Trichinosis is one of the most wide spread helminthic zoonoses. In Korea, its presence was first confirmed in 1998 as encysted larvae in the biopsied muscle of patient, who ate the raw flesh of a badger (
Sohn et al., 2000). Another a small outbreak originating from a wild boar took placed in a mountainous area of Kangwon-do, Korea (
Park et al., 2001). In this study, we performed a molecular biological study to identify the two Korean
Trichinella isolates from two outbreaks at the species level.
Parasites were isolated and maintained in ICR mice. The mouse carcasses, infected with two Korean isolates, were sent to the
Trichinella Reference Center at the Laboratory of Parasitology of the Instituto Superiore di Sanita in Rome, Italy. Muscle larvae (ML) were collected after artificially digesting the mouse carcass (
Pozio, 1987) and washed three times in distilled water. After washing, individual ML were stored in 5 µl of H
2O at -30℃ until used.
For the identification of the ML of the first outbreak (isolate code ISS623), a single ML was placed in 14 ml of Tris-HCl (pH 7.6), overlaid with mineral oil, heated at 90℃ for 10 min, treated with 100 mg/ml of proteinase K at 55℃ for 3 hr, and heated again at 90℃ for 10 min. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was carried out using SB2 primers, which are specific for
Trichinella spiralis (forward 5'-CTCCACTTACGCAATGCACG-3' and reverse 5'-ACACCAAACGGCAACTGCTA-3') (
Wu et al., 1997) and by PCR-RFLP with the primer set Ts43CA (forward 5'-ATGCGAAATATACATTTTTCTTA-3' and reverse 5'-TTAGCTGTATGGGCAAGG-3'), and this was followed by
RsaI restriction for
T. nativa and
T. britovi, in accordance with the protocol of Wu et al. (
1999). Muscle larvae from the reference strains of
T. spiralis (code ISS3),
T. nativa (code ISS10), and
T. britovi (code ISS2) were used as controls (
La Rosa et al., 1992).
To identify ML originating from the second outbreak (isolate code ISS1078), a 0.1 µl solution of 0.1 M Tris-HCL (pH 7.6) and 1.9 µl of H
2O was added to the larva, overlaid with mineral oil, and heated at 90℃ for 10 min. Then, 0.4 µl of proteinase K and 2.6 µl of H
2O were added to the larva at 48℃ for 3 hr and at 90℃ for 10 min. PCR was performed using 4 µl of a single larva preparation, 0.1 µl
Taq DNA polymerase (Takara, Otsu, Shiga, Japan), 5 µl 10X PCR buffer, 4 µl dNTPs, 0.7 µl of primers (I-V primer sets) (
Zarlenga et al, 1999), 0.5 µl DMSO, and H
2O up to 50 µl. Amplifications consisted of 35 cycles of: denaturation at 94℃ for 30 sec, annealing at 62℃ for 20 sec and at 58℃ for 30 sec, and elongation at 72℃ for 1 min. The MLs of reference strains were used as controls. The ISS numbers of the isolates refers to the code of the
Trichinella at the Reference Center (
Pozio et al., 1989).
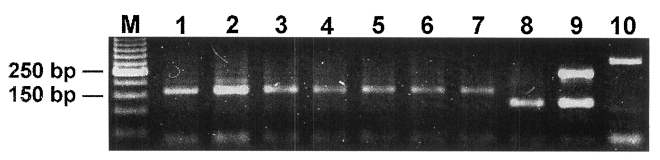
All of the ML from the mice infected with two Korean
Trichinella isolates showed a band similar to that of
T. spiralis larvae of the reference strain (
Fig. 1).
Trichinosis is generally diagnosed by detecting larvae in biopsied muscle and/or by the detection of antibody in the serological test without species differentiation. Recently, rapid and sensitive genotyping tools for
Trichinella have been developed, and studies on the differentiation of genotypes and species of
Trichinella have been performed successfully by several investigators (
Gasser et al., 1998;
Appleyard et al., 1999;
Nagano et al., 1999;
Wu et al., 1999;
Zarlenga et al., 1999). Gasser et al. (
1998) identified 7 isolates from mainland China by PCR-based SSCP. Wu et al. (
1999) applied PCR-RFLP analysis to identify 5 species, i.e.
T. spiralis,
T. nativa,
T. britovi,
T. pseudospiralis and
T. nelsoni, and 3 phenotypes of uncertain taxonomic status (
Trichinella T5, T6 and T8).
Of the 7 isolates from the mainland China, 5 were identified as
T. spiralis and the results upon the other two were identical with those of
T. nativa and
Trichinella T6 (
Gasser et al., 1998). The Japanese isolates from wild animals were identified as
T. britovi by random amplified polymorphic DNA (
Pozio et al., 1996). In the present study, PCR-RFLP and multiple-PCR found that both Korean isolates (ISS623 and ISS1078) showed the same molecular pattern as that of a
T. spiralis reference strain.
According to the new taxonomic scheme, nematodes belonging to the genus
Trichinella are divided into 7 valid species,
T. spiralis,
T. nativa,
T. britovi,
T. pseudospiralis,
T. nelsoni,
T. murrelli and
T. papuae (
Murrell and Pozio, 2000). Among them,
T. spiralis has the widest geographical distribution and the largest range of host species. The majority of human infections are caused by this species (
Capo and Despommier, 1996;
Murrell and Pozio, 2000). However, since the various genotypes or species of
Trichinella are distributed worldwide including Asia,
Trichinella isolates should be examined in detail. In this study, we have identified two Korean
Trichinella isolates infecting human as
T. spiralis.
References
- 1. Appleyard GD, Zarlenga D, Pozio E, Gajadhar AA. Differentiation of Trichinella genotypes by polymerase chain reaction using sequence-specific primers. J Parasitol 1999;85:556-559.
- 2. Capo V, Despommier DD. Clinical aspects of infection with Trichinella spp. Clin Microbiol Rev 1996;9:47-54.
- 3. Gasser RB, Zhu XQ, Monti JR, Dou L, Cai X, Pozio E. PCR-SSCP of rDNA for the identification of Trichinella isolates from mainland China. Mol Cell Probes 1998;2:27-34.
- 4. La Rosa G, Pozio E, Rossi P, Murrell KD. Allozyme analysis of Trichinella isolates from various host species and geographic regions. J Parasitol 1992;78:641-646.
- 5. Murrell KD, Pozio E. Trichinellosis: the zoonosis that won't go quietly. Int J Parasitol 2000;30:1339-1349.
- 6. Nagano I, Wu Z, Matsuo A, Pozio E, Takahashi Y. Identification of Trichinella isolates by polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism of the mitochondrial cytochrome c-oxidase subunit I gene. Int J Parasitol 1999;29:1113-1120.
- 7. Park HY, Huh S, Moon KS, Min HY. Trichinellosis in a group occurred in Inje-gun, Kangwon-do, due to raw eating of wild pig in February, 2001. Abstracts of the 42nd Annual Meeting of the Korean Society for Parasitology. 2001.
- 8. Pozio E. Isoenzymatic typing of 23 Trichinalla isolates. Trop Med Parasitol 1987;38:111-116.
- 9. Pozio E, La Rosa G, Rossi P. Trichinella reference centre. Parasit Today 1989;5:169-170.
- 10. Pozio E, La Rosa G, Yamaguti T, Saito S. Trichinella britovi from Japan. J Parasitol 1996;82:847-849.
- 11. Sohn WM, Kim HM, Chung DI, Yee ST. The first human case of Trichinella spiralis infection in Korea. Korean J Parasitol 2000;38:111-115.
- 12. Wu Z, Nagano I, Fukumoto S, et al. Polymerase chain reaction primers to identify Trichinella spiralis or T. pseudospiralis. Parasitol Int 1997;46:149-154.
- 13. Wu Z, Nagano I, Pozio E, Takahashi Y. Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) for the identification of Trichinella isolates. Parasitology 1999;118:211-218.
- 14. Zarlenga DS, Chute MB, Martin A, Kapel CMO. A multiplex PCR for unequivocal differentiation of all encapsulated and non-encapsulated genotypes of Trichinella. Int J Parasitol 1999;29:1859-1867.
Fig. 1Electrophoretic patterns after multiplex-polymerase chain reaction amplification of Trichinella larvae originating from a badger and from a wild boar in Korea. Lane M, 100 bp ladder; lanes 1-3, larvae from the badger (isolate code ISS623); lanes 4-6, larvae from the wild boar (isolate code ISS1078); lane 7, Trichinella spiralis reference larva (code ISS3); lane 8, T. nativa reference larva (code ISS10); lane 9, T. britovi reference larva (code ISS2); lane 10, T. pseudospiralis reference larva (code ISS13).

Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- From wildlife to humans: The global distribution of Trichinella species and genotypes in wildlife and wildlife-associated human trichinellosis
Cody J. Malone, Antti Oksanen, Samson Mukaratirwa, Rajnish Sharma, Emily Jenkins
International Journal for Parasitology: Parasites and Wildlife.2024; 24: 100934. CrossRef - The dynamics of Trichinella spiralis epidemiology: Out to pasture?
K.D. Murrell
Veterinary Parasitology.2016; 231: 92. CrossRef - The induction of the collagen capsule synthesis by Trichinella spiralis is closely related to protease-activated receptor 2
Mi Kyung Park, Min Kyoung Cho, Shin Ae Kang, Bo Young Kim, Hak Sun Yu
Veterinary Parasitology.2016; 230: 56. CrossRef - Immune Correlates of Resistance to Trichinella spiralis Reinfection in Mice
Ki-Back Chu, Sang-Soo Kim, Su-Hwa Lee, Dong-Hun Lee, Ah-Ra Kim, Fu-Shi Quan
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2016; 54(5): 637. CrossRef - Chemotherapeutic drugs for common parasitic diseases in Korea
Sun Huh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2013; 56(6): 513. CrossRef - An Outbreak of Trichinosis with Molecular Identification of Trichinella sp. in Vietnam
Nguyen Van De, Nguyen Vu Trung, Nguyen Hong Ha, Vu Thi Nga, Nguyen Minh Ha, Pham Thanh Thuy, Le Van Duyet, Jong-Yil Chai
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2012; 50(4): 339. CrossRef - Molecular characterization of 45kDa aspartic protease of Trichinella spiralis
Jong Nam Park, Sang Kyun Park, Min Kyoung Cho, Mi-Kyung Park, Shin Ae Kang, Dong-Hee Kim, Hak Sun Yu
Veterinary Parasitology.2012; 190(3-4): 510. CrossRef - The Fifth Outbreak of Trichinosis in Korea
Ji-Young Rhee, Sung-Tae Hong, Hye-Jung Lee, Min Seo, Suk-Bae Kim
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2011; 49(4): 405. CrossRef - The epidemiology of human trichinellosis in China during 2004–2009
J. Cui, Z.Q. Wang, B.L. Xu
Acta Tropica.2011; 118(1): 1. CrossRef - World distribution of Trichinella spp. infections in animals and humans
Edoardo Pozio
Veterinary Parasitology.2007; 149(1-2): 3. CrossRef - Characterisation of Trichinella isolates from Bulgaria by molecular typing and cross-breeding
R. Kurdova, N. Müller, N. Tsvetkova, L. Michov, D. Georgieva, M. Ivanova, B Gottstein
Veterinary Parasitology.2004; 123(3-4): 179. CrossRef