Abstract
A case of periocular dirofilariasis has been diagnosed in Iran. A 27-yr old female referred with a history of edema and redness in the left eye since 2 wk ago. On slit lamp examination, a moving thread-like worm was seen in the subconjunctival area. Two days later, a 126 mm long, live filaria worm was extracted from the lower lid subcutaneous tissue. The worm was diagnosed as, likelihood, Dirofilaria immitis on microscopic examinations. The present case suggests that D. immitis can cause periocular infections.
-
Key words: Dirofilaria immitis, dirofilariasis, subconjunctival infection
INTRODUCTION
Infection of the eye and periocular tissue by parasite species is rare. But there are reports of parasitic infections in this area, for example,
Loa loa,
Onchocerca, and
Dirofilaria [
1-
3]. Dirofilaria is a kind of filaria which rarely infects humans as a zoonotic infection [
4-
8]. The life cycle of this parasite is the same as that of other filariae; microfilariae are in the blood of wild and domestic animals such as the dog, cat, and raccoon, and transmission occurs to humans by infected mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) bites. Infection manifests as subcutaneous nodules (
Dirofilaria repens) or peripheral pulmonary nodules (
Dirofilaria immitis). In rare cases, eyes and periocular tissues can be involved [
4-
8]. The life cycle of these parasites do not complete in the human body, and they will not produce any microfilariae. Therefore, extracting parasites from the involved tissue is a definitive treatment [
1,
3].
CASE DESCRIPTION
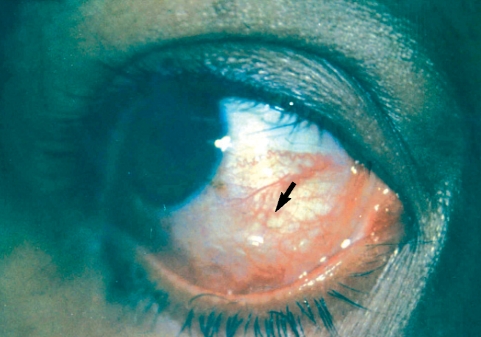
A 27-yr old primigravid nullipara woman in her second trimester of gestation with the complaints of redness and swelling of the left eye since 10 days ago referred to our clinic. The patient also noted redness and swelling of the right eye and then of the frontal area from 2 days ago. One wk ago episcleritis was diagnosed, and in slit lamp examination a helical and mobile mass with swelling and redness around it was observed in the inferior bulbar conjunctiva (
Fig. 1).
In general examination, the heart, lungs, abdomen, and extremities were normal, and the past medical history was positive for a 10 × 5 mm erythematous nodule on her right upper extremity 8 wk before. The history of bites and infestations was negative. In her physical examination, there were no signs of cutaneous lesions mentioned in her past medical history. Paraclinical studies including the serum chemistry, C-reactive protein (CRP), fasting blood sugar (FBS), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), creatinine (Cr), and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) were normal. Her complete blood count (CBC) revealed normal differentiation without eosinophilia. Her post-partum chest x-ray was normal.
The patient was transferred to the operation room with suspicious diagnosis of subconjunctival worm where subconjunctival mass had been faded away. Two days later, the mass in the conjunctiva appeared for a second time and the patient rapidly transferred to the operation room. A viable worm as long as about 126 mm was extracted with topical anesthesia.
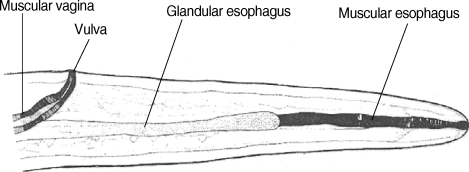
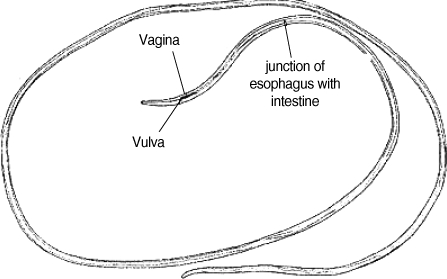
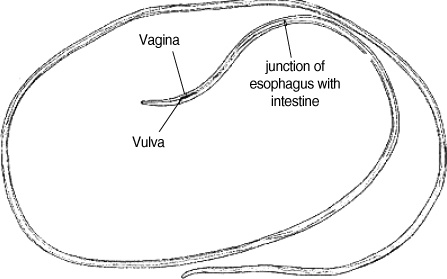
The surgically extracted worm was fixed in 10% formalin solution and was sent to the Parasitology Department of Public Health School of Tehran University, where it was kept in lactophenol azocarmin for clearance and staining. Then, it was mounted in Canada balsam. Camera lucida drawing was done, and the worm was measured. The worm was at a juvenile stage, and measured 126 mm in length and 0.75 mm in width. The body was smooth, and the tail was round. The whole esophagus from the anterior end measured 1.25 mm. The vulva opening was situated in the anterior part of the esophagus 2.2 mm from the frontal region behind the muscular esophagus. Microfilariae were detected in the uterus, and the worm was possibly
D. immitis (
Figs. 2,
3). In a year follow-up of the patient, no signs of
recurrence were observed.
DISCUSSION
Dirofilariasis is a parasitic disease of both wild and domestic animals which sometimes present as a zoonotic disease in humans. Microfilariae are transmitted to humans by different kinds of insects, most likely mosquitoes. Ocular infections by dirofilarias have been reported in different parts of the world [
1,
3]. Infection is around eyes under the conjunctiva and rarely can penetrate the eye ball itself. In an expanding survey in France from 60 cases of infection with
Dirofilaria, the most common site of infection was the subcutaneous tissues (nodule form) of the head and neck area, followed by the upper limb, thorax, and conjunctiva [
2].
Rare cases of infection in the cheek, breast, and inguinal area also existed [
7]. Internal organ infections also exist with the lungs as the most common site in which
D. immitis was the most common species in the form of peripheral nodules. Rare cases of infection in the pancreas, testis, and appendix have also been reported [
4].
D. repens was the most common species which infects subcutaneous and subconjunctival tissues [
6]. But the most common one which infects humans was
D. immitis which results in peripheral pulmonary nodules. There are some reports of subcutaneous nodules caused by this species of
Dirofilaria [
4].
Helminthologically different filarial infections in Iran are from reptiles, birds, rodents, camels, cows, dogs, foxes, and jackals [
9]. Infections seen in humans were
Setaria from the cow,
D. immitis from the dog,
D. repens from the fox and jackal.
Setaria is seen among cattle in northern areas.
D. repens, subcutaneous worms in foxes and jackals, is seen in mountainous parts of Iran. Setaria has only 1 human case reported, and is easily identified by a cuticular ring around the mouth and trigeminated tail. The vagina is situated in the muscular area. It is difficult to distinguish
D. immitis from
D. repens, and it needs extensive experience.
D. repens is similar to
D. immitis but the cuticula contain ridges, and tail is rectangular. Juvenile
D. immitis has no ridges in the cuticle, and the tail is round.
D. immitis is a very common filaria of stray dogs and sheep dogs in the right ventricle of the heart and causes disabilities in dogs [
9]. Infected dogs are unable to follow the sheep kept in the yards. Microfilariae in the blood of sick dogs are transmitted through mosquito biting. In Iran, reports of human dirofilariasis are very limited. Athari [
8] reported 1 case of
D. repens infection in the frontal subcutaneous area. Siavashi and Maseud [
5] reported 2 cases of
D. repens infections, one causing a small nodule on the 5th finger and the other in the wrist, both in north of Iran. Other reports from Iran include 1 case of
D. repens infection in an eye, 1 case of
D. immitis infection in the testis area, 1 case of
Dirofilaria infection in the subcutaneous nodule. In addition, 4 cases of
Dirofilaria infections were reported; 2 caused pulmonary involvement and suspected as
D. immitis and the other 2 in the subcutaneous nodule [
8-
11]. All 4 cases were reported from west of Iran.
In review of literature all reports about dirofilariasis, in which subconjuctival tissue or periocular tissue was extracted, was related to
D. repens infections [
1,
3,
6,
7]. The present case is the first report of infection in the subconjunctiva due to
D. immitis. In dirofilariasis patients, microscopic examination of the worm is important because diagnosis of dirofilariasis indicates extraction as the definitive treatment without systemic therapy. The present case showed that subconjunctival infections by dirofilariasis should be considered in Iran, and
D. immitis can cause subconjuctival and periocular infections.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Dr Tanim Eqbal Eftekhaari from Infectious Disease Research Center of Hormozgan University and Medical Sciences, Neda Mir Sepahi from Health School Parasitology department of Tehran University for their collaboration. The authors would like to thank Farzan Institute for Research and Technology for technical assistance.
References
Fig. 1A helical mass under the bulbar conjunctiva of the dirofilariasis patient.
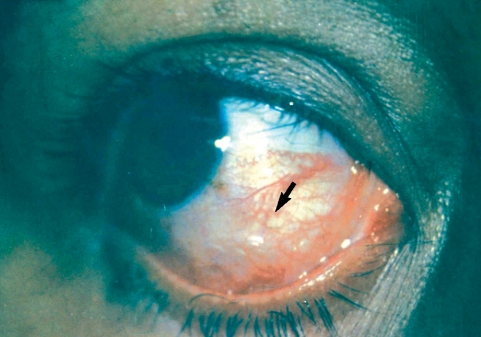
Fig. 2Microscopic view of the head part of the extracted Dirofilaria.

Fig. 3The Dirofilaria worm isolated from the anterior chamber of the eye of the present case, from Bandar Abbas, south of Iran.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- Prevalence and molecular characterization of Dirofilaria immitis in road killed canids of northern Iran
Meysam Sharifdini, Mahan Karimi, Keyhan Ashrafi, Mostafa Soleimani, Hamed Mirjalali
BMC Veterinary Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Polymerase chain reaction: A novel way to detect ocular dirofilariasis
Arkaprava Pradhan, Muthusamy Raman, Jyotirmay Biswas
Indian Journal of Ophthalmology.2022; 70(7): 2620. CrossRef - Orbital Dirofilariasis Masquerading As Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma
Farzad Pakdel, Hadi Ghadimi, Zohreh Nozarian, Fahimeh Asadi Amoli, Niloofar Pirmarzdashti, Morteza Karimi, Mohamad Mehrpour
Journal of Ophthalmic and Vision Research.2022; 17(4): 587. CrossRef - Lymphatic filariasis in Asia: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Negar Bizhani, Saeideh Hashemi Hafshejani, Neda Mohammadi, Mehdi Rezaei, Mohammad Bagher Rokni
Parasitology Research.2021; 120(2): 411. CrossRef - Review ofDirofilariaspp. infection in humans and animals in Iran
Faham Khamesipour, Saeed Nezaratizade, Bahareh Basirpour, Bahareh Chelgerdi Dehkordi, Sana Sadat Afzal, Parya Kheyri, Shadan Shojaat, Sakineh Akbari, Seyed Hossein Hejazi
Research in Veterinary Science and Medicine.2021; 1: 5. CrossRef - Filarial worms: a systematic review and meta-analysis of diversity in animals from Iran with emphasis on human cases
Ezatollah Ghasemi, Sadegh Shamsinia, Ali Taghipour, Davood Anvari, Saeed Bahadory, Seyyed Ali Shariatzadeh, Bahareh Kordi, Hamidreza Majidiani, Hassan Borji, MohammadReza Chaechi Nosrati, Ali Yousefi, Morteza Shams
Parasitology.2020; 147(9): 909. CrossRef - Molecular characterization of ocular dirofilariasis: a case report of Dirofilaria immitis in south-eastern Iran
Razieh Parsa, Ali Sedighi, Iraj Sharifi, Mehdi Bamorovat, Saeid Nasibi
BMC Infectious Diseases.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Dirofilaria immitis immunoreactive proteins in serodiagnosis
Majid Khanmohammadi, Reza Falak, Ahmad Reza Meamar, Elham Razmjou, Kobra Mokhtarian, Mehdi Arshadi, Nasrin Shayanfar, Lame Akhlaghi
Parasite Immunology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A detailed review of the mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) of Iran and their medical and veterinary importance
Shahyad Azari-Hamidian, Behzad Norouzi, Ralph E. Harbach
Acta Tropica.2019; 194: 106. CrossRef - Ocular dirofilariasis by Dirofilaria immitis in a child in Iran: A case report and review of the literature
Hadi Mirahmadi, Alireza Maleki, Raheleh Hasanzadeh, Mohammad Bagher Ahoo, Iraj Mobedi, Ali Rostami
Parasitology International.2017; 66(1): 978. CrossRef - Human ocular onchocerciasis caused byOnchocerca lupi(Spirurida, Onchocercidae) in Iran
G. Mowlavi, F. Farzbod, A. Kheirkhah, I. Mobedi, D.D. Bowman, S.R. Naddaf
Journal of Helminthology.2014; 88(2): 250. CrossRef - Zoonotic helminths affecting the human eye
Domenico Otranto, Mark L Eberhard
Parasites & Vectors.2011;[Epub] CrossRef - Seroprevalence of canine heartworm disease in Kerman, southeastern Iran
Baharak Akhtardanesh, Mohammad Hossein Radfar, Darioush Voosough, Nasim Darijani
Comparative Clinical Pathology.2011; 20(6): 573. CrossRef - A case of Dirofilaria immitis presenting as an intramuscular soft tissue mass
S. Teerthanath, S. Hariprasad
Indian Journal of Pathology and Microbiology.2011; 54(2): 428. CrossRef - Orbital Dirofilariasis in Iran: A Case Report
Sepideh Tavakolizadeh, Iraj Mobedi
The Korean Journal of Parasitology.2009; 47(4): 397. CrossRef