1992;30:101-112.
- 48. Im KI. Pathogenic free-living amoebae. Korean J Parasitol 1990;28(Suppl):29-39.
- 49. Im KI. Pathogenic free-living amoebae in Korea (Editorial). JAMA / Korea 1996;11:7-8.
- 50. Im KI, Chung PR, Kim TU. Cell-mediated immunity in experimental amoebic meningoencephalitis. Korean J Parasitol 1989;27:73-77.
- 51. Im KI, Kim DS. Acanthamoebiasis in Korea: two new cases with clinical cases review. Yonsei Med J 1998;39:478-484.
- 52. Im KI, Kim SJ, Deung YK, Soh CT. Observation on ultrastructure and enzyme activity of free-living amoebae. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1976;7:40-50.
- 53. Im KI, Lee KT. Failure of immunization with Naegleria fowleri in mice born to immune mothers. Korean J Parasitol 1985;23:151-155.
- 54. Im KI, Lee KT, Soh CT, Kidson C. Hybridoma secreting monoclonal antibody for free-living amoeba. J Korean Med Assoc 1983;26:157-162.
- 55. Im KI, Oh HS. Immunological tests by anti-free-living amoebas serum produced in experimental animals. I. Immobilization of free-living amoebas in vitro by rabbit antiserum. Korean J Parasitol 1978;16:41-46.
- 56. Im KI, Ryu JS. Passive immunity by splenocyte transfer against amebic meningoencephalitis in mice. Korean J Parasitol 1988;26:169-173.
- 57. Im KI, Ryu JS, Lee KT. Immunodepression during experimental Naegleria meningoencephalitis in mice. Korean J Parasitol 1987;25:195-198.
- 58. Im KI, Shin HJ. Acanthamoeba sohi, n.sp., a pathogenic Korean isolate YM-4 from a freshwater fish. Korean J Parasitol 2003;41:181-188.
- 59. Im KI, Shin HJ, Hong YP eds, Acanthamoeba sohi n. sp.(Family Acanthamoebidae); a new species isolated in Korea with genomic DNA study. Program and Abstracts of the 36th annual meeting of The Korean Society for Parasitology. 1994. Korea: 18.
- 60. Im KI, Shin HJ, Seo DW, Jeon SH, Kim TE. Pathogenicity of Korean isolates of Acanthamoeba by observing the experimental infection and zymodemes of five isoenzymes. Korean J Parasitol 1999;37:85-92.
- 61. Im KI, Soh CT. Immunological tests by anti-free-living amoebas serum produced in experimental animals. II. Indirect fluorescent antibody titers of anti-free-living amoebas serum produced in rabbits. Korean J Parasitol 1978;16:134-139.
- 62. Jantzen H. Control of actin synthesis during the development of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Devel Biol 1981;82:113-126.
- 63. John DT, John RA. Enhancement of virulence of Naegleria fowleri by growth in Vero-cell cultures. J Parasitol 1994;80:149-151.
- 64. Josephson SL, Weik RR, John DT. Concanavalin Ainduced agglutination of Naegleria. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1977;26:856-858.
- 65. Jung G, Saxe CL III, Kimmel AR, Hammer JA III. Dictyostelium discoideum contains a gene encoding a myosin I heavy chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989;86:6186-6190.
- 66. Jung SY. In vivo transfection system of the nfa1 gene cloned from pathogenic Naegleria fowleri. 2004, Ajou University School of Medicine; Doctoral Thesis.
- 67. Kim CK, Choi HJ, Im KI, Soh CT. Study on the agglutinability of free-living amoebae with phytoagglutinin in consideration with their pathogenicity. Yonsei J Med Sci 1979;12:34-44.
- 68. Kim DS, Yong TS, Ryu JS, Im KI, Lee KT. The role of thymus in protective immunity to Naegleria fowleri. Yonsei J Med Sci 1986;19:1-12.
- 69. Kim JJ, Kim MK, Park IW, Lee HB. Acanthamoeba keratitis in contact lens wearer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 1995;36:2042-2047.
- 70. Kim KH, Shin CO, Im KI. Natural killer cell activity in mice infected with free-living amoeba with reference to their pathogenicity. Korean J Parasitol 1993;31:239-248.
- 71. Kim MJ, Shin CO, Im KI. Cell-mediated immunity in mice infected with Acanthamoeba culbertsoni. Korean J Parasitol 1990;28:143-154.
- 72. Kim OK, Im KI, Lee KT, Choe RC. Effect of prednisolone treatment on the experimental inducement of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. Korean J Parasitol 1985;23:165-172.
- 73. Kim SY, Syms MJ, Holtel MR, Nauschuetz KK. Acanthamoeba sinusitis with subsequent dissemination in an AIDS patient. Ear Nose Throat J 2000;79:168. 171-174.
- 74. Kim TU, Im KI, Cho YD. A biochemical study on the cytolytic substance of Acanthamoeba culbertsoni. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1989;20:32-35.
- 75. Kim YJ, Kim JJ, Min DY, Soh CT. Correlation of isoenzyme patterns and the pathogenicity of free-living amoebae collected in Korea. Yonsei J Med Sci 1984;17:320-340.
- 76. Kim YJ, Shin HJ, Im KI. Analysis of blastogenesis of lymphocytes and their subpopulations in mice infected with Naegleria fowleri. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1993;24:1-12.
- 77. Kim YK, Kim TU, Joung IS, Im KI. A comparative study on hydrolase activities in Acanthamoeba culbertsoni and A. royreba. Korean J Parasitol 1988;26:95-106.
- 78. Kong HH, Chung DI. PCR and RFLP variation of conserved region of small subunit ribosomal DNA among Acanthamoeba isolates assigned to either A. castellanii or A. polyphaga. Korean J Parasitol 1996;34:127-134.
- 79. Kong HH, Chung DI. Ultrastructural changes of Acanthamoeba cyst of clinical isolates after treatment with minimal cysticidal concentration of polyhexamethylene biguanide. Korean J Parasitol 1998;36:7-13.
- 80. Kong HH, Chung DI. A riboprinting scheme for identification of unknown Acanthamoeba isolates at species level. Korean J Parasitol 2002;40:25-31.
- 81. Kong HH, Kim TH, Chung DI. Purification and characterization of a secretory serine proteinase of Acanthamoeba healyi isolated from GAE. J Parasitol 2000;86:12-17.
- 82. Kong HH, Park JH, Chung DI. Interstrain polymorphisms of isoenzyme profiles and mitochondrial DNA fingerprints among seven strains assigned to Acanthamoeba polyphaga. Korean J Parasitol 1995;33:331-340.
- 83. Kong HH, Seo SA, Shin CO, Im KI. The effect of active immunization with Acanthamoeba culbertsoni in mice born to immune mother. Korean J Parasitol 1993;31:157-163.
- 84. Lai S, Asgari M, Henney HR Jr. Non-radioactive DNA probe and polymerase chain reaction procedures for the specific detection of Acanthamoeba. Mol Cell Probes 1994;8:81-89.
- 85. Lee DK, Lee KT, Im KI. Changes in the pathogenicity of Naegleria fowleri by serial brain passage in mice. Korean J Parasitol 1983;21:234-240.
- 86. Lee HS, Shin HJ, La MS, Im KI. The effect of silica on the development of experimental Acanthamoeba meningoencephalitis with reference to the macrophage role in mice. Korean J Parasitol 1994;32:259-266.
- 87. Lee KR, Shin CO, Im KI. Natural killer cell activity in Naegleria fowleri infected mice. Korean J Parasitol 1991;29:267-277.
- 88. Lee SG, Im KI, Lee KT. Protective immunity against Naegleria meningoencephalitis in mice. Korean J Parasitol 1985;23:293-299.
- 89. Lee SG, Shin HJ, Im KI. Study on the cell-mediated immunity in experimental Naegleria spp. infections. Korean J Parasitol 1989;27:177-186.
- 90. Lee SM, Choi YJ, Chung DI. Contamination of Acanthamoeba in contact lens care system. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc 1997;38:756-761.
- 91. Lee YW, Kim TU, Joung IS, Chung PR, Lee KT. An experimental study on the cytotoxicity of free-living amoebae. Yonsei J Med Sci 1986;19:358-370.
- 92. Lynch TJ, Brzeska H, Miyata H, Korn ED. Purification and characterization of a third isoform of myosin I from Acanthamoeba castellanii. J Biol Chem 1989;264:19333-19339.
- 93. Lyu CJ, Shin CO, Im KI. Interleukin-2 production and alteration of T cell subsets in mice infected with Naegleria fowleri. Korean J Parasitol 1993;31:249-257.
- 94. Ma P, Viscesvara GS, Martinez AJ, Theodore FH, Daggett PM, Sawyer TK. Naegleria and Acanthamoeba infections: Review. Rev Infect Dis 1990;12:490-513.
- 95. Martinez AJ, Garcia CA, Halks-Miller M, Arce-Vela R. Granulomatous amebic encephalitis presenting as a cerebral mass lesion. Acta Neuropathol 1980;51:85-91.
- 96. Martinez AJ, Visvesvara GS. Free-living, amphizoic, and opportunistic amebas. Brain Pathol 1997;7:583-598.
- 97. Martinez AJ, Visvesvara GS, Chandler FW. In Connor DH, Chandler FC, Schwartz DA, Manz HJ, Lack EE eds, Free-living amebic infections. Pathology of infectious diseases. 1997, Vol II:Stamford, CT. Appleton & Lange; pp 1163-1176.
- 98. Mathers WD, Goldberg MA, Sutphin JE, Dikoff JW, Folberg R. Coexistent Acanthamoeba keratitis and herpetic keratitis. Arch Ophthalmol 1997;115:714-718.
- 99. Mckerrow JH, Cohen FE, Craik CS, Sakanari JA. In Wermuth C.G., Koga N., Konig H., Metcalf B.W. eds, New approaches to isolation, expression and molecular modeling of proteases. Medicinal Chemistry for the 21st Century. 1992, Oxford. Blackwell Science; pp 107-118.
- 100. Menelaos C, Alan JG. Physiological characterization of Acanthamoeba strains. J Protozool 1986;33:304-309.
- 101. Michel R, Muller KD, Amann R, Schmid EN. Legionella-like slender rods multiplying within a strain of Acanthamoeba sp. isolated from drinking water. Parasitol Res 1998;84:84-88.
- 102. Myung CO, Lee KY, Im KI. Effects of zinc deficiency on immune response in mouse. Korean J Nutr 1988;21:113-121.
- 103. Na BK, Cho JH, Song CY, Kim TS. Degradation of immunoglobulins, protease inhibitors and interleukin-1 by a secretory proteinase of Acanthamoeba castellanii. Korean J Parasitol 2002;40:93-99.
- 104. Nellen W, Gallwitz D. Actin genes and actin messenger RNA in Acanthamoeba castellanii. J Mol Biol 1982;159:1-18.
- 105. Neumeister B, Schoniger S, Faigle M, Eichner M, Dietz K. Multiplication of different Legionella species in Mono Mac 6 cells and in Acanthamoeba castellanii. Appl Environ Microbiol 1997;63:1219-1224.
- 106. Niederkorn JY, Alizadeh H, Leher H, McCulley JP. The pathogenesis of Acanthamoeba keratitis. Microbes Infect 1999;1:437-443.
- 107. North MJ, Mottram JC, Coombs GH. Cysteine proteinases of parasitic protozoa. Parasitol Today 1990;6:270-275.
- 108. Page FC. Taxonomic criteria for limax amoebae, with descriptions of 3 new species of Hartmannella and 3 of Vahlkampfia. J Protozool 1967a;14:499-521.
- 109. Page FC. Re-definition of the genus Acanthamoeba with descriptions of three species. J Protozool 1967b;14:709-724.
- 110. Page FC. An Illustrated Key to Freshwater and Soil Amoebae. 1976, Ambleside, Cumbria. Freshwater Biological Association; Scientific Publication No. 34.
- 111. Page FC. A new key to fresh water and soil gymnamoebae. 1988, Cumbria, England. Fresh Water Biological Association; pp 1-122.
- 112. Park H, Ko MY, Paik MK, Soh CT, Seo JH, Im KI. Cytotoxicity of a cysteine proteinase of adult Clonorchis sinensis. Korean J Parasitol 1995;33:211-218.
- 113. Park H, Soh CT, Seo JH, Im KI. Proteinase activity of Naegleria spp. with special reference to their pathogenicity. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1993;24:13-29.
- 114. Park KM, Ryu JS, Im KI. Blastogenic responses of splenic lymphocytes to Naegleria fowleri lysates and T-cell mitogen in mice with primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. Korean J Parasitol 1987;25:1-6.
- 115. Park JT, Jeong YE, Ahn TI. Changes in profiles of major proteins in encysting Acanthamoeba castellanii. Korean J Biol Sci 2002;6:341-347.
- 116. Park YS. Identification of differentially expressed mouse mRNA induced by the infection of Acanthamoeba culbertsoni via DDRT-PCR analysis. 1996, Yonsei University College of Medicine; Doctoral Thesis.
- 117. Pernin P, Bouikhsain I, De Jonckheere JF, Petavy AF. Comparative protein patterns of three thermophilic non-pathogenic Naegleria isolates and two Naegleria fowleri strains by isoelectric focusing. Int J Parasitol 1983;13:113-118.
- 118. Philippe M, Vinckier D, Dubremetz JF, Schrevel J. The three cortical membranes of the gregarines (parasitic Protozoa). III. Comparative studies of the membrane proteins among different sporozoan species during their vegetative phase. J Protozool 1982;29:424-430.
- 119. Pollard TD, Cooper JA. Acting and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Ann Rev Biochem 1986;55:987-1035.
- 120. Pussard M. Le genre Acanthamoeba Volkonsky 1931 (Hartmannellidae-Amoebida). Protistologica 1966;2:71-93.
- 121. Pussard M, Pons R. Morphologie de la paroi kystique et taxonomic du genre Acanthamoeba (Protozoa, Amoebida). Protistologica 1977;13:557-598.
- 122. Rege AA, Herrera PR, Lopez M, Dresden MH. Isolation and characterization of a cysteine proteinase from Fasciola hepatica adult worms. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1989;35:89-96.
- 123. Rhim JK. Proteinase activity of Acanthamoeba culbertsoni with reference to pathogenicity. 1997, Yonsei University College of Medicine; Dortoral Thesis.
- 124. Ringstead JR, Jager BV, Suk DS, Visvesvara GS. Probable Acanthamoeba meningoencephalitis in a Korean child. Am J Clin Pathol 1976;66:723-730.
- 125. Rivera MA, Padhya TA. Acanthamoeba: a rare primay cause of rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 2002;112:1201-1203.
- 126. Ryu JS, Im KI. The production and characterization of anti-Naegleria fowleri monoclonal antibodies. Korean J Parasitol 1992;30:33-41.
- 127. Ryu JR, Soh CT, Im KI. Ultrastructural observation of Naegleria fowleri trophozoite in mouse brain and axenic culture. Korean J Parasitol 1984;22:259-266.
- 128. Sawyer TK, Griffin JL. Acanthamoeba comandoni and A. astronyxis: Taxonomic characteristics of mitotic nuclei, "centrosomes" and cysts. J Protozool 1971;18:382-388.
- 129. Sawyer TK, Griffin JL. A proposed new family, Acanthamoebidae n. fam. (order Amoebida), for certain cyst-forming filose amoebae. Trans Am Microsc Soc 1975;94:93-98.
- 130. Sawyer TK, Visvesvara GS, Harke BA. Pathogenic amoebas from brackish and ocean sediments, with a description of Acanthamoeba hatchetti. n. sp. Science 1977;196:1324-1325.
- 131. Schuster FL, Visvesvara GS. Efficacy of novel antimicrobials against clinical isolates of opportunistic amebas. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1998;45:612-618.
- 132. Schuster FL, Visvesvara GS eds, Comparative biology of Balamuthia mandrillaris isolates. 2001. XI International Congress of Protozoology. July 15-19; Salzburg, Austria: 84.
- 133. Selby DM, Chandra RS, Rakusan TA, Loechelt B, Markle BM, Visvesvara GS. Amebic osteomyelitis in a child with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a case report. Pediatr Pathol Lab Med 1998;18:89-95.
- 134. Seo JH, Yong TS, Im KI. Biochemical studies on proteinase in Acanthamoeba culbertsoni. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1991;22:21-28.
- 135. Seo SA, Yong TS, Im KI. The maintenance of free-living amoebae by cryopreservation. Korean J Parasitol 1992;30:151-153.
- 136. Shin HJ, Cho MS, Jung SY, et al. Cytopathic changes in rat microglial cells induced by pathogenic Acanthamoeba culbertsoni: Morphology and cytokine release. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2001;8:837-840.
- 137. Shin HJ, Cho MS, Jung SY, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a gene encoding a 13.1 kDa antigenic protein of Naegleria fowleri. J Eukaryot Microbiol 2001b;48:713-717.
- 138. Shin HJ, Cho MS, Kim HJ, Im KI. Isoenzyme patterns and phylogenetic relationships in Acanthamoeba spp. isolated from contact lens containers in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1999;37:229-236.
- 139. Shin HJ, Cho MS, Kim HI, Im KI. In vitro cytotoxicity of Acanthamoeba spp. isolated from contact lens container in Korea by crystal violet staining and LDH release assay. Korean J Parasitol 2000;38:99-102.
- 140. Shin HJ, Cho MS, Kim HI, et al. Apoptosis of primary-culture rat microglia cells induced by pathogenic Acanthamoeba spp. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2000b;7:510-514.
- 141. Shin HJ, Im KI. Analysis of antigenic specificities of Naegleria fowleri using EITB. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1992b;23:9-13.
- 142. Shin HJ, Im KI, Choe RS. Effect of splenectomy on development of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. Korean J Parasitol 1985;23:156-164.
- 143. Shin HJ, Kim CH, Im KI. Immunological approach for classification of free-living amoeba in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1992;30:289-298.
- 144. Shin HJ, La MS, Im KI. Cytotoxicity of Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 (Korean isolate). Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1993;24:31-38.
- 145. Sogin ML. Evolution of eukaryotic microorganisms and their small subunit ribosomal RNAs. Am Zool 1989;29:487-499.
- 146. Soh EY, Shin HJ, Im KI. The protective effects of monoclonal antibodies in mice from Naegleria fowleri infection. Korean J Parasitol 1992;30:113-123.
- 147. Steinert M, Birkness K, White E, Fields B, Quinn F. Mycobacterium avium bacilli grow saprozoically in coculture with Acanthamoeba polyphaga and survive within cyst walls. Appl Environ Microbiol 1998;64:2256-2261.
- 148. Stevens AR, O'Dell WD. In vitro growth and virulence of Acanthamoeba. J Parasitol 1974;60:884-885.
- 149. Stratford MP, Griffiths AJ. Variations in the properties and morphology of cysts of Acanthamoeba castellanii. J Gen Microbiol 1978;108:33-37.
- 150. Symmers W. St. C. Sr. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis in Britain. Br Med J 1969;4:449-454.
- 151. Tyndall RZ, Willaert E, Stevens A, Nicholson A. Pathogenic and enzymatic characteristics of Acanthamoeba isolated from cultured tumor cells. Protistologica 1979;15:17-22.
- 152. Visvesvara GS. Classification of Acanthamoeba. Rev Infect Dis 1991;13(Suppl 5):S369-S372.
- 153. Visvesvara GS, Balamuth W. Comparative studies on related free-living and pathogenic amebae with special reference to Acanthamoeba. J Protozool 1975;22:245-256.
- 154. Visvesvara GS, Martinez AJ, Schuster FL, Leitch GJ, Wallace SV, Sawyer KK. Leptomyxid ameba, a new agent of amebic meningoencephalitis in humans and animals. J Clin Microbiol 1990;28:2750-2756.
- 155. Visvesvara GS, Schuster FL, Martinez AJ. Balamuthia mandrillaris, n. g, n. sp., agent of amebic meningoencephalitis in humans and other animals. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1993;40:504-514.
- 156. Visvesvara GS, Stehr-Green JK. Epidemiology of free-living ameba infections. J Protozool 1990;37:25S-33S.
- 157. Volkonsky M. Hartmannella castellanii Douglas et classification des Hartmannelles. Arch Zool Exp Gen 1931;72:317-339.
- 158. Whang YN, Min DY, Soh CT. Immunologic response of mice against free-living amoeba (Acanthamoeba sp.). Yonsei J Med Sci 1980;13:259-273.
- 159. Willaert E. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. A selected bibliography and tabular survey of cases. Ann Soc Belge Med Trop 1974;54:429-440.
- 160. Willaert E, Stevens AR, Healy GR. Retrospective identification of Acanthamoeba culbertsoni in a case of amoebic meningoencephalitis. J Clin Pathol 1978;31:717-720.
- 161. Wong MM, Karr SL Jr, Chow CK. Changes in the virulence of Naegleria fowleri maintained in vitro. J Parasitol 1977;63:872-878.
- 162. Wylie DC, Vanaman TC. Purification and characterization of Acanthamoeba calcium-binding proteins. Methods Enzymol 1987;139:50-68.
- 163. Yu HS, Hwang MY, Kim TO, et al. Phylogenetic relationships among Acanthamoeba spp. based on PCR-RFLP analyses of mitochondrial small subunit rRNA gene. Korean J Parasitol 1999;37:181-188.
- 164. Yun HC, Kim KY, Park SY, et al. Cloning of a cysteine proteinase gene from Acanthamoeba culbertsoni. Mol Cells 1999;9:491-496.
- 165. Yun HC, Park SJ, Kong HH, Chung DI. Isolation of genes induced in Naegleria fowleri during mouse brain passage. Eur J Protistol 2002;38:105-111.
Fig. 1Trophozoites of Acanthamoeba Korean isolates YM-1 (A), YM-2 (B), YM-3 (C) and YM-4 (Acanthamoeba sohi) (D).
Fig. 2Hydrolases activity in trophozoite extracts and in culture media of
Acanthamoeba culbertsoni and
A. royreba (
Kim et al., 1988).
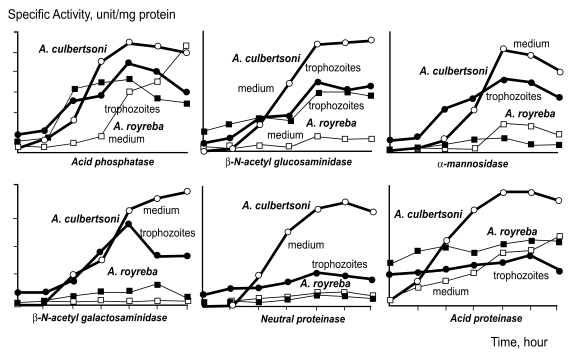
Fig. 3Vertical transmission of immunity in
Naegleria fowleri infected mice (
Ahn et al., 1986).

Fig. 4A sagitally sectioned mouse brain infected intranasally with Acanthamoeba sohi.

Fig. 5Mouse brain tissue infected experimentally with Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-2. Arrows indicate trophozoites.

Fig. 6Survival of mice infected experimentally with
Acanthamoeba Korean isolates (
Im et al., 1999).
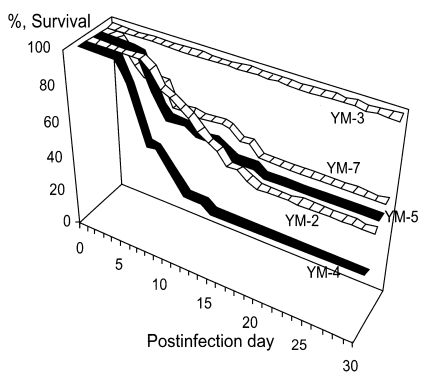
Fig. 7The zymographic profile in
Acanthamoeba Korean isolates and
Acanthamoeba spp. for reference. N; long-term cultivated, P; mouse brain-passaged (
Im et al., 1999).
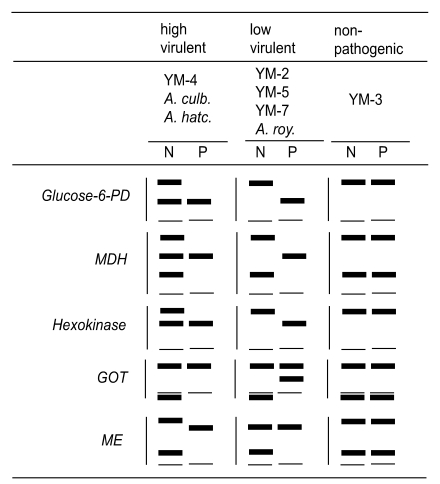
Fig. 8Microscopic findings of a skin biopsy of meningoencephalitis case 3; Acanthamoeba trophozoites are shown well differentiated from surrounding cells by a clear space.
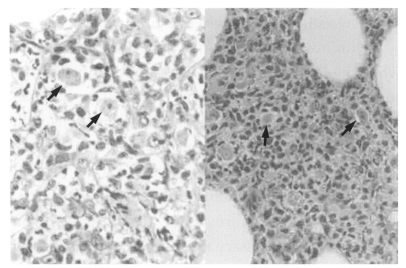
Fig. 9
Acanthamoeba trophozoite detected in case 6 with keratitis.
Table 1.Sample sources of Acanthamoeba Korean isolates and other reference free-living amoeba
Table 1.
|
Species/strain designation |
Isolated from |
Submitted by |
Pathogenicity in mice |
|
Naegleria sp. YM-1 |
sewage |
|
pathogenic |
|
Acanthamoeba sp. |
YM-2 |
water puddle |
|
pathogenic |
|
YM-3 |
storing reservoir |
|
non-pathogenic |
|
YM-4 |
freshwater fish gill |
|
pathogenic |
|
YM-5 |
sewage |
|
- |
|
YM-6 |
bronchial washing |
|
- |
|
YM-7 |
corneal scraping |
|
- |
|
Naegleria fowleri, 0359 |
|
Jadin, J.B. |
pathogenic |
|
Naegleria gruberi, EGB |
|
Schuster, F.L. |
non-pathogenic |
|
Acanthamoeba castellanii, ADCC30898 |
|
Chung, D.I. |
- |
|
Acanthamoeba culbertsoni
|
|
Jadin, J.B. |
pathogenic |
|
Acanthamoeba hatchetti
|
|
Molet, B. |
|
|
Acanthamoeba healyi, ATCC30866 |
|
Chung, D.I. |
|
|
Acanthamoeba lenticulata, PD2 |
|
Molet, B. |
|
|
Acanthamoeba triangularis, SH621 |
|
Molet, B. |
|
|
Acanthamoeba polyphaga, Ap |
|
Schuster, F.L. |
|
Table 2.Mortality of mice infected experimentally with
Acanthamoeba spp. of long-term cultivated in axenic medium, and also of serial mouse brain passage (
Im et al., 1999)
Table 2.
|
Amoebae |
Mortality in mice
|
|
long-term cultivated |
after brain passage |
|
Acanthamoeba sp., |
YM-2 |
5.7 |
47.4 |
|
“ |
YM-3 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
|
“ |
YM-4 |
2.9 |
65.5 |
|
“ |
YM-5 |
0.0 |
43.8 |
|
“ |
YM-7 |
11.5 |
38.9 |
|
Acanthamoeba culbertsoni
|
3.3 |
60.0 |
|
Acanthamoeba hatchetti
|
5.0 |
75.0 |
|
Acanthamoeba royreba
|
9.5 |
16.7 |
Table 3.The cytotoxicity of
Acanthamoeba spp. against the Chinese hamster ovary cells (
Im et al., 1999)
Table 3.
|
Amoebae |
Before brain passage
|
After brain passage
|
|
100a)
|
50 |
25 |
12.5 |
100 |
50 |
25 |
12.5 |
|
Acanthamoeba sp., |
YM-2 |
22.3 |
14.9 |
12.7 |
4.2 |
99.9 |
48.4 |
32.3 |
19.7 |
|
YM-3 |
56.4 |
40.4 |
31.9 |
21.3 |
66.7 |
36.9 |
29.8 |
21.7 |
|
YM-4b)
|
59.6 |
25.5 |
19.1 |
9.6 |
94.0 |
54.4 |
32.7 |
30.9 |
|
YM-5 |
50.0 |
23.4 |
17.0 |
14.9 |
62.7 |
23.4 |
21.2 |
12.2 |
|
YM-7 |
48.9 |
24.5 |
13.8 |
82.5 |
82.5 |
38.8 |
23.1 |
18.9 |
|
Acanthamoeba culbertsoni
|
31.9 |
12.7 |
14.9 |
13.8 |
44.3 |
21.3 |
19.9 |
26.4 |
|
Acanthamoeba hatchetti
|
35.1 |
15.9 |
11.7 |
11.7 |
93.4 |
47.4 |
36.8 |
26.4 |
|
Acanthamoeba royreba
|
47.9 |
35.1 |
31.9 |
37.1 |
72.4 |
41.5 |
36.7 |
27.3 |