Abstract
Cystic echinococcosis is a zoonotic parasitic disease caused by Echinococcus species. Tanzania is one of the endemic countries with cystic echinococcosis. This study focussed on identifying genotypes of Echinococcus spp. in Tanzania. We collected 7 cysts from cattle in Mwanza municipal (n=4) and Loliondo district (n=3). The cysts from Mwanza were all E. ortleppi and fertile. In contrast, the cysts from Loliondo were all E. granulosus sensu stricto and sterile. Two from the 4 cysts were a new haplotype of E. ortleppi (G5). These results can improve the preventive and control programs for humans and livestock in Tanzania. To our knowledge, this study is considered the first to identify the genotype and haplotype of Echinococcus spp. in Tanzania.
-
Key words: Echinococcus granulosus, sensu stricto, Echinococcus ortleppi, Tanzania, genetic phylogeny, cattle
INTRODUCTION
Cystic echinococcosis (CE) is a parasitic zoonosis caused by
Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato (s.l.) [
1]. The recent taxonomic classification of
E. granulosus s.l. based on genetic information from both mitochondrial and nuclear genes proposed 5 species have been demarcated from the 10 genotypes (G1 to G10):
E. granulosus sensu stricto (s.s.) (genotypes G1–G3),
E. equinus (genotype G4),
E. ortleppi (genotype G5),
E. canadensis (genotypes G6–G10), and
E. felidis [
2,
3]. In addition,
E. granulosus s.l. has intraspecific microdiversity within and between sub-populations that constructed haplotype networks associated with the hosts and geographic distribution [
4,
5]. The variations in the genotypes of
E. granulosus s.l. may affect the location, fertility of cysts, the severity of CE infection in intermediate hosts, and response to chemotherapy [
1].
E. granulosus s.s. shows a large geographical distribution and host range [
6,
7].
It was reported that CE is endemic in Tanzania [
8] and prevalent in the intermediate hosts [
9] and human [
10,
11]. A retrospective survey in Ngorongoro district (one of the Maasai areas) in the northern Tanzania reported CE prevalence in humans, 10 cases per 100,000 people per year [
12]. In the same district, incidence of CE was estimated as 63.8% in sheep, 34.7% in goats, and 48.7% in cattle [
9]. The data on the prevalence and genetic diversity of
Echinococcus spp. in the African countries including Tanzania is scarce. This situation calls for an investigation on the genetic features of CE in Tanzania. Therefore, this study was, conducted to clarify the genotypes of
Echinococcus spp. from cattle, an intermediate host in Tanzania.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study area and sample collection
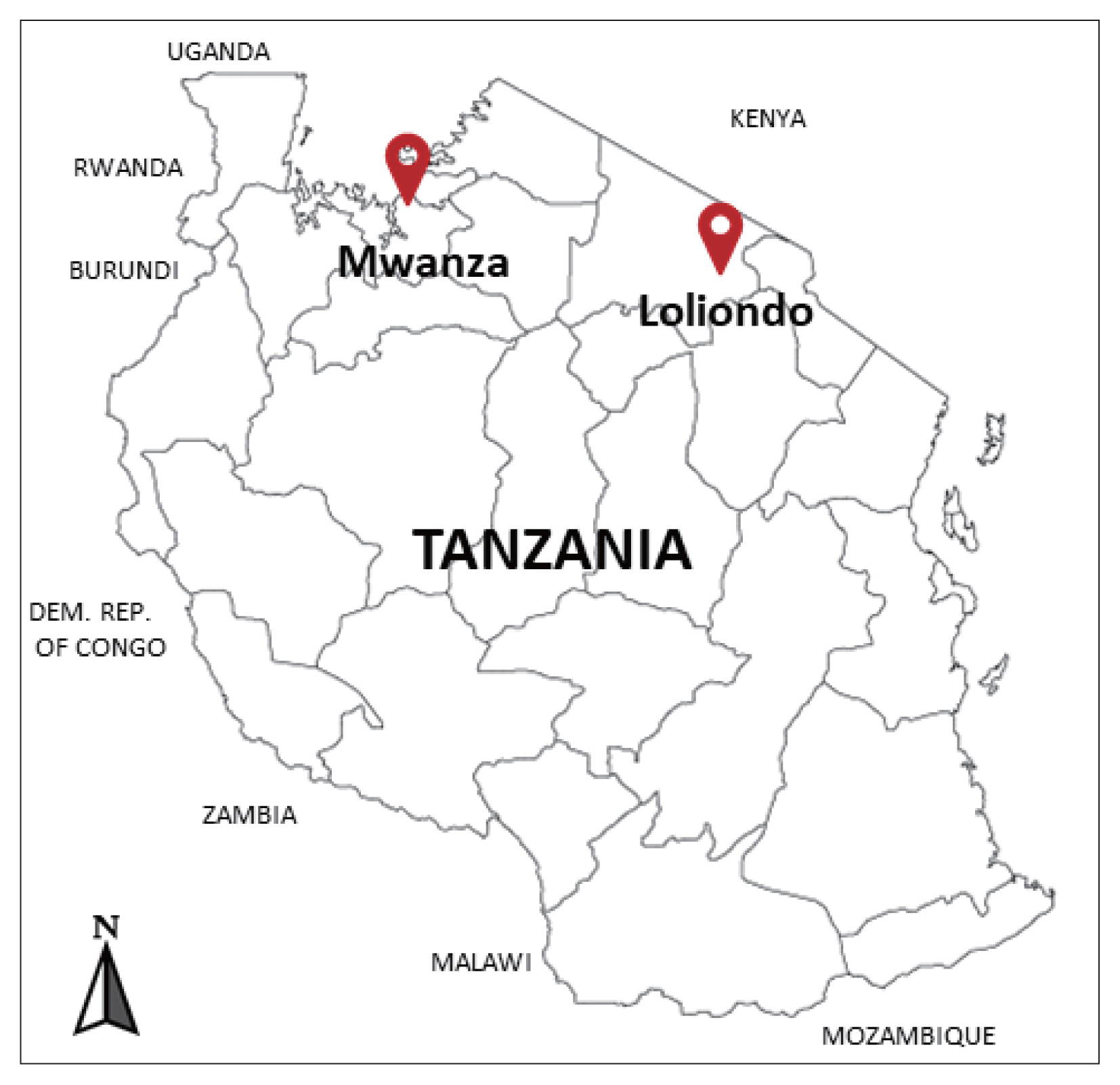
The cysts were collected between December 2018 and February 2019 from the lung of indigenous cattle breed (Tanzania Shorthorn Zebu) in slaughterhouses located in 2 regions; one in the city area (Mwanza, northwestern Tanzania) (2°31′ 0″S, 32°54′ 0″E), and the other in a far remote area (Loliondo, northern Tanzania) (2° 3′ 0″S, 35° 37′ 0″E) a specialized territory of Maasai people (
Fig. 1).
A single hydatid cyst was collected from each carcass of cattle during the general postmortem inspection in the slaughterhouses. The collected cysts were individually kept in 70% ethanol in a plastic lab container and transferred to a laboratory. The germinal layer and hydatid liquid were separated for further study. A total of 7 cysts from the lung were sampled, 4 in Mwanza and 3 in Loliondo. The cysts collected in Mwanza were coded as EG_TZ01, EG_TZ03, EG_TZ06, and EG_TZ07, while those in Loliondo as EG_TZ10, EG_TZ12, and EG_TZ13.
Morphological analysis on the cysts
All cysts were assessed for protoscoleces and rostellar hooks in the germinal layer, and hydatid fluid using a dissecting microscope [
13]. The protoscoleces found in the fertile cysts (
Fig. 2) were isolated and stained in Hoyer’s medium [
14]. The rostellar hooks of
E. granulosus s.l. protoscoleces were analyzed for 5 variables: number per rostellum, blade and total lengthes according to the protocol of Ponce Gordo and Cuesta Bandera [
15]. The obtained measurements were compared with previous studies from Iran [
16], Jordan [
17], Poland [
18], and Spain [
15] (
Table 1).
The CE DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (QIAGEN®) according to the manufacturer’s protocol with some modifications. A small (<2 mm) piece of germinal layer kept in 70% ethanol was washed within PBS using a shaker overnight, and collected by centrifuging at 8,000 rpm. The samples were crushed with a pestle and motor, genomic DNA was extracted and kept at −20°C until use.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was carried out targeting the mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase 1 (
cox1) gene. A primer pair JB3 (5′-TTT TTT GGG CAT CCT GAG GTT TAT-3′) and JB4.5 (5′-TAA AGA AAG AAC ATA ATG AAA ATG-3′) was used to amplify a 408 bp fragment of the
cox1 gene [
19]. The PCR reaction mix was in 40 μl volume, containing 8 μl HiPi Plus 5× PCR Master Mix, 12.5 pmol each forward and reverse primers, 26 μl distilled water, and 4–20 ng CE DNA. The PCR reaction was carried out using an automatic thermal cycler (SuperCycler SC-200, Kyratec, Mansfield/Queensland, Australia), whereby a pre-denaturation was set for 3 min at 95°C. Thirty-five cycles of DNA denaturation for 30 sec at 95°C, annealing for 30 sec at 47°C, and extention for 1 min at 72°C, with a final extension at 72°C for 10 min. The PCR products were run on 1% agarose gel, and the images were taken on a gel-imaging device (Gel Doc
TM XR+System, BIO-RAD, Hercules, California, USA).
The amplicons were sequenced by a biomolecular company (Cosmogenetech Co, Daejeon, KOREA),and aligned using Geneious software Version 9.0 [
20]. The sequenced samples were trimmed and assembled using De novo sequence assemblers, and subjected to homolog search In NCBI (
http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST.cgi).
The obtained sequences were compared with the reference sequences of
E. granulosus s.s. and
E. ortleppi from the GenBank to observe the phylogenetic relationships between individuals.
Taenia asiatica were added as an outgroup [
21]. MEGA v.6 software (
https://www.megasoftware.net/resources) [
22] and maximum likelihood (ML) method [
23] were used to root the phylogenetic tree. The Bayesian information criterion (BIC) value was determined with the HKY +I (Hasegawa-Kishino-Yano+invariant sites) method, with 1,000 bootstrap replications estimated to get high confidence. According to mutation steps, the haplotype networks were generated using the NETWORK software that depends on statistical parsimony after creating the data file for the cox1 genetic locus. Finally, DNA Sequence Polymorphism analyses were performed by utilizing the DnaSP v.6 software to estimate several measures of DNA sequence variation within and between populations [
24].
RESULTS
Fertility of cysts and morphology of protoscolex
All cysts (n=4) in the Mwanza were confirmed fertility, while those (n=3) in Loliondo were found sterile. The rostellar hooks (28–36) were lined in 2 rows. Total length of large hooks was 24.5 μm (22.2–29.5) and small hooks was 17.2 μm (14.8–19.7). The blade length of large and small hooks were 17.2 μm (14.8–19.7) and 8.1 μm (7.4–9.8), respectively (
Table 1).
The 7 DNA samples were amplified by PCR and yielded 408 bp fragments as partial
cox1. The resulting gene sequences were translated into amino acids under the flatworm mitochondrial genetic code conditions and uploaded to the GenBank with accession numbers (MN540096-MN540101 and MW729426). The DNAs of EG_TZ03, EG_TZ06, and EG_TZ07 (MN540101, MN540100, and MN540099) obtained from Mwanza showed 100% sequence similarity to
E. ortleppi genotype (G5) (MH428013, JX854035, and MK492625) from India and Egypt [
25]. However, EG_TZ01 (MW729426) showed 99.4% similarity, one substitution (373 G/A), to
E. ortleppi genotype (G5) from India and Egypt [
25]. This single nucleotide substitution results in a nonsynonymous change at position 126 with Alanine to Threonine.
The EG_TZ10 and, EG_TZ13 from Loliondo showed 100% similarity with
E. granulosus s.s. (G1) sequences) from Australia [
26], and (MH542383) from Iran [
27]. The sequence of EG_TZ12 from Loliondo showed 99.4% similarity with those of EG_TZ10 and EG_TZ13, with single nucleotide substitution (135 C/T). At the same time, the sequence of EG_TZ12 showed 100% similarity with
E. granulosus s.s. (G1) sequences from Mongolia, China [
28], and Jordan [
6] (MK370108, AB491414, and JQ250806).
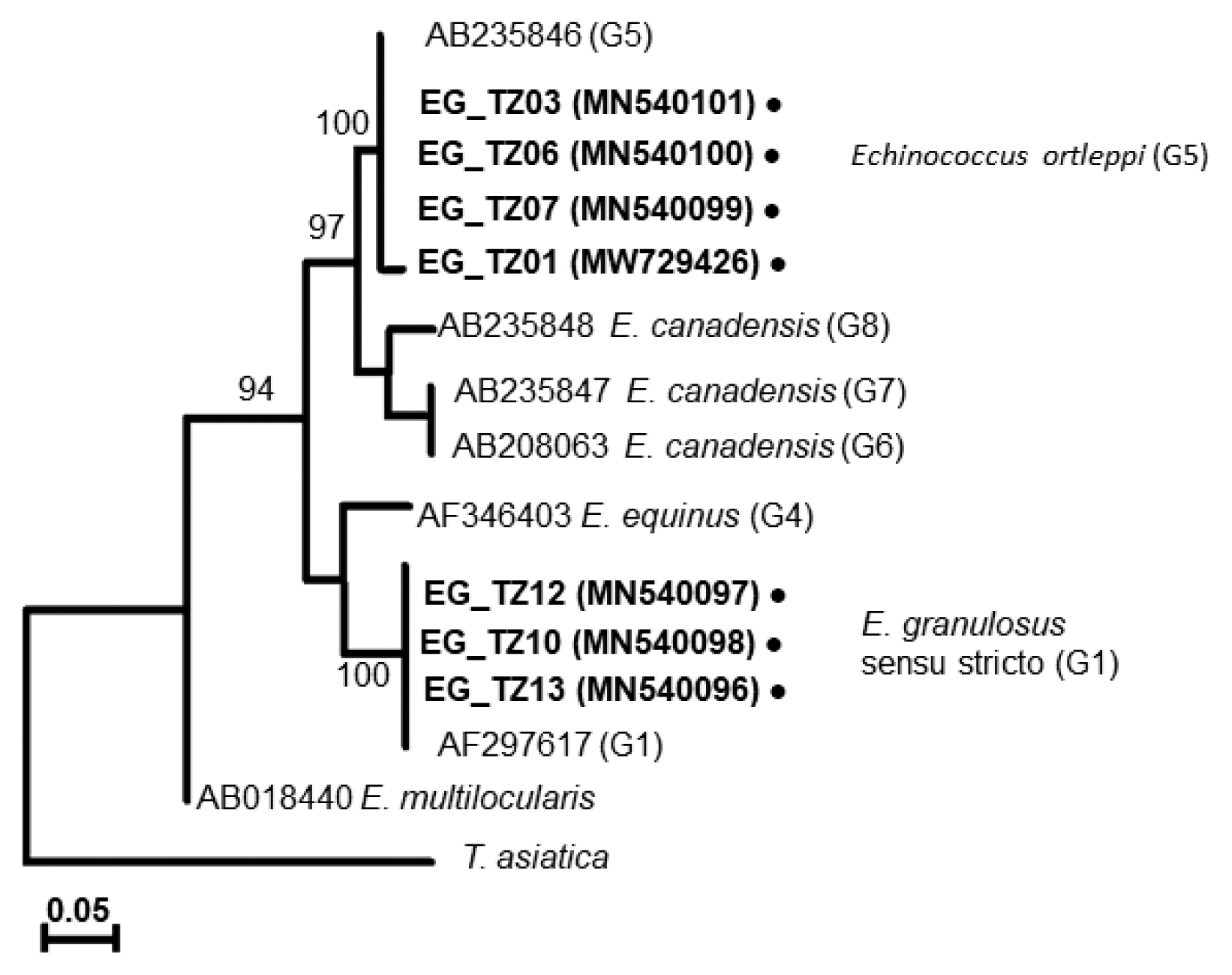
A phylogenetic tree drawn with the collected samples revealed 2 main clades: one with
E. granulosus s.s. (G1), another with
E. ortleppi (G5) (
Fig. 3), distinguished from the previously reported
Echinococcus genotypes [
29–
34] (
Supplementary Table S1). In Loliondo, all isolated samples were identified to genotype (G1), and sequences were divided into 2 haplotypes (marked as EgTZ01 and EgTZ02). One sample (EG_TZ12) grouped with the haplotypes from Iran, China, Jordan, Peru, and Mongolia [
6], the other 2 samples (EG_TZ10 and EG_TZ13) grouped with one haplotype of Iran, Turkey, Armenia, and Australia. [
26].
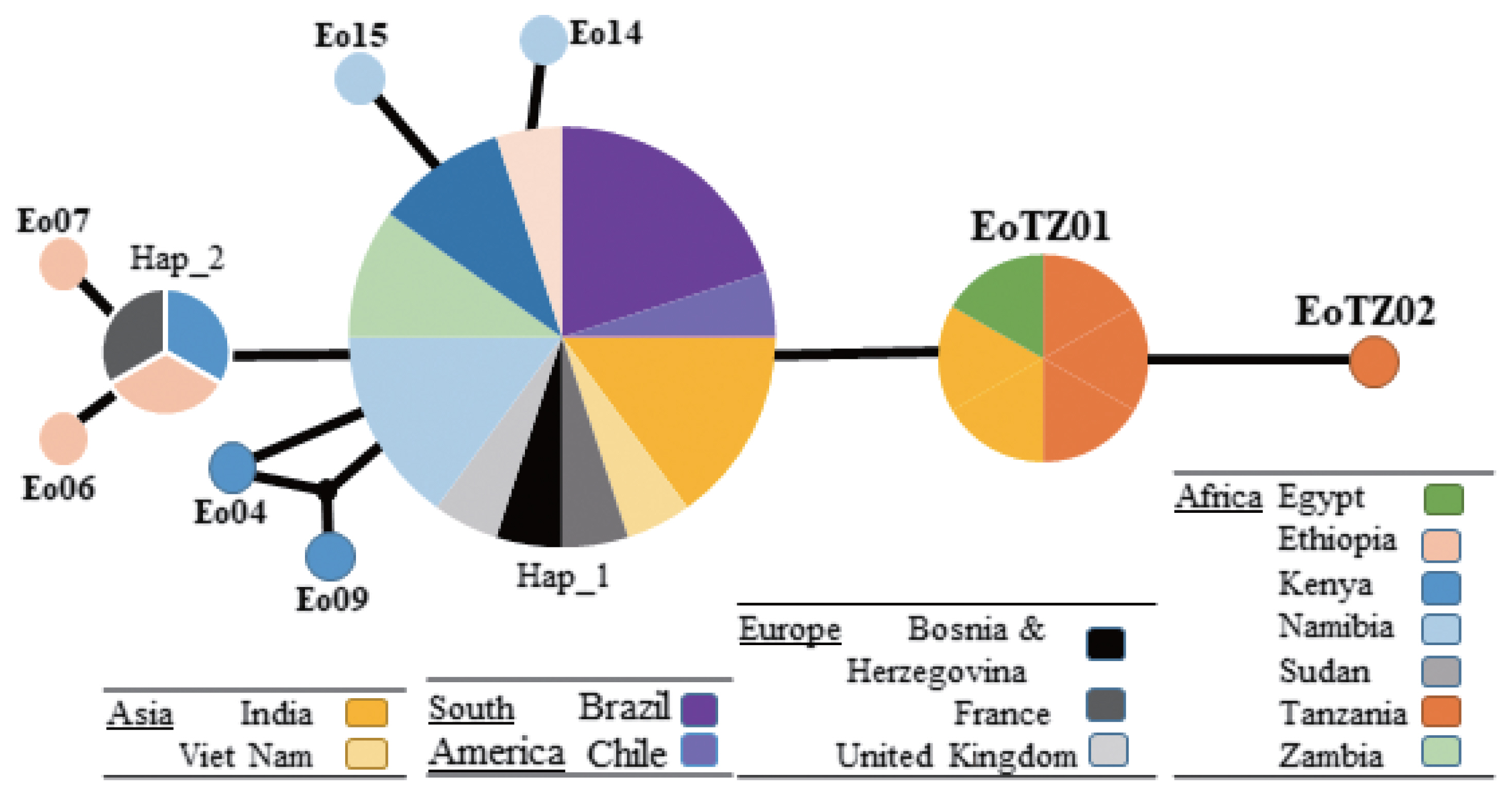
In Mwanza, 2 haplotypes were found in the 4 collected samples under the genotype (G5). A new haplotype (EoTZ02) was found from one sample (EG_TZ01), and another haplotype (EoTZ01) was found from the other 3 samples. The haplotypes from Mwanza were grouped with all reported sequences. As a result, 10 haplotypes (Hap 1, Hap 2, Eo04, Eo06, Eo07, Eo09, Eo14, Eo15, EoTZ02, and EoTZ02) were inferred from the
E. ortleppi isolates’ sequences, which included 10 polymorphic sites. The haplotype network had an orbit-shaped profile with a dominant haplotype in the center similar to previously reported common haplotypes in Africa, Asia, Europe, and South America. However, both of the haplotypes from Mwanza belonged to the minor haplotypes. A haplotype network of
E. ortleppi (G5) was illustrated (
Fig. 4) to understand the phylogenetic relationships between the haplotypes from this study and other Sub-Saharan countries [
35] (
Supplementary Table S1).
DISCUSSION
In the present study, the CE was only found in the cattle of the exanimated carcasses in Mwanza and Loliondo. However, numerous studies reported that livestock such as sheep, goats [
36], and pigs [
37] are at risk of CE infection in Tanzania. The small ruminants play an essential role in the life cycle of
Echinococcus spp., compared to other animals [
36].
In Africa, particularly in Algeria, Ethiopia, Morocco, and Tunisia, the dominant genotype is (G1); it infects the intermediate host (sheep, camel, cattle, and goat), humans, and the definitive host (dogs) [
38,
39]. However, other studies revealed that the
E. canadensis (G6) was the dominant genotype in Sudan [
39], Egypt [
40], Mauritania [
41], and Nigeria [
42].
The present study found that the
E. granulosus s.s. (G1–G3) in cattle from Loliondo has a similar predominant haplotype (G1) to the one previously described from Australia [
26], China, Iran, Jordan, Mongolia, and Peru [
6]. The similarity of the obtained genotype
E. granulosus s.s. is related to its population expansions during the anthropogenic movement of intermediate and definitive hosts [
28]. It was mentioned that the origin of
E. granulosus s.s. was from Middle East [
6]. Hence, it can be assumed that
E. granulosus s.s. in Tanzania comes from the Middle East via the migration of the intermediate and definitive hosts.
The present study obtained the main genotype
E. ortleppi (G5) infecting cattle only in Mwanza, Tanzania. In Africa,
E. ortleppi CEs were reported from the livestock (cattle, goat, camel and, pig), wildlife (oryx) [
35], and human [
43].
E. ortleppi (G5) was the predominant genotype that causes echinococcosis in Namibia and Zambia [
39]. In contrast, in other African countries, the proportion of infected animals with
E. ortleppi was low [
39,
43].
Although it is interesting to note that different genotypes were found in small numbers of slaughtered cattle in 2 distant regions, it is somewhat difficult to guess the dominant genotype from these results. In addition, we predicted the existence of other species such as
E. felidis in Loliondo district because this land uses wildlife-controlled areas inhabited predominantly by Maasai, who practice traditional pastoralism. Also, the disease was reported in wildlife in neighbor countries (Uganda) [
9]. However, to our knowledge, this is the first molecular report of
E. ortleppi and
E. granulosus s.s. infection in the intermediate host from Tanzania. Both species of
Echinococcus reported in this study are pathogens to humans with a significant public health concern [
1,
9], which sets the basis to explore further whether
E. ortleppi and
E. granulosus s.s. are also responsible for human infection in Tanzania.
The haplotypes in this study differed in low intraspecific diversity compared with the predominant haplotypes of
E. ortleppi genotype reported from the neighboring countries (Kenya and Zambia) and Brazil, France, and Namibia [
35]. The low intraspecific diversity was also reported [
35] compared to 178 cases of
E. ortleppi in Sub-Saharan Africa, Europe, and South America.
The fertility of cysts is one of the essential factors for the spread of the parasites in the environment and continuity of the life cycle of
Echinococcus species. The cysts of the
E. ortleppi in cattle are usually fertile [
35] as obtained in Mwanza.
The morphological characteristic of protoscoleces, the number and length of rostellar hooks, have been used to distinguish species and strains of
Echinococcus [
44]. The rostellar hooks in Tanzanian samples had a similar size to that of Spanish ones [
15] and smaller than that of Jordanes [
44] and Iranian [
16] (
Table 1). However, with the morphology characteristic of protoscoleces only, we cannot find a way to distinguish the species of
E. granulosus as did Ihsan et al. [
17]. The identification of
Echinococcus species should not be based only on the morphology of rostellar hooks of protoscoleces.
In conclusion, our findings obtained that cattle may play a significant part in the life cycle of CE, highlighting the possibility of potential transmission risks to the human population and other intermediate hosts in Tanzania. More importantly, we obtained the molecular data E. granulosus s.s. and E. ortleppi for the first time in Tanzania; additional epidemiological research on the prevalence of this species and its involvement in humans, stray dogs, and wildlife to understand CE in Tanzania better are required.
Supplementary Information
Notes
-
We have no conflict of interest related to this work.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation (NRF) with the project “Research life and the Evolutionary ecology of pathogenic Neodermata and construction of a database for species information” (Grant No. 2020R1I1A3A04037914) and the program of Korea Research Fellowship (Grant No. 2020 H1D3A1A02081496).
Fig. 1Investigated areas for collection of the echinococcal cysts from the cattle in Mwanza municipal and Loliondo district, Tanzania.
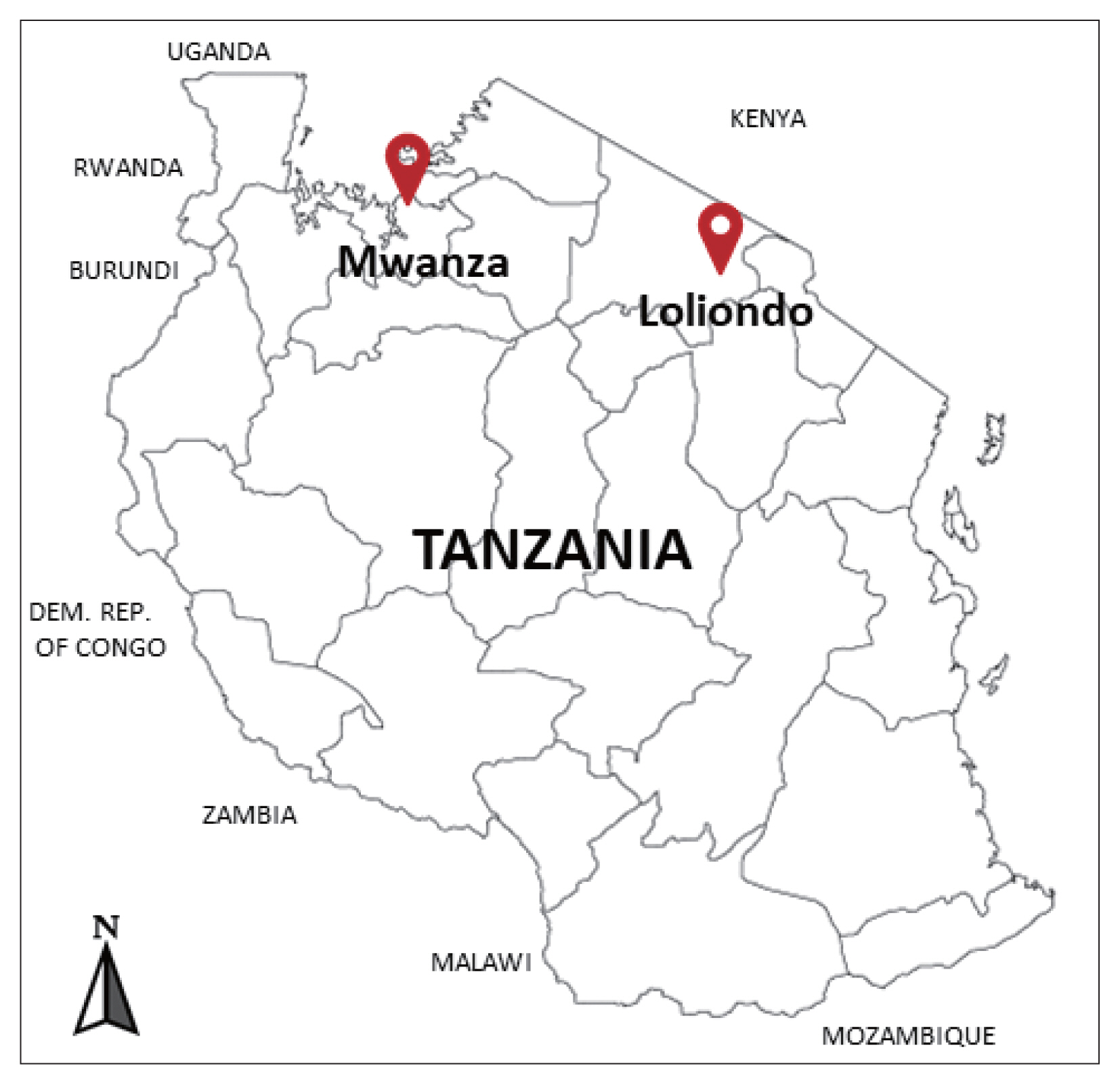
Fig. 2Protoscoleces of Echinococcus ortleppi isolated from the cattle in Mwanza, Tanzania. (A) An invaginated scolex. (B) An evaginated scolex. (C) An evaginated scolex presenting rostellar hooks. (D) Hooks of a cyst. Scale bar (A–C)=50 μm, (D)=10 μm.

Fig. 3A phylogenetic tree based on cox1 sequences of Echinococcus cysts collected from Tanzanian cattle.
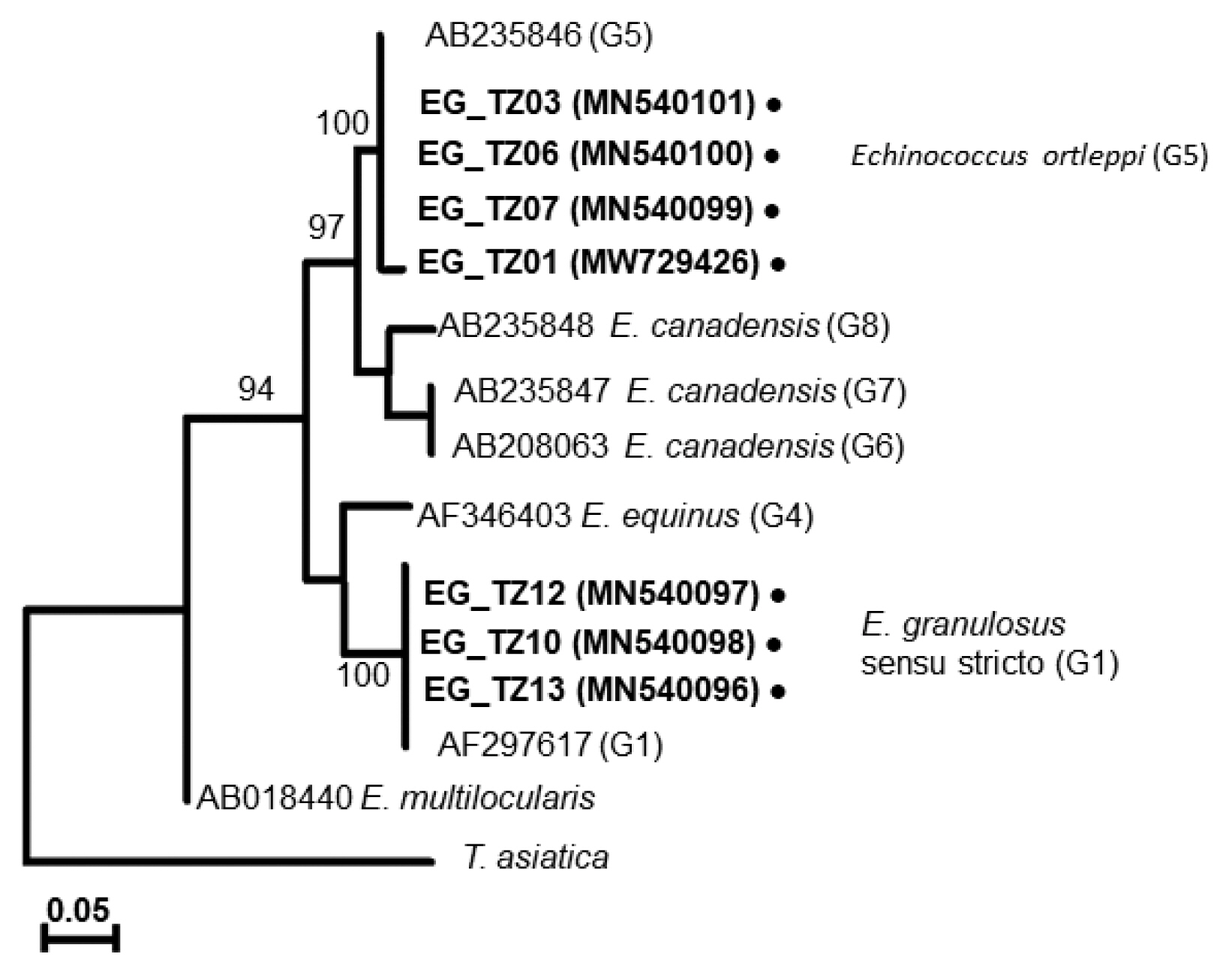
Fig. 4Haplotype networks generated using cox1 of Echinococcus ortleppi cysts isolated from various geographic locations. Circle size is relative to haplotype frequency. Small circles indicate additional mutational steps.

Table 1Morphometric and molecular data of protoscoleces of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato isolated from Europe (Spain, Poland), Asia (Jordan, Iran), and Africa (Tanzania)
Table 1
|
Origin |
Host |
Total no. of hooks |
Large hooks (μm) |
Small hooks (μm) |
Molecular character |
Reference |
|
|
|
Total length |
Blade length |
Total length |
Blade length |
|
Iran |
Sheep |
35.2±2.5 |
23.9±1.9 |
11.9±1.0 |
19.2±1.7 |
7.8±1.4 |
G1 |
[16] |
|
Human |
35.2±2.5 |
23.8±1.5 |
11.6±1.3 |
19.2±2.6 |
8±1.1 |
G1 |
|
|
Cattle |
37.2±2.3 |
27.4±2.1 |
13.8±1.6 |
21.1±2 |
9.7±2.1 |
G1 |
|
|
|
Jordan |
Sheep |
33±1.8 (29–36) |
25.7±0.9 (24–28) |
14.7±0.9 (13–17) |
22.2±1.0 (21–24) |
10.8±0.9 (9–14) |
ND |
[17] |
|
Human |
50±4.3 (45–56) |
23.4±1.1 (21–26) |
14.5±1.2 (11–18) |
19.3±1.9 (14–21) |
11.8±1.2 (8–14) |
ND |
|
|
Cattle |
29±1.8 (28–32) |
26.1±0.9 (24–28) |
15.4±1.0 (13–17) |
22.1±1.1 (19–24) |
11.1±0.9 (9–13) |
ND |
|
|
|
Poland |
Sheep |
31±2.5 (27–37) |
25±0.8 (24–27) |
12.6±0.3 (12–13) |
20.8±1.1 (18–22) |
9±0.8 (8.1–10) |
G1 |
|
|
Human |
31.5 (28–39) |
27.2 (24–32) |
13.8 (10.8–17.6) |
9.6 (14.4–26) |
9.6 (7.2–13) |
G7 |
[18] |
|
|
Spain |
Sheep |
(32–38) |
(23.7–25.4) |
(12.1–13) |
(20.7–22.4) |
(8.3–9.2) |
ND |
[15] |
|
Human |
(28–39) |
(21.9–23) |
(12.0–12.8) |
(19.3–20.3) |
(8.7–9.4) |
ND |
|
|
Cattle |
(32–36) |
(24.2–24.7) |
(12.6–13.1) |
(20.8–21.4) |
(8.8–9.4) |
ND |
|
|
|
Tanzania (Mwanza) |
Cattle |
33 (28–38) |
24.5 (22.16–29.52) |
14.8 (12.3–17.2) |
17.2 (14.8–19.7) |
8.1 (7.4–9.9) |
G5 |
Present study |
References
- 1. Wen H, Vuitton L, Tuxun T, Li J, Vuitton DA, Zhang W, McManus DP. Echinococcosis: advances in the 21st century. Clin Microbiol Rev 2019;32:e00075-18. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00075-18
- 2. Bowles J, Blair D, McManus DP. Genetic variants within the genus Echinococcus identified by mitochondrial DNA sequencing. Mol Biochem Parasitol 1992;54:165-173. https://doi.org/10.1016/0166-6851(92)90109-W
- 3. Romig T, Ebi D, Wassermann M. Taxonomy and molecular epidemiology of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato. Vet Parasitol 2015;213:76-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.07.035
- 4. Kinkar L, Laurimäe T, Balkaya I, Casulli A, Zait H, Irshadullah M, Sharbatkhori M, Mirhendi H, Rostami-Nejad M, Ponce-Gordo F, Rehbein S, Kia EB, Simsek S, Šnábel V, Umhang G, Varcasia A, Saarma U. Genetic diversity and phylogeography of the elusive, but epidemiologically important Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto genotype G3. Parasitology 2018;145:1613-1622. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182018000549
- 5. Laurimäe T, Kinkar L, Romig T, Omer RA, Casulli A, Umhang G, Gasser RB, Jabbar A, Sharbatkhori M, Mirhendi H, Ponce-Gordo F, Lazzarini LE, Soriano SV, Varcasia A, Rostami Nejad M, Andresiuk V, Maravilla P, González LM, Dybicz M, Gawor J, Šarkūnas M, Šnábel V, Kuzmina T, Saarma U. The benefits of analysing complete mitochondrial genomes: Deep insights into the phylogeny and population structure of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato genotypes G6 and G7. Infect Genet Evol 2018;64:85-94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2018.06.016
- 6. Yanagida T, Mohammadzadeh T, Kamhawi S, Nakao M, Sadjjadi SM, Hijjawi N, Abdel-Hafez SK, Sako Y, Okamoto M, Ito A. Genetic polymorphisms of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto in the Middle East. Parasitol Int 2012;61:599-603. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2012.05.014
- 7. Thompson RC, Lymbery AJ. Echinococcus and Hydatid Disease; Wallingford, USA: CAB International; 1995. http://researchrepository.murdoch.edu.au/id/eprint/13362
- 8. Eckert J, Gemmell MA, Meslin FX, Pawlowski ZS. WHO/OIE manual on echinococcosis in humans and animals: a public health problem of global concern; 2002. Paris, France: World Organization for Animal Health (Office international des epizooties); https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/42427/929044522X.pdf
- 9. Ernest E, Nonga HE, Kassuku AA, Kazwala RR. Hydatidosis of slaughtered animals in Ngorongoro district of Arusha region, Tanzania. Trop Anim Health Prod 2009;41:1179-1185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-008-9298-z
- 10. Macpherson CN, Craig PS, Romig T, Zeyhle E, Watsghinger H. Observations on human echinococcosis (hydatidosis) and evaluation of transmission factors in the Maasai of northern Tanzania. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 1989;83:489-497. https://doi.org/10.1080/00034983.1989.11812377
- 11. Jusabani AM, Kalambo CF, Jusabani M, Surani S. Myocardial echinococcosis: rare manifestation of a common parasitic disease in northern Tanzania. Cureus 2020;12:e8681. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.8681
- 12. Ernest E, Nonga HE, Kynsieri N, Cleaveland S. A retrospective survey of human hydatidosis based on hospital records during the period 1990–2003 in Ngorongoro, Tanzania. Zoonoses Public Health 2010;Dec. 57:124-129. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1863-2378.2009.01297.x
- 13. Galindo M, Gonzalez MJ, Galanti N. Echinococcus granulosus protoscolex formation in natural infections. Biol Res 2002;35:365-371. http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S0716-97602002000300011
- 14. Cielecka D, Salamatin R, Garbacewicz A. Usage of the Hoyer’s medium for diagnostics and morphological studies of some parasites. Wiad Parazytol 2009;55:265-270. (in Polish). https://europepmc.org/article/med/19856844
- 15. Gordo FP, Bandera CC. Differentiation of Spanish strains of Echinococcus granulosus using larval rostellar hook morphometry. Int J Parasitol 1997;27:41-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0020-7519(96)00173-7
- 16. Arbabi M, Pirestani M, Delavari M, Hooshyar H, Abdoli A, Sarvi S. Molecular and morphological characterizations of Echinococcus granulosus from human and animal isolates in Kashan, Markazi Province, Iran. Iran J Parasitol 2017;12:177-187. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5527027/
- 17. Said IM, Abdel-Hafez SK, Al-Yaman FM. Morphological variation of Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces from hydatid cysts of human and various domestic animals in Jordan. Int J Parasitol 1988;18:1111-1114. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-7519(88)90083-5
- 18. Sałamatin R, Kowal J, Nosal P, Kornaś S, Cielecka D, Jańczak D, Patkowski W, Gawor J, Kornyushin V, Golab E, Šnábel V. Cystic echinococcosis in Poland: genetic variability and the first record of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto (G1 genotype) in the country. Parasitol Res 2017;116:3077-3085. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5618-4
- 19. Morgan JA, Blair D. Relative merits of nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacers and mitochondrial CO1 and ND1 genes for distinguishing among Echinostoma species (Trematoda). Parasitology 1998;116:289-297. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182097002217
- 20. Olsen C, Qaadri K, Moir R, Kearse M, Buxton S, Cheung M. Geneious R7: A Bioinformatics Platform for Biologists. Newark, USA. Biomatters, Inc; 2014, https://www.eposters.net/pdfs/geneious-r7-a-bioinformatics-platform-for-biologists.pdf
- 21. Jeon HK, Kim KH, Eom KS. Complete sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Taenia saginata: comparison with T. solium and T. asiatica. Parasitol Int 2007;56:243-246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parint.2007.04.001
- 22. Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 2013;30:2725-2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
- 23. Felsenstein J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 1981;17:368-376. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01734359
- 24. Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sánchez-DelBarrio JC, Guirao-Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, Sánchez-Gracia A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol Biol Evol 2017;34:3299-3302. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx248
- 25. Sharma M, Sehgal R, Fomda BA, Malhotra A, Malla N. Molecular characterization of Echinococcus granulosus cysts in north Indian patients: identification of G1, G3, G5 and G6 genotypes. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2013;7:e2262. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002262
- 26. Rojas CA, Ebi D, Gauci CG, Scheerlinck JP, Wassermann M, Jenkins DJ, Lightowlers MW, Romig T. Microdiversity of Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto in Australia. Parasitology 2016;143:1026-1033. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182016000445
- 27. Barazesh A, Sarkari B, Sarısu G, Hami M, Mikaeili F, Aydın A, Ekici A, Ebrahimi S. Comparative genotyping of Echinococcus granulosus infecting livestock in Turkey and Iran. Turkiye Parasitol Derg 2019;43:123-129. https://doi.org/10.4274/tpd.galenos.2019.6117
- 28. Nakao M, Li T, Han X, Ma X, Xiao N, Qiu J, Wang H, Yanagida T, Mamuti W, Wen H, Moro PL, Giraudoux P, Craig PS, Ito A. Genetic polymorphisms of Echinococcus tapeworms in China as determined by mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. Int J Parasitol 2010;40:379-385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.09.006
- 29. Nakao M, Yokoyama N, Sako Y, Fukunaga M, Ito A. The complete mitochondrial DNA sequence of the cestode Echinococcus multilocularis (Cyclophyllidea: Taeniidae). Mitochondrion 2002;1:497-509. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1567-7249(02)00040-5
- 30. Nakao M, McManus DP, Schantz PM, Craig PS, Ito A. A molecular phylogeny of the genus Echinococcus inferred from complete mitochondrial genomes. Parasitology 2007;134:713-722. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182006001934
- 31. Le TH, Pearson MS, Blair D, Dai N, Zhang LH, McManus DP. Complete mitochondrial genomes confirm the distinctiveness of the horse-dog and sheep-dog strains of Echinococcus granulosus. Parasitology 2002;124:97-112. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182001008976
- 32. Denk D, Boufana B, Masters NJ, Stidworthy MF. Fatal echinococcosis in three lemurs in the United Kingdom—a case series. Vet Parasitol 2016;218:10-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.12.033
- 33. Kinkar L, Laurimäe T, Sharbatkhori M, Mirhendi H, Kia EB, Ponce-Gordo F, Andresiuk V, Simsek S, Lavikainen A, Irshadullah M, Umhang G, Oudni-M’rad M, Acosta-Jamett G, Rehbein S, Saarma U. New mitogenome and nuclear evidence on the phylogeny and taxonomy of the highly zoonotic tapeworm Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto. Infect Genet Evol 2017;52:52-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2017.04.023
- 34. Hodžić A, Alić A, Šupić J, Škapur V, Duscher GG. Echinococcus ortleppi, the cattle strain in a crested porcupine (Hystrix cristata): a new host record. Vet Parasitol 2018;256:32-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.05.004
- 35. Addy F, Wassermann M, Banda F, Mbaya H, Aschenborn J, Aschenborn O, Koskei P, Umhang G, DE LA, Rue M, Elmahdi IE, Mackenstedt U, Kern P, Romig T. Genetic polymorphism and population structure of Echinococcus ortleppi. Parasitology 2017;144:450-458. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0031182016001840
- 36. Miran MB, Kasuku AA, Swai ES. Prevalence of echinococcosis and Taenia hydatigena cysticercosis in slaughtered small ruminants at the livestock-wildlife interface areas of Ngorongoro, Tanzania. Vet world 2017;10:411-417. https://doi.org/10.14202/vetworld.2017.411-417
- 37. Ngowi HA, Kassuku AA, Maeda GE, Boa ME, Willingham AL. A slaughter slab survey for extra-intestinal porcine helminth infections in northern Tanzania. Trop Anim Health Prod 2004;36:335-340. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TROP.0000026663.07862.2a
- 38. Terefe Y, Addy F, Alemu S, Mackenstedt U, Romig T, Wassermann M. Genetic characterization of Echinococcus species in eastern Ethiopia. Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Reports 2019;17:100302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vprsr.2019.100302
- 39. Ohiolei JA, Li L, Ebhodaghe F, Yan HB, Isaac C, Bo XW, Fu BQ, Jia WZ. Prevalence and distribution of Echinococcus spp. in wild and domestic animals across Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transbound Emerg Dis 2020;2345-2364. https://doi.org/10.1111/tbed.13571
- 40. Amer S, Helal IB, Kamau E, Feng Y, Xiao L. Molecular characterization of Echinococcus granulosus sensu lato from farm animals in Egypt. PLoS One 2015;10:e0118509. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0118509
- 41. Bardonnet K, Piarroux R, Dia L, Schneegans F, Beurdeley A, Godot V, Vuitton DA. Combined eco-epidemiological and molecular biology approaches to assess Echinococcus granulosus transmission to humans in Mauritania: occurrence of the ‘camel’ strain and human cystic echinococcosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 2002;96:383-386. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0035-9203(02)90369-X
- 42. Ohiolei JA, Yan HB, Li L, Magaji AA, Luka J, Zhu GQ, Isaac C, Odoya ME, Wu YT, Alvi MA, Muku RJ, Fu BQ, Jia WZ. Cystic echinococcosis in Nigeria: first insight into the genotypes of Echinococcus granulosus in animals. Parasites Vectors 2019;12:392. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3644-z
- 43. Mogoye BK, Menezes CN, Wong ML, Stacey S, von Delft D, Wahlers K, Wassermann M, Romig T, Kern P, Grobusch MP, Frean J. First insights into species and genotypes of Echinococcus in South Africa. Vet Parasitol 2013;196:427-432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.03.033
- 44. Kamhawi S, Hijjawi N, Abu-Gazaleh A, Abbass M. Prevalence of hydatid cysts in livestock from five regions of Jordan. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 1995;89:621-629. https://doi.org/10.1080/00034983.1995.11812996
 , Seongjun Choe1
, Seongjun Choe1 , Barakaeli Abdieli Ndosi1,2
, Barakaeli Abdieli Ndosi1,2 , Hansol Park1
, Hansol Park1 , Yeseul Kang1
, Yeseul Kang1 , Chatanun Eamudomkarn1,3, Tilak Chandra Nath1,4
, Chatanun Eamudomkarn1,3, Tilak Chandra Nath1,4 , Sunmin Kim1, Hyeong-Kyu Jeon1
, Sunmin Kim1, Hyeong-Kyu Jeon1 , Dongmin Lee1,*
, Dongmin Lee1,* , Keeseon S. Eom1,*
, Keeseon S. Eom1,*