Abstract
Ticks, blood-sucking ectoparasites, spread diseases to humans and animals. Haemaphysalis longicornis is a significant vector for tick-borne diseases in medical and veterinary contexts. Identifying protective antigens in H. longicornis for an anti-tick vaccine is a key tick control strategy. Enolase, a multifunctional protein, significantly converts D-2-phosphoglycerate and phosphoenolpyruvate in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in cell cytoplasm. This study cloned a complete open reading frame (ORF) of enolase from the H. longicornis tick and characterized its transcriptional and silencing effect. We amplified the full-length cDNA of the enolase gene using rapid amplification of cDNA ends. The complete cDNA, with an ORF of 1,297 nucleotides, encoded a 432-amino acid polypeptide. Enolase of the Jeju strain H. longicornis exhibited the highest sequence similarity with H. flava (98%), followed by Dermacentor silvarum (82%). The enolase motifs identified included N-terminal and C-terminal regions, magnesium binding sites, and several phosphorylation sites. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis indicated that enolase mRNA transcripts were expressed across all developmental stages of ticks and organs such as salivary gland and midgut. RT-PCR showed higher transcript levels in syn-ganglia, suggesting that synganglion nerves influence enolase,s role in tick salivary glands. We injected enolase double-stranded RNA into adult unfed female ticks, after which they were subsequently fed with normal unfed males until they spontaneously dropped off. RNA interference significantly (P<0.05) reduced feeding and reproduction, along with abnormalities in eggs (no embryos) and hatching. These findings suggest enolase is a promising target for future tick control strategies.
-
Key words: Double-stranded RNA, knockdown, real-time PCR, RNA interference, transcript, vaccine
Introduction
Haemaphysalis longicornis is a common tick in Korea and is widely recognized in many nations, ranging from Australia to far east Asia.
H. longicornis causes economic losses of livestock due to irritation from blood sucking and functions as an infection vector, lowering the quality of the leather.
H. longicornis is a vector for
Rickettsia spp.,
Anaplasma spp.,
Borrelia spp.,
Babesia spp.,
Francisella spp.,
Bartonella spp.,
Coxiella spp., and severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus [
1].
Tick control is challenging because most of the acaridae are treatment-resistant [
2]. Determining a molecular biological approach would be helpful in identifying potential proteins that play a role in the tick life cycle. These proteins could be used to design a vaccine target based on a better understanding of tick biology. Tick salivary enolase and its related proteins are important for tick research. The enolase of
H. longicornis is highly expressed in the salivary gland.
Enolase from the Jeju strain
H. longicornis tick has been identified and confirmed [
3]. However, information on tick enolase is limited and the exact mechanisms need to be further evaluated. Enolase plays a vital role in triggering an immune response that aids the body in defending against the infection. Previous research has indicated that enolase could serve as a promising target for managing
trypanosomatid parasites,
Nilaparvata lugens, argasid ticks like
Ornithodoros moubata, and
Haemaphysalis flava [
4–
6].
RNA interference (RNAi) is a simple and rapid method of silencing gene expression.
Caenorhabditis elegans was the first organism in which RNAi was used to determine the functional state of a gene [
7]. Currently, RNAi is successfully used in tick gene functional studies [
8]. RNAi experiments and immunization trials showed that enolase could also be involved in the regulation of tick reproduction, indicating new potential control strategies [
9]. Cloning and characterization of enolase could help to more fully understand the tick-host relationship and its physiological roles in tick biology.
In the present study, we silenced salivary enolase using RNAi to investigate its role in feeding and reproduction. Here, we report the cloning, expression, and functional analysis of the enolase gene from the salivary gland and which may help to select antigens as vaccine candidates
Materials and Methods
Tick maintenance and collection of ticks
The H. longicornis Jeju strain has been cultured in our laboratory since 2003. The ticks were reared by feeding on the ear of specific pathogen-free New Zealand White rabbits (Samtako, Osan, Korea), using tape and kept in an incubator at 25°C and 95% humidity. Animals used in our experiments were treated under the ethical guidelines of the Jeonbuk National University Animal Care and Use Committee (JBNU 2022-094).
RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
For cDNA synthesis, total RNA was extracted from adult ticks using a total RNA extraction kit (RiboEx, GeneAll Biotechnology, Seoul, Korea) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA concentration was quantified using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Subsequently, cDNA was synthesized from adult, nymph, larva using a WizScript cDNA synthesis kit (Wizbio solutions, Seongnam, Korea) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The samples were stored at −70°C.
Cloning of enolase cDNA
To clone a complete open reading frame (ORF) of enolase from
H. longicornis, we aligned enolase-encoding nucleotide sequences from different species and designed degenerated forward primer enolase-DF and reverse primer enolase-DR (
Supplementary Table S1). PCR amplification was performed using EzPCR HS Plus 5X PCR master mix (Elpis-Biotech, Daejeon, Korea) with a master cycler gradient (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany). PCR conditions were as follows: 95°C for 3 min followed by 33 cycles at 95°C for 30 sec, 54°C for 30 sec, and 1 min at 72°C with a final extension at 10 min at 72°C. PCR products were visualized using 1.2% agarose gel electrophoresis. A 247-bp (
Supplementary Fig. S1) amplified PCR product was excised and purified using the EZ-Pure Gel Extraction Kit Ver. 2 (Enzynomics, Daejeon, Korea) according to the manufacturer,s instructions. The purified DNA fragment was cloned into an All in One vector (BIOFACT, Daejeon, Korea) according to the manufacturer,s instructions. Positive clones were sequenced and analyzed to determine the complete ORF.
Nucleotides and the deduced amino acid sequences were analyzed using the online EMBOSS translation program (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/stt/emboss_transeq/). The 1,297-bp sequence, corresponding to 432 amino acid sequence was compared with other known enolase sequences from the NCBI database using sequence alignment software T-coffee (
http://tcoffee.crg.cat/apps/tcoffee/do:regular) [
10]. Multiple sequence alignment was performed using T-coffee (
http://tcoffee.crg.cat/apps/tcoffee/do:regular) [
10] combined with Bio Edit software ver 7.2.1 implementing the Clustal W algorithm. Identity percentage of enolase nucleotides and amino acid were assessed by multiple alignment tool Clustal Omega [
11] (
Fig. 1). A phylogenetic tree was constructed with MEGA X software using neighbor-joining (NJ) methods [
12].
The enolase PCR product was joined to a T7 promotor sequence using T7 promotor-linked (at both 5′ and 3′ ends) as described previously [
13] with oligonucleotide primers (
Supplementary Table S1). T7 promoter-linked oligonucleotide primers, forward primer DsE-F (double-stranded RNA enolase forward) and reverse primer DsE-R (double-stranded RNA enolase reverse) for the enolase gene were used to generate the template for double-stranded RNA (dsRNA;
Supplementary Table S1). PCR amplification profile was as follows: 95°C for 2 min followed by 6 cycles at 95°C for 30 sec, 57°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 1 min, and 28 cycles at 95°C for 20 sec, 75°C for 30 sec, and 72°C for 1 min, with a final extension at 72°C for 5 min. PCR bands were visualized using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. PCR products were purified using the EZ-Pure PCR Purification Kit ver. 2 (Enzynomics, Korea) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. dsRNA was synthesized from T7-linked DNA using the HI Scribe T7 High Yield RNA Synthesis Kit (New England Bio Labs, Ipswich, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The dsRNA concentration was measured using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer, and aliquots were stored at −70°C until the next use.
Adult unfed female (
n=20) and male ticks (
n=20) were collected. The injection dose for the target gene was selected as described previously [
14,
15]. The ticks placed ventral side up on double sticky tape. Ticks were then injected with dsRNA through the membrane of the 4th coxa under a dissecting microscope. Group A (20 female ticks) was injected with 500 ng/tick of enolase dsRNA. Group B was injected with injection buffer (10 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.0 and 1 mM EDTA) as a control [
13]. Ticks were injected with dsRNA as previously described [
16,
17] using a Hamilton 33-gauge needle. After injection, ticks were kept overnight in a 25°C incubator with high humidity to maintain survival. Injected ticks in each group were mixed with an equal number of male ticks and then attached to 4 SPF rabbit ears. To observe gene silencing, 3 female ticks from each group were collected after 5 days of feeding. RNA was extracted describe above and reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) and real-time PCR were performed for gene expression analysis. The remaining ticks were left to feed up to the spontaneous drop-down. Feeding time, blood engorgement, egg mass weight, and hatching rate were recorded.
To determine enolase gene expression in different developmental stages (eggs, larvae, nymph, and adult ticks) [
18,
19] and 2 partially engorged females were removed for salivary gland midgut collection, cDNA was subjected to RT-PCR and qPCR analyses as described in our previous experiments [
19]. RT-PCR was performed with EzPCR HS Plus 5X PCR master mix (Elpis-Biotech) with a master cycler gradient kit (Eppendorf) as described above using gene-specific forward and reverse primers (
Supplementary Table S1). To measure the enolase gene expression levels before and after knockdown, qPCR was performed using a One-Step SYBR Green Prime Script RT-PCR Kit II with a Thermal Cycler Dice system (Perfect Real Time, Takara, Kyoto, Japan) with gene-specific primers used in RT-PCR. Actin gene (GenBank accession no: AY254898.1) was used as the internal controls (
Supplementary Table S1). qPCR condition was as follows: 95°C for 5 min followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec, 56°C for 30 sec, 72°C for 30 sec, and final dissociation. Data were normalized with actin, and the ΔΔCt value was calculated [
21].
Statistical analysis was performed using Student’s t-test (unpaired and unequal variances) and one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison tests with Graph Pad Prism 5 (Graph Pad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). Values are presented as the mean±SD. P-values <0.05 were considered statistically significant compared with the control group.
Results
Cloning and sequence analyses of the partial cDNA encoding H. longicornis enolase
Enolase is responsible for phosphorylation of many enzymes in eukaryotic cells [
22]. We identified a complete ORF of enolase cDNA from Jeju strain
H. longicornis extending from 1 to 1,297 bp using PCR and cloning. We deposited the sequence into to the GenBank database under accession number ON871822. The corresponding amino acid sequences verified using EMBOSS translation programs (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/st/emboss_transeq) represented 432 amino acid polypeptides. The theoretical molecular mass was 46,850.31 Da, with the isoelectric point of 5.91 using ExPASy, the Molecular Biology Server of the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics (
https://www.expasy.org). We identified motifs through Interpro analysis (
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence-search), Alignment showed conserved active enolase sites in the amino acid sequence. The position of the enolase N-terminal domain at position 3–134 amino acids, enolase C-terminal domain at 142–432, enolase signature sequence at 341–354, metal binding site (D 246, I 290, V 317), casein kinase II phosphorylation site at 238–241, protein kinase C phosphorylation site at 354–356, and tyrosine kinase phosphorylation site at 50–57, were predicted in the Conserved Domains database (CDD-NCBI) [
23] and ScanProsite [
24] indicated the identity of enolase (
Supplementary Fig. S2).
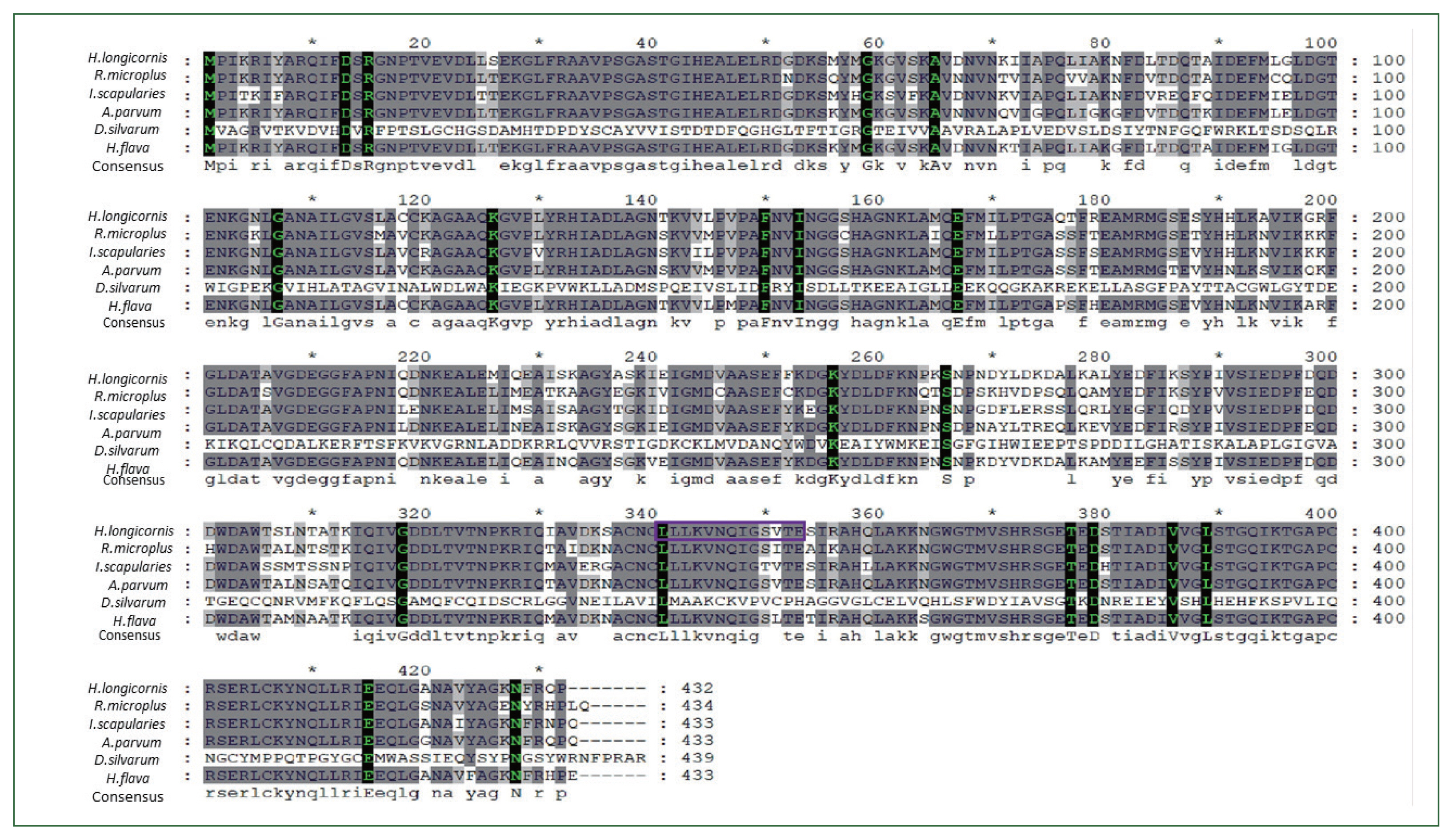
Based on cloning and sequencing, an entire ORF of enolase of the Ixodidae tick
H. longicornis was identified and enolase nucleotides and matching amino acid sequences were highly conserved across many taxa. Enolase amino acid and nucleotide sequences from tick species
Dermacentor silvarum (XM_037726356.1),
Ixodes scapularies (XM_029979980.4),
Rhipicephalus microplus ((MW678616.1),
Amblyomma parvum (GBBL01001179.1), and
Haemaphysalis flava (KM191327.1) were collected from the NCBI database and compared for identity with the
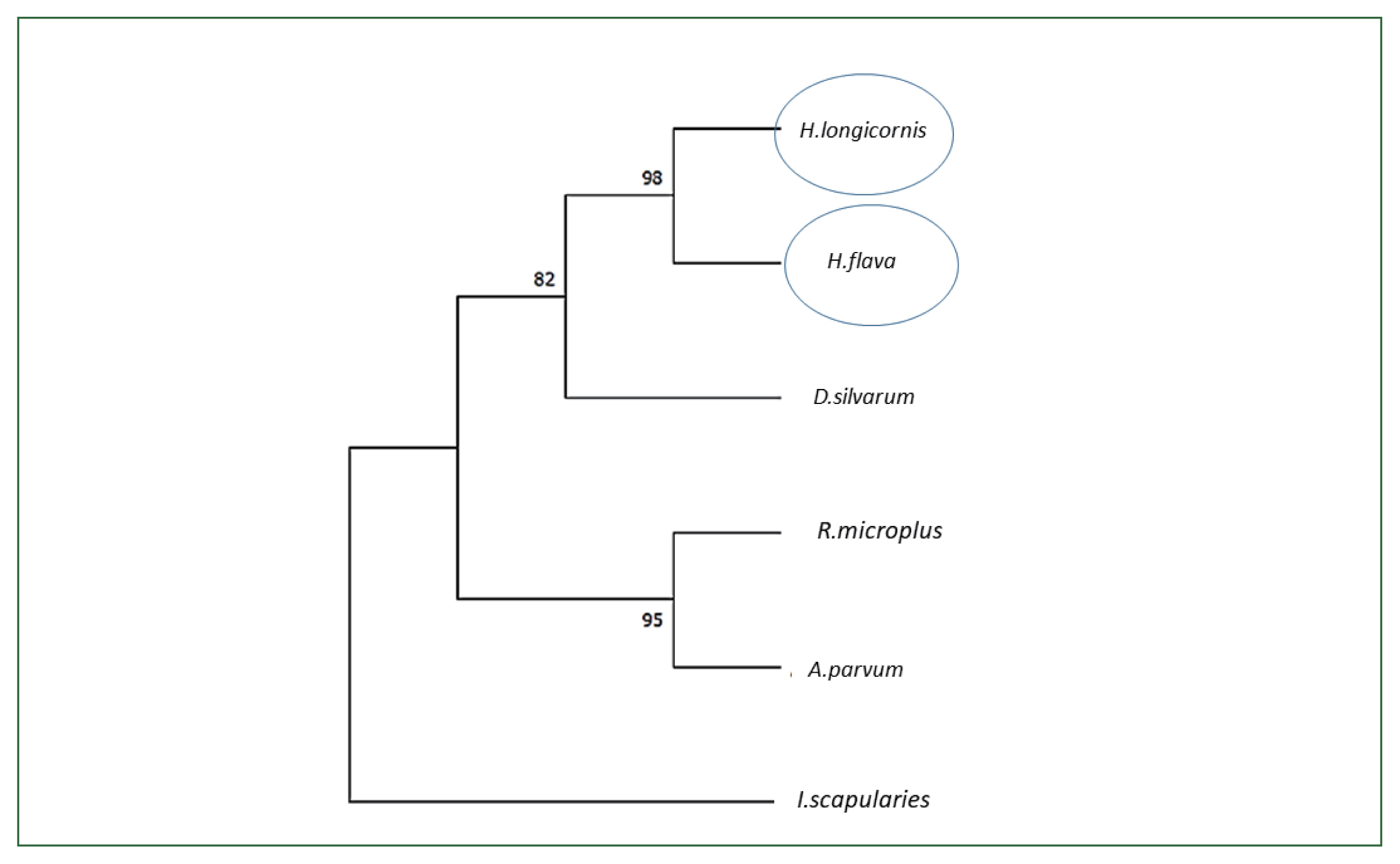
H. longicornis enolase sequence. When we conducted the phylogenetic analysis with the amino acid sequences using NJ with Poisson corrections [
23], the Jeju strain
H. longicornis had the highest sequence similarity with the enolase of
H. flava (98%) followed by
Dermacentor silvarum (82%) (
Fig. 2).
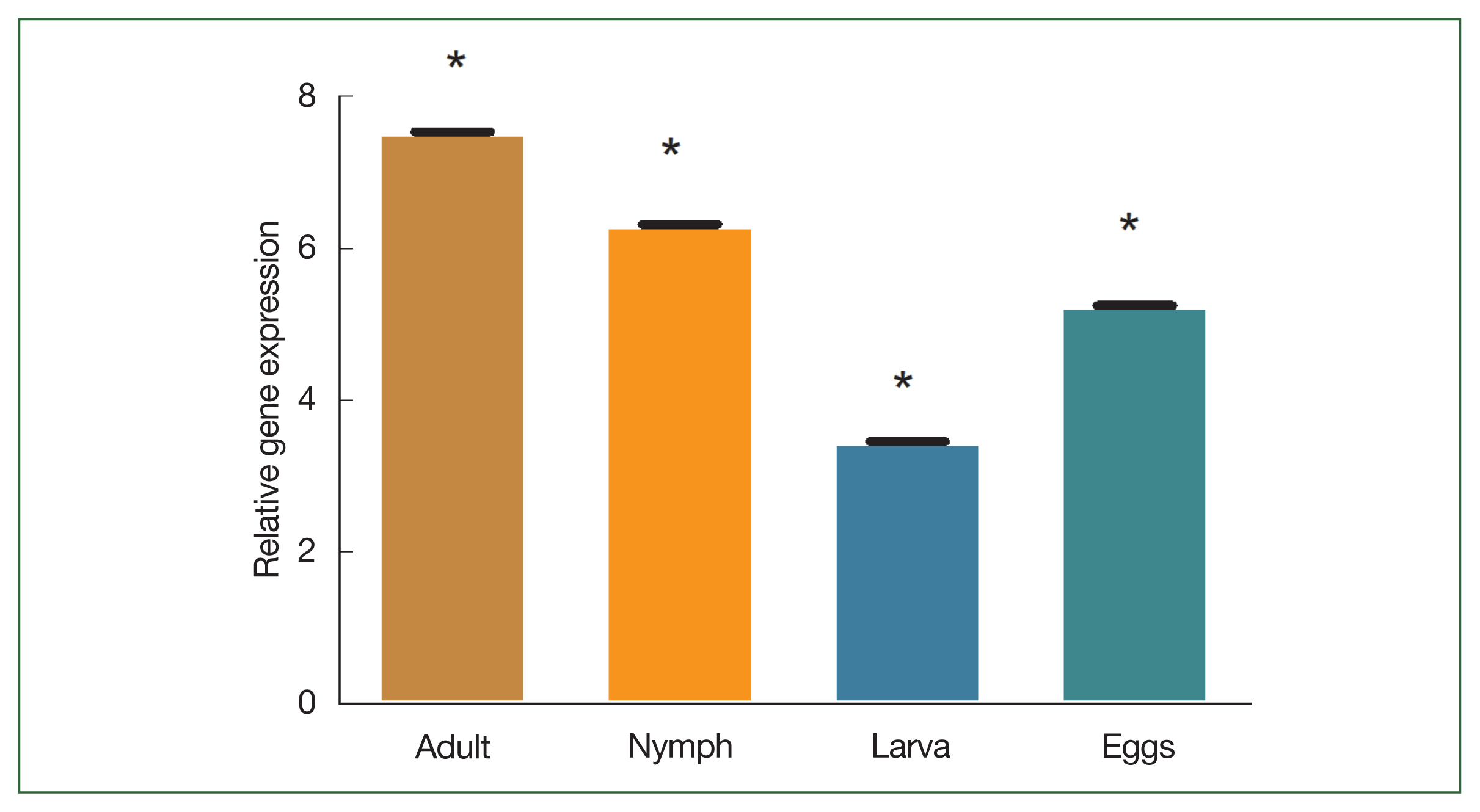
The blood feeding capability of larvae, nymphs, and adults differs from one stage to another. For transcriptional analysis of enolase, total RNA from different life stages were extracted. Adult tick midgut fed and unfed were subjected to RT-PCR and qPCR. Enolase mRNA transcripts were detected in all developmental stages. Conventional PCR showed significantly higher enolase expression at the tissue level in different life stages. In addition, enolase was not detected in the hemolymph of
H. longicornis ticks fed for 7 days (
Supplementary Fig. S1). The degree of transcription was measured using qPCR. In the adult stage, enolase mRNA transcription was relatively higher than in other developmental stages. The expression level of enolase mRNA was higher in adult ticks compared to nymph, larvae, and egg. The expression level of enolase in nymphs, adults, eggs and larvae was 6.33-, 7.56-, and 5.26, 3.46-fold respectively.
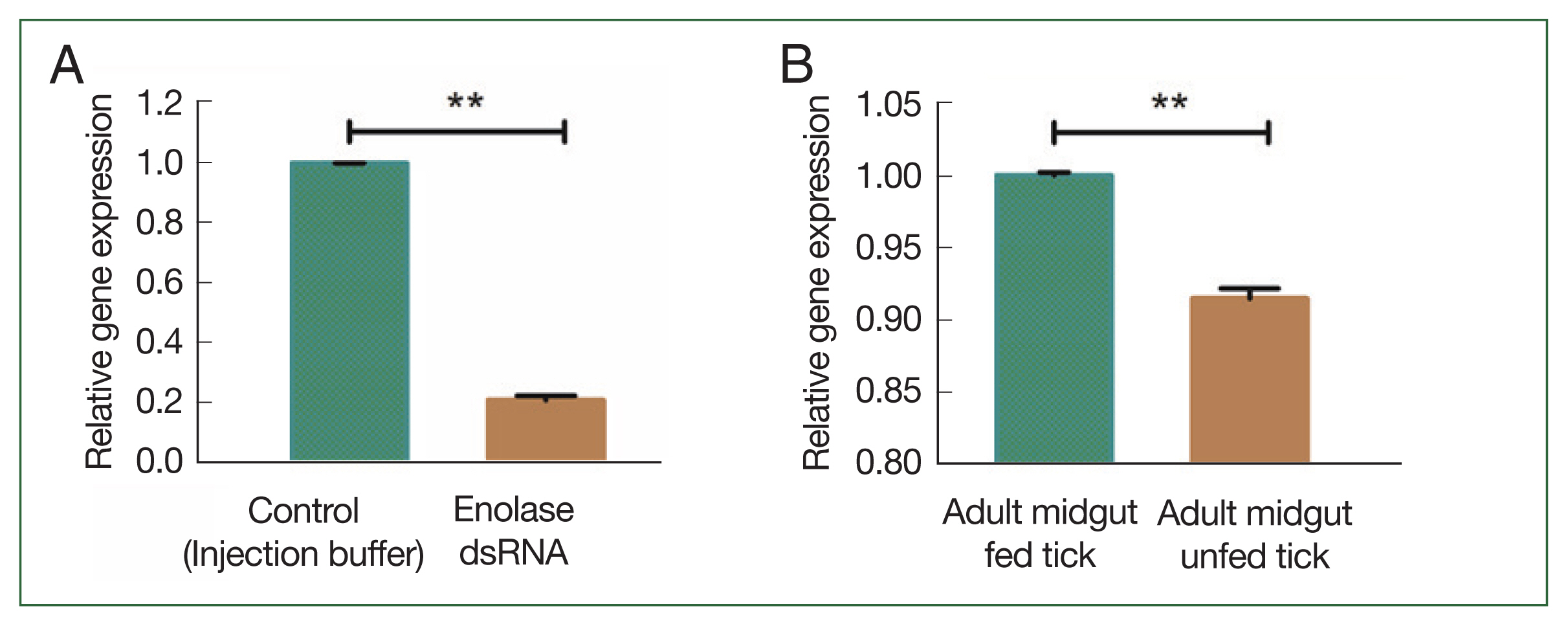
Unfed adult female ticks were injected with enolase or unrelated dsRNA, after which they were allowed to feed on a rabbit’s ear with an equal number of male ticks. Enolase knockdown was confirmed by using qPCR analysis. After 5 days of attachment, enolase expression in dsRNA-injected ticks was compared with that of control ticks. Knockdown adult ticks had low enolase expression compared with the control group (
Fig. 3A). Enolase expression in the midgut of fed ticks was higher than in unfed ticks (
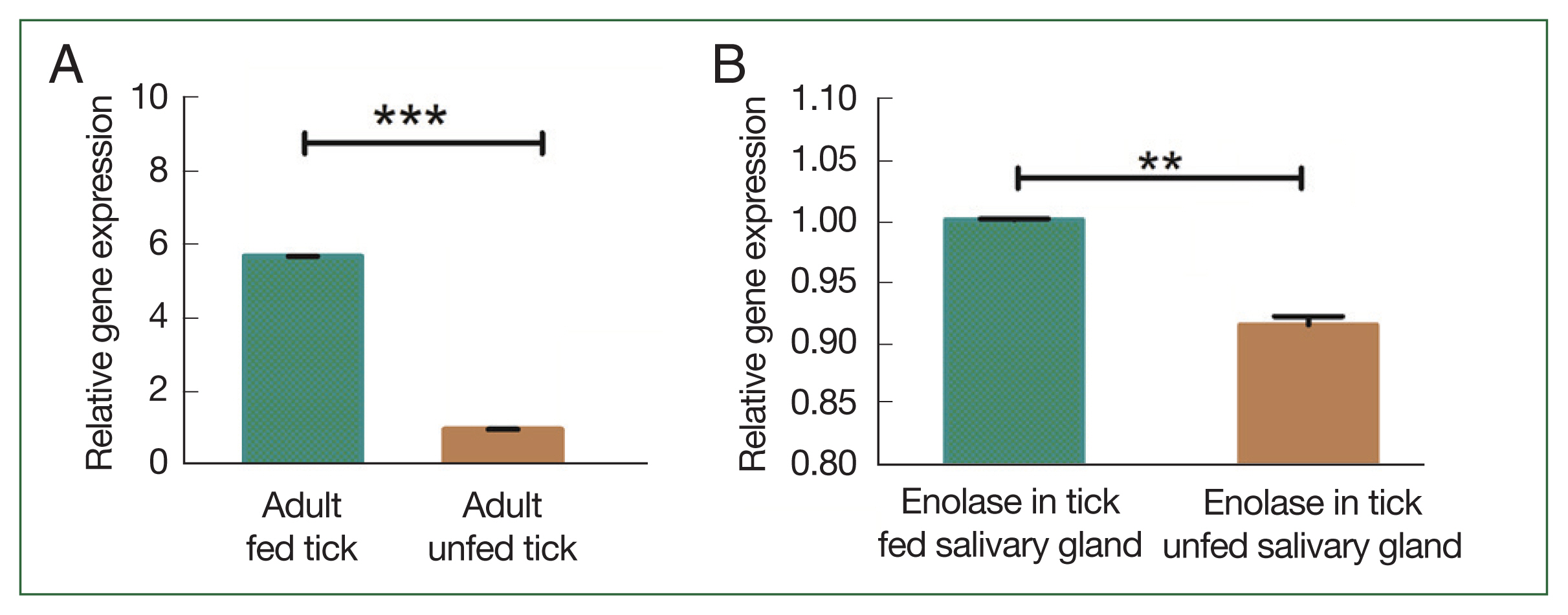
Fig. 3B). In adult ticks after a blood meal, enolase mRNA expression levels in the salivary gland and midgut were significantly higher (1.002-fold) than in that of unfed ticks 0.92-fold (
Fig. 4A). Notably, enolase expression in the salivary gland (5.68-fold) of fed ticks had higher enolase expression than in the salivary gland of unfed (0.98-fold) adult female ticks (
Fig. 4B). Enolase expression in adult, nymph, larvae, and eggs is shown in
Fig. 5. However, significant variation regarding attachment rates (75%), feeding (11 days), and ovipositional period (21–33 days) was observed (
Table 1). Egg abnormalities were visible in enolase dsRNA-treated ticks (
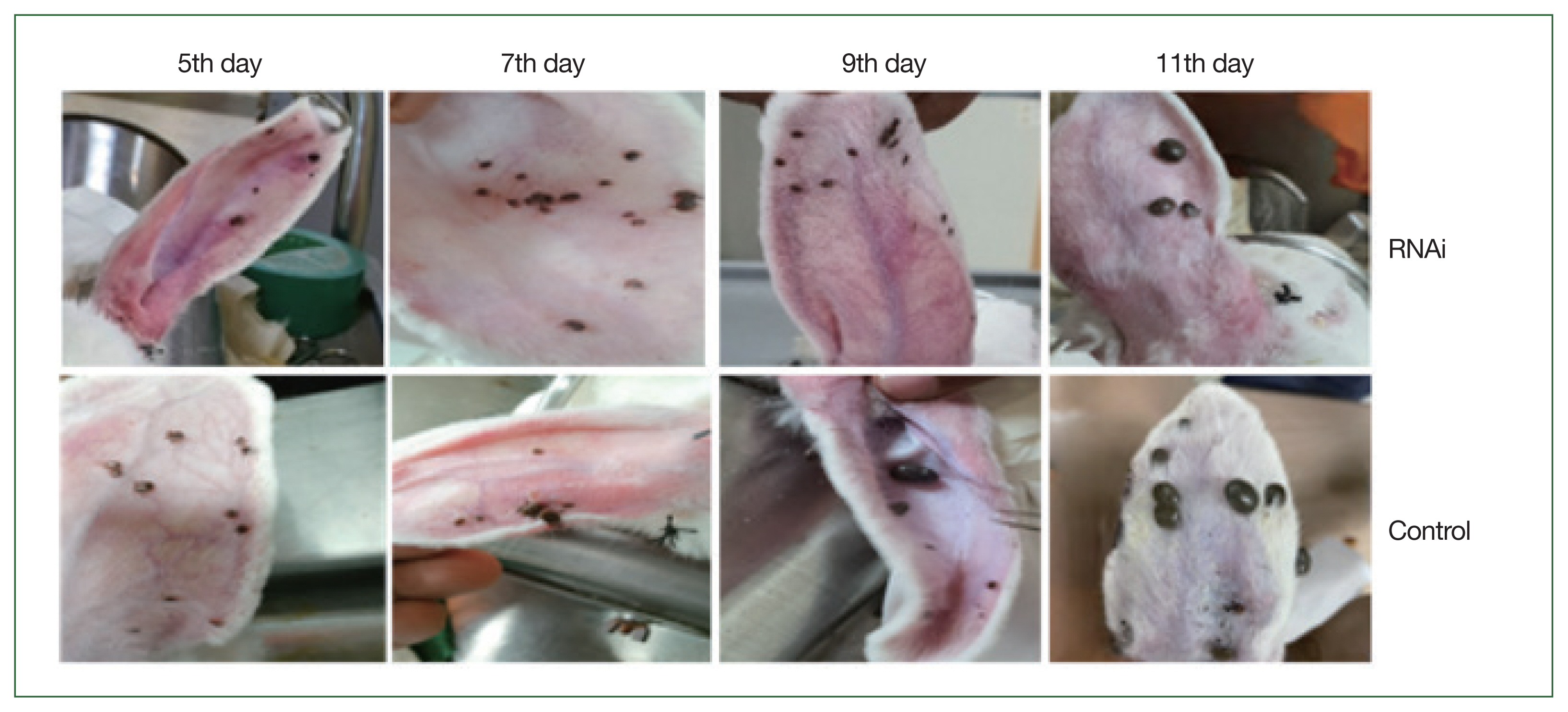
Fig. 6). Phenotypic changes in ticks are shown in
Fig. 7. Phenotypical changes in dsRNA-treated adult female ticks were easily differentiated from those of control ticks (
Fig. 7).
To verify the effects of enolase, engorgement weight and feeding duration were analyzed after spontaneous dropdown of the injected ticks. Enolase knockdown caused a significant increase (
P<0.05) in feeding duration and decreased engorgement weight compared with the control group (
Table 1). The average engorgement weight of enolase dsRNA-injected ticks was 148.38 mg, while that of the control group was 440 mg.
To assess the impact of enolase on reproduction, egg mass and hatchability were examined after spontaneous dropdown of enolase dsRNA-injected ticks. Enolase dsRNA abrogated egg production, and enolase dsRNA-injected ticks showed significantly reduced egg mass (average: 20.6 mg) compared with the control group (average: 380 mg;
Table 1) (
P<0.05). The egg hatching rate of 53% was also significantly reduced (
P<0.05) compared with that of the control group (
Table 1).
Discussion
Many researchers have reported that enolase is present in multiple species such as plants, parasites, and bacteria [
25–
27] as well as in
Ornithodoros moubata tick [
9]. During blood feeding, ticks secrete an excess number of components into saliva to facilitate blood collection from the vertebrate host. Saliva consists of anti-immunomodulatory, anti-vasodilator, anti-coagulant, anti-complement, and anti-platelet aggregation factors [
28]. Recently, sialo transcriptome analysis of
H. flava showed the presence of significant amounts of an enolase-like homologous protein in salivary fluid in the adult and nymph stages [
29]. Enolase, involved not only in glycolysis [
21] and gluconeogenesis, but also in metabolic process [
31]. Enolase is typically found in the cytosol [
32], but it can translocate to the cell surface in response to inflammatory signals [
33]. On the cell surface, enolase functions as a plasminogen receptor [
34,
35] stimulating fibrinolysis and breakdown of the extracellular matrix. Fibrinolysis may be crucial for ticks to break up any clots that may develop during feeding and to stop the ingested blood meal from clotting in the tick midgut.
The importance of enolase in feeding and reproduction was identified by using gene silencing. Knockdown of the enolase gene resulting in dysfunction in blood-sucking and reproduction in
Ornithodoros moubata ticks [
9]. Therefore, research on the enolase gene may offer a novel perspective on how to manage ticks and diseases transmitted by ticks. The genetic and functional significance of enolase in ticks such as
H. longicornis and other species is unclear despite its mention in several organismal transcriptome investigations.
In the present study, the full-length cDNA of of
H. longicornis enolase was composed of 1,300-bp-long, encompassing a 1,297-bp-long ORF. Sequence analysis showed that enolase contained 20 domains and several motifs, including the membrane re-association region LLKVNQIGSVTE (
Fig. 1). The molecular characteristics of enolase showed similar structural features in the hard tick
H. flava [
29] and the soft tick
O. moubata [
9]. The phylogenetic analysis confirmed a close relationship among the tick species
R. microplus,
D. silvarum, H. flava, A. parvum, and
I. scapularies (
Fig. 3).
Expression of enolase genes have been reported to vary depending on stages and tissues. In
H. longicornis, serpin-2 is expressed in the nymph and adult stages in the salivary gland, but not in the midgut [
36]. Conversely, enolase is present in the blood feeding stage [37]. Hemolymph in engorged adult
H. flava was discovered using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in an earlier investigation [38].
In the present study, RNAi-induced knockdown of enolase gene significantly decreased tick attachment compared with the control group (75% vs. 100%,
P<0.05) (
Table 1) and also decreased their engorgement weight (148±0.002 vs. 440±0.01 mg/adult tick), and reproduction (
Table 1). In adults, enolase subsequently increased feeding duration (11±0.82 days) compared with the control group (8±0.5 days) (
Table 1). Furthermore, egg hatching was significantly reduced (53% vs. 93%). In addition, the egg-laying rate and egg quality of female ticks were significantly decreased, as previously reported [37]. The enolase-silenced ticks showed much lower egg mass (20.6±0.011 mg/tick) than the control group (380±0.01 mg/tick), which might be caused by their delayed blood feeding capability. When a tick is feeding on blood, enolase activity increases. Enolase silencing disrupts glycolysis process, interfere with ATP production, and stops the fibrinolysis process, causing blood to clot. Th ticks lost their ability to suck blood. Ticks can rapidly intake blood in the middle period of blood feeding. Thus, to maintain blood flow, secreted salivary proteins are essential for tick survival because they aid in preventing host hemostasis [39].
qRT-PCR analysis of enolase mRNA levels revealed much higher expression in salivary glands, midgut, and synganglia of fed ticks than in other tissues examined. This result suggests that enolase plays an important role in tick blood feeding, which is in agreement with previous reports on enolase anticoagulation [
9,
29]. The TCA cycle and other energy metabolism pathways in the salivary gland cells and other organs are more active when ticks transition into the blood-feeding stage, enabling faster conversion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins from the host,s blood into ATP via the respiratory chain. Most organs in ticks rapidly develop after a short duration of blood feeding [37].
Enolase expression was regulated in salivary glands and other bodily tissues after silencing with RNAi. The salivary gland of the tick produces a variety of bioactive compounds necessary for tick feeding [
8]. Our results revealed that enolase is crucial for tick blood feeding, indicating a new target for tick prevention. Future research on enolase in relation to a vaccine strategy will aid in design of tick control measures.
Notes
-
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
-
Conceptualization: Haque MS, Rahman MK, Islam MS
Data curation: Haque MS, Rahman MK, Islam MS
Formal analysis: Haque MS, Rahman MK, Islam MS
Funding acquisition: You MJ
Investigation: Haque MS
Methodology: Haque MS, Rahman MK, You MJ
Project administration: You MJ
Resources: You MJ
Software: Haque MS, Rahman MK
Supervision: Islam MS, You MJ
Validation: Haque MS
Visualization: Rahman MK
Writing – original draft: Haque MS
Writing – review & editing: Haque MS, Islam MS, You MJ
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries (IPET) through the Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs Convergence Technologies Program for Educating Creative Global Leaders, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (grant number: 320005-4).
Fig. 1Multiple alignment of enolase amino acid sequence in ticks. The alignment of enolase amino acid sequence from Dermacentor silvarum (XM_037726356.1), Ixodes scapularis (XM_029979980.4), Rhipicephalus microplus (MW678616.1), Amblyomma parvum (GBBL01001179.1), and Haemaphysalis flava (KM191327.1). Asterisks indicate conserved residues. Motifs are indicated by boxed letters.
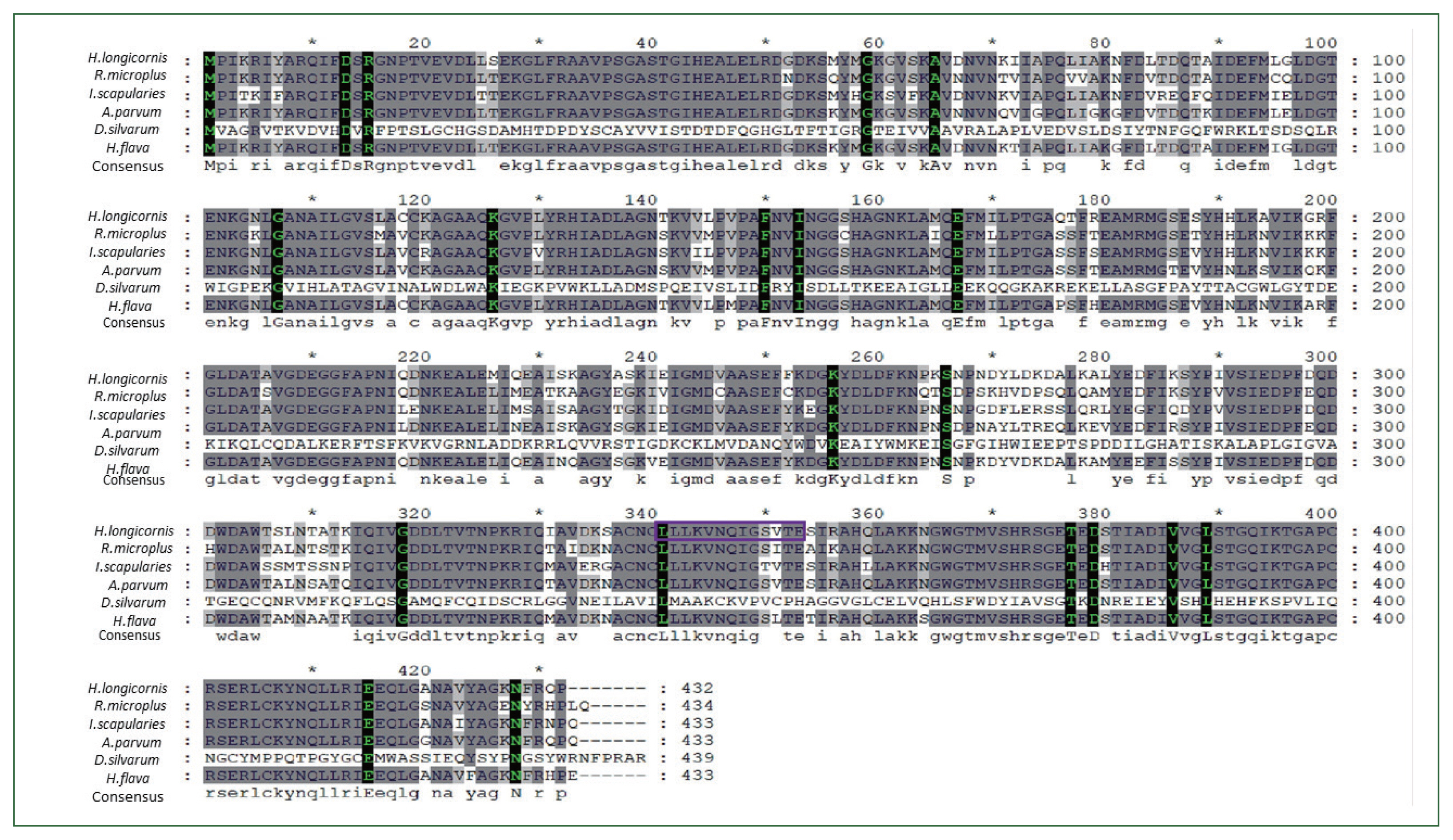
Fig. 2Phylogenetic analysis of enolase from H. longicornis. Bootstrap proportions are indicated at branches. Sequences with NJ involving Poisson corrections and bootstrap analysis of 500 replicates. H. longicornis and R. flava are in the same clade.
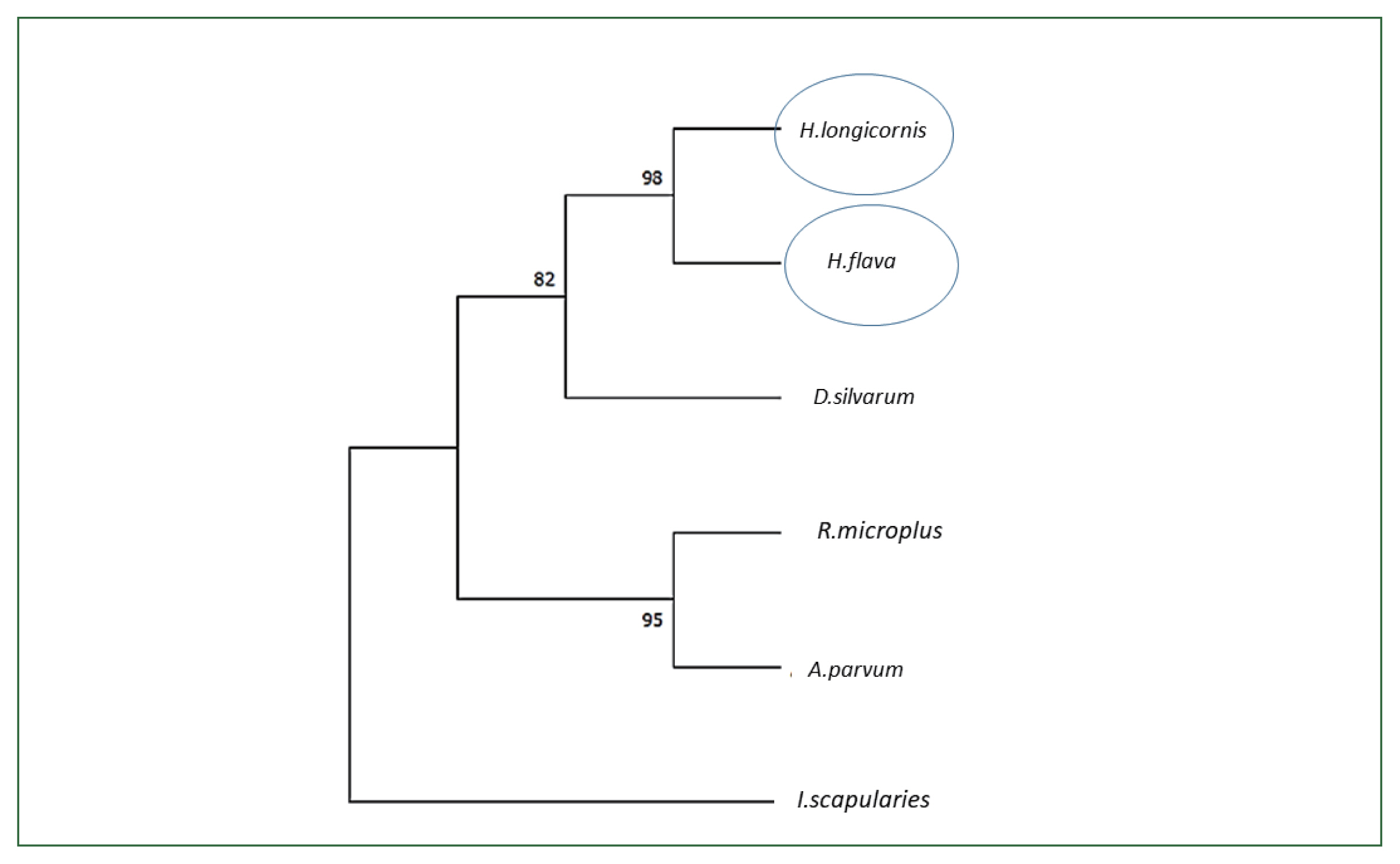
Fig. 3Transcriptional profiles of enolase (A) knockdown of enolase compared with the control group; (B) enolase expression in fed and unfed midguts of adult females. **P<0.001 by Student’s t-test.
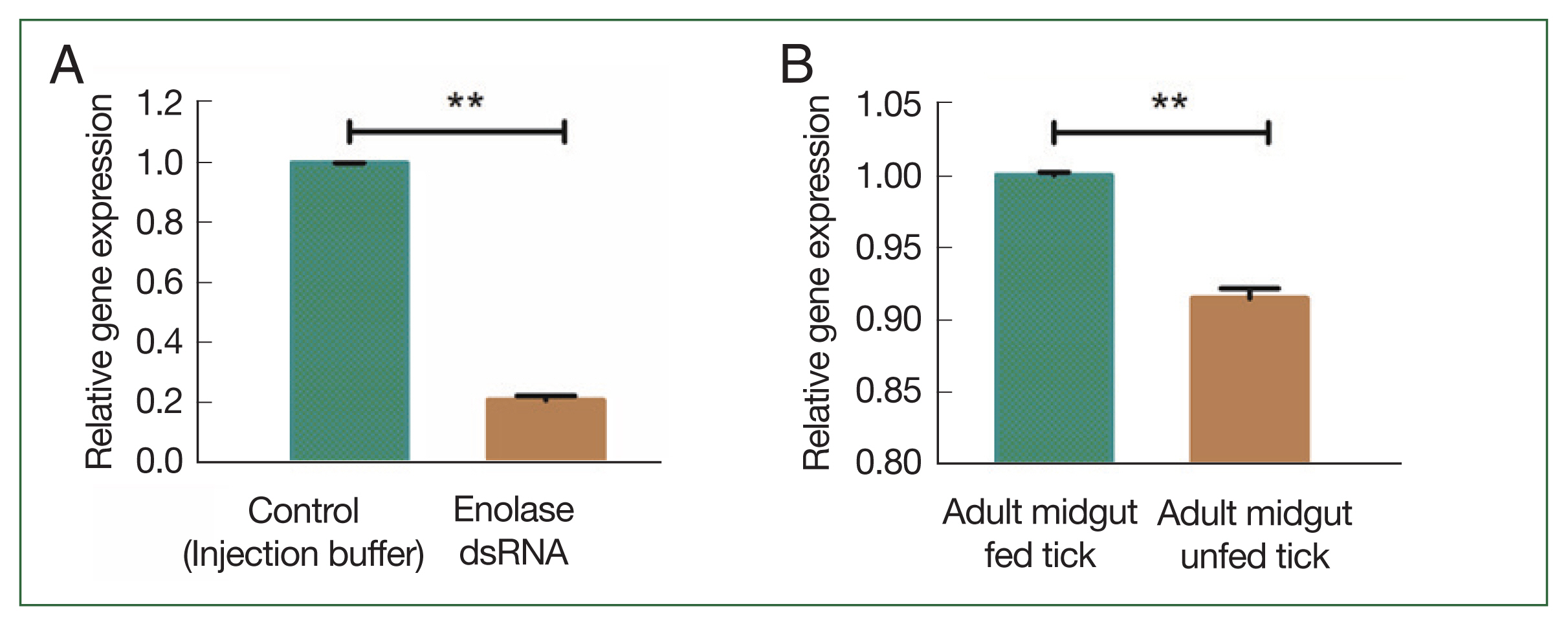
Fig. 4Transcriptional profiles of enolase at different developmental stages (A) enolase expression in unfed versus fed adult ticks. (B) Enolase expression in salivary glands of unfed versus fed adult ticks. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 by Student’s t-test.
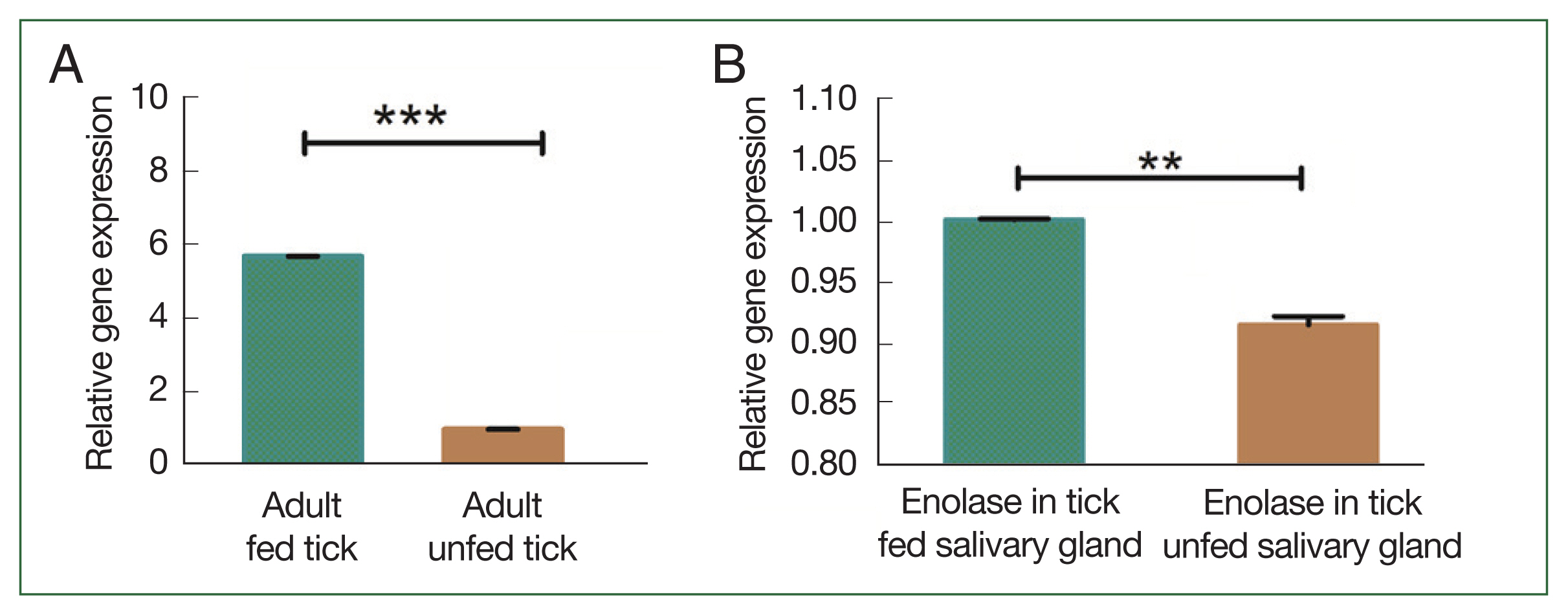
Fig. 5Transcriptional profiles of enolase expression in adult, nymph, larvae, and egg. *P<0.05 by Student’s t-test.
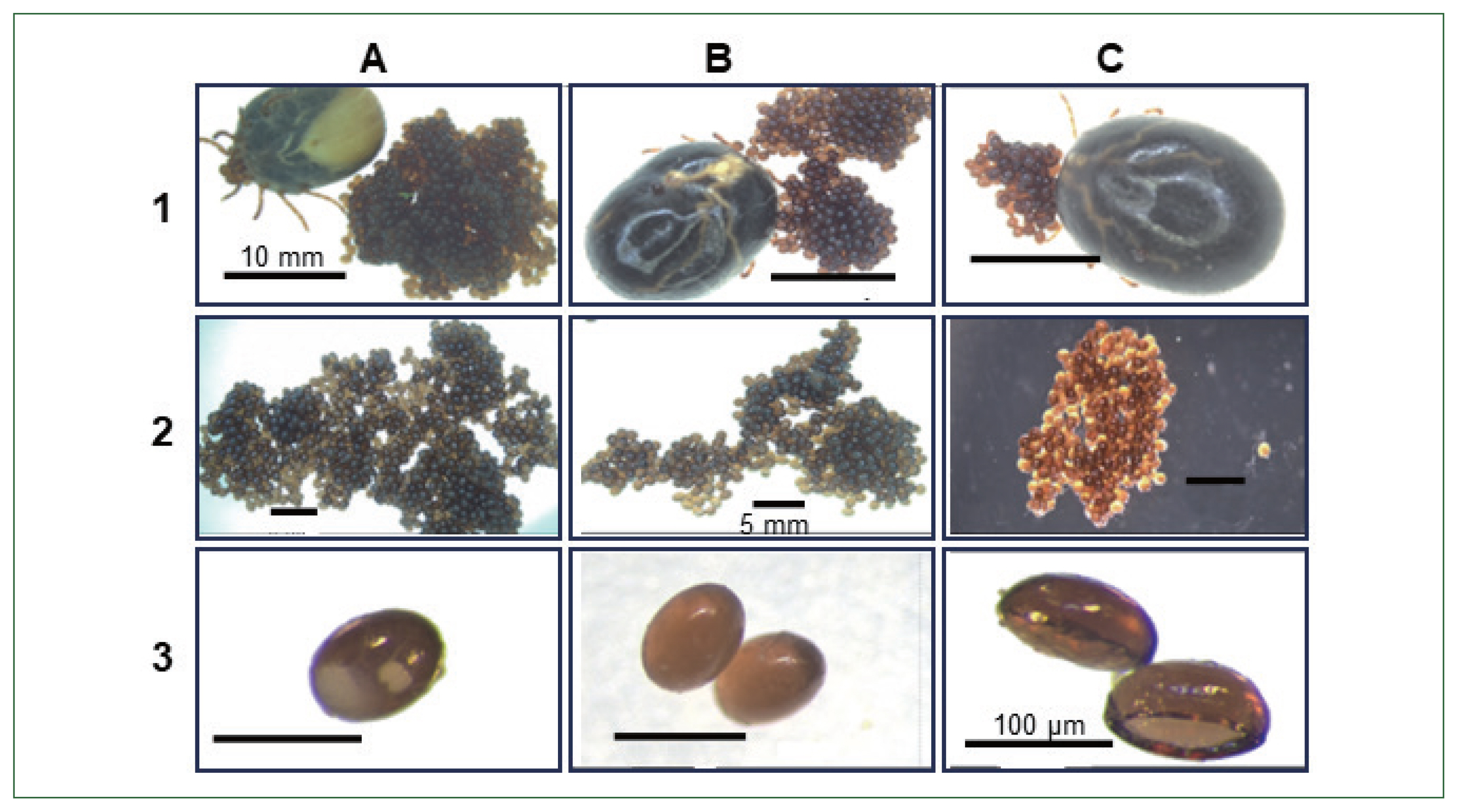
Fig. 6Phenotypic changes in tick (Haemaphysalis longicornis) egg morphology and reduce egg hatching ability compared with. 1, non-injected; 2, buffer control; 3, enolase dsRNA-treated group; (A, B) control ticks, eggs and Control tick eggs containing embryos; (C) enolase dsRNA-treated ticks after spontaneous drop-down, eggs, Abnormal eggs (no embryos).
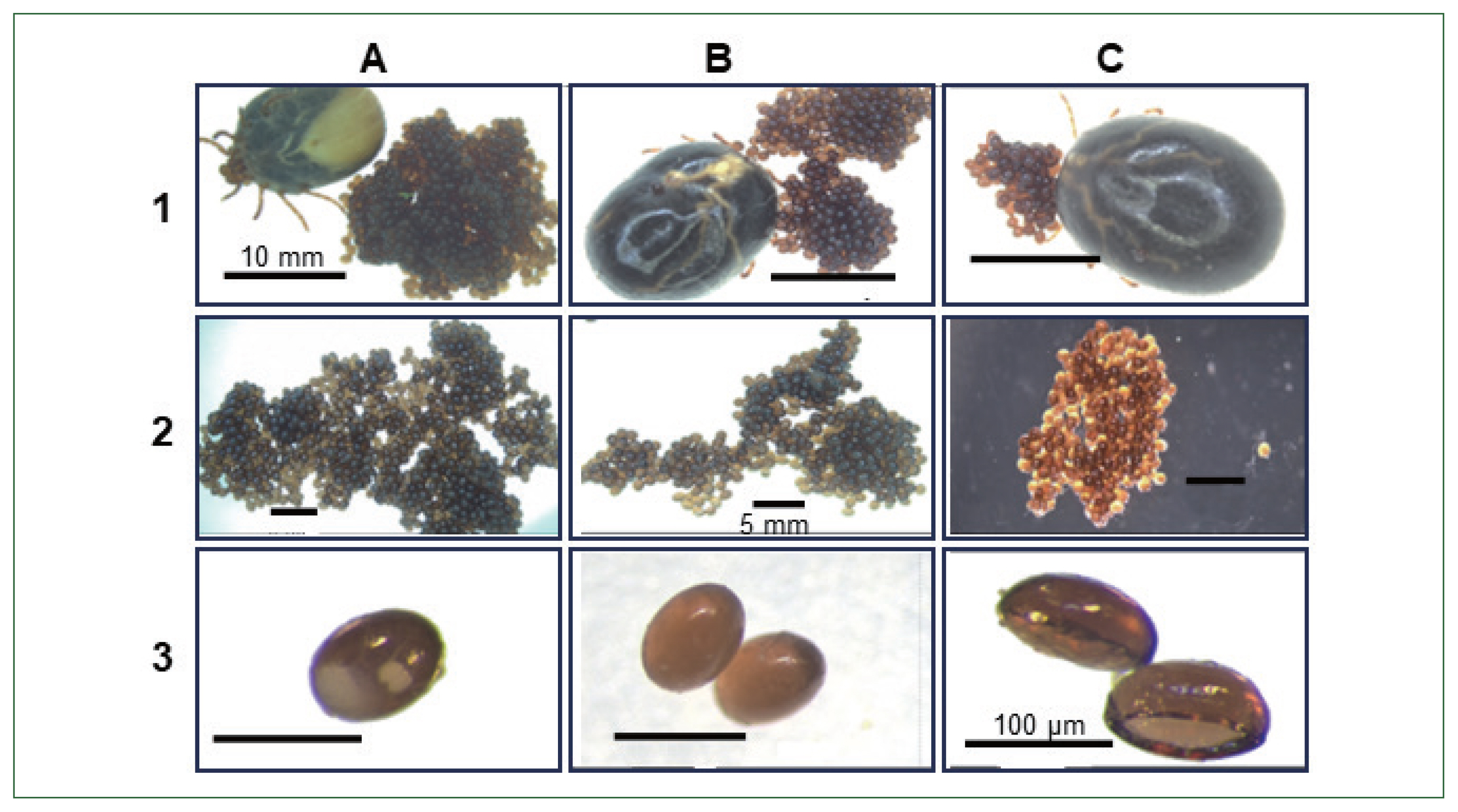

Fig. 7Morphological changes of adult H. longicornis after RNAi silencing of enolase. Upper panel shows RHAi induced enolase knockdown ticks and lower panel represents control ticks.
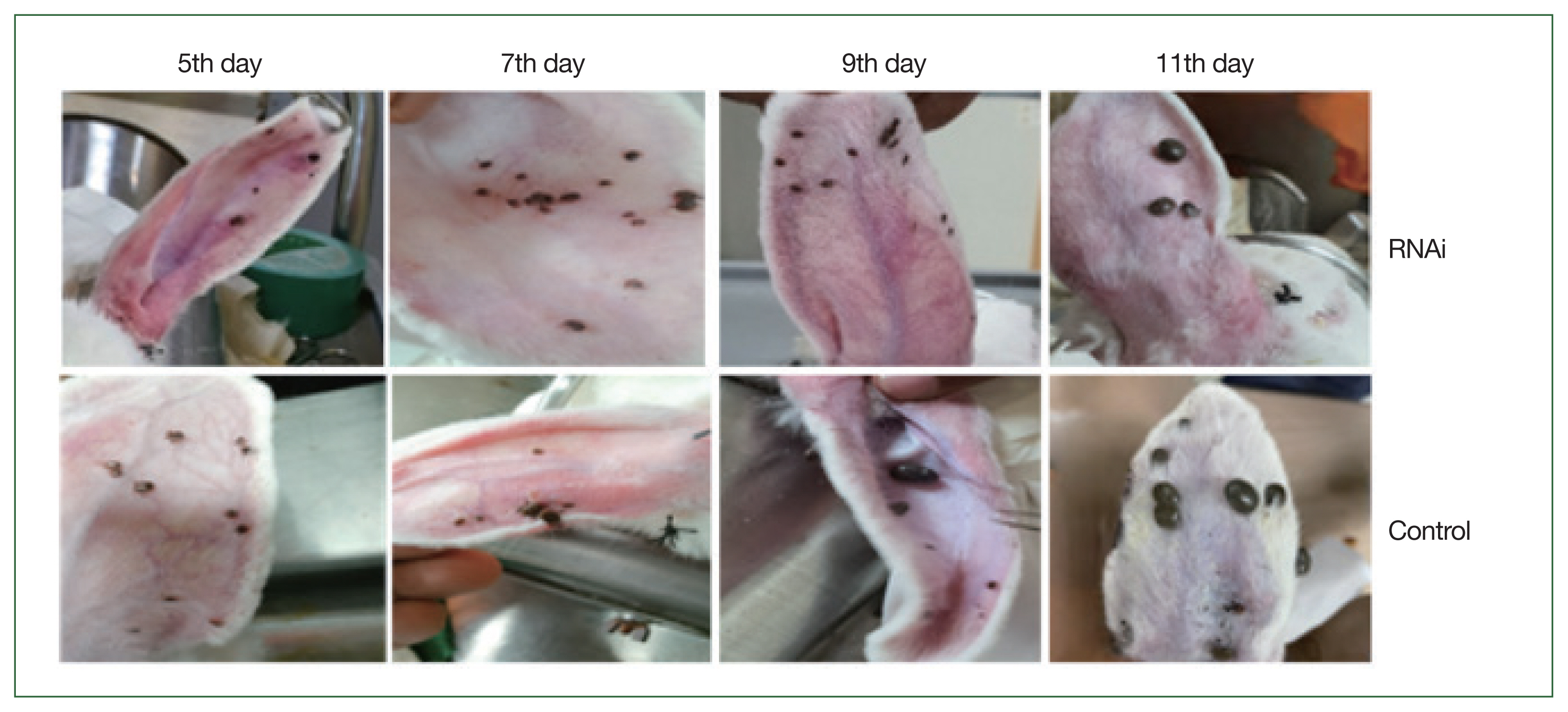
Table 1Effects of enolase dsRNAi treatment on adult female tick blood engorgement, egg mass weight, and egg hatching rate
a
Table 1
|
Groups |
Death rate after injection (%) |
Attachment rate at 24 h (%) |
Feeding duration (days) |
Engorgement weight (mg/tick) |
Egg mass weight (mg/tick) |
Egg hatching rate (%) |
|
dsRNA |
5 |
75±1.11 |
11±0.82 |
148±0.002 |
20.6±0.011 |
53±1.73 |
|
Control |
0 |
100±0.0 |
8±0.5 |
440±0.01 |
380±0.01 |
93±1.58 |
References
- 1. Chae JB, Cho YS, Cho YK, Kang JG, Shin NS, et al. Epidemiological investigation of tick species from near domestic animal farms and cattle, goat, and wild boar in Korea. Parasites Hosts Dis 2019;57(3):319-324. https://doi.org/10.3347/kjp.2019.57.3.319
- 2. Abbas RZ, Zaman MA, Colwell DD, Gilleard J, Iqbal Z. Acaricide resistance in cattle ticks and approaches to its management: the state of play. Vet Parasitol 2014;203(1–2):6-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.03.006
- 3. Tirloni L, Islam MS, Kim TK, Diedrich JK, Yates JR, et al. Saliva from nymph and adult females of Haemaphysalis longicornis: a proteomic study. Parasit Vectors 2015;8(1):338. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-0918-y
- 4. Díaz-Martín V, Manzano-Román R, Oleaga A, Encinas-Grandes A, Pérez-Sánchez R. Cloning and characterization of a plasminogen-binding enolase from the saliva of the argasid tick Ornithodoros moubata. Vet Parasitol 2013;191(3–4):301-314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.09.019
- 5. Wang WX, Li KL, Chen Y, Lai FX, Fu Q. Identification and function analysis of enolase gene NlEno1 from Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Hemiptera:Delphacidae). J Insect Sci 2015;15(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/iev046
- 6. Xu XL, Cheng TY, Yang H. Enolase, a plasminogen receptor isolated from salivary gland transcriptome of the ixodid tick Haemaphysalis flava. Parasitol Res 2016;115(5):1955-1964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-4938-0
- 7. Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1998;391(6669):806-811. https://doi.org/10.1038/35888
- 8. Rahman MK, Kim B, You M. Molecular cloning, expression and impact of ribosomal protein S-27 silencing in Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae). Exp Parasitol 2020;209:107829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exppara.2019.107829
- 9. Díaz-Martín V, Manzano-Román R, Oleaga A, Encinas-Grandes A, Pérez-Sánchez R. Cloning and characterization of a plasminogen-binding enolase from the saliva of the argasid tick Ornithodoros moubata. Vet Parasitol 2013;191(3–4):301-314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.09.019
- 10. Di Tommaso P, Moretti S, Xenarios I, Orobitg M, Montanyola A, et al. T-Coffee: a web server for the multiple sequence alignment of protein and RNA sequences using structural information and homology extension. Nucleic Acids Res 2011;39(suppl):W13-W7. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr245
- 11. Sievers F, Wilm A, Dineen D, Gibson TJ, Karplus K, et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol Syst Biol 2011;7:539. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2011.75
- 12. Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 2018;35(6):1547-1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
- 13. Rahman MK, Saiful Islam M, You M. Impact of subolesin and cystatin knockdown by RNA interference in adult female Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) on blood engorgement and reproduction. Insects 2018;9(2):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects9020039
- 14. de la Fuente J, Kocan KM, Almazán C, Blouin EF. RNA interference for the study and genetic manipulation of ticks. Trends Parasitol 2007;23(9):427-433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2007.07.002
- 15. Karim S, Miller NJ, Valenzuela J, Sauer JR, Mather TN. RNAi-mediated gene silencing to assess the role of synaptobrevin and cystatin in tick blood feeding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005;334(4):1336-1342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.036
- 16. de la Fuente J, Almazán C, Blouin EF, Naranjo V, Kocan KM. Reduction of tick infections with Anaplasma marginale and A. phagocytophilum by targeting the tick protective antigen subolesin. Parasitol Res 2006;100(1):85-91. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-006-0244-6
- 17. Commins SP, James HR, Kelly LA, Pochan SL, Workman LJ, et al. The relevance of tick bites to the production of IgE antibodies to the mammalian oligosaccharide galactose-α-1, 3-galactose. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2011;127(5):1286-1293. e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2011.02.019
- 18. Kocan KM, Manzano-Roman R, de la Fuente J. Transovarial silencing of the subolesin gene in three-host ixodid tick species after injection of replete females with subolesin dsRNA. Parasitol Res 2007;100(6):1411-1415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-007-0483-1
- 19. Rahman MK, You M. Molecular cloning and transcriptional and functional analysis of glycogen synthase kinase-3β in Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari, Ixodidae). Parasite 2019;26:39. https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2019038
- 20. Pfaffl MW. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2001;29(9):e45. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
- 21. Pancholi V. Multifunctional α-enolase: its role in diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 2001;58(7):902-920. https://doi.org/10.1007/pl00000910
- 22. Sigrist CJA, De Castro E, Cerutti L, Cuche BA, Hulo N, et al. New and continuing developments at PROSITE. Nucleic Acids Res 2012;41(database issue):344-347. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1067
- 23. Cao H, Zhou Y, Chang Y, Zhang X, Li C, et al. Comparative phosphoproteomic analysis of developing maize seeds suggests a pivotal role for enolase in promoting starch synthesis. Plant Sci 2019;289:110243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110243
- 24. Quintero-Troconis E, Buelvas N, Carrasco-López C, Domingo-Sananes M, González-González L, et al. Enolase from Trypanosoma cruzi is inhibited by its interaction with metallocarboxypeptidase-1 and a putative acireductone dioxygenase. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 2018;1866(5–6):651-660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2018.03.003
- 25. Salazar N, de Souza MCL, Biasioli AG, da Silva LB, Barbosa AS. The multifaceted roles of Leptospira enolase. Res Microbiol 2017;168(2):157-164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resmic.2016.10.005
- 26. Neelakanta G, Sultana H. Tick saliva and salivary glands: what do we know so far on their role in arthropod blood feeding and pathogen transmission. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022;11:816547. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.816547
- 27. Xu XL, Cheng TY, Yang H. Enolase, a plasminogen receptor isolated from salivary gland transcriptome of the ixodid tick Haemaphysalis flava. Parasitol Res 2016;115(5):1955-1964. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-016-4938-0
- 28. Avilán L, Gualdrón-López M, Quiñones W, González-González L, Hannaert V, et al. Enolase: a key player in the metabolism and a probable virulence factor of trypanosomatid parasites-perspectives for its use as a therapeutic target. Enzyme Res 2011;2011:932549. https://doi.org/10.4061/2011/932549
- 29. Piast M, Kustrzeba-Wójcicka I, Matusiewicz M, Banaś T. Molecular evolution of enolase. Acta Biochim Pol 2005;52(2):507-513.
- 30. Haque A, Ray SK, Cox A, Banik NL. Neuron specific enolase: a promising therapeutic target in acute spinal cord injury. Metab Brain Dis 2016;31(3):487-495. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9801-6
- 31. de la Torre-Escudero E, Manzano-Román R, Pérez-Sánchez R, Siles-Lucas M, Oleaga A. Cloning and characterization of a plasminogen-binding surface-associated enolase from Schistosoma bovis. Vet Parasitol 2010;173(1–2):76-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.06.011
- 32. Díaz-Ramos À, Roig-Borrellas A, García-Melero A, López-Alemany R. α-Enolase, a multifunctional protein: its role on pathophysiological situations. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012;2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/156795
- 33. Imamura S, Junior IdSV, Sugino M, Ohashi K, Onuma M. A serine protease inhibitor (serpin) from Haemaphysalis longicornis as an anti-tick vaccine. Vaccine 2005;23(10):1301-1311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2004.08.041
- 34. Ren S, Zhang B, Xue X, Wang X, Zhao H, et al. Salivary gland proteome analysis of developing adult female Haemaphysalis longicornis ticks: molecular motor and TCA cycle-related proteins play an important role throughout development. Parasit Vectors 2019;12(1):1-16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3864-2
- 35. Liu L, Yan F, Zhang L, Wu ZF, Duan DY, Cheng TY. Protein profiling of hemolymph in Haemaphysalis flava ticks. Parasit Vectors 2022;15(1):1-12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-022-05287-7
- 36. Xu XL, Cheng TY, Yang H, Yan F, Yang Y. De novo sequencing, assembly and analysis of salivary gland transcriptome of Haemaphysalis flava and identification of sialoprotein genes. Infect Genet Evol 2015;32:135-142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2015.03.010