Abstract
A new species of Acanthamoeba was isolated from a freshwater fish in Korea and tentatively named Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 (Korean isolate YM-4). The trophozoites were 11.0-23.0 µm in length and had hyaline filamentous projections. Cysts were similar to those of A. culbertsoni and A. royreba, which were previously designated as Acanthamoeba group III. Acanthamoeba YM-4 can survive at 40℃, and its generation time was 19.6 hr, which was longer than that of A. culbertsoni. In terms of the in vitro cytotoxicity of lysates, Acanthamoeba YM-4 was weaker than A. culbertsoni, but stronger than A. polyphaga. On the basis of the mortality of experimentally infected mice, Acanthamoeba YM-4 was found to be highly virulent. The isoenzymes profile of Acanthamoeba YM-4 was similar to that of A. royreba. An anti-Acanthamoeba YM-4 monoclonal antibody, McAY7, was found to react only with Acanthamoeba YM-4, and not with A. culbertsoni. Random amplified polymorphic DNA marker analysis and RFLP analysis of mitochondrial DNA and of 18S small subunit ribosomal RNA, placed Acanthamoeba YM-4 in a separate cluster on the basis of phylogenetic distances. Thus the Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-4 was identified as a new species, and assigned as Acanthamoeba sohi.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba, pathogenicity, restriction fragment length polymorphism, phylogeny
INTRODUCTION
The ubiquitous distribution of small free-living amoebae in nature, and the ability of certain species to survive and grow especially in freshwater, suggesting a role in human and animal disease (
Ma et al., 1990). The small free-living amoebae,
Acanthamoeba spp.,
Naegleria spp. and
Balamuthia mandrillaris, are distributed worldwide, and thus provide a potential source of meningoencephalitis or keratoconjunctivitis infection for humans and other mammals.
Based on differences in size as well as on the morphologic characters of the cysts, in 1977 Pussard and Pons recognized three groups within the genus
Acanthamoeba. However, species differentiation based on morphology alone may not always be correct. Thus, many attempts have been made to include other features, such as isoenzyme profiles and restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP) of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), in the classification of
Acanthamoeba (
Bogler et al., 1983;
De Jonckheere, 1983). The classification of
Acanthamoeba spp. at the subgenus level has been attempted by riboprinting, e.g., by RFLP analysis of the 18S small subunit ribosomal RNA (srRNA) gene by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) (
Chung et al, 1998). Kong and Chung (
2002) described a riboprinting scheme for the identification of unknown
Acanthamoeba Korean isolates at the species level by using the PCR-RFLP of 18S srRNA using four kinds of restriction enzymes. In addition, the interstrain polymorphisms of the isoenzyme profiles and the RFLP patterns of mtDNA were observed in seven strains of
Acanthamoeba polyphaga and four strains of
Acanthamoeba castellanii (
Kong et al., 1995).
This paper described the identification of the Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-4 at the species level based on morphologic characteristics, biochemical and molecular genetic criteria, by reviewing previous reports and adding some new figures and experimental data for 18S srDNA RFLP. Moreover, we propose a new species, Acanthamoeba sohi (Korean isolate YM-4), isolated from the gills of a freshwater fish collected in a fish market in Seoul, Korea, as presented in the 36th annual meeting of The Korean Society for Parasitology in 1994.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Isolation of Korean isolate YM-4
Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-4 was isolated from the gills of a fresh water fish collected in a fish market in December 10, 1977. The gills of the freshwater fish,
Carassius auratus, were dissected and separated. The sample obtained was cut into small pieces and aseptic sterilized physiologic saline was added. Small amounts of the sediment obtained by centrifugation were transferred to the surface of a non-nutrient agar plate previously streaked with killed
Escherichia coli. Amoeba colonies were selected from the agar plates. The strain CDC-Fish-SK submitted to Dr. G. S. Visvesvara (Division of Parasitic Diseases, Center for Disease Control, Atlanta, USA) by Dr. J. Yang (
Moura et al., 1992) was the original Korean isolate YM-4.
Cultivation
The culture medium was composed of 1.5% Bactoagar containing 14 mg of neomycin, 3,750 units of nystatin and 2.0 ml of heat-killed E. coli suspended in 100 ml of distilled water. Amoeba colonies were maintained in continuous culture on the surface of a non-nutrient agar plate, and transferred aseptically to axenic CGV medium in June 1984. Pure ameba cultures were established by aseptically placing a portion of a single colony on agar medium and by preparing subcultures at weekly intervals. These were then placed in axenic liquid CGV medium at 37℃ in a CO2 incubator. CGV medium was composed bactocasitone 20 gm, glucose 1gm, folic acid 2 mg, biotin 20 µg, NaCl 5 mg, penicillin (50 × 104 units), streptomycin (5 × 104), and distilled water (1,000 ml).
Biological, biochemical, immunological, molecular and genetic characteristics of Acanthamoeba YM-4
The morphologic characteristics, biochemical and molecular genetic criteria are described by reviewing previous reports. In this report, some new figures and experimental data for 18S srDNA RFLP has been added. The 18S-srDNAs (or srRNA) of
Acanthamoeba YM-4 and of reference amoebae were amplified by PCR with primer encoding the 18S-srRNA gene and digested with six restriction endonucleases, i.e.,
Dde I,
Hae III,
Hinf I,
Msp I,
Rsa I and
Sau I (Sigma). Amplified DNAs were loaded on 1% agarose horizontal gel. A phylogenic tree based on the RFLPs of the 18 srDNA of
Acanthamoeba spp. was constructed as described previously (
Shin et al., 1998).
RESULTS
1. Descriptions of Acanthamoeba sohi, n. sp.
Synonym: Acanthamoeba YM-4, Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 and Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-4.
Type host: Fresh water fish and experimental animals.
Habitats: Fresh water.
Locality: South Korea.
Type specimens: Trophozoites are deposited in the Department of Parasitology, Yonsei University, College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea.
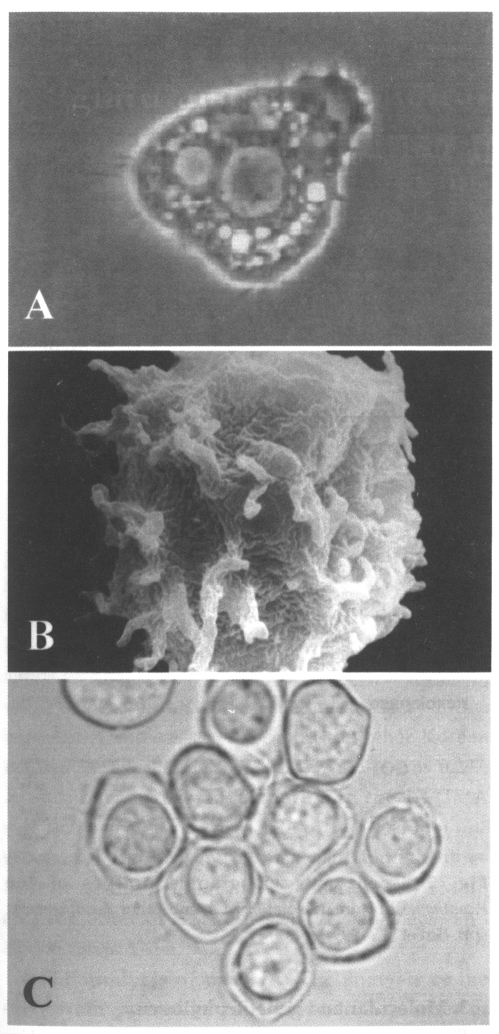
Morphology: The dimentions of living trophozoites and cysts from culture media were determined with an ocular micrometer and photographed under a phase-contrast microscope. The trophozoite of
A. sohi is a small filose amoeba with features typical of the genus of
Acanthamoeba; i.e., locomotive form, elongate to broad, measuring 11.0-23.0 µm long when grown in liquid medium; hyaline and filamentous projections; usually uninucleate; no flagellate stage and no detectable centrosome-like organelles; numerous food vacuoles (
Fig. 1A, B). The feeding form is variable in shape and size; refractive, and without a wide, clear, hyaline anterior zone of protoplasm. Nuclear division is accompanied by the disappearance of the nuclear membrane and of nucleoli during the late prophase.
A. sohi has a small and refractive cyst with a nearly circular ectocyst and oval or some irregular endocyst (
Fig. 1C); of diameter, 7.0-14.0 µm (measured on agar). Based upon the morphological characteristics of trophozoites and cysts,
Acanthamoeba YM-4 (
A. sohi) was found to resemble
A. culbertsoni and
A. royreba (
Shin et al., 1992a;
Shin et al., 1997). Cysts of
Acanthamoeba YM-7 (Korean isolate serial number) were similar to those of
A. polyphaga, which was designated as a member of
Acanthamoeba group II by the classification key of Pussard and Pons (
1977). Morphologically
Acanthamoeba YM-4 and YM-5 belong to
Acanthamoeba group III.
Generation time: The generation time of
Acanthamoeba YM-4 was compared with
A. culbertsoni and
A. polyphaga AP strain (
Shin et al., 1993). At 37℃, the generation time of YM-4 was 19.1 hr, (
A. culbertsoni 18.7 hr,
A. polyphaga 19.4 hr). At 25℃, the generation times of
Acanthamoeba YM-4,
A. culbertsoni and
A. polyphaga were 25.7 hr, 24.2 hr and 18.2 hr. and at 40℃, the generation time of YM-4 (19.6 hr) was longer than that of
A. culbertsoni (17.8 hr).
2. Biological characteristics
Cytotoxicity: Acanthamoeba YM-4 was compared with
A. culbertsoni and
A. royreba with respect to its cytotoxic effect upon Chinese hamster ovary cells (
Shin et al., 1993). The in vitro cytotoxicity of
Acanthamoeba YM-4 using trophozoite lysate was weaker than that of
A. culbertsoni, but stronger than that of
A. polyphaga (
Table 1).
Pathogenicity and virulence: Acanthamoeba Korean isolates and reference
Acanthamoeba spp. have been demonstrated to be pathogenic to experimental mice, and to induce death when inoculated intranasally (
Im et al., 1999). Based on infected mouse mortality,
Acanthamoeba YM-4 and
A. culbertsoni were found to be highly virulent,
Acanthamoeba YM-2, YM-5,
A. royreba and
A. castellanii to have low virulence, and
Acanthamoeba YM-3 to be nonpathogenic (
Table 2).
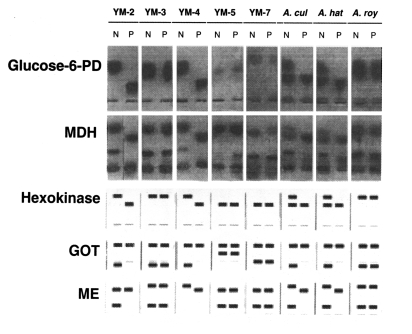
Biochemistry: The zymodeme patterns of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), malate dehyrogenase (MDH), hexokinase (HK), glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase (GOT) and malic enzyme (ME) of
Acanthamoeba spp. differed for the Korean isolates (
Fig. 2), especially between
Acanthamoeba YM-4 and
A. royreba (
Han et al., 1982;
Im et al., 1999). According to the result of Moura et al. (
1992), the isoenzymes profile of
Acanthamoeba YM-4 (CDC-Fish-SK in this paper) is similar to
A. royreba.
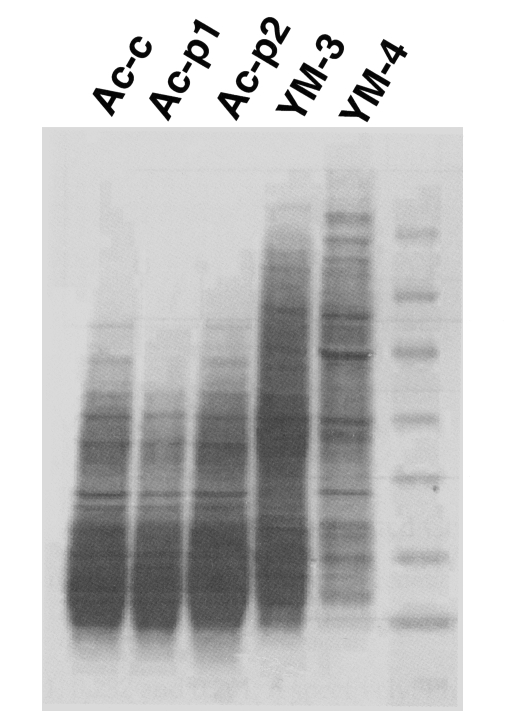
Immunology: As a result of the SDS-PAGE profile of the lysate of
Acanthamoeba YM-4, 16 major protein fractions were found to be similar to those of
A. culbertsoni, but
Acanthamoeba YM-4 exhibited distinctly different protein fractions patterns when compared with
A. royreba and
A. polyphaga (
Fig. 3). Cross-reactivity experiments were performed in the various amoebae by ELISA using anti-
Acanthameoba YM-4 monoclonal antibody, McAY 7 (IgG1, 43 kDs by EITB), which was found to react only with
Acanthamoeba YM-4, and not with
A. culbertsoni (
Shin et al., 1992b).
3. Molecular and genetic phylogeny
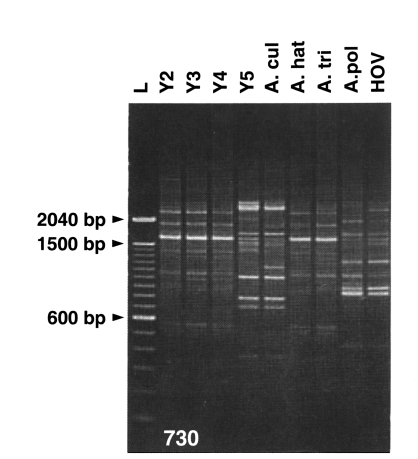
Random amplified polymorphic DNA marker analysis: The genetic status of
Acanthamoeba spp. was investigated by random amplified polymorphic DNA marker analysis (
Fig. 4). Four
Acanthamoeba Korean isolates and other reference
Acanthamoeba spp. were analyzed by RAPD-PCR using arbitrary decamer primers (
Hong et al., 1995). The similarity index between
A. hatchetti and
A. triangularis was found to be 0.833. The mean similarity indices between three Korean isolates (
Acanthamoeba YM-2, YM-3, YM-4) and two other species (
A. hatchetti and
A. triangularis) were 0.959 and 0.832. The mean similarity index between
Acanthamoeba YM-5 and the other Korean isolates (
Acanthamoeba YM-2, YM-3, YM-4) was 0.237. A phonogram reconstructed using the UPGMA method revealed the presence of two groups; one group of
A. hatchetti, and
A. triangularis, and the three Korean isolates (
Acanthamoeba YM-2, YM-3, YM-4), and the other of
A. culbertsoni,
A. polyphaga, and
Acanthamoeba YM-5.
RFLP analysis of mtDNA: The analysis of the interstrain variability of nucleotide sequences of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) offers a molecular means of determining overall genotype differences; restriction endonuclease analysis has proven a powerful tool for revealing mtDNA phylogenic relationships among closely related organisms. RFLP analysis of mtDNA was found to be useful in the classification of members to the genus
Acanthamoeba (
Shin and Im, 1996;
Shin et al., 1997). The RFLP analysis of
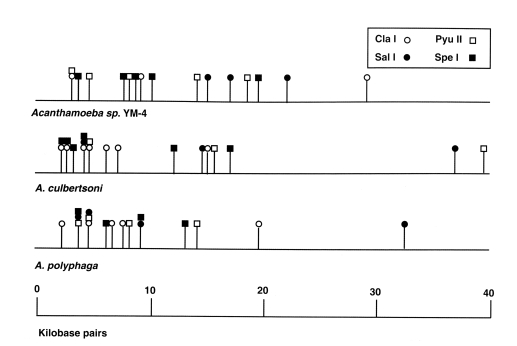
Acanthamoeba mtDNA was accomplished using five restriction enzymes;
Hae III,
Hind III,
Cla I,
Pvu II and
Sal I. Each restriction enzyme produced approximately 3-15 fragments (
Fig. 5). The mtDNA genome size, calculated by the summation of restriction fragments, averaged 46.4 kbp in
Acanthamoeba YM-4, 48.3 kbp in
A. culbertsoni and 48.8 kbp in
A. polyphaga. The estimated genetic divergence was 10.1% between
Acanthamoeba YM-4 and
A. culbertsoni, and 9.9% between
Acanthamoeba YM-4 and
A. polyphaga.
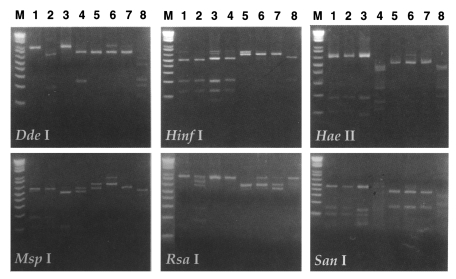
RFLP analysis of 18S srDNA: The 18S-srDNAs (or srRNA) of
Acanthamoeba YM-4 was amplified by PCR with primer encoding the 18S-srRNA gene, and the products obtained were digested with restriction endonucleases (
Fig. 6). RFLP analysis was applied to the classification of the
Acanthamoeba Korean isolates (YM-4, YM-5 and YM-7), and compared with the reference amoebae,
A. culbertsoni,
A. polyphaga and
A. royreba (
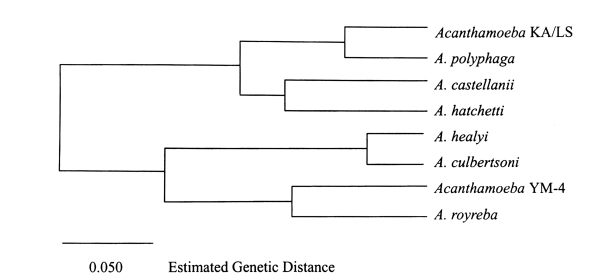
Shin et al., 1998). The genetic distance between
A. culbertsoni and
Acanthamoeba YM-5 was 0.070, and between
Acanthamoeba YM-4 and
A. polyphaga 0.364. Moreover, genetic divergence was not observed between
A. culbertsoni and
Acanthamoeba YM-4. According to this result,
Acanthamoeba YM-7 is a similar species to
A. polyphaga, and
Acanthamoeba YM-5 and
A. polyphaga are different species, but
Acanthamoeba YM-5 is related closely to
A. culbertsoni. Our RFLP result gave a genetic distance of 0.105 between
Acanthamoeba YM-4 and
A. royreba (
Fig. 7), which were closer species among the reference amoebae. The genetic distances between
Acanthamoeba YM-4 and
A. polyphaga,
A. culbertsoni and
A. castellanii were 0.341, 0.232 and 0.201, respectively. Phylogenetic relationships placed
Acanthamoeba YM-4 in a separate cluster (
Fig. 7).
DISCUSSION
Acanthamoeba spp. is an amphizoic amoebae, which belongs to the genus
Acanthamoeba Volkonsky 1931, emend Page (
1967), and was incorporated into the family Acanthamoebidae by Sawyer and Griffin (
1975). Pathogenic free-living amoebae belong to the genera
Acanthamoeba and
Naegleria. Group taxonomy, including pathogenic free-living amoebae, was clarified and updated at the generic level by P.C. Page (
1967), who published a taxonomic key (
Page, 1976). The genus
Naegleria Alexeieff 1912, emend Calkins 1913, belongs to the family Vahlkampfiidae. The genus
Acanthamoeba Volkonsky 1931, emend Page (
1967), was included in the family Acanthamoebidae Sawyer and Griffin (
1975). The genus
Acanthamoeba was established in 1931, and until recently considerable confusion existed in terms of its taxonomic status. In 1966, Pussard stated that spindle shape is not a satisfactory feature for intergeneric differentiation but considered the characteristic morphology of the cyst to be a decisive character at the generic level and recognized the genus
Acanthamoeba. In 1967, Page considered the presence of acanthopodia and the structure of the cyst to be sufficiently distinctive and concluded that the generic designations of
Acanthamoeba and
Hartmannella were justified. In 1975, Visvesvara and Balamuth identified clearly demonstrable differences not only in the trophozoite and cyst stages of
Acanthamoeba and
Hartmannella, but also in their nutritional requirements and serologic responses. Sawyer and Griffin created the family Acanthamoebidae in 1975, and Page created the suborder Acanthopodina under the order Amoebida. However, Page separated
Acanthamoeba and
Hartmannella at the ordinal level by creating a new order, Acanthopodida, which includes the family Acanthamoebidae and placed
Hartmannella in the family Hartmannellidae, order Euamoebida.
As a result of experiments and reviews based on morphological characteristics, pathogenicity to mice, in vitro cytotoxicity, isoenzyme patterns and RFLP analysis of mtDNA and 18S srRNA, Acanthamoeba YM-4 was found to differ significantly from A. culbertsoni, A. polyphaga, and A. royreba and other reference Acanthamoeba spp. Thus, the Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-4 should be identified as a new species, assigned as Acanthamoeba sohi. The Korean isolate YM-4 was proposed as new species, Acanthamoeba sohi, at the 36th annual meeting of The Korean society for Parasitology in 1994. This new species is named in honor of Dr. Chin-Thack Soh, a Emeritus Professor of Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
References
- 1. Bogler SA, Zarley CD, Burianek LL, Fuerst PA, Byers TJ. Interstrain mitochondrial DNA polymorphism detected in Acanthamoeba by restriction endonuclease analysis. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1983;8:145-163.
- 2. Chung DI, Yu HS, Hwang MY, et al. Subgenus classification of Acanthamoeba by riboprinting. Korean J Parasitol 1998;36:69-80.
- 3. De Jonckheere J. Isoenzyme and total protein analysis by agarose isoelectric focusing and toxonomy of the genus Acanthamoeba. J Protozool 1983;30:701-706.
- 4. Han KS, Min DY, Soh CT. Study on isoenzyme patterns of free-living Amoebae, Acanthamoeba species. Yonsei J Med Sci 1982;15:75-86.
- 5. Hong YP, Oh SH, La MS, Im KI. Genetic status of Acanthamoeba spp. Korean isolates on the basis of RAPD markers. Korean J Parasitol 1995;33:341-348.
- 6. Im KI, Shin HJ, Hong YP. Acanthamoeba sohi n. sp. (Family Acanthamoebidae); a new species isolated in Korea with genomic DNA study. Program and Abstracts of the 36th Annual Meeting of The Korean Society for Parasitology. 1994. Korea: 18.
- 7. Im KI, Shin HJ, Seo DW, Jeon SH, Kim TE. Pathogenicity of Korean isolates of Acanthamoeba by observing the experimental infection and zymodemes of five isoenzymes. Korean J Parasitol 1999;37:85-92.
- 8. Kong HH, Park JH, Chung DI. Interstrain polymorphisms of isoenzyme profiles and mitochondrial DNA fingerprints among seven strains assigned to Acanthamoeba polyphaga. Korean J Parasitol 1995;33:331-340.
- 9. Kong HH, Chung DI. A riboprinting scheme for identification of unknown Acanthamoeba isolates at species level. Korean J Parasitol 2002;40:25-31.
- 10. Ma P, Visvesvara GS, Martinez AJ, Theodore FH, Daggett PM, Sawyer TK. Naegleria and Acanthamoeba infections: Review. Rev Inf Dis 1990;12:490-513.
- 11. Moura H, Wallace S, Visvesvara GS. Acanthamoeba healyi N. sp. and the isoenzyme and immunoblot profiles of Acanthamoeba spp., Group 1 and 3. J Protozool 1992;39:573-583.
- 12. Page FC. Redefinition of the genus Acanthamoeba with description of three species. J Protozool 1967;14:709-724.
- 13. Page FC. An Illustrated Key to Freshwater and Soil Amoebae. 1976, Ambleside, Cumbria. Freshwater Biological Association; Scientific Publication No. 34.
- 14. Pussard M. Le genre Acanthamoeba Volkonsky 1931 (Hartmannellidae-Amoebida). Protistologica 1966;2:71-93.
- 15. Pussard M, Pons R. Morphologie de la paroi kystique et taxonomic du genre Acanthamoeba (Protozoa, Amoebida). Protistologica 1977;13:557-598.
- 16. Sawyer TK, Griffin JL. A proposed new family, Acanthamoebidae n. fam. (order Amoebida), for certain cyst-forming filose amoebae. Trans Am Microsc Soc 1975;94:93-98.
- 17. Shin HJ, Kim CH, Im KI. Immunological approach for classification of free-living amoeba in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 1992a;30:289-298.
- 18. Shin HJ, Im KI. Analysis of antigenic specificities ofNaegleria fowleri using EITB. Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1992b;23:9-13.
- 19. Shin HJ, La MS, Im KI. Cytotoxicity of Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 (Korean isolate). Yonsei Rep Trop Med 1993;24:31-38.
- 20. Shin HJ, Im KI. Restriction site maps of mitochondrial DNA for Acanthamoeba strain in Korea. Ajou Med J 1996;1:163-168.
- 21. Shin HJ, Im KI, Jeon KW. Restriction endonucleaseanalysis of mitochondrial DNA of Acanthamoeba sp. YM-4 (Korean isolate). Korean J Parasitol 1997;35:119-125.
- 22. Shin HJ, Ji YJ, Cho MS, Kim HI, Park YH, Im KI. Molecular approach on classification of Acanthamoeba Korean isolates using 18S-srRNA analysis. Ajou Med J 1998;3:122-130.
- 23. Visvesvara GS, Balamuth W. Comparative studies on related free-living and pathogenic amoebae with special reference to Acanthamoeba. J Protozool 1975;22:245-256.
Fig. 1Trophozoites of Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-4 in locomotion by a light miroscope (A) and scanning electronic microscope (B), the animals are slightly broad, and have numerous fine spike-like micropseudopodia. Cysts have a nearly circular ectocyst and oval or some irregular endocyst (B).

Fig. 2Isoenzyme zymographic profiles of the
Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-4, and other
Acanthamoeba spp. (
Im et al., 1999).

Fig. 3Protein profiles by SDS-PAGE of trophozoite lysates of the Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-4 and of A. culbertsoni obtained before (Ac-c) and after (Ac-p1,2) mouse brain passage.

Fig. 4Amplified DNA profiles of
Acanthamoeba spp. using a primer of 730. Y4,
Acanthamoeba YM-4; A. cul,
Acanthamoeba culbertsoni; A. hat,
Acanthamoeba hatchetti; A. tri,
Acanthamoeba triangularis; A. pol,
Acanthamoeba polyphaga. L, DNA ladder marker (
Hong et al., 1995).

Fig. 5Unique profile of the mitochondrial DNA map of
Acanthamoeba Korean isolate YM-4 (
Shin and Im, 1996).

Fig. 6RFLP patterns of 18S srDNA of Acanthamoeba spp. digested with six restriction endonucleases. Lanes 1-8, Acanthamoeba culbertsoni, A. healyi, A. castellanii, A. polyphaga, A. hatchetti, A. royreba, Acanthamoeba YM-4 and Acanthamoeba sp. KA/LS5. M, DNA size marker (1 kb ladder).

Fig. 7Dendrogram of the estimated genetic distances of the 18S srDNA of Acanthamoeba spp. by UPGMA cluster analysis.

Table 1.Cytotoxicity of Acanthamoeba lysates on Chinese hamster ovarian cells
Table 1.
|
Groups |
Cytotoxicity activity (%)
|
|
1:1a)
|
1:2 |
1:4 |
1:8 |
1:64 |
|
Acanthamoeba YM-4 |
100 |
99.9 |
88.5 |
67.4 |
38.7 |
|
A. culbertsoni
|
100 |
100 |
100 |
100 |
99.3 |
|
A. polyphaga
|
60.7 |
31.5 |
5.1 |
5.1 |
4.1 |
Table 2.Mortality of the mice infected intranasally with
Acanthameoba spp. (
Im et al., 1999)
Table 2.
|
Amoeba strains |
No. of mice |
Number of dead mice in each post-inoculation day
|
Mortality (%) |
|
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
………………… |
30 |
|
YM-2 |
19 |
|
|
|
3 |
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
9 (47.4) |
|
YM-3 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 (0.0) |
|
YM-4 |
29 |
3 |
5 |
4 |
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
19 (65.5) |
|
YM-5 |
32 |
|
1 |
3 |
4 |
2 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
14 (43.8) |
|
YM-7 |
18 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 (38.9) |
|
A. culbersoni
|
30 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
|
1 |
1 |
|
4 |
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
18 (60.0) |
|
A. hatchetti
|
20 |
|
1 |
3 |
7 |
|
2 |
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
15 (75.0) |
|
A. royreba
|
18 |
|
|
|
1 |
1 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 (16.7) |