Abstract
We conducted both the small subunit ribosomal DNA (SSU rDNA) polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) and mitochondrial (mt) DNA RFLP analyses for a genetic characterization of Acanthamoeba isolates from contact lens storage cases of students in Seoul, Korea. Twenty-three strains of Acanthamoeba from the American Type Culture Collection and twelve clinical isolates from Korean patients were used as reference strains. Thirty-nine isolates from contact lens storage cases were classified into seven types (KA/LS1, KA/LS2, KA/LS4, KA/LS5, KA/LS7, KA/LS18, KA/LS31). Four types (KA/LS1, KA/LS2, KA/LS5, KA/LS18) including 33 isolates were regarded as A. castellanii complex by riboprints. KA/LS1 type was the most predominant (51.3%) in the present survey area, followed by KA/LS2 (20.9%), and KA/LS5 (7.7%) types. Amoebae of KA/LS1 type had the same mtDNA RFLP and riboprint patterns as KA/E2 and KA/E12 strains, clinical isolates from Korean keratitis patients. Amoebae of KA/LS2 type had the identical mtDNA RFLP patterns with A. castellanii Ma strain, a corneal isolate from an American patient as amoebae of KA/LS5 type, with KA/E3 and KA/E8 strains from other Korean keratitis patients. Amoebae of KA/LS18 type had identical patterns with JAC/E1, an ocular isolate from a Japanese patient. Three types, which remain unidentified at species level, were not corresponded with any clinical isolate in their mtDNA RFLP and riboprint patterns. Out of 39 isolates analyzed in this study, mtDNA RFLP and riboprint patterns of 33 isolates (84.6%) were identical to already known clinical isolates, and therefore, they may be regarded as potentially keratopathogenic. These results suggest that contact lens wearers in Seoul should pay more attention to hygienic maintenance of contact lens storage cases for the prevention of Acanthamoeba keratitis.
-
Key words: Acanthamoeba, contact lens storage cases, genetic characterization, keratopathogens, Seoul
INTRODUCTION
Free-living amoebae of the genus
Acanthamoeba are ubiquitous in nature and are found in diverse habitats such as soil, water, dust, air-conditioning units, contact lenses and lens cases (
Marciano-Cabral et al., 2000). Several species of
Acanthamoeba leads to serious human diseases, including vision-threatening amoebic keratitis, especially in contact lens wearers, and fatal granulomatous amoebic encephalitis (GAE) in compromised patients. Recent increase in the number of
Acanthamoeba keratitis cases are resulted partly by the increased use of contact lenses (
Illingworth and Cook, 1998;
Schaumberg et al., 1998). A recent study showed that the contamination rate of contact lens storage cases by
Acanthamoeba in Korea was 15.1% (
Lee et al., 1997a) which the rate is much higher than that reported in the west. Lee et al. (
1997a) emphasized the fact that the determination of keratopathogenicity of
Acanthamoeba isolates from the contaminated contact lens storage cases are urgently needed. However, for the time being, there are no established animal models to evaluate the corneal virulence of
Acanthamoeba isolates. Therefore, the evaluation of pathogenic potential of
Acanthamoeba isolates relies on the indirect methods such as genetic characterization and comparisons of the molecular genetic data with clinical isolates from infected corneas (
Lee et al., 1997b).
Acanthamoeba can be easily identified at the generic level because of their trophozoites and cysts have distinctive morphology (
Chung et al., 1998). However, there have been many disputes concerning the validity of morphologic features alone as a tool for identification of
Acanthamoeba isolates at the species level. The morphology of cyst can change according to different culturing conditions and is highly variable even in the same strain.
Several non-morphological methods such as alloenzyme analysis, restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), RFLP of small subunit ribosomal DNA (ssu rDNA) and sequence analysis of ssu rDNA have been recently applied (
De Jonckheere, 1983;
Byers et al., 1990;
Chung et al., 1998;
Stothard et al., 1998). Studies of alloenzyme patterns have suggested other groupings of
Acanthamoeba strains which are not consistent with that devised by Pussard and Pons (
1977). In addition, Kong et al. (
1996) and Chung et al. (
1996) reported intraspecific heterogeneity of the restriction phenotypes of mtDNA and the zymograms of several alloenzymes of
Acanthamoeba.
The examination of restriction-enzyme-site polymorphism of ssu rDNA amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has recently been used to establish taxonomic relationships among
Entamoeba spp. (
Clark and Diamond, 1997),
Naegleria spp. (
De Jonckheere, 1994) and
Acanthamoeba spp. (
Kong and Chung, 1996;
Chung et al., 1998). In the present study, the authors used rDNA PCR-RFLP and mtDNA RFLP analyses to identify and characterize the isolates from contact lens storage cases of students in Seoul, Korea, with special references to their keratopathogenic potential.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Acanthamoeba isolation, cloning and axenization
From contact lens storage cases of students in Seoul, Korea,
Acanthamoeba were isolated and cloned according to the method described by Lee et al. (
1997a). For axenization, a piece of agar plate (0.5×1 cm) covered with the cysts of a clone was treated with 0.1 N HCl for 24 hour and washed three times with glass distilled water. it was then placed in PYG medium (
Lee et al., 1997b) at 25℃.
Twenty-three
Acanthamoeba strains (
Table 1) were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD). Twelve clinical isolates from Korean keratitis patients were also used as reference strains.
mtDNA of 39
Acanthamoeba isolates and reference strains extracted according to the method described by Yagita and Endo (
1990) were digested with 1-6 units of restriction enzyme at 37℃ for 2 hours, or sometimes overnight, in 20 µl reaction volume with the buffers specified for each restriction enzyme (
EcoR I,
Bgl II and
Xba I, Promega, U.S.A.;
Sst I, Gibco BRL, U.S.A., and
Sal I,
Cla I,
Hpa I and
Pvu II, Poscochem, Korea). Digested DNA was electrophoresed in 0.7% agarose gel at 4 v/cm for 1-2 hours. The gel was stained with ethidium bromide for 15 minutes and washed with glass distilled water for 30 minutes. The RFLP pattern of mtDNA of isolates was observed and photographed under an UV transilluminater. The
Hind III digested λ phage DNA was used as the size marker.
The chromosomal DNA of each strain was extracted from
Acanthamoeba trophozoites according to the method described by Kong and Chung (
1996). PCR was performed as described by Chung et al. (
1998). The PCR products of 39
Acanthamoeba isolates were checked by electrophoresis in 1.5% agarose gel at 4 V/cm for 1.5 hours. The amplified ssu rDNA was examined by digestion with eight restriction endonucleases (
Msp I,
Hae III,
Hha I,
Hinf I,
Dde I,
Alu I,
Taq I, and
Sau 96 I; Poscochem, Korea) for 2 hr. The digested DNA was electrophoresed in 2.5% agarose gel (agarose 3 : Nusieve 1) for 1.5 hr. Amplisize
R (Biorad, USA) was used as a size marker. The gel was stained, washed and photographed as described elsewhere. To differentiate small DNA fragments, which were unclear in agarose gel, digested samples were electrophoretically separated in 15% polyacrylamide gel using TBE buffer.
RESULTS
Mitochondiral DNA restriction phenotypes
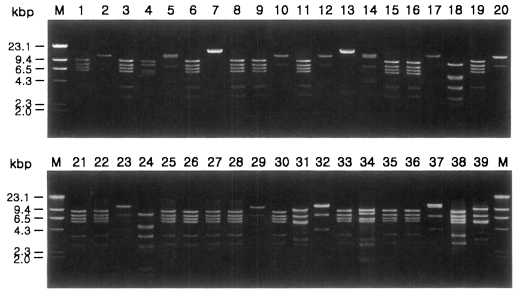
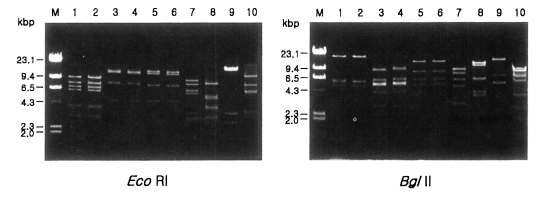
Fig. 1 shows agarose-gel electrophoretic patterns of
EcoR I digested mtDNA from 39
Acanthamoeba isolates. A total of 7 different restriction phenotypes emerged for the isolates by 8 kinds of restriction endonucleases (
Table 2). The most common type was KA/LS1, 20 isolates out of 39 (51.3%), followed by KA/LS2, 8 (20.9%) and KA/LS5, 3 (7.7%). The other 8 isolates divided into 4 different types (KA/LS4, KA/LS7, KA/LS18 and KA/LS31) evenly.
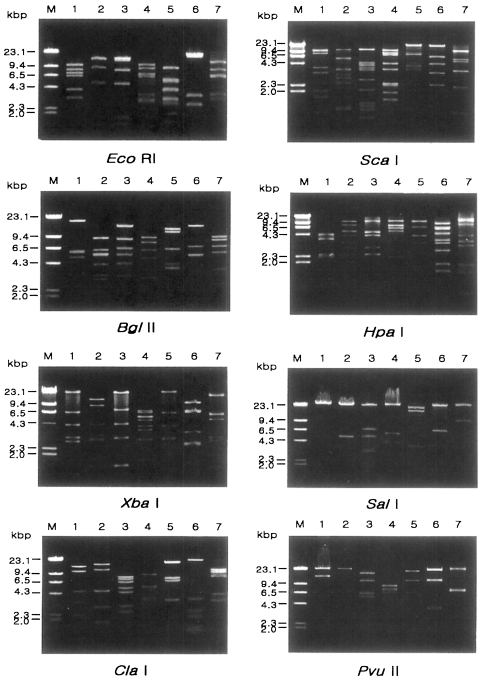
Fig. 2 represents representative patterns by each restriction enzyme.
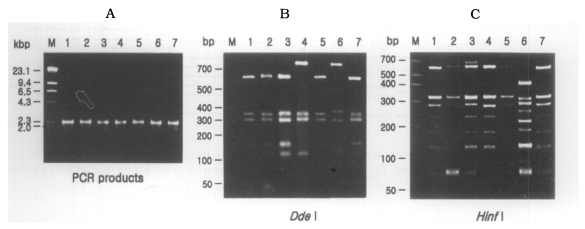
rDNA PCR-RFLP
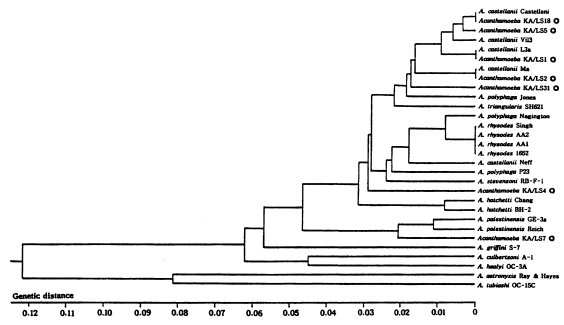
The size of PCR products was approximately 2,300 bp. A total of 7 different rDNA PCR-RFLP patterns (KA/LS1, KA/LS2, KA/LS5, KA/LS4, KA/LS18, KA/LS7 and KA/LS31) emerged for 39 isolates from contact lens storage cases of lens wearers in Seoul. Inferred from a distance matrix table (data not shown) based on the proportions of homologous fragments and estimates of genetic divergence among 7 groups and 23 reference strains, a dendrogram (
Fig. 3) was generated by UPGMA (PHYLIP ver 3.5).
On the basis of rDNA PCR-RFLP, 33 out of 39 isolates were assigned to A. castellanii species complex, and two isolates to A. palestinensis. Remaining four isolates showed peculiar riboprint patterns. Twenty (KA/LS1 type) out of 33 isolates assigned to A. castellanii complex showed identical rDNA PCR-RFLP patterns to A. lugdunensis L3a strain. Eight isolates (KA/LS2 type) shared identical riboprint pattern with A. castellanii Ma strain. Five isolates (KA/LS5 and KA/LS18) revealed very similar riboprint patterns with A. castellanii Castellani strain.
DISCUSSION
Ribosomal RNA gene analysis has been used in phylogenetic studies of unculturable microbes (
Weidner et al., 1996) and for the classification of morphologically indistinguishable protozoa (
Clark et al., 1995;
Clark and Diamond, 1997;
Chung et al., 1998), and it has been generally accepted. The sequence of SSU rDNA is very useful as molecular data for phylogeny and taxonomy; however, the generation of sequence data is labor intensive and expensive, therefore, more than one isolate of a species is rarely analysed. Riboprinting, RFLP analysis of a PCR amplified rRNA gene is simple, inexpensive and fast, and can be used for the classification of
Acanthamoeba spp. (
Chung et al., 1998) especially when a large number of new isolates must be analysed for the survey.
Among the thirty-nine
Acanthamoeba isolates obtained from contact lens storage cases, 37 isolates belonged exclusively to the morphological group II. The high prevalence of morphological group II
Acanthamoeba was previously reported by Lee et al. (
1997a). Almost all amoebic keratitis have been caused by infection with morphological group II
Acanthamoeba in Korea (Hahn et al., personal communication). Furthermore, 31 isolates (79.5%) shared the identical mtDNA RFLP patterns (
Table 2) with corneal isolates from amoebic keratitis patients; 20 isolates shared the identical mtDNA RFLP with KA/E2 or KA/E12, the corneal isolates from Korean patients, three with KA/E3, other corneal isolate, and eight with Ma strain, the corneal isolates from an American patient.
Lee et al. (
1997b) reported that KA/E2 type was the most prevalently isolated from contact lens cases in the Southeast region (Pusan and Taegu) in Korea. The results of the present survey were similar: KA/E2 type was the most prevalent (
Table 3). However, Ma type, which had not been isolated from the survey of the Southeast regions, was isolated at a rate of 20.5% in this survey. Ma type was the most prevalently isolated type (50.0%) from lens storage cases in the Southwest regions (Kwangju and Chonju) in Korea (unpublished data). Therefore, the results in this survey should be intermediate between those in the Southeast and Southwest regions in Korea.
These results showed that the riboprints and mtDNA RFLP patterns of great majority of Acanthamoeba isolates from the lens cases of Korean lens wearers were the same as those of the clinical isolates which could probably be regarded as keratopathogens. More attention should be paid to the prevention of Acanthamoeba contamination and to the disinfection of contact lens storage cases.
References
- 1. Byers TJ, Hugo ER, Stewart VJ. Genes of Acanthamoeba: DNA, RNA and protein sequences. J Protozool 1990;37:17S-25S.
- 2. Chung DI, Kong HH, Yu HS, Oh YM, Yee ST, Lim YJ. Biochemical and molecular characterization of a strain KA/S2 of Acanthamoeba castellanii isolated from Korean soil. Korean J Parasitol 1996;34:79-85.
- 3. Chung DI, Yu HS, Hwang MY, et al. Subgenus classification of Acanthamoeba by ribo-printing. Korean J Parasitol 1998;36:69-80.
- 4. Clark CH, Diamond LS. Intraspecific variation and phylogenetic relationships in the genus Entamoeba as revealed by ribo-printing. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1997;44:142-154.
- 5. Clark CG, Martin DS, Diamond LS. Phylogenetic relationships among anuran trypanosomes as revealed by riboprinting. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1995;42:92-96.
- 6. De Jonckheere JF. Isoenzyme and total protein analysis by agarose isoelectric focusing and taxonomy of the genus Acanthamoeba. J Protozool 1983;30:701-706.
- 7. De Jonckheere JF. Riboprinting of Naegleria spp.: Small-subunit versus large-subunit rDNA. Parasitol Res 1994;80:230-234.
- 8. Douglas M. Notes on the classification of the amoeba found by Castellani in cultures of a yeast-like fungus. J Trop Med London 1930;33:258-259.
- 9. Illingworth CD, Cook SD. Acanthamoeba keratitis. Surv Ophthalmol 1998;42:493-508.
- 10. Jones DB, Visvesvara GS, Robinson NM. Acanthamoeba polyphage keratitis and Acanthamoeba uveitis associated with fatal meningoencephalitis. Trans Ophthalmol Soc UK 1975;95:221-232.
- 11. Kong HH, Chung DI. PCR and RFLP variation of conserved region of small subunit ribosomal DNA among Acanthamoeba isolates assigned to either A. castellanii or A. polyphaga. Korean J Parasitol 1996;34:127-134.
- 12. Lee SM, Choi YI, Chung DI. Contamination of Acanthamoeba in contact lens care system. Korean J Ophthalmol Soc 1997;38:756.
- 13. Lee SM, Choi YI, Ryu HW, Kong HH, Chung DI. Species identification and molecular characterization of Acanthamoeba isolated from contact lens paraphernalia. Korean J Ophthalmol 1997;11:39-50.
- 14. Lewis EJ, Sawyer TK. Acanthamoeba tubiashi n. sp. a new species of fresh-water Amoebida (Acanthamoebidae). Trans Am Micro Soc 1979;98:543-549.
- 15. Ma P, Willaert E, Juechter KB, Stevens AR. A case of keratitis due to Acanthamoeba in New York, and features of 10 cases. J Infect Dis 1981;143:662-667.
- 16. Marciano-Cabral F, Puffenbarger R, Cabral GA. The increasing importance of Acanthamoeba infections. J Eukaryot Microbiol 2000;47:29-36.
- 17. Moura H, Wallace S, Visvesvara GS. Acanthamoeba healyi n. sp. and the isoenzyme and immunoblot profiles of Acanthamoeba spp., Groups 1 and 3. J Protozool 1992;39:573-583.
- 18. Nagington J, Watson PG, Playfair TJ, McGill J, Jones BR. Amebic infection of the eye. Lancet 1974;2:1537-1540.
- 19. Neff RJ. Purification, axenic cultivation, and description of a soil amoeba, Acanthamoeba sp. J Protozool 1957;4:176-182.
- 20. Page FC. Re-definition of the genus Acanthamoeba with descriptions of three species. J Protozool 1967;14:709-724.
- 21. Pussard M, Pons R. Morphologie de la paroi kystique et taxonomie du genre Acanthamoeba (Protozoa, Amoebida). Protistologica 1977;13:557-598.
- 22. Ray DL, Hayes RE. Hartmannella astronyxis: A new species of free-living amoeba. Cytology and life cycle. J Morphol 1954;95:159-188.
- 23. Reich K. Studien er die Bodenprotozoen palstinos. Arch Protistenkd 1993;79:76-97.
- 24. Sawyer TK. Acanthamoeba griffini, a new species of marine amoeba. J Protozool 1971;18:650-654.
- 25. Sawyer TK, Nerad TA, Lewis EJ, McLaughlin SM. Acanthamoeba stevensoni n. sp. (Protozoa: Amoebida) from sewage-contaminated shellfish beds in Raritan bay, New York. J Protozool 1993;40:742-746.
- 26. Sawyer TK, Visvesvara GS, Harke BA. Pathogenic amoebas from brackish and ocean sediments, with a description of Acanthamoeba hatchetti, n. sp. Science 1977;196:1324-1325.
- 27. Schaumberg DA, Snow KK, Dana MR. The epidemic of Acanthamoeba keratitis: where do we stand? Cornea 1998;17:3-10.
- 28. Singh BN. Nuclear division in nine species of small free-living amoeba and its bearing on the classification of the order Amoebida. Phil Trans Roy Soc London, Ser B 1952;236:405-461.
- 29. Singh BN, Das SR. Studies on pathogenic and non-pathgenic small free-living amoebae and the bearing of nuclear division on the classification of the order amoebida. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 1970;259:435-476.
- 30. Stothard DR, Schroeder-Diedrich JM, Awwad MH, et al. The evolutionary history of the genus Acanthamoeba and the identification of eight new 18S rRNA gene sequence types. J Eukaryot Microbiol 1998;45:45-54.
- 31. Weidner S, Arnold W, Puhler A. Diversity of uncultured microorganisms associated with the seagrass Halophila stipulacea estimated by restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of PCR-amplified 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 1996;62:766-771.
- 32. Yagita K, Endo T. Restriction enzyme analysis of mitochondrial DNA of Acanthamoeba strains in Japan. J Protozool 1990;37:570-575.
Fig. 1Agarose gel electrophoretic restriction fragment patterns by EcoR I of mitochondrial DNA of Acanthamoeba 39 isolates. M, Hind III digested λ phage DNA as a DNA size standard.

Fig. 2Agarose gel eletrophoretic restriction fragment patterns of mitochondrial DNA of seven different types of Acanthamoeba by eight kinds of restriction enzymes. M, Hind III digested λ phage DNA as a DNA size standard. Lane 1, KA/LS1; 2, KA/LS2; 3, KA/LS5; 4, KA/LS4; 5, KA/LS18; 6, KA/LS7; 7, KA/LS31.

Fig. 3(A) Agarose gel electrophoretic pattern of PCR products of SSU rDNA of 7 types of Acanthamoeba isolates; M, Hind III digested λ phage DNA. (B)(C) Electrophoretic patterns of restriction fragments of PCR product from 7 types of Acanthamoeba isolates by Dde I and Hinf I; B, Agarose gel; C, Polyacrylamide gel; M, 50 bp ladder (BM, Germany); Lane 1, KA/LS1; 2, KA/LS2; 3, KA/LS5; 4, KA/LS4; 5, KA/LS18; 6. KA/LS7; 7, KA/LS31.

Fig. 4UPGMA phenogram of 7 different types and 23 reference strains of Acanthamoeba based on the SSU rDNA PCR-RFLP analyses. ◎; 7 different types of Acanthamoeba isolates from contact lens storage cases.

Fig. 5Comparative mitochondrial DNA RFLP patterns of Acanthamoeba isolated from contact lens storage cases with those of reference strains from keratitis. Lane 1, KA/LS1; 2, KA/E2; 3, KA/LS2; 4, Ma; 5, KA/LS5; 6, KA/E3; 7, KA/LS4; 8, KA/LS18; 9, KA/LS7; 10, KA/LS31; M, Hind III digested λ phage DNA.

Table 1.List of Acanthamoeba 35 reference strains
Table 1.
|
No. |
Strain |
ATCC No. |
Virulence |
Environmental source |
Geographic source |
Reference |
Former species designation |
|
1 |
Castellani |
30011 |
+ |
yeast culture |
England |
Douglas (1930) |
A. castellanii
|
|
2 |
L3a |
50240 |
+ |
swimming pool |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1997) |
A. lugdunensis
|
|
3 |
Vil3 |
50241 |
nda)
|
swimming pool |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1997) |
A. quina
|
|
4 |
Jones |
30461 |
+ |
keratitis |
U.S.A. |
Jones et al. (1975) |
A. polyphaga
|
|
5 |
SH621 |
50254 |
nd |
human feces |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1997) |
A. triangularis
|
|
6 |
Nagington |
30873 |
+ |
keratitis |
England |
Nagington et al. (1974) |
A. polyphaga
|
|
7 |
Singh |
30973 |
— |
soil |
England |
Singh (1952) |
A. rhysodes
|
|
8 |
1652 |
50253 |
— |
soil |
Morocco |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. mauritaniensis
|
|
9 |
AA2 |
50238 |
— |
soil |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. divionensis
|
|
10 |
AA1 |
50251 |
— |
soil |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. paradivionensis
|
|
11 |
Neff |
30010 |
— |
soil |
U.S.A. |
Neff (1957) |
A. castellanii
|
|
12 |
Ma |
50370 |
+ |
keratitis |
U.S.A. |
Ma et al. (1981) |
A. castellanii
|
|
13 |
P23 |
30871 |
— |
fresh-water |
U.S.A. |
Page (1967) |
A. polyphaga
|
|
14 |
Chang |
30898 |
+ |
fresh water |
U.S.A. |
Byers et al.(1990) |
A. castellanii
|
|
15 |
BH-2 |
30730 |
+ |
ocean sediment |
U.S.A. |
Sawyer et al.(1977) |
A. hatchetti
|
|
16 |
RB-F-1 |
50388 |
nd |
ocean sediment |
U.S.A. |
Sawyer et al. (1993) |
A. stevensoni
|
|
17 |
S-7 |
30731 |
+ |
beach-bottom |
U.S.A. |
Sawyer (1971) |
A. griffini
|
|
18 |
Ray & Hayes |
30137 |
nd |
soil |
U.S.A. |
Ray & Hayes (1954) |
A. astronyxis
|
|
19 |
OC-15C |
30867 |
nd |
river |
U.S.A. |
Lewis & Sawyer (1979) |
A. tubiashi
|
|
20 |
A-1 |
30171 |
+ |
tissue culture |
U.S.A. |
Singh & Das (1970) |
A. culbertsoni
|
|
21 |
OC-3A |
30866 |
+ |
GAEb)
|
U.S.A. |
Moura et al. (1992) |
A. healyi
|
|
22 |
GE-3a |
50252 |
— |
swimming pool |
France |
Pussard & Pons (1977) |
A. pustulosa
|
|
23 |
Reich |
30870 |
— |
soil |
Israel |
Reich (1933) |
A. palestinensis
|
|
24 |
KA/E1 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
25 |
KA/E2 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
26 |
KA/E3 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
27 |
KA/E4 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
28 |
KA/E5 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
29 |
KA/E6 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
30 |
KA/E7 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
31 |
KA/E8 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
32 |
KA/E9 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
33 |
KA/E10 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
34 |
KA/E11 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
|
35 |
KA/E12 |
— |
+ |
keratitis |
Korea |
— |
— |
Table 2.Isolates of Acanthamoeba spp. from contact lens paraphernalias and restriction phenotypes of SSU rDNA and mitochondrial DNA
Table 2.
|
Isolates |
rDNA RFLP phenotype |
Mt DNA RFLP phenotype |
finally assigned species |
associated pathogenic strains |
|
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS2 |
KA/LS2 |
KA/LS2 |
A. castellanii
|
Ma |
|
KA/LS3 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS4 |
KA/LS4 |
KA/LS4 |
? |
— |
|
KA/LS5 |
KA/LS5 |
KA/LS5 |
A. castellanii
|
KA/E3, KA/E8 |
|
KA/LS6 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS7 |
KA/LS7 |
KA/LS7 |
? |
— |
|
KA/LS8 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS9 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS10 |
KA/LS2 |
KA/LS2 |
A. castellanii
|
Ma |
|
KA/LS11 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/SL12 |
KA/LS2 |
KA/LS2 |
A. castellanii
|
Ma |
|
KA/LS13 |
KA/LS7 |
KA/LS7 |
? |
— |
|
KA/LS14 |
KA/LS5 |
KA/LS5 |
A. castellanii
|
KA/E3, KA/E8 |
|
KA/LS15 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS16 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS17 |
KA/LS2 |
KA/LS2 |
A. castellanii
|
Ma |
|
KA/LS18 |
KA/LS18 |
KA/LS18 |
A. castellanii
|
JAC/E1a)
|
|
KA/LS19 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS20 |
KA/LS2 |
KA/LS2 |
A. castellanii
|
Ma |
|
KA/LS21 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS22 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS23 |
KA/LS2 |
KA/LS2 |
A. castellanii
|
Ma |
|
KA/LS24 |
KA/LS18 |
KA/LS18 |
A. castellanii
|
JAC/E1 |
|
KA/LS25 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS26 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS27 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS28 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS29 |
KA/LS2 |
KA/LS2 |
A. castellanii
|
Ma |
|
KA/LS30 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS31 |
KA/LS31 |
KA/LS31 |
? |
— |
|
KA/LS32 |
KA/LS2 |
KA/LS2 |
A. castellanii
|
Ma |
|
KA/LS33 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS34 |
KA/LS4 |
KA/LS4 |
? |
— |
|
KA/LS35 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS36 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS37 |
KA/LS5 |
KA/LS5 |
A. castellanii
|
KA/E3, KA/E8 |
|
KA/LS38 |
KA/LS1 |
KA/LS1 |
A. lugdunensis
|
KA/E2, KA/E12 |
|
KA/LS39 |
KA/LS31 |
KA/LS31 |
? |
— |
Table 3.Comparison of mtDNA RFLP type of Acanthamoeba isolates from contact lens paraphernalias of different areas of Korea
Table 3.
|
Type |
Seoul |
Southeast |
Southwest |
Total |
|
KA/E2 |
20 (51.3%) |
18 (64.3%) |
8 (19.0%) |
46 (43.8%) |
|
KA/E3 |
3 (7.7%) |
1 (3.6%) |
21 (50.0%) |
25 (23.8%) |
|
A. castellanii Ma |
8 (20.5%) |
0 (0.0%) |
9 (21.4%) |
17 (16.2%) |
|
Others |
8 (20.5%) |
9 (32.1%) |
4 (9.5%) |
17 (16.2%) |
|
Total |
39 |
28 |
42 |
105 |